Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is an old version of this entry, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Subjects:
Environmental Sciences
Mercury contamination in the Amazon arising from both natural sources and intensive mining activities in the region is a significant public health concern. This metal is used to separate Au from sediments.
- environmental impact
- mining impact
- ecotoxicology
1. Introduction
The vast geographical extension of the Amazon region, covering approximately 7 million km2, is characterized by remarkable biological diversity and complex ecosystems, including both aquatic and terrestrial environments [1,2,3]. However, this region has been experiencing increasing pressure owing to the intensified encroachment of human activities. The mining sector is one of the main drivers of this pressure. This increase in mining activities has led to the deterioration of vegetation cover and soil erosion, culminating in the degradation of forest areas [4,5,6]. The Scientific Panel for the Amazon identifies these human activities as the primary catalysts for forest degradation, impacting multiple aspects of the ecosystem [7].
In the Amazon, the progression of artisanal and small-scale gold mining (ASGM) is primarily driven by the discovery of new gold deposits and stimulated by the profitability of this activity. Its expansion into indigenous territories, which started during the 1980s, was facilitated by weak environmental law enforcement and intense lobbying activities, leading to various socio-environmental implications [8].
This ongoing trend continues to challenge environmental governance [9,10]. Contemporary illegal mining activities in the Brazilian Amazon have experienced exponential growth, increasing by more than 90% since 2017, leading to major forest loss in 2020 [10,11,12,13,14,15], especially during the COVID-19 pandemic [16].
Furthermore, the exploitation of forest resources contributes substantially to the environmental degradation of the Amazon, with small-scale mining playing a crucial role in countries such as Suriname, Ecuador, Peru, and Guyana [17,18,19,20,21].
Gold prospectors employ rudimentary extraction methods involving the use of mercury to capture dense gold particles through gravitational concentrations of water–ore slurry [22]. With their disregard for efficiency and safety, much of the Hg0 used by these miners is discharged in mining tailings, in turn contaminating the surrounding water resources [11,23,24,25,26]. This practice eventually leads to the formation of the most toxic and bioavailable form of Hg, methylmercury (CH3Hg+), through the conversion of aqueous Hg2+ and Hg0 by sulfate-reducing bacteria in anoxic aquatic environments. CH3Hg+ then moves further up the freshwater food chain via aquatic plant roots and reaches fish trophic levels, where it bioaccumulates and biomagnifies in higher concentrations in the tissues of top predators. This feeding habit as well as the uptake of aqueous CH3Hg+ from fish gills is expected to cause high bioaccumulation in the liver, brain, and muscle, with the latter pathway directly affecting the cardiovascular system [27]. High levels of CH3Hg+ affects cellular function, leading to irreversible neurological damage in animals and humans [28,29].
Therefore, the contaminated aquatic food chain poses a significant threat to vulnerable Amazonian populations dependent on fishing for subsistence and nutrition from fish as their primary source of animal protein, as it is also their main gateway to Hg exposure [12,15,26,30,31,32]. CH3Hg+ comprises approximately 80% of the total mercury found in human hair, and its presence in the biological matrix indicates chronic mercury exposure. Hair, as the biomarker of Hg, is generally preferred over blood, urine, or other tissues, owing to the ease of collecting samples, its non-intrusive nature, and its ability to record long-term exposure.
This situation prompted the World Health Organization (WHO) and regional Common Market of the South (MERCOSUR) to publish references on Hg threshold levels for food safety and human exposure.
On the other hand, the Amazon naturally exhibits high levels of Hg from volcanic sources in the Andes, as evidenced by its presence in forest soil, which is carried to tributaries through erosion and then to rivers where the contaminant is diluted and adheres to sediments [33,34,35,36]. However, mining can hasten the release and mobilization of natural inorganic Hg through deforestation and erosion, as well as elemental Hg introduced for the amalgamation process [37,38].
2. Mercury Contamination Distribution in the Amazon Region
2.1. Overview of THg Levels in Animal Research
The results of these studies demonstrated that ecotoxicological research on Hg is predominantly conducted in aquatic ecosystems, mostly comprising fish species, considering exposure to indigenous and riverside communities in major rivers and tributaries. Therefore, to facilitate a more effective statistical overview, records that used fish muscle as a THg biomarker were reviewed separately.
Accordingly, the predominance of fish muscle tissue could be plotted and categorized into predatory and non-predatory feeding guilds. The boxplots for fish indicate the distribution of THg into the following categories: all fish muscle (median 0.440 µg/g and interquartile range (IQR) 0.820 µg/g), predatory fish muscle (median 0.690 µg/g and IQR 0.900 µg/g), and non-predatory muscle (median 0.210 µg/g and IQR 0.300 µg/g). Predatory fish, classified as carnivores, exhibit THg ranges above the guidelines established by WHO, with levels being 1 µg/g and 0.5 µg/g, respectively, for predatory and non-predatory fish. In contrast, the non-predatory group, which included omnivores and other species, displayed significantly lower THg levels, suggesting a safe mean level (Figure 6).
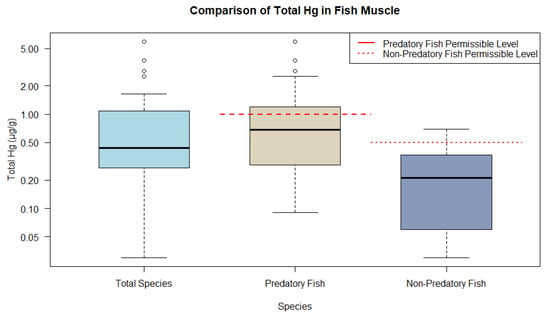
Figure 6. Representations of THg ranges in fish muscle tissue from animal research compared to WHO and MERCOSUR guidelines.
Accordingly, the highest frequencies of studies in the main tributaries of the Amazon River were for Plagioscion squamosis Yesus, Serrasalmus rhombeus, and Cichla spp. The carnivorous guild had the highest THg values (ranging from 0.086 to 5.920 μg/g), with a mean of 1.058 μg/g, followed by the omnivores (0.029 μg/g to 0.700 μg/g), with a mean of 0.316 μg/g, and the detritivores (0.064 μg/g to 0.370 μg/g), with a mean of 0.180 μg/g.
Additionally, studies evaluating fish in hydroelectric reservoirs and dam regions showed that Puruzinho and Catalão Lakes presented higher mercury concentrations of S. rhombeus (mean 0.789 μg/g, and range of 0.029 to 1.640 μg/g) [71,81,84]. On the other hand, the reservoirs of Belo Monte and Jirau Hydroelectric Plants showed high concentrations of mercury in S. rhombeus (0.480 μg/g) and lower concentrations in Triportheus albus (0.132 μg/g) [90,94].
Variation from 0.010 to 17.900 µg/g of THg across ecoregions can be observed. Most sampling points were recorded in the southern Amazon forests, with a mean mercury level of 0.890 µg/g (range 0.016 to 11.570 µg/g), followed by the western Amazon forests, with a mean mercury level of 1.700 µg/g (range 0.150 to 17.420 µg/g). The least abundant points were recorded in the Guyana ecoregion, with a mean mercury level of 1.570 µg/g (range 0.165 to 5.920 µg/g).
The Brazilian territory has the highest concentration of scientific reports, including the Amazon River and its major tributaries, with emphasis on the Madeira and Tapajós Rivers. Specifically, the Madeira River basin, which acts as a boundary between bioregions, has a mean mercury level of 0.470 µg/g in fish (range 0.014 to 4.046 µg/g). Also, Brazil Rondônia, near the region of Porto Velho, and the Tapajós River have a mean of 0.69 µg/g (range 0.0740 to 1.510 µg/g). Additionally, the Madre de Dios River basin in Peru has a mean of 0.720 µg/g of mercury (range 0.200 to 3.720 µg/g), while the mean mercury level in fish of the Amazon River was 0.673 µg/g (range 0.050 to 1.490 µg/g) (Figure 7).
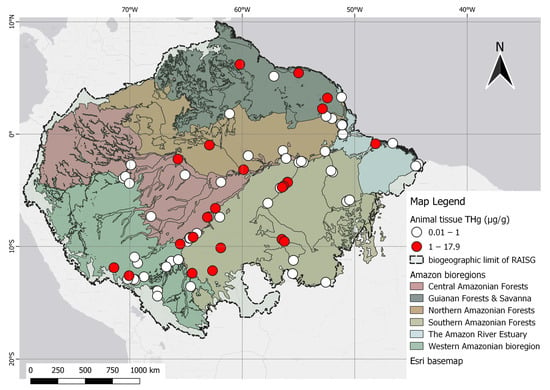
Figure 7. Spatial distribution of animal studies categorized by THg levels in fish in relation to the permissible reference concentration of 1.0 µg/g in the human diet, as established by WHO.
The highest levels of THg reported in the Amazon were in the skin tissues of Panthera onca (17.900 µg/g) and the hepatic tissue of Arapaima gigas (17.400 µg/g). In Brazil, the highest value of mercury in predatory fish was found in the black piranha (S. rhombeus), a carnivore, at 1.640 µg/g [84]. The highest muscle mercury concentration in countries outside Brazil was found in a study carried out at Oxbow Lakes, a natural protected area in Madre de Dios Province, Peru, at 3.170 µg/g, and along the Mazaruni River in Guyana, at 5.920 µg/g, both of which are areas close to mining activities [101,107].
2.2. Overview of THg Levels in Human Research
All categories analyzed exceeded the WHO guidelines for Hg in hair, suggesting that indigenous populations are exposed to higher levels of Hg, which may have implications for the health of these populations (Figure 8).
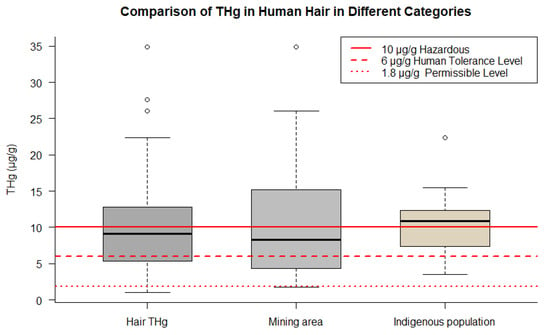
Figure 8. Comparison of THg concentrations in human hair across different groups. The figure points out data for overall samples, indigenous populations, and mining areas.
The total hair THg in humans ranged from 1.030 to 27.620 µg/g. Notably, it can distinguish the following groups: children, who had a mean of 8.81 µg/g (range 1.030 to 22.380 µg/g); indigenous populations, with a mean of 13.190 µg/g (range 2.060 to 34.900 µg/g); women of reproductive age, including mothers, pregnant women, and lactating women, who had a mean of 7.710 µg/g (range 2.120 to 12.80 µg/g); riverside populations, with mean concentrations of 10.610 µg/g (range 3.070 to 22.380 µg/g); and, finally, a mean of 11.930 µg/g (range 1.740 to 34.90 µg/g) reported for individuals living in mining areas.
Only two studies do not consider total human mercury concentrations in hair. One reported data from the breast milk (mean 0.010 µg/g THg) of lactating women to estimate exposure to neurotoxic metals influenced by small-scale mining in infants in Porto Velho, Rondônia, Brazil [154]. Another reported blood levels (mean 0.021 µg/g THg) in Amazonian juvenile populations in Cuniã, Brazil [155].
It should be noted that the indigenous community is well represented, especially in the Munduruku reserve/community in the Tapajós basin and in studies in the Madre de Dios region in Peru, as part of cohort studies [136,144,147] where comparisons were made between native demographics and mining hotspots, together with respective controls around the Amarakaeri Communal Reserve. Pregnant women, women of reproductive age, and juveniles received particular attention owing to their heightened vulnerability to mercury exposure. Interestingly, one study revealed that occupational Hg exposure from mining remained lower than levels observed in riverside communities, as exemplified by the riverside population of Itaituba (20 µg/g THg) compared to the mining region of Serra Pelada (1 µg/g THg) [146].
The spatial representation of human research is highest in the southern forest bioregion with 34 records. In this area, the highest density was recorded in the Tapajós basin, followed by western Amazon ecoregions with 28 records. The remaining studies were conducted in the other three regions.
The human data presented spatial trends nearly identical to studies concentrated in the Tapajós and Madeira River basins in Brazil and Madre de Dios in Peru. Evidence of three classes of THg gradients, along with several high-Hg points, can be visualized as deep red dots scattered across the map. This feature has also been observed in the northern and western areas of the Amazon Forest, including studies conducted in the state of Amazonas, Roraima in Brazil, and Nariño in the Colombian Amazon. These observations are illustrated in Figure 9.
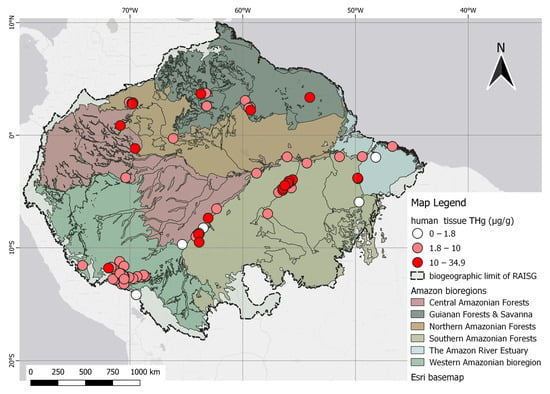
Figure 9. Spatial distribution of human studies according to THg levels, categorized as permissible (1.8 µg/g), dangerous (10 µg/g), and above the dangerous level (>10 µg/g).
2.3. Mining
Many studies have reported on Hg in regions with mining activities in floodplain areas, including all classes of Amazonian floodplains, grouped according to Dinerstein et al. [56]. It was possible to observe tributaries with intense mining activity near the sampling points, which are grouped on the map into classes according to distances, i.e., of 0–20 km, 20–50 km, and above 50 km, relative to mining polygons. The mining polygons (orange scheme) comprise a combination of datasets consisting of global mining footprints [58] with a layer of illegal mining, as adapted from RAISG [44].
Floodplain areas were specifically included in the analysis to represent zones of high water retention and the accumulation of mining tailings, which are factors that can contribute to Hg concentrations in the environment [84,156]. Notably, the extent of illegal mining is more widely recognized by initiatives such as RAISG, the data from which indicate an overlap of these activities with the studied areas. In particular, these illegal operations are prevalent in the western regions of the Napo River, an important tributary of the Amazon River basin, affecting the sample collection areas situated in the border zones that separate Peru, Colombia, and Brazil. Moreover, illegal mining activity is intense along the Madre de Dios River basin in Peru, with operations extending close to the designated sample collection areas. Certain sample points with close proximity classes (up to 20 km, and 20 km to 50 km) intersect with mining zones.
Highlights for animal studies from these points are in the Mazaruni River basin region in Guyana and the downstream Suriname River region, despite the low representation of study articles. Regions with significant research overlap and mining activity in the interior include the Tapajós basin, close to the Munduruku Reserve and Itaituba, and the Itacaiúnas River basin, situated between the Xingu and Tocantins River basins in Brazil.
Based on distance classification, mercury concentrations within a 20 km radius of the georeferenced mining sites (closest) had a mean of 0.870 µg/g (range 0.033–5.920 µg/g) for fish, wherein Serrasalmus spp. was the most frequently mentioned. The approximation category between 20 and 50 km had a mean of 0.506 µg/g (range 0.022 to 1.510 µg/g), and within this distance category, Plagioscion squamosis Yesus was the most cited fish species. Although higher, the mean muscle THg concentrations in fish closest to mining activity are still slightly below the 1 µg/g limit, indicating a permissible level for predatory fish, but it does exceed the permitted dietary reference of Hg set at 0.50 µg/g for their non-predatory counterparts. Figure 10 shows the point data for animal records, which are mapped alongside polygons that indicate small-scale mining.
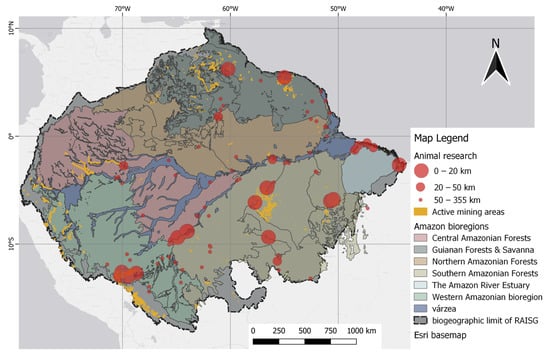
Figure 10. Spatial distribution of animal studies relative to mining polygons. Distance classes, as indicated by the 20 km and 50 km markers, were defined by the difference in point size.
Research on human tissues has also been mapped along with the geospatial information of mining and indigenous territories. The results of human studies show that the highest number of studies were conducted close to the illegal mining polygons of RAISG in the Madre de Dios and Tapajós basins. The Madeira River basin is also the subject of a high number of studies, but with less illegal mining activity. This is because illegal mining follows the river flow, likely the result of alluvial mining activities. Consequently, the cities of Itaituba and Marabá, both in the Tapajós basin, are among the most frequent sample areas near illegal mining activities, reported in high numbers.
Despite limited spatial representation in the north, some studies have highlighted the presence of mining activities. Among these, small-scale mining has been reported in the mountainous region of Marudi, which is located in Guyana [145]. Another point of interest is the Lawa River basin situated in French Guiana [8]. Additionally, the Yanomami indigenous region in Roraima, Brazil, which is in the Uraricoera River basin, is also mentioned [152]. Although limited in number, these studies hold significant value because of their proximity to mining areas in the Guiana Shield.
The human samples closest to mining areas up to 20 km had a mean THg of 4.301 µg/g (1 to 11.61 µg/g), while human samples at a distance of 20 km to 50 km had a mean of 6.782 µg/g (0.01 to 12.80 µg/g). Notably, all studies conducted within a 20 km radius of mining areas were also within a 17 km radius of indigenous territories. Figure 11 shows human studies related to mining polygons.
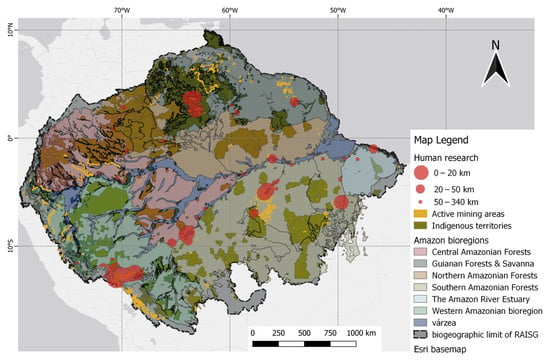
Figure 11. Spatial distribution of human studies relative to mining polygons. Distance classes, as indicated by the 20 km and 50 km markers, were defined by the difference in point size. Native/indigenous territories were included as darker overlays.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/toxics12030204
This entry is offline, you can click here to edit this entry!
