The investigation presented in
Table 2 above indicates that the real part of the dielectric permittivity ε
r (dielectric constant) with frequency varies for each sample, falling within the range of 3.14 to 3.98. This corresponds to the inverse relationship between frequency and ε
r [
32]. However, no consistent pattern is discernible, indicating that the particular value of ε
r is contingent upon the soil sample.
Over the years, various chemical and physical strategies have been investigated to decide on SWC, and a large body of knowledge is now available on the concept with programs [
25,
35]. Additionally, during the growth phase, there was a significant variation in the monthly trend and vegetation feedback, indicating that soil types significantly impacted dielectric characteristics. This implies that soil water in sand has dielectric properties similar to pure water, which has no dispersion between 50 MHz and 1 GHz [
36]. The SWC is dynamic and heterogenetic within spatiotemporal areas due to differences in soil properties, plant type, weather, terrain, and human interruptions. This hinders the development of correct, powerful, non-destructive, and monetary quantification techniques for measuring SWC [
36,
37,
38]. As soil conductivity increases, resistance decreases and effective capacitance increases. This effect is negligible until the resistance hits 1/ωC when the effective capacitance doubles. The probe frequency is lowered as the effective capacitance increases with an additional resistance reduction resulting from using TDRs to measure dielectric characteristics. Rainfall, irrigation, and agricultural practices can all exacerbate soil water logging [
39], and capacitance sensors can measure the charge time of a capacitor built using a medium to determine the dielectric permittivity of the medium. In FDR, the residual frequency that gauges the amount of water in the soil is found by controlling the oscillator frequency [
23].
Soil dielectric permittivity models use SWC, compactness, hardness, structures, and quality indicators to find relationships between dielectric permittivity and water content [
40]. However, sensitivity analysis and calibration models are rarely documented, restricting their use in soil remediation, agricultural soil ecological monitoring, and environmental geo-technology. These models examine the plant nutrient content, soil profile changes, soil thermal capacity, and water resources using dielectric permittivity and physicochemical factors such as salinity, temperature, and water content.
Over the years, several mathematical models have been constructed, but it is still unknown how accurate and comprehensive they are. For most soils, the Topp et al. [
41] model was considered appropriate; however, different functions are required for fine-textured soils containing layered clay minerals. There has been variation in other models' robustness, precision, and usefulness. It is important to gather and categorize mathematical models of TDR because previous research has focused on restricted numbers and their kinds [
17,
42]. The effectiveness of TDR mathematical models in predicting soil water content has also been reported in earlier research; however, these studies only examined a small number of models and soils [
11,
42]. This review aims to synthesize available dielectric-property-based mathematical models relating apparent permittivity to water content, providing an updated understanding of their development, applications, and monitoring.
In this paper, we investigate the basic principles and recent developments in SWC assessments based on dielectric characteristics and how they relate to the water content of soil using capacitance sensors, FDR, GPR, and TDR. Along with discussing the dielectric models for SWC measurements, we examine all related equations of the dielectric permittivity models and present results from various experiments in the measurement of SWC using dielectric properties. We further extensively discuss the application of dielectric models in SWC and present some TDR mathematical models used for dielectric permittivity based on SWC and methodological classifications for GPR-based SWC measurement. Finally, we substantiate our findings by examining the applications and configurations of dielectric sensors, their challenges and prospects, and trends in using dielectric properties for SWC measurement.
2. Dielectric Models for Soil Water Content Measurements
Due to soil–water interactions, modelling wet soil parameters requires calibration for different soil types [
43,
44]. The most accurate method is direct field calibration of the petro-physical model, although it is rarely used and necessitates labour-intensive auxiliary measurements [
43]. Dielectric measurements are the foundation for operating many field soil water content sensors, both experimental and commercial [
45,
46]. Their range of operation covers several MHz to several GHz, depending on the measuring technique and kind of sensor.
Diffusion, volume mixing, and empirical models are the three types of soil dielectric models. Empirical models are used to study the relationship between the dielectric permittivity and the volume of water content for various types of soil [
47,
48,
49]. The mixing models consider the dielectric permittivity and the percentage of volume of the solid, liquid, and gas phases of soil [
50]. Rayleigh, linear, and root mean square models are representative models [
38,
51,
52]. Diffusion models describe the soil as a homogeneous four-phase mixture using depolarization factors to capture the microscopic effects of continuous and scattered phases [
47].
The accuracy of water content estimates can be improved by designing these sensors to match the compositions, textures, and capacities for retaining moisture [
10]. Effective calibration techniques are also essential to ensure accurate measurements accounting for variations or discrepancies in sensor data [
53]. It should be noted that frequent calibration adjustments and checks further improve the accuracy of sensor readings [
29,
54]. Additionally, to minimize errors associated with generic sensors and provide reliable data for well-informed decision-making in agricultural and environmental applications, an efficient strategy for precise water content estimates can be established by combining various sensors tailored for particular soil types with rigorous calibration procedures.
Table 3 summarizes the models based on dielectric properties for SWC. Although the TDR technique describes a close relationship between dielectric properties and SWC, actual experiments show that soil environments influence the measurement results [55]. Topp’s relation allows the derivation of the values of soil dielectric properties from known water content profiles [
56].
This empirical model used TDR between 1 MHz and 1 GHz to measure
εr for numerous mineral soils. It is written as follows:
where
ɛr is the dielectric properties (dielectric permittivity) and
θ is the volumetric water content of the soil. They also stated the following inverse relation:
Soil containing more water or organic matter requires a different calibration:
The tools for measuring plant water stress depend on the characteristics and use of the soil. Given the energy plants use to draw water from the soil, soil suction may be a more accurate measure than volumetric water content (VWC). Given the variations in sensor response times, a proper sampling frequency is essential. The ideal method may also depend on the physical characteristics of the soil, such as its texture and capacity to swell or contract. For this reason, GWC is usually used to increase calibrations and validate readings of virtually all VWC measurements, whether in situ or remotely. If there is a dielectric sensor, there might be a way to transform electromagnetic field observations into SWC.
Radiofrequency modulations measure SWC, which influences dielectric permittivity and are used to measure energy storage in the soil. The imaginary component represents energy loss, while the real component represents energy storage. All electromagnetic soil sensors rely on true dielectric permittivity measurements, which are closely correlated with variations in water content [
20]. Using the imaginary component allows for estimating accurate electrical conductivity in the 1 to 75 MHz range. Capacitance, measured in farads, is the electrical charge storage unit connected to the actual component. Other factors, such as bulk density and porosity, also impact some equations that relate dielectric permittivity to soil water content. Using data from prior studies [
9,
20,
57,
58] and the idea of combining models [
59], the following equations were presented:
This equation is used for
θ𝜃 <
θ𝜃t, while for
θ𝜃 >
θ𝜃t, the following equation is used:
where
εi is the dielectric properties of ice,
εw = the dielectric properties of water,
εa = dielectric properties of the air, and
εr is the dielectric properties of rock (i.e.,
εi = 3.2,
εw = 80, and
εa = 1). At the same time, θ
t is the transition moisture (0.16–0.33), 𝔶 is the porosity of soil (0.5), and
𝛶𝛶 is the fitting parameter (0.3–0.5) [
59].
Also, the study by Malicki et al. [
60] proposed an empirical model using TDR and 62 soil samples, including mineral, organic, pot, artificial, sea, river and forest litter, to determine the SWC. The results show an uncertainty of 0.03 at a 0.05 increment for minerals and organic components (ɛ < 𝔶 < ɛ + 0.05) in the SWC.
Another physical model was proposed by Roth et al. [
51] with an equation based on the dielectric mixing model, which was tested on various soil types using TDR with an error value of no more than 0.013 cm
3cm
−3 [
51], resulting in the following equation:
Robinson et al. [
61] sought to provide a unique equation for coarse-textured, layered soil utilizing TDR and coarse-grained quartz and glass beads.
In their study, Gardner et al. [
62] utilized capacitance measurement to determine SWC and found it ranging from 1.08 to 1.49; they also used multiple linear regression analysis to fit the data, which can be presented as:
where
𝜌𝜌 is the dry bulk density value ranging from 1.08 to 1.49.
Table 3. Summary of all equations of dielectric permittivity models.
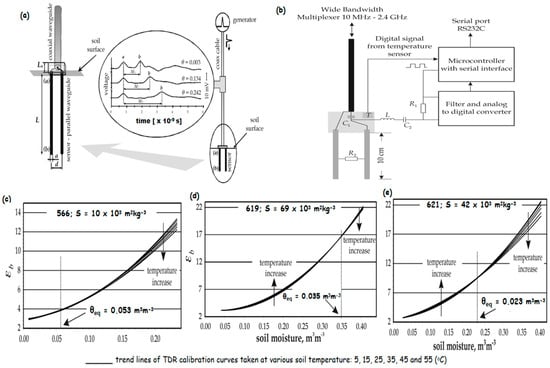
Figure 1. Experimental setups and calibration results for TDR: (
a) simultaneous measurement of electrical conductivity and SWC (the time distance between two reflections (
a) and (
b) are calculated using successive reflections. The reflectograms show voltage changes in soil dielectric permittivity, water content, and electric conductivity. The time (∆
t) required for the pulse to cover the double length of metal rods increases with soil dielectric permittivity, resulting in a decrease in pulse amplitude); (
b) a TDR probe, equipped with electronics, is used to monitor soil temperature and electrical conductivity; (
c–
e) TDR calibration curves for three different soil temperatures, where S stands for soil specific surface area and θeq for equilibrium moisture, which accounts for temperature variations [
65].
Based on
Figure 1a, a fast-sampling oscilloscope records the first pulse from the generator to the sensor in real time, analyzing the electromagnetic wave travel path and calculating the time distance between reflections. Three reflectograms are created for each scenario, representing voltage as a function of time at the selected feeder point. To assess soil electrical conductivity, the study used two 10 cm long TDR probes that were equipped with an analog-to-digital converter, a digital output temperature sensor, a microcontroller, and a serial interface (
Figure 1b). The electrical conductivity of the soil sample was determined using a low-frequency conductivity formula and a voltage drop on a reference resistor. The microcontroller produced a square wave at 100 kHz without polarizing the electrode–soil system, distinguishing between higher frequency TDR signals and lower frequencies [
65]. The study also found that the bulk dielectric permittivity (
εb) decreases when the water content is below θeq (water content value) and increases when the water concentrations are above θeq (
Figure 1c–e). The temperature-induced exchange of water particles explains the temperature effect. All soils, except soil 562, show values of bulk dielectric permittivity at 5 °C compared to 55 °C with high water content, with medium-value soils showing the largest difference [
65,
66].
Many variables, such as temperature, salinity, density, and clay content in the case of SWC dielectric sensors, can affect how accurately SWC is measured [
12,
16]. These variables impact the soil’s dielectric permittivity spectrum, as do dielectric dispersion, bound water relaxation, and interphase events [
44,
67,
68]. Consequently, low-frequency device manufacturers frequently offer several calibrations suitable for different types of soil, typically distinguishing between mineral and organic soils or focusing on soil texture [
69,
70,
71]. However, the user can also perform customized calibrations based on the experimental procedures or layout. Park et al. [
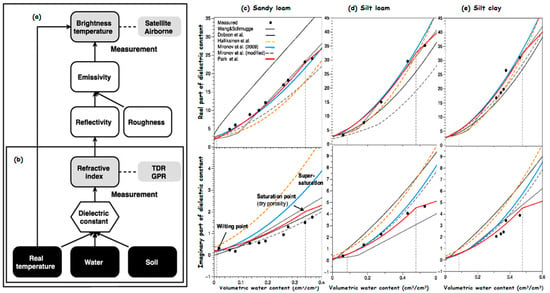
58] revealed that SWC and the bound water and moisture content, influenced by soil particle composition, affect the dielectric permittivity of the soil. Although TDR and GPR use temperature and texture data to determine refractive index, effective dielectric permittivity, and soil water content, remote sensing assesses brightness temperature (
Figure 2a,b). Our study uses laboratory experiments and compares the results with widely used models, validating new approaches in the C band (
Figure 2c–e). A logarithmic model is developed to consider the composition of the mesoscopic particles and the bound water content, enhancing the accuracy of calculating the dielectric permittivity of cohesive soils.
Figure 2. Dielectric constant of the moist soil experiment: (
a) TDR and GPR sensing setup, (
b) dielectric constant connection between targeted soil properties and the estimated sensors parameters, (
c) sandy loam soil of the C band at 5 GHz, (
d) silt loam at 4 GHz, and (
e) silt clay at 6 GHz [
58].
Not all soil types can be accurately estimated by factory-generic calibrations for SWC sensors, especially those that rely on dielectric permittivity sensing [
10]. This study revealed that high-electric conductivity soils have a greater relative inaccuracy in SWC due to the spatial heterogeneity of farmland soils, and laboratory calibration is required. According to soil-specific calibration, accurate estimations with 0.05 m3m−3 errors are possible at certain locations. Therefore, it is recommended that the accuracy of the SWC be verified using factory-calibrated commercial sensors before conducting studies on extractable soil water, microbial processes, greenhouse gas fluxes, and spatial variability.
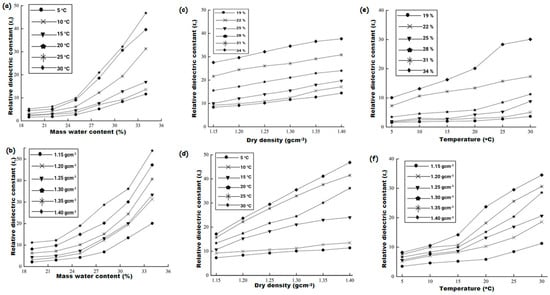
According to Xu et al. [
47], the fundamental structure of the soil is affected by the relative dielectric permittivity, which increases with increasing water content (
Figure 3a). With increased water content, free water also becomes more polarized, increasing the dielectric permittivity (
Figure 3b). The dielectric properties of the soil particles are also influenced by their compaction since the soil's dry density influences the particles' spacing. The dry density also increases the contact area between the soil particles (
Figure 3c,d). Large pores and a low dielectric permittivity characterize laterite, which has significant water absorption. The dielectric permittivity impacts Pore water and water film thickness, which rises with temperature and water content. Because temperature enhances the thermal movement of water molecules, altering density, viscosity, and polarizability, it substantially impacts the dielectric characteristics of the soil. The polarization ability of soil pore water accelerates as temperature rises due to an increase in the relative dielectric permittivity (
Figure 3e,f). This growth continues at a dry density of 1.15 g/cm−3, particularly when the water content is greater than 28% (
Figure 3e). At 15 °C, the relative dielectric permittivity increases with temperature (
Figure 3f).
Figure 3. Correlation between the relative dielectric constant and water content at (
a) ρd = 1.20 gcm
−3 and (
b) T = 20 °C; dry density at (
c) T = 15 °C and (
d) ω = 28%, and temperature at (
e) ρd = 1.15 gcm
−3 and (
f) ω = 28% [
47].
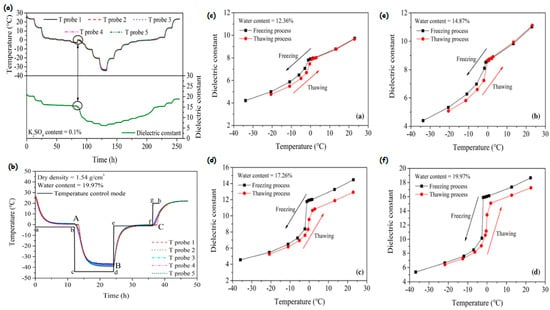
According to a study by [
38], there are variations in the data obtained from five temperature probes due to the various locations and refrigeration effects. The dielectric permittivity alters with temperature and may be classified into linear and non-linear stages (
Figure 4b). The use of five probes improves the accuracy of soil sample temperature measurement. According to the study, during freezing, the dielectric permittivity drops linearly with the increase in temperature, whereas at lower temperatures, it decreases rapidly and slowly. Volumetric fractions and soil components affect how the soil dielectric permittivity varies. After 10 h, a silty clay sample containing 0.1% K
2SO
4 stabilized, suggesting a 12 h hold period (
Figure 4a). However, a sudden increase in temperature and a significant decrease in the dielectric permittivity was observed due to latent heat release during the transformation of water into ice [
72,
73].
Figure 4. Dielectric constant modelling and measurement. (
a) The time-temperature dielectric curve of silty clay samples; (
b) soil temperature changes (the temperature probes coincided with each other in the a–b and g–h stages but showed a visible difference in the c–d and e–f stages, especially during periods of decreasing temperature); (
c–
f) the dielectric constants of silty clay samples are subject to temperature variations and alter with varied water concentrations [
38].
3. Remote Sensing Based on Dielectric Properties of Soil Moisture
Soil moisture measurements are typically point measurements acquired using various techniques or embedded sensors such as TDR, FDR, and capacitance [
74]. These measurements are considered truthful on the ground because of their close contact with the soil. However, they have limited spatial coverage, necessitating the installation of a large or dense sensor network to monitor large field areas, which can lead to operational and maintenance costs. Improved remote sensing methods for precise soil moisture evaluation have been made possible by developments in dielectric property-based soil water content measurements [
28,
31,
49,
75]. This connection facilitates important information on the dynamics of soil moisture, allowing for effective monitoring in wide regions and better decision-making in environmental management, hydrology, and agriculture [
76,
77]. Based on the dielectric characteristics of the soil, microwave remote sensing techniques determine the moisture content of the soil using electromagnetic radiation in the microwave area [
78]. While passive sensors record electromagnetic radiation that is present in the environment, active sensors—such as synthetic aperture radar and ground-penetrating radar—measure electromagnetic radiation that they produce.
Understanding soil variability may be greatly aided by RS, particularly in regions with little soil sample availability or difficult topography [
28,
58]. It is useful for mapping soil characteristics, identifying erosion, and providing high-resolution data on soil parameters such as moisture content and organic carbon concentration [
18,
19,
79]. The ability to see through clouds and vegetation, sensitivity to changes in soil moisture content, and a spatial resolution that can range from a few meters to several kilometres, depending on the sensors used and its altitude above the Earth’s surface, are just a few of the advantages that microwave remote sensing has over other methods [
75,
80,
81]. This makes it possible to accurately estimate soil moisture content, even in heavily forested or overcast areas. However, remote soil moisture detection using dielectric characteristics has several challenges and drawbacks. For example, it is challenging to create precise models because of the intricate link between soil moisture content and dielectric permittivity. The dielectric permittivity of the soil can be influenced by several factors, such as salinity, temperature, and texture, which can result in inaccurate soil moisture estimations [
17,
82]. Due to the attenuation of electromagnetic radiation, the penetration depth of remote sensing methods is restricted, and their spatial resolution might not be adequate for applications that require precise information on small-scale variations in soil moisture content.
The most recent databases, modelling strategies, ground, near-surface, and satellite remote sensing techniques have been created to quantify surface, near-surface, and root zone soil moisture at different temporal and geographical resolutions [
78,
83,
84]. Spatial soil moisture networks and spatiotemporal SM data are being used more and more to increase our knowledge of hydrological processes, identify trends in the hydrological cycle, test hydrological models, define spatial soil moisture dynamics, and validate satellite RS observations [
78,
85,
86]. However, disparities in the scaling between in situ measurements and satellite sensor resolution and disconnects between the detecting depth of ground and distant sensors pose difficulties for the validation testing of coarse-scale SM products. Although increasing numbers of soil moisture networks are in situ, they do not always indicate the broader surrounding region.
Furthermore, studies have demonstrated the possibility of employing optical and thermal satellite measurements to estimate soil moisture at a high spatial resolution, such as the study of Alexandridis et al. [
87], who estimated root zone soil moisture using straightforward ancillary data and energy balance fluxes. The variation in precision was explained by factors such as the types of land cover, the class of soil texture, the time difference between the data sets, and the presence of rain events. With an eight-day time step and a spatial resolution of 250 m, the approach can estimate SM maps at the catchment scale. The possibility of employing optical and thermal band data to estimate soil moisture is demonstrated by both investigations in which surface soil moisture was obtained to give more information on the fusion of microwaves to acquire soil moisture at spatial and temporal resolutions. Using GPS sensor readings, Koch et al. [
88] created a novel method for capturing soil moisture based on changes in GPS signal intensity caused by fluctuations in the soil’s dielectric permittivity. The utilization of L-band microwave remote sensing data is the approach's primary benefit, making it appealing for use as validation data for SM products. It also allows for continuous extrapolation at typical locations and complementing satellite data with high geographical coverage but poor temporal precision. The bulk SM of the top soil layer is measured by GPS antennas positioned at a certain soil depth, making it appropriate for global sensors.
Furthermore, Li, et al. [
89] introduced the GPR-SWC neural network architecture, which enables the rapid inversion of volumetric SWC at field size via the common offset GPR technique. The model correctly pinpoints various volumetric SWC borders regarding temporal depth, with a maximum error of less than 0.10 cm
3 × cm
−3. Furthermore, the expected values of the soil sample and field values exhibit minimal variation, which aligns with the general trend of changing TDR detection levels. The study uses farm GPR data to reveal that GPR-SWC can invert the soil’s water content.
Torres-Rua [74] also estimated surface soil moisture using meteorological data and Landsat 7 using a Bayesian machine learning technique. The study took advantage of the precision and uncertainty of conventional methodologies for Landsat vegetation indices and surface energy balance products. Because the relevant vector machine technique is based on statistical modelling, it does not incorporate embedded uncertainty into the suggested soil moisture model. It is recommended that quality control processes be used to validate spatial data, particularly for gap filling, spatial evapotranspiration, and component products used in energy balancing. In remote sensing applications, autocorrelation is anticipated in spatial data; however, statistical behaviour in the vector learning machine model is related to the surface soil moisture observed. Future research could anticipate spatial evapotranspiration rate and soil water content for irrigation water balancing operating systems and estimate soil moisture at deeper depths. Implementing procedures to measure and reduce the influence of data sources and model uncertainty on outcomes is necessary.
4. Applications of Dielectric Models in Soil Water Content Measurements
With the use of dielectric permittivity measurements, understanding SWC is crucial for many applications in agriculture, hydrology, environmental management, remote sensing, and soil salinity [
11]. By examining how water moves through various soil types, scientists may improve their models that forecast floods and droughts. By evaluating the effects of changing land use on the amount of water in the soil, environmental management can guarantee the sustainability and health of ecosystems. RS applications, such as tracking soil water content using satellite data, can enhance climate models and global water cycles [
90]. These measures may also be used to determine the salinity of the soil, which is crucial for agriculture and the health of the environment. This allows farmers to make informed decisions about crop selection and irrigation practices [
30]. The results of various experiments on measuring SWC using dielectric properties are extensively discussed in
Table 4.
Table 4. Results of various experiments in the measurement of SWC using dielectric properties.
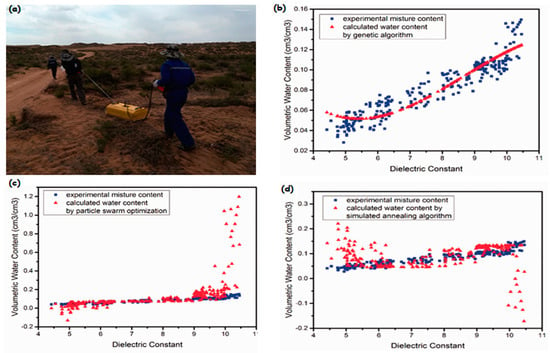
The experimental setup of GPR is a quick and safe technique used for in-situ measurements of underground media in various fields (
Figure 5) [
1,
108,
109]. For data collection, the system makes use of a shielding antenna linked to the ground at 100 MHz [
100]. Furthermore, using simulated annealing techniques and genetic algorithms, researchers looked at the experimental water content and the relative dielectric permittivity (
Figure 5a–d).
Figure 5. The actual picture of data collection and the intelligent group algorithm optimizes the results: (
a) GPR detection process, (
b) results from the genetic algorithm for the sand constants, (
c) results from the particle swarm optimization for the sand constants, and (
d) optimized results from the simulated annealing algorithm optimized results for constants of sand [
100].
Given that the GPR approach relies on the lifetime of a reflector at a known intensity and that translation procedures rely on a dielectric permittivity evaluation, we must perform determinations and validations [
20,
23]. The link between soil dielectric permittivity and SWC also varies, which limits its enormous software program. The study in [
98] reveals that simple regression models for determining SWC in degraded peatlands are insufficient. The calibration curve provides an acceptable error of 0.04 cm
3cm
−3, but the broken-line models are empirical equations that require further research. The study finds that the parameters of the broken-line model correspond to the biodiversity index and bio-indices, which help determine the SWC in degraded peatlands when utilizing the TDR technique. The multivariate approach offers a precise and non-destructive way to assess soft and hard slopes and estimate the state of the surface water content [
47]. To increase the precision of measuring the dielectric permittivity of the soil during the freezing and thawing processes, a novel test procedure has been created [
38]. To guarantee the right temperature, a 12 h thermostatic time is needed. The findings indicate that the dielectric permittivity of the soil increases as the levels of water, NaCl, and K
2SO
4 increase; however, the new empirical model makes the positive temperature range more significant [
38].
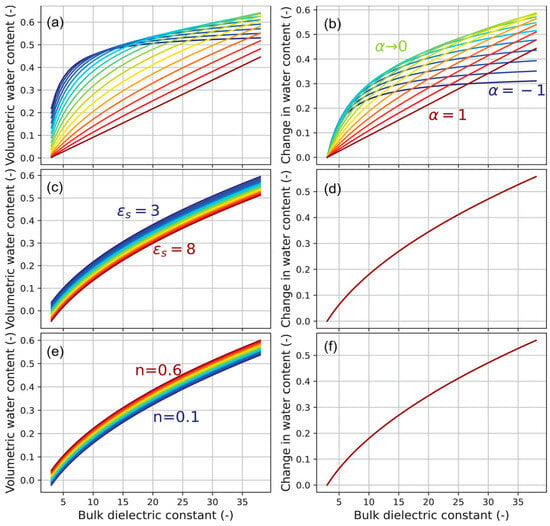
To evaluate the uncertainty limit of a dielectric probe to detect the liquid water content in variably frozen soils, the dielectric mixing model has been extended to frozen circumstances [
102]. To describe the characteristic curves of soil freezing, this tiny uncertainty limit is helpful, but due to the regional diversity of soil parameters, the field calibration of dielectric devices presents challenges [
71,
110]. Both gravimetric measurements and those performed with the same instrument installed are undertaken on many samples to calibrate the probe. Although laborious, this is essential, since an improperly calibrated probe is worse than one that is not. Depending on the application, one may choose to field-calibrate. Amankwah et al. [
102] further plotted the mixing models with the most sensitive parameter, α, which influences the intercept of the relationship for the absolute water content, as seen in
Figure 6. Nevertheless, ε
s and
n are insensitive to variations in water content. Given that the most sensitive parameter is arbitrarily fixed by the empirical model, it can be inferred that α is the least suitable value for varying soil conditions.
Figure 6. Evaluation of the sensitivity of the mixing model to soil-dependent characteristics. (
a,
b) Variations involve adjusting α within −1 and 1; (
c,
d) different dielectric constants of the soil between 3 and 8; (
e,
f) variation n within 0.1 and 0.6 [
102]. (The colors shows the changes in the three unknown parameters, taking realistic upper and lower bound for each parameter).
Researchers have increasingly considered the impact of factors such as bulk density, porosity, temperature, and dielectric permittivity on soil properties [
60,
62,
111]. The most popular model (
Table 5) is more versatile and sophisticated and can be applied to soils with varying bulk densities or porosities; other studies have taken into account the effects of water dielectric permittivity and temperature [
99].
Table 5. Overview and summary of physical, empirical, and semi-empirical-based TDR mathematical models used for dielectric permittivity based on SWC.
The study by [
92] reveals that the permittivity of clay minerals and clayey soils is significantly influenced by Maxwell–Wagner relaxation processes, which shift the permittivity from the high-frequency to the low-frequency end. The results of the investigation demonstrate the sensitivity of the soil permittivity response, with slight variations producing large variations. This response is influenced by variables such as conductivity, porosity, ECw, and the heuristic parameter. The permittivity dispersion below 100 MHz is approximated using a model that allows substantial interaction between inclusions. In clay soils, Maxwell–Wagner relaxation processes predominate, and the dielectric response is determined by the phase composition and geometry.
The soil permittivity is controlled by the SWC, which is determined by the travel time between an antenna and a reflector target [
119]. SWC is measured using GPR, and information about SWC is immediately retrieved from GPR data in the frequency domain using frequency shift algorithms [
120]. Some techniques, referred to as “dielectric permittivity methods” begin by measuring the permittivity of the soil (
Table 6) and then calculate the SWC by using an empirical equation or on-site calibration to establish the link between the two parameters.
Table 6. Methodological classifications and related references for GPR-based SWC measurements.
When the dielectric permittivity is converted from GPR to volumetric SWC, relationships must be used. Typically, GPR connections are generated via TDR calibration. GPR fills the gap between satellite-based large-scale measurements and sensor-based small-scale observations by combining TDR and GPR [
24]. The approach works by analyzing high-frequency electromagnetic waves (3–30 GHz) emitted by the surface soil layer and detecting reflected waves [
124]. The rate of attenuation of GPR signals in soil is influenced by the dielectric permittivity of the soil.
The combination of TDR and FDR methods can provide more precise and reliable measurements of SWC because TDR measures the time differences between transmitted and reflected pulses, while FDR measures the phase change and attenuation of the reflected signal [
125]. This information is used to determine the distance to the reflection point and the material’s dielectric permittivity. Combining TDR and FDR can also improve measurement accuracy by minimizing noise and interference. TDR can also be used to calibrate FDR readings, creating a calibration curve that relates FDR results to soil water content [
126,
127]. The combination of TDR and FDR technologies in SWC can improve irrigation schedules, reduce water waste, reveal the health and resilience of wetlands, forests, and other ecosystems, as well as being used to monitor soil moisture levels in dams, levees, and other structures, identifying possible stability issues before they become serious in geotechnical engineering [
127].
By measuring the volumetric water content of the soil using the TDR, the study by [
128] was able to identify differences within the Wiener and Hashin–Shtrikman limits. The high viscosity of the soil significantly influenced the bound water, leading to high Topp formula values.
Table 7 further shows the applications and configurations of dielectric sensors for measuring water content. However, the Looyenga formula, the Maxwell–Garnett model, and the differential effective medium model were found to be more effective. The study suggests that considering the distribution of water and gas in the soil can result in a weighted average of single-phase calculations.
Table 7. Application and configuration of dielectric sensors for water content measurement using TDR.
According to mixture theory, the dielectric permittivity increases with the SWC at both positive and negative temperatures [
38,
135]. A higher water content causes the volumetric proportion of water to increase and the proportion of air at the pores to decrease, so an increase in SWC lowers the dielectric permittivity in negative temperatures [
135]. Using data from the immersion technique to estimate the dielectric permittivity of solid materials [
93], a method for calibrating mixing models may reduce uncertainty in indirect estimates of bound water permittivity and parameters of bound water permittivity models. A conjecture suggests that the significant slope increase in Andosols after the water content exceeds a threshold value is due to increased dielectric properties (temperature, water content) due to lower frequencies at higher water content, likely due to bulk water polarization attenuation of the incident electromagnetic wave. The combination of TDR measurements and effective frequency estimations to gain a better understanding of electromagnetic properties and the impact of phase configuration on soil structure may also affect broadband electromagnetic wave attenuation.
5. Challenges, Prospects, and Trends in Using Dielectric Properties to Measure SWC
5.1. Challenges
Dielectric properties-based soil water content measurement techniques offer significant advantages over traditional methods. They provide non-destructive, continuous, and rapid measurements of soil water content, making them valuable tools for agriculture, hydrology, and environmental sciences [
47,
77,
103]. However, challenges related to calibration, sensor placement, soil heterogeneity, integration with other technologies, and data analysis need to be addressed to advance this field. The difficulty of measuring water near surfaces, particularly its dielectric behavior, is a significant obstacle to understanding its behavior. New techniques are improving our understanding of water at interfaces [
92]. Determining the correlation between soil types and dielectric properties poses a challenge in the calibration and validation of dielectric sensors for SWC monitoring. Furthermore, a complete understanding of the influence of soil mass on the measurement of SWC is lacking in existing studies. There remains concern regarding the validity of widely used dielectric response-based techniques and their applicability to different types of soils and water content. To fully understand how these factors affect SWC measurement and how useful these methods are for precise measurements, more research is required.
By simulating an uncharged silica surface, Kargas et al. [
37] discovered that surfaces can impede the ability of water molecules to rotate up to 10 nm away. The orientation of the dipole is changed by the structural arrangement of the confined water, not by electrostatic forces caused by the hydration of ions or negatively charged surfaces [
102]. There is still disagreement about whether the drop in the dielectric profile is a reflection of the intrinsic or ionic characteristics of the water. When the solution is confined to spheres or nanotubes, the dielectric value drops due to a variety of molecular causes, such as electrostatic forces, molecule ordering, hydrogen bonding breaking, and water orientation. The characteristics of the surface, whether hydrophilic or hydrophobic, also affect the water structure. It is challenging to determine a general relationship between dielectric properties and SWC in a variety of soil types due to the complexity of soil composition, which includes varying levels of organic matter, mineral content, and pore structure [
22]. Furthermore, temperature affects the dielectric characteristics, which can cause errors in SWC measurements. The accuracy of SWC tests based on dielectric characteristics can potentially be affected by high salinity and electrical conductivity levels.
Furthermore, the manufacturer’s dielectric equation for a capacitance sensor is usually based on different fixed mineral soils, but the data presented may be derived primarily from highly porous sand, leading to a difference between the factory-calibrated values and real values [
136,
137,
138]. The problem lies in the difference in bulk density found in different soil types, which inherently can hold more or less water. Calibration for each type of soil texture and bulk density is necessary to avoid misleading and potentially meaningless measurements. Furthermore, the variations between sensors account for a large portion of the measurement errors in soil water content. Instead of calibrating sensors for sensor-to-sensor variation, manufacturers frequently advise calibrating sensors for variations in bulk density and soil texture. This can result in errors in irrigation scheduling, catchment water budgeting, and scientific modeling. It is strongly advised that each sensor be calibrated separately to guarantee perfect precision rather than depending on the sensor-to-sensor variation.
Measurements of the dielectric permittivity could also lead to errors in soil water content sensors because the dielectric characteristics of water, soil, and air are used in these measurements, as well as electromagnetic measurements [
3,
20]. The calibration and validation of the dielectric sensor must take into account several characteristics, such as soil compaction, texture, and organic matter concentration, which can be difficult to achieve. An additional problem is spatial diversity in the physical and chemical properties of the soil, since the heterogeneity of SWC within a particular area could be missed by a single sensor. Furthermore, the accuracy of SWC measurements may be affected by imperfections in the soil structure that interfere with the electromagnetic field produced by the dielectric sensors. However, the dielectric permittivity can be impacted by changes in temperature and highly clayed soil. Furthermore, results can be greatly affected by salinity or electrical conductivity, which makes it difficult for inexpensive TDR and capacitance sensors to reliably measure in soils with EC values greater than 1 dS/m. Finally, there might have been a mistake in the sensor calibration process used by the manufacturer. It is not advisable to assume that manufacturers have the necessary equipment or know-how to calibrate their sensors correctly.
5.2. Prospective and Future Trends
The dielectric models used for a dielectric measurement technique such as TDR, FDR, or GPR depend on the desired precision of the user and known field conditions [
43]. Geographical and temporal soil porosity information is typically unavailable for field use, but can be obtained for laboratory calibration [
129]. Maintaining constant porosity variation between field application and calibration is challenging, so a generalized porosity constant is recommended [
43]. However, ambiguity can cause problems for models with high porosity sensitivity, which limits their applicability to agricultural soils with systematic variations in porosity.
Because dielectric characteristics are sensitive to changes in water content, they are used to quantify SWC. This methodology presents several opportunities and future directions for measuring soil moisture because it consists of enhanced precision and accuracy, non-destructive and instantaneous monitoring, incorporation with remote sensing technologies, multi-sensor fusion methodologies, and progressions in sensor design and downsizing. Prospective developments involve the use of machine learning algorithms and data-driven methodologies to construct more resilient calibration models, the integration of heterogeneity components of the soil, and the formulation of validation and standardization procedures. Furthermore, future developments in calibration model refinement will be driven by advances in our understanding of dielectric behavior in heterogeneous soil systems. This involves looking at interactions with soil salinity, temperature impacts, and frequency-dependent effects. To take into account particular environmental conditions and user requirements, application-specific calibration models will also be built. Overall, increased precision, non-destructive monitoring, integration with remote sensing technologies, multi-sensor fusion techniques, advances in sensor design, machine learning applications, a better comprehension of dielectric behavior, and application-specific modeling are all potential uses of dielectric properties for SWC measurement in the future.
A wide range of soil conditions may not be adequately represented by existing TDR mathematical models [
139]. Although there are databases for soil physical parameters such as moisture, pressure, and temperature, there are no databases for apparent soil dielectric permittivity [
94,
140]. It is necessary to have a database containing information on bulk density, pH, electrical conductivity, soil texture, and water content [
11,
20]. This will enable the evaluation of current TDR mathematical models and improve the understanding of soil properties. SWC is important when analyzing soil water regimes, and the gravimetric approach is the most accurate. Since soil samples must be withdrawn for ongoing monitoring, radioactive technologies such as gamma-ray attenuation and neutron scattering are generally accepted as non-destructive in situ methods for measuring soil water content [
17,
141]. For effective and accurate functioning, the procedures require proper soil calibration and additional precautions due to environmental and health risks. Other widely used methods include capacitance, FDR, TDR, GPR, and passive microwave approaches [
142]. These approaches are simple to operate, but require calibration for each soil and, occasionally, for each sensor, which vary in size, precision, and cost.
Modern inversion techniques provide improved subsurface information, and linked inversion can extract hydraulic parameters from time-lapse SWC data [
8,
143]. However, these techniques have drawbacks, such as the intricate TDR and GPR operations and their sensitivity to temperature, electrical conductivity, and bulk density [
5,
55,
144,
145]. The effectiveness of these sensors is limited by the impacts of dielectric losses in clay and salinized soils. Once must remove the electrical conductivity of the soil sample before using capacitance sensors for the SWC measurement. When examining the results of the SWC measurements, it is imperative to differentiate between active and reactive components [
3,
32,
73]. It should also be noted that the electrical capacitance-based dielectric permittivity has a strong correlation with the SWC, with an increase in reduction under near-saturation conditions and a low increase in speed when the water content is small. This relationship should be limited to cases where electrical capacitance remains unchanged during measurement, and suggests that the modified model should propose a more extensive suitability and have more fundamental physical meanings than the existing models.
Steady-state dielectric procedures are more accurate, faster, and cheaper than gravimetric approaches [
82]. The dielectric data are continuous and can be saved online or transmitted to a computer. Dielectric procedures are popular because they are quick, in situ, non-destructive, and precise [
107]. The dielectric properties of water have been used to measure the SWC at high frequencies because the dielectric permittivity is predicted by electromagnetic waves or pulses in the soil. However, more research is needed on down- and up-scaling methodologies and large-scale modeling to achieve valid SWC estimates [
129]. Dielectric permittivity-based approaches can accurately and efficiently monitor SWC on a broad scale, and instrumentation improvements, such as multichannel high-speed measurements and 5G network architecture, can facilitate data processing and mathematical analysis [
129]. Interpretation approaches require well-defined and continuous reflections that require substantial and spatially continuous subsurface dielectric permittivity contrast. However, the wavelength-based method, which uses existing thermal conductivity models for soil texture and composition, can be used without laboratory calibrations, but has a larger measurement error because of soil type variations, requiring alternative models.
6. Conclusions
In conclusion, this review document explores recent advances in soil water content measurements based on dielectric properties. It discusses various techniques, methods, advantages, limitations, sensor technologies, data processing algorithms, and calibration procedures. The paper emphasizes the importance of understanding dielectric properties and their influence on soil water content determination, providing valuable information to researchers, practitioners, and stakeholders in agriculture, environmental monitoring, and hydrology. The review article serves as a resource to advance knowledge and promote innovation in the measurement of soil water content. Through our findings, it has become clear that technological advancements in dielectric-based soil water content measurements have significantly improved the efficiency and accuracy of SWC monitoring, allowing real-time data collection for agricultural, environmental, and geotechnical applications. In addition, theoretical developments have led to a deeper understanding of the complex interactions between soil properties and dielectric permittivity, allowing for a more precise estimation of soil water content. These findings have identified that advanced modeling techniques and data analysis methods have further enhanced the interpretation of dielectric measurements, facilitating the extraction of valuable information about soil water dynamics and spatial variability. Lastly, these measurements have been instrumental in optimizing irrigation practices, assessing the impact of soil water on crop health, and monitoring water resources in both agricultural and natural ecosystems. More research is needed to improve the accuracy and reliability of soil water content measurements based on dielectric properties, including examining soil variations, integrating advanced data processing techniques, and developing new sensor designs.