The micro- and nano-machining techniques applied to solid materials have yielded remarkable success in the semiconductor industry by integrating complex functionalities into microscale devices, thus spearheading the modern electronics revolution. Extending similar miniaturization strategies to process and assemble soft matter for creating multileveled functional structures over various length scales presents significant scientific and practical potential. Soft matter, including liquid crystals (LC), colloids, polymers, and biological substances, exhibits widespread influence across nature, living organisms, daily life, and industry. The biomimetic properties, responsiveness to stimuli, and efficacy in controlled release and sensing make soft matter extensively applicable in biology and chemistry.
- droplet
- liquid crystal
- soft matter
- microfluidics
- laser micro–nano-machining
- 3D printing
- emulsions
- laser injection
- microfabrication
- lab on a chip
1. Introduction
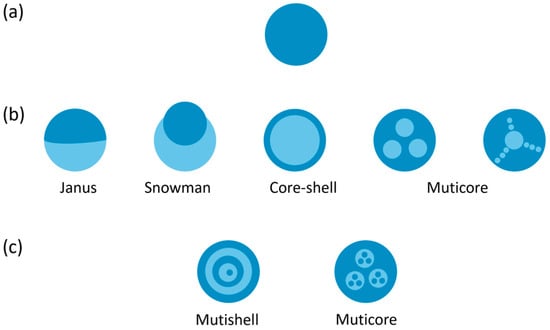
2. Typical Droplet Structure of Soft Matter
2. Applications of Droplet Microsystems in Optics and Photonics
2.1. Droplet Lasers
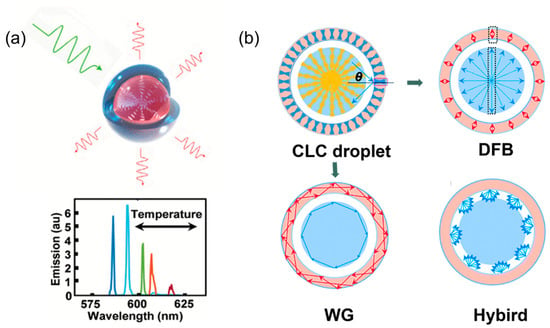
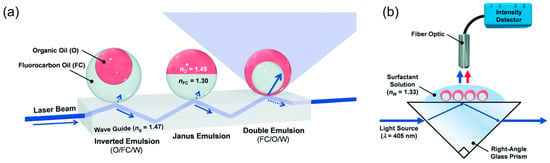
2.2. Waveguide
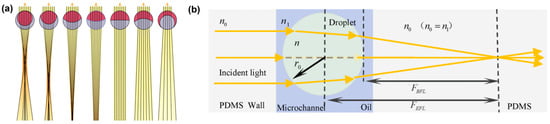
2.3. Microlens
2.4. Display and Information Tags
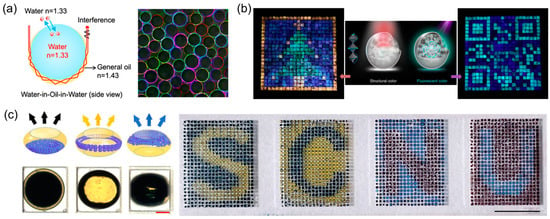
2.5. Other Applications
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/mi15030337
References
- Li, R.; Hu, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, D. Micro- and Nanocrystals of Organic Semiconductors. Acc. Chem. Res. 2010, 43, 529–540.
- Truby, R.L.; Lewis, J.A. Printing soft matter in three dimensions. Nature 2016, 540, 371–378.
- Kim, T.I.; McCall, J.G.; Jung, Y.H.; Huang, X.; Siuda, E.R.; Li, Y.; Song, J.; Song, Y.M.; Pao, H.A.; Kim, R.H.; et al. Injectable, cellular-scale optoelectronics with applications for wireless optogenetics. Science 2013, 340, 211–216.
- Chen, H.Q.; Wang, X.Y.; Bisoyi, H.K.; Chen, L.J.; Li, Q. Liquid Crystals in Curved Confined Geometries: Microfluidics Bring New Capabilities for Photonic Applications and Beyond. Langmuir 2021, 37, 3789–3807.
- Zhongcan, O. Physics Entry: Soft Matter; China Encyclopedia Press: Beijing, China, 2009; Volume 74.
- Honaryar, H.; Amirfattahi, S.; Niroobakhsh, Z. Associative Liquid-In-Liquid 3D Printing Techniques for Freeform Fabrication of Soft Matter. Small 2023, 19, e2206524.
- Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Palacio-Betancur, V.; Kim, Y.K.; Delalande, L.; Tsuei, M.; Yang, Y.; de Pablo, J.J.; Abbott, N.L. Reconfigurable Multicompartment Emulsion Drops Formed by Nematic Liquid Crystals and Immiscible Perfluorocarbon Oils. Langmuir 2019, 35, 16312–16323.
- Sanchez Barea, J.; Lee, J.; Kang, D.K. Recent Advances in Droplet-based Microfluidic Technologies for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. Micromachines 2019, 10, 412.
- Schroen, K.; Berton-Carabin, C.; Renard, D.; Marquis, M.; Boire, A.; Cochereau, R.; Amine, C.; Marze, S. Droplet Microfluidics for Food and Nutrition Applications. Micromachines 2021, 12, 863.
- Moragues, T.; Arguijo, D.; Beneyton, T.; Modavi, C.; Simutis, K.; Abate, A.R.; Baret, J.-C.; deMello, A.J.; Densmore, D.; Griffiths, A.D. Droplet-based microfluidics. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2023, 3, 32.
- Kim, J.W.; Han, S.H.; Choi, Y.H.; Hamonangan, W.M.; Oh, Y.; Kim, S.H. Recent advances in the microfluidic production of functional microcapsules by multiple-emulsion templating. Lab Chip 2022, 22, 2259–2291.
- Zhai, C.; Hu, C.; Li, S.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, T.; Li, H.; Hu, X. The formation principle of micro-droplets induced by using optical tweezers. Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 279–286.
- Long, F.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Ren, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Xu, G. Recent Progress of Droplet Microfluidic Emulsification Based Synthesis of Functional Microparticles. Glob. Chall. 2023, 7, 2300063.
- Wu, Q.; Pan, C.; Shi, P.; Zou, L.; Huang, S.; Zhang, N.; Li, S.-S.; Chen, Q.; Yang, Y.; Chen, L.-J.; et al. On-demand transdermal drug delivery platform based on wearable acoustic microneedle array. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 477, 147124.
- Makhoul-Mansour, M.M.; Freeman, E.C. Droplet-Based Membranous Soft Materials. Langmuir 2021, 37, 3231–3247.
- Wang, H.; Xiong, X.; Yang, L.; Cui, J. Droplets in soft materials. Droplet 2022, 1, 110–138.
- Wang, K.; Ma, E.; Cui, H.; Wang, H. Amphiphilic micromotors as active demulsifiers for rapid oil–water separation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 640, 158272.
- Ghosh, K.; Lopez-Pamies, O. Elastomers filled with liquid inclusions: Theory, numerical implementation, and some basic results. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2022, 166, 104930.
- Style, R.W.; Boltyanskiy, R.; Allen, B.; Jensen, K.E.; Foote, H.P.; Wettlaufer, J.S.; Dufresne, E.R. Stiffening solids with liquid inclusions. Nat. Phys. 2015, 11, 82–87.
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Han, J.; Yang, L.; Li, J.; Song, Z.; Wang, T.; Zhu, J. Advanced liquid crystal-based switchable optical devices for light protection applications: Principles and strategies. Light. Sci. Appl. 2023, 12, 11.
- Priyadharshana, P.A.N.S.; Shen, T.-Z.; Hong, S.-H.; Song, J.-K. Widely Tunable GRIN Lenses Using Negative Dielectrophoretic Manipulation of Phosphate Nanosheets Colloid. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2022, 10, 2102429.
- Shen, T.-Z.; Perera, K.N.A.; Masud, A.R.; Priyadharshana, P.A.N.S.; Park, J.-Y.; Wang, Q.-H.; Hong, S.-H.; Song, J.-K. A dual-frequency photonic crystal nanocolloid with hue- and brightness-tunable structural colors. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2023, 4, 101343.
- Li, S.-L.; Wang, S.-H.; Luo, W.-C.; You, L.-Q.; Li, S.-S.; Chen, L.-J. Optofluidic tunable broadband distributed Bragg reflector based on liquid crystal polymer composites. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 33603–33612.
- Wu, J.-B.; Wu, S.-B.; Hu, W. Azimuthal orientation guided topological defect evolution across the nematic-smectic phase transition. Phys. Rev. B 2023, 108, 224107.
- Wu, S.-B.; Wu, J.-B.; Cao, H.-M.; Lu, Y.-Q.; Hu, W. Topological Defect Guided Order Evolution across the Nematic-Smectic Phase Transition. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2023, 130, 078101.
- Datsyuk, V.V.; Izmailov, I.A. Optics of microdroplets. Physics-Uspekhi 2001, 44, 1061–1073.
- Concellon, A.; Zentner, C.A.; Swager, T.M. Dynamic Complex Liquid Crystal Emulsions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 18246–18255.
- Guo, J.K.; Hong, S.H.; Yoon, H.J.; Babakhanova, G.; Lavrentovich, O.D.; Song, J.K. Laser-Induced Nanodroplet Injection and Reconfigurable Double Emulsions with Designed Inner Structures. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1900785.
- Park, S.; Lee, S.S.; Kim, S.H. Photonic Multishells Composed of Cholesteric Liquid Crystals Designed by Controlled Phase Separation in Emulsion Drops. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e2002166.
- Kang, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Fernandez-Nieves, A.; Reichmanis, E. Amplified Photon Upconversion by Photonic Shell of Cholesteric Liquid Crystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 5708–5711.
- Franklin, D.; Ueltschi, T.; Carlini, A.; Yao, S.; Reeder, J.; Richards, B.; Van Duyne, R.P.; Rogers, J.A. Bioresorbable Microdroplet Lasers as Injectable Systems for Transient Thermal Sensing and Modulation. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 2327–2339.
- Che, K.J.; Yang, Y.J.; Lin, Y.L.; Shan, Y.W.; Ge, Y.H.; Li, S.S.; Chen, L.J.; Yang, C.J. Microfluidic generation of cholesteric liquid crystal droplets with an integrative cavity for dual-gain and controllable lasing. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 3116–3122.
- Humar, M.; Musevic, I. 3D microlasers from self-assembled cholesteric liquid-crystal microdroplets. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 26995–27003.
- Capocefalo, A.; Quintiero, E.; Conti, C.; Ghofraniha, N.; Viola, I. Droplet Lasers for Smart Photonic Labels. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 51485–51494.
- Allen, K.W.; Darafsheh, A.; Abolmaali, F.; Mojaverian, N.; Limberopoulos, N.I.; Lupu, A.; Astratov, V.N. Microsphere-chain waveguides: Focusing and transport properties. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 021112.
- Peddireddy, K.; Jampani, V.S.R.; Thutupalli, S.; Herminghaus, S.; Bahr, C.; Muševič, I. Lasing and waveguiding in smectic A liquid crystal optical fibers. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 30233–30242.
- Zeininger, L.; Weyandt, E.; Savagatrup, S.; Harvey, K.S.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Swager, T.M. Waveguide-based chemo- and biosensors: Complex emulsions for the detection of caffeine and proteins. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 1327–1331.
- Liu, C.; Zheng, Y.; Yuan, R.Y.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, J.B.; Zhao, Y.R.; Wang, X.; Li, X.W.; Xing, Y.; Wang, Q.H. Tunable Liquid Lenses: Emerging Technologies and Future Perspectives. Laser Photonics Rev. 2023, 17, 30233–30242.
- Nagelberg, S.; Zarzar, L.D.; Nicolas, N.; Subramanian, K.; Kalow, J.A.; Sresht, V.; Blankschtein, D.; Barbastathis, G.; Kreysing, M.; Swager, T.M.; et al. Reconfigurable and responsive droplet-based compound micro-lenses. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14673.
- Liang, L.; Hu, X.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, S.; Hu, Q.; Liang, M.; Ai, Y. Tunable and Dynamic Optofluidic Microlens Arrays Based on Droplets. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 14938–14946.
- Zhong, Y.; Yu, H.; Wen, Y.; Zhou, P.; Guo, H.; Zou, W.; Lv, X.; Liu, L. Novel Optofluidic Imaging System Integrated with Tunable Microlens Arrays. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 11994–12004.
- Geng, Y.; Kizhakidathazhath, R.; Lagerwall, J.P.F. Encoding Hidden Information onto Surfaces Using Polymerized Cholesteric Spherical Reflectors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2100399.
- Yang, C.-j.; Chen, D. Researches and applications of cholesteric liquid crystal droplets. Chin. J. Liq. Cryst. Disp. 2022, 37, 1070–1078.
- Wang, C.; Yan, Z.; Gong, C.; Xie, H.; Qiao, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Chen, Y.C. Multicolor Light Mixing in Optofluidic Concave Interfaces for Anticounterfeiting with Deep Learning Authentication. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 10927–10935.
- Guo, J.K.; Vij, J.K.; Song, J.K. Tunable Transfer of Molecules between Liquid Crystal Microdroplets and Control of Photonic Crystallinity in Isolated Microdroplets. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2017, 5, 1700119.
- Schwartz, M.; Lenzini, G.; Geng, Y.; Ronne, P.B.; Ryan, P.Y.A.; Lagerwall, J.P.F. Cholesteric Liquid Crystal Shells as Enabling Material for Information-Rich Design and Architecture. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1707382.
- Noh, J.; Liang, H.-L.; Drevensek-Olenik, I.; Lagerwall, J.P.F. Tuneable multicoloured patterns from photonic cross-communication between cholesteric liquid crystal droplets. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 806–810.
- Lin, P.; Yan, Q.; Wei, Z.; Chen, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Huang, Z.; Wang, X.; Cheng, Z. Chiral Photonic Crystalline Microcapsules with Strict Monodispersity, Ultrahigh Thermal Stability, and Reversible Response. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 18289–18299.
- Shang, Y.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, G.; Chen, D.; Wang, J.; Jiang, L. Integrated sensing from the synergetic color change of the center/brush of cholesteric liquid crystal particles. Sci. China Mater. 2022, 65, 2565–2577.
- Li, D.-Y.; Wang, W.; Chu, L.-Y.; Deng, N.-N. Tunable Structural Coloration in Eccentric Water-in-Oil-in-Water Droplets. Nano Lett. 2023, 23, 9657–9663.
- Yang, Y.; Kim, J.B.; Nam, S.K.; Zhang, M.; Xu, J.; Zhu, J.; Kim, S.-H. Nanostructure-free crescent-shaped microparticles as full-color reflective pigments. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 793.
- Liu, M.; Fu, J.; Yang, S.; Wang, Y.; Jin, L.; Nah, S.H.; Gao, Y.; Ning, Y.; Murray, C.B.; Yang, S. Janus Microdroplets with Tunable Self-Recoverable and Switchable Reflective Structural Colors. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2207985.
- Qin, L.; Liu, X.; He, K.; Yu, G.; Yuan, H.; Xu, M.; Li, F.; Yu, Y. Geminate labels programmed by two-tone microdroplets combining structural and fluorescent color. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 699.
- Qu, C.; Li, X.; Zhao, N.; Zhou, S.; Wang, J.; Yao, L.; Liu, Y. A three-state label programmed using a three-color microsphere of structural, fluorescent and dye colors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2023, 11, 9649–9656.
- Li, J.; Xie, S.; Meng, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhan, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Shui, L.; Zhou, G.; Feringa, B.L.; Chen, J. Dynamic Control of Multiple Optical Patterns of Cholesteric Liquid Crystal Microdroplets by Light-Driven Molecular Motors. CCS Chem. 2024, 6, 427–438.
- Mattich, I.; Sendra, J.; Galinski, H.; Isapour, G.; Demirörs, A.F.; Lattuada, M.; Schuerle, S.; Studart, A.R. Magnetic Manipulation of Superparamagnetic Colloids in Droplet-Based Optical Devices. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2023, 11, 9649–9656.
- Shen, S.; Feng, H.; Deng, Y.; Xie, S.; Yi, Z.; Jin, M.; Zhou, G.; Mulvaney, P.; Shui, L. A reflective display based on the electro-microfluidic assembly of particles within suppressed water-in-oil droplet array. Light Sci. Appl. 2023, 12, 290.
- Huang, C.; Shang, Y.; Hua, J.; Yin, Y.; Du, X. Self-Destructive Structural Color Liquids for Time–Temperature Indicating. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 10269–10279.
- Tan, H.; Park, S.-Y. Poly(acrylic acid) Hydrogel Microspheres for a Metal-Ion Sensor. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 1039–1048.
- Concellón, A.; Fong, D.; Swager, T.M. Complex Liquid Crystal Emulsions for Biosensing. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 9177–9182.
- Noh, K.G.; Park, S.Y. Smart molecular-spring photonic droplets. Mater. Horiz. 2017, 4, 633–640.
- Bao, P.; Paterson, D.A.; Harrison, P.L.; Miller, K.; Peyman, S.; Jones, J.C.; Sandoe, J.; Evans, S.D.; Bushby, R.J.; Gleeson, H.F. Lipid coated liquid crystal droplets for the on-chip detection of antimicrobial peptides. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 1082–1089.
- Paterson, D.A.; Du, X.; Bao, P.; Parry, A.A.; Peyman, S.A.; Sandoe, J.A.T.; Evans, S.D.; Luo, D.; Bushby, R.J.; Jones, J.C.; et al. Chiral nematic liquid crystal droplets as a basis for sensor systems. Mol. Syst. Des. Eng. 2022, 7, 607–621.
- Yu, H.; Wang, K.; Szilvasi, T.; Nayani, K.; Bao, N.; Twieg, R.J.; Mavrikakis, M.; Abbott, N.L. Design of Chemoresponsive Soft Matter Using Hydrogen-Bonded Liquid Crystals. Materials 2021, 14, 1055.
- Li, S.-L.; Chen, Z.-Y.; Chen, P.; Hu, W.; Huang, C.; Li, S.-S.; Hu, X.; Lu, Y.-Q.; Chen, L.-J. Geometric phase-encoded stimuli-responsive cholesteric liquid crystals for visualizing real-time remote monitoring: Humidity sensing as a proof of concept. Light Sci. Appl. 2024, 13, 27.
- Yuan, Z.; Han, M.; Li, D.; Hao, R.; Guo, X.; Sang, S.; Zhang, H.; Ma, X.; Jin, H.; Xing, Z.; et al. A cost-effective smartphone-based device for rapid C-reaction protein (CRP) detection using magnetoelastic immunosensor. Lab Chip 2023, 23, 2048–2056.
- Chen, Q.-M.; Wang, H.-C.; Wang, G.-Y.; Xu, C.-T.; Tan, Q.-G.; Duan, W.; Lu, Y.-Q.; Hu, W. Color-selective optical edge detection enabled by thermally stimulated cholesteric liquid crystals. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2023, 123, 251101.
