Mares are seasonal polyestric. The morphology of the healthy equine endometrium is influenced by the season of the year, the stage of the endometrial cycle, as well as the presence of endometrial diseases. The latter have an impact on the wellbeing of individual mares and can also inflict major financial losses for the horse breeding industry. The microscopic examination of an endometrial biopsy is an important diagnostic tool, since it can also detect subclinical diseases. This review provides an overview about morphological and molecular features of the healthy and diseased equine endometrium. It reviews the diagnostic findings of inflammatory and degenerative endometrial disease of mares, as well as the current state of knowledge regarding their cellular and molecular pathogenesis. It further shows that the comparative evaluation of morphological features and molecular characteristics of the healthy and diseased equine endometrium is an important prerequisite for the identification of disease-associated molecular markers, which in turn will facilitate the development of diagnostic and predictive biomarkers, as well as novel prophylactic and therapeutic options. Although currently numerous molecular data are already available, future studies are required to establish their translation into clinical practice.
- Equine
- Endometrium
- Health
- Disease
- Pathophysiology
- Molecular Features
- Mare
- Endometrial biopsy
Overview
Mares are seasonal polyestric and the endometrial morphology is influenced by the season of the year [1-4], external factors such as lightening and temperature [3] as well as the stage of the endometrial cycle [1,2].
Endometrial diseases of mares are an important cause of subfertility [1,2,5] and can inflict major financial losses for the horse breeding industry. Endometrial diseases include endometrosis (synonym: periglandular fibrosis), endometritis, glandular differentiation disorders, and angiosis (synonym: angiosclerosis) as well as their subtypes [1,2,4-7]. The concurrent presence of several endometrial diseases in an individual mare is a common finding [1,5]. As a physiological reaction, mating or breeding evokes transient inflammation with a duration of less than 72 hrs [5,8,9]. Some mares, however, develop persisting post-breeding endometritis; these are referred to as “susceptible mares” [9,10].
The microscopic examination of an endometrial biopsy is an important diagnostic tool, since it can detect all types of endometrial diseases including subclinical diseases [5]. Moreover, it allows to determine the stage of the endometrial cycle [2,11]. The incidence and degree of some endometrial diseases are influenced by factors of the mare such as age and numbers of parturitions [5,6,7,12]. Microscopic findings in the endometrial biopsy of a mare, however, need to be interpreted under consideration of signalment of the mare, clinical history and season of the year [2,4,5,13].
Based on the detection of certain microscopic findings, i.e. incidence and degree of endometritis, periglandular fibrosis and lymphatic lacunae, as well as endometrial atrophy during the breeding season, together with the length of barrenness, the categorization scheme of Kenney and Doig [1] is used for prognostication of the fertility of an individual mare. Subsequently, glandular maldifferentiation [13-15], angiosclerosis [6,13,16], subtype of endometrosis [5,17], older age of the mare [5,13] and a previous long-term use of the mare in athletic performances [18] have been revealed as further factors of reduced fertility.
The pathogenesis of some endometrial diseases such as nonsuppurative endometritis [5,19] and endometrosis [5,7,20] has still not been revealed in detail. No routinely available treatment exists for endometrosis [7,20]. Moreover, nonsuppurative endometritis often persists despite treatment [5,10]. Notably, endometrial neoplasia is a rare finding in mares [21].
Over the last years, scientific investigations on equine endometrial pathology focused on the characterization of disease-associated cellular and molecular mechanisms [15,17,19,22-32]. Obtained data have diagnostic value and will assist to gain further insights into the molecular pathogenesis of endometrial diseases [15,17,19,22-32]. In addition, they will likely help to design novel prophylactic regimes and treatment options [20]. Certain molecular markers have the be considered as potential biomarkers for equine endometrial health and disease, since they identify morphological and functional cellular alterations associated with endometrial diseases [15,17,23-27,29-32] and their cellular expression patterns can be visualized and quantified using immunohistochemistry [17,24,25,29,30,32,33]. For example, unphysiological expression of estrogen and progesterone receptors predicts altered hormonal responsiveness of the equine endometrium [17,24]. Changes in the physiological immunoreaction for intermediate filaments and associated proteins are consistent with an abnormal cellular differentiation [24,31,32]. Deviations in the expression of secretory proteins by glandular epithelia will likely cause alterations in the composition of the uterine milk as essential nutrition of the early equine conceptus [17,25]. Changes in the immunostaining for components of the innate immune defense, i.e. β-defensin and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1, suggest alterations of endometrial immunity mechanisms [29,30].
Conclusions
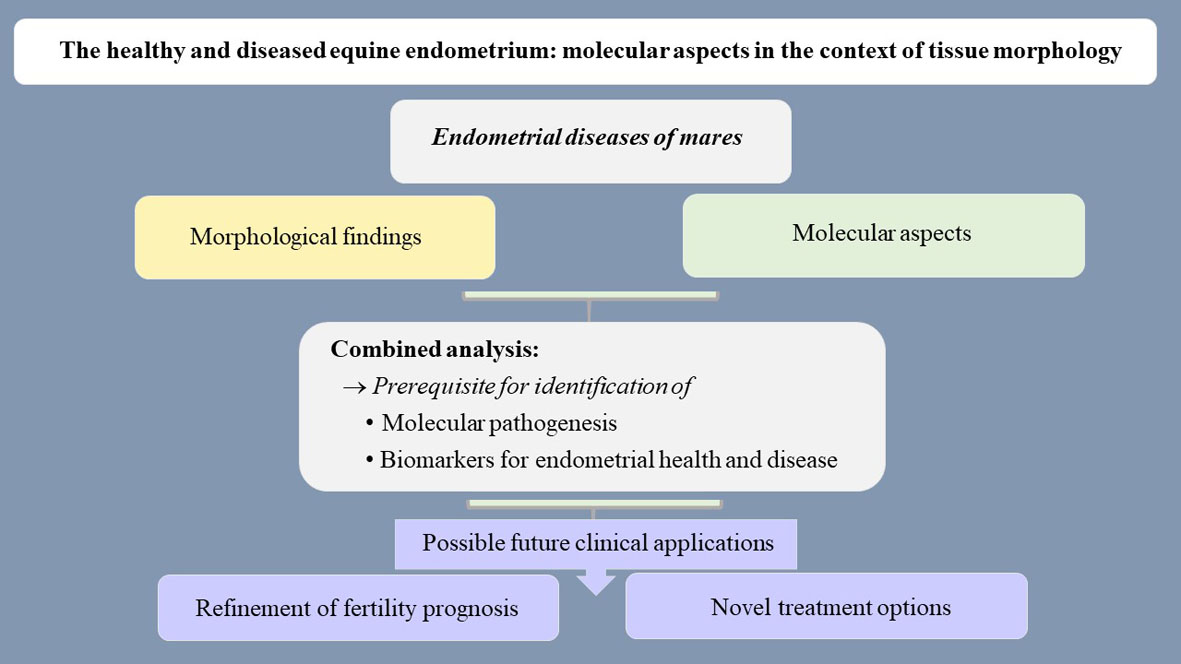
The combined evaluation of morphological findings and associated molecular features indicates that some examined molecular markers have the potential to serve as biomarkers for endometrial health and disease [34]. A biomarker is a biological parameter that can be objectively evaluated and indicates a normal or abnormal biological process or a response to an intervention, e.g. an immunohistochemical marker with diagnostic or prognostic value or merit for the prediction of a treatment response [35,36].
In the equine endometrium, molecules with potential to serve as biomarkers include estrogen and progesterone receptors, intermediate filaments, secretory proteins and components of the innate immune defense [34]. The comparative assessment of molecular markers within the healthy and diseased equine endometrium will likely help to identify and quantify cellular dysfunctions associated with endometrial diseases and their subtypes [34]. Obtained data could assist to more precisely estimate the fertility prognosis of an individual mare [34]. In addition, they are a prerequisite for the development of novel prophylactic regimes and treatment options [20,34]. Additional studies are required to establish the translation of research data into clinical practice.
The content of this article is summarized in Figure 1.
References
- Kenney, R.M.; Doig, P.A. Equine endometrial biopsy. In Current therapy in theriogenology, 2nd; Morrow, D.A., Ed.; WB Saunders: Philadelphia, USA, 1986, pp. 723-729.
- Schoon, H.-A.; Schoon, D.; Klug, E. Uterusbiopsien als Hilfsmittel für Diagnose und Prognose von Fertilitätsstörungen der Stute. Pferdeheilkunde 1992, 8, 355-362.
- Aurich, C. Reproductive cycles of horses. Reprod. Sci. 2011, 124, 220-228.
- Killisch, R.; Böttcher, D.; Theuß, T.; Edzards, H.; Martinsson, G.; Einspanier, A.; Gottschalk, J.; Schoon, H.-A. Seasonal or pathological findings? Morphofunctional characteristics of the equine endometrium during the autumn and spring transition. Dom. Anim. 2017, 52, 1011-1018.
- Schoon, H.-A.; Schoon, D.; Klug, E. Die Endometriumbiopsie bei der Stute im klinisch-gynäkologischen Kontext. Pferdeheilkunde 1997, 13, 453-464.
- Grüninger, B.; Schoon, H.-A.; Schoon, D.; Menger, S.; Klug, E. Incidence and morphology of endometrial angiopathies in mares in relationship to age and parity. J Comp. Pathol. 1998, 119, 293-309.
- Buczkowska, J.; Kozdrowski, R.; Nowak, M.; Ra, A.; Mrowiec, J. Endometrosis - significance for horse reproduction, pathogenesis, diagnosis, and proposed therapeutic methods. J. Vet. Sci. 2014, 17, 547-554.
- Katila, T. Onset and duration of uterine inflammatory response of mares after insemination with fresh semen. Reprod. Mono. 1995, 1, 515–517.
- Troedsson, M.H.T. Uterine clearance and resistance to persistent endometritis in the mare. Theriogenology 1999, 52, 461–471.
- LeBlanc, M.M.; Causey R.C. Clinical and subclinical endometritis in the mare: both threats to fertility. Dom. Anim. 2009, 44, 10-22.
- Brunckhorst, D.; Schoon, H.-A.; Bader, H.; Sieme, H. Morphologische, enzyme- and immunhistologische Charakteristika des endometrialen Zyklus der Stute. Fertilität 1991, 7, 44-51.
- Ebert, A.; Schoon, D.; Schoon, H.-A. Age-related endometrial alterations in mares – biopsy findings of the last 20 years. In Leipziger Blaue Hefte, 7th Leipzig Veterinary Congress, 8th International Conference on Equine Reproductive Medicine; Rackwitz, R., Pees, M., Aschenbach, J.R., Gäbel, G., Eds.; Lehmanns Media GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2014; Volume 2, pp. 230–232.
- Schoon, H.-A.; Schoon, D. The category I mare (Kenney and Doig 1986): expected foaling rate 80-90% - fact or fiction? Pferdeheilkunde 2003, 19, 698-701.
- Schoon, H.-A.; Schoon, D.; Wiegandt, I.; Bartmann, C.-P.; Aupperle, H. “Endometrial maldifferentiation”- a clinically significant diagnosis in equine reproduction? Pferdeheilkunde 1999, 15, 555-559.
- Häfner, I.; Schoon, H.-A.; Schoon, D.; Aupperle, H. Glanduläre Differenzierungsstörungen im Endometrium der Stute – Lichtmikroskopische und immunhistologische Untersuchungen. Pferdeheilkunde 2001, 17, 103-110.
- Schoon, D.; Schoon, H.-A.; Klug, E. Angioses in the equine endometrium – pathogenesis and clinical correlations. Pferdeheilkunde 1999, 15, 541-546.
- Lehmann, J.; Ellenberger, C.; Hoffmann, C.; Bazer, F.W.; Klug, J.; Allen, W.R.; Sieme, H.; Schoon, H.-A. Morpho-functional studies regarding the fertility prognosis of mares suffering from equine endometrosis. Theriogenology 2011, 76, 1326-1336.
- Kilgenstein, H.J.; Schöniger, S.; Schoon, D.; Schoon, H.-A. Microscopic examination of endometrial biopsies of retired sports mares: an explanation for the clinically observed subfertility? Vet. Sci. 2015, 99, 171-179.
- Rudolph, N.; Schoon, H.-A.; Schöniger S. Immunohistochemical characterization of immune cells in fixed equine endometrial tissue: a diagnostic relevant method. Pferdeheilkunde - Equine Medicine 2017, 33, 524-537.
- Mambelli, L.I.; Mattos, R.C.; Winter, G.H.Z.; Madeiro, D.S.; Morais, B.P.; Malschitzky, E.; Miglino, M.A.; Kerkis, A.; Kerkis, I. Changes in expression pattern of selected endometrial proteins following mesenchymal stem cells infusion in mares with endometrosis. Plos one 2014, 9, e97889.
- Agnew, D.W.; MacLachlan, N.J. Tumors of the genital system. In Tumors in domestic animals, 5th; Meuten, D.J., Editor; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, New Jersey, USA, 2016; pp. 689-722.
- Aupperle, H.; Steiger, K.; Reischauer, A.; Schoon, H.-A. Ultrastructural and immunohistochemical characterization of the physiological and pathological inactivity of the equine endometrium. Pferdeheilkunde 2003, 19, 629-632.
- Aupperle, H.; Schoon, D.; Schoon, H.-A. Physiological and pathological expression of intermediate filaments in the equine endometrium. Vet. Sci. 2004, 76, 249-255.
- Hoffman, C.; Ellenberger, C.; Mattos, R.C.; Aupperle, H.; Dhein, S.; Stief, B.; Schoon, H.-A. The equine endometrosis: new insights into the pathogenesis. Reprod. Sci. 2009, 111, 261-278.
- Hoffmann, C., Bazer, F.W.; Klug, J.; Aupperle, H.; Ellenberger, C.; Schoon, H.-A. Immunohistochemical and histochemical identification of proteins and carbohydrates in the equine endometrium. Expression patterns for mares suffering from endometrosis. Theriogenology 2009, 71, 264-274.
- Schöniger, S.; Gräfe, H.; Schoon, H.-A. Beta-defensin is a component of the endometrial immune defence in the mare. Pferdeheilkunde 2013, 29, 335-346.
- Rebordão, M.R.; Galvão, A.; Szóstek, A.; Amaral, A.; Mateus, L.; Skarzynski, D.J.; Ferreira-Dias, G. Physiopathologic mechanisms involved in mare endometrosis. Dom. Anim. 2014, 49(S4), 82-87.
- Klose, K.; Schoon, H.-A. Periglandular inflammatory cells in the endometrium of the mare – A physiological defence mechanisms which impacts on the development of endometrosis. Pferdeheilkunde 2016, 32, 15-23.
- Schöniger, S.; Böttcher, D.; Theuß, T.; Gräfe, H.; Schoon, H.-A. New insights into the innate immune defences of the equine endometrium: in situ and in vitro expression pattern of beta-defensin. Pferdeheilkunde 2016, 32, 4-14.
- Schöniger, S.; Gräfe, H.; Richter, F.; Schoon, H-A. Expression of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 as transcript and protein in the healthy and diseased equine endometrium. Vet. Sci. 2018, 118, 278-287.
- Bischofberger, L.; Szewczyk, K.; Schoon,-A. Unequal glandular differentiation of the equine endometrium – a separate endometrial alteration? Pferdeheilkunde - Equine Medicine 2019, 35, 304–315.
- Minkwitz, C.; Schoon, H.-A.; Zhang, Q.; Schöniger, S. Plasticity of endometrial epithelial and stromal cells – A new approach towards the pathogenesis of equine endometrosis. Dom. Anim. 2019, 54, 835-845.
- Aupperle, H.; Özgen, S.; Schoon, H.-A.; Schoon, D.; Hoppen, H.O.; Sieme, H.; Tannapfel, A. Cyclical endometrial steroid hormone receptor expression and proliferation intensity in the mare. Equine Vet. J. 2000, 32, 228-232.
- Schöniger, S.; Schoon, H.-A. The healthy and diseased equine endometrium: a review of morphological features and molecular analyses. Animals (Basel) 2020, 10, pii: E625.
- Moore,E.; Kirwan, J.; Doherty, M.K.; Whitfield, P.D. Biomarker discovery in animal health and disease: the application of post-genomic technologies. Biomarker Insights 2007, 2,185–196.
- Taylor, C.R. Introduction to predictive biomarkers: definitions and characteristics. In Predictive biomarkers in oncology, Badve, S., Kumar G.L., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 3-18.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/ani10040625