Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is an old version of this entry, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Subjects:
Engineering, Electrical & Electronic
Due to damage to the network of nerves that regulate the muscles and feeling in the shoulder, arm, and forearm, brachial plexus injuries (BPIs) are known to significantly reduce the function and quality of life of affected persons. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), a considerable share of global disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) is attributable to upper limb injuries, including BPIs. Telehealth can improve access concerns for patients with BPIs, particularly in lower-middle-income nations.
- telehealth
- brachial plexus injuries
- rehabilitation
- robotic
- deep reinforcement learning (DRL)
1. Introduction
Telehealth emerges as a promising solution to the barriers faced in accessing rehabilitation services for BPIs in lower-middle-income countries. Telehealth can bridge the gap between rural patients and quality healthcare services by leveraging technology. The need for telehealth is further compounded by current global trends, where, according to the World Health Organization, DALYs attributable to upper limb injuries, including BPIs, have seen an estimated increase of 3% over the last decade. In countries like Pakistan, where 64% of the population resides in rural areas [1], implementing telehealth services can significantly reduce the burden of disability and improve the overall quality of life for individuals with BPIs.
Technologies are used to remotely provide clinical information and health-related services in telehealth, a fast-developing area of healthcare. This field has many uses, one of which is rehabilitation, where robotics is very important. Through interactive and customized rehabilitation experiences, robotic technologies in telehealth go beyond conventional telemedicine. Relatively speaking, these remote-controlled robotic systems allow for more accurate and consistent therapy sessions than traditional in-person therapies offer. In particular, for conditions like BPIs, where consistent and targeted exercises are essential for recovery, this robotics integration with telehealth has revolutionized patient care.
A network of nerves called the brachial plexus emerges from the spinal cord, passes through the armpit and neck, and then splits off to become the nerves responsible for upper limb sensation and muscle control. It includes the muscles and skin of the chest, shoulder, arm, and hand as well as the roots, trunks, divisions, cords, and branches that supply that innervation. Many impairments can arise from BPIs, which are typically caused by trauma, tumors, or inflammation. These can include, but are not limited to, paralysis in extreme cases, loss of feeling, and muscle weakness, as shown in Figure 1. Such injuries can have a significant negative effect on a patient’s functionality and quality of life, requiring specialized care and rehabilitation techniques. BPIs can occur due to various reasons such as trauma, tumors, or inflammation.
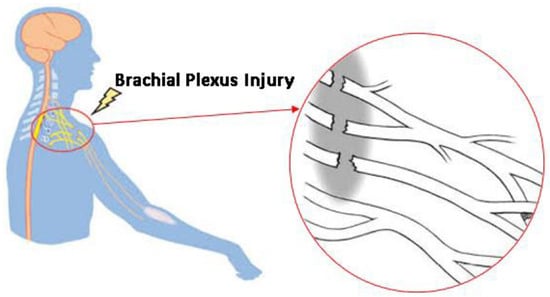
Figure 1. Damage to the complex network of nerves that control the muscles due to a BPI.
For instance, motor vehicle accidents, especially motorcycle crashes, account for a substantial percentage of traumatic BPIs, as shown in Figure 2, which provides an essential visual summary of the varied mechanisms leading to BPIs, with each panel (A–F) depicting a distinct accident scenario that highlights the complexity and diversity of BPI causes, aiding in quick and clear comprehension. These injuries can range from minor, which might involve stretching the nerves, to severe cases, such as avulsion, where the nerve roots are torn from the spinal cord. The severity and location of the damage significantly influence the functional outcome. According to a study conducted in [2,3], over 60% of BPI patients suffer from impairments in activities of daily living, with an estimated 27% facing significant chronic pain.
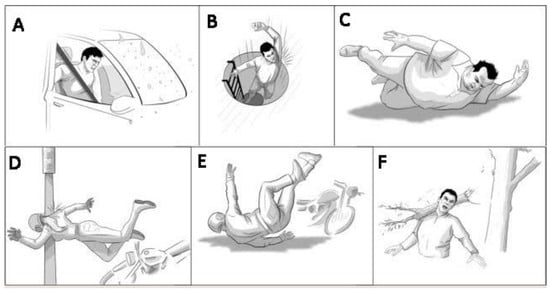
Figure 2. Different accidental occurrences of BPIs: (A) car accident, (B) dropping from a height, (C) obese human falling down, (D) high-speed bike accident and pole collision, (E) bike accident on the road, and (F) heavy object hit on shoulder.
Rehabilitation plays a critical role in the management of BPIs. Early intervention and a well-structured rehabilitation program can significantly improve affected individuals’ functional outcomes and quality of life [4]. The rehabilitation process usually involves physical therapy, occupational therapy, and sometimes surgical interventions. Physical therapy focuses on maintaining the range of motion, reducing pain, and strengthening the muscles around the shoulder and arm. Occupational therapy is vital for enabling the patient to regain the ability to perform daily activities [5].
While rehabilitation is crucial, access to quality healthcare and rehabilitation services remains a significant challenge, especially in lower-middle-income countries. Rural areas in these countries often lack the necessary infrastructure and qualified healthcare professionals to provide specialized care for patients with BPIs. Additionally, travel to urban areas with better healthcare facilities is often not feasible due to financial constraints and the debilitating nature of the injury. Consequently, many patients with BPIs in these areas do not receive the much-needed rehabilitation services, leading to poor functional outcomes and a reduced quality of life.
2. Telehealth Rehabilitation Applications
Telehealth rehabilitation had its roots in the 1960s, when some hospitals and university medical centers started experimenting with telemedicine to reach patients in remote areas. However, it was not until the advent of the internet and advancements in telecommunications technology in the 1990s that telehealth began to take form. Telehealth has been gaining momentum over the past two decades, and its application in rehabilitation is diverse. One notable example is the development of the InMotion ARM, a telehealth robotic system that allows for remote physical therapy for stroke patients [7].
Furthermore, robotic assistance in telerehabilitation has proven to be a groundbreaking advancement; [8] presented an extensive study on how robots have been instrumental in rehabilitating patients with neuromuscular disorders. This work especially delves into upper and lower limb exercises, stressing the role of robots in aiding patients in performing high-intensity repetitive tasks, which is crucial for neuroplasticity. The authors showed how robots can objectively measure patients’ movements and improvements.
Jin et al. [9] have demonstrated the efficacy of deep reinforcement learning (DRL) in improving post-stroke limb function, whereas Majhi and Kashyap [10] have explored adaptive algorithms for patient-specific therapy adjustments. Furthermore, the work by Wang et al. [11] has been instrumental in showcasing how DRL can optimize engagement levels during robotic-assisted therapy. These studies underscore the potential of DRL to enhance the adaptability and personalization of rehabilitation protocols according to motor rehabilitation.
Another instance is Teleswallowing Rehabilitation, which assists in the remote assessment and management of dysphagia in elderly patients [12,13]. These examples scratch the surface of what has been accomplished in telehealth rehabilitation, where systems have been developed for various types of physical impairments, speech therapy, and more. Robotics has been a key component in advancing rehabilitation methods. For example, the Lokomat, developed by Hocoma, is a robotic gait therapy device widely used in rehabilitating individuals with spinal cord injuries and stroke [14]. Another example is the ArmeoPower, a robotic exoskeleton for arm and arm rehabilitation, also for patients with stroke or spinal cord injuries [15,16,17].
Telehealth rehabilitation has also been influential in managing chronic pain, as discussed by [18,19,20]. Their work focuses on internet-delivered treatment for chronic pain management. It also delves into how integrating psychological approaches into telehealth platforms has helped in better pain management. Moreover, telerehabilitation is increasingly seen as a viable method for managing cardiovascular diseases. In a study by [21,22,23,24,25], a home-based telerehabilitation program was studied for patients with heart failure. The study elucidated how telerehabilitation could effectively enhance the exercise capacity and quality of life of patients with chronic heart diseases. An interesting approach is also observed in a research work by [26,27], where the authors developed a tele-treatment program for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). They designed a service platform that includes exercise, education, and counselling, supported by a triage function. Godine et al. in [28] addressed the novel approaches in telehealth for behavioral management in individuals with neurological conditions. They discussed various telerehabilitation interventions, such as cognitive behavioral therapy, motivational interviewing, and mindfulness-based stress reduction, that can be leveraged to manage symptoms and enhance the quality of life. Moreover, integration with electronic health records (EHRs) has emerged as an essential feature in telehealth rehabilitation. According to [29], EHR integration enables efficient information sharing, leading to better coordination in care processes.
Interactive online platforms have enabled the remote delivery of physical therapy. Johnson et al. in [30] explored an online platform, PhysiTrack, which allowed physical therapists to design personalized exercise programs. Patients from their homes could access these. The study demonstrated that patients using PhysiTrack showed better exercise adherence and reported higher satisfaction levels than in traditional physical therapy. Robotics is another domain that has greatly advanced telehealth rehabilitation. In a study [31] by Radder et al., telerehabilitation robotics were shown to be effective in providing intensive task-specific training, especially for stroke patients. The study highlighted that robotic devices could deliver repetitive training tasks, which are often required for neuromuscular rehabilitation. A study [32] by Patel et al. showcased the use of kinematic sensors and smart textiles to remotely monitor patients’ movements during physical therapy. These real-time data were critical for providing feedback to both the patient and the therapist, allowing for more targeted and effective therapy. Virtual reality (VR) has been another significant advancement. Laver et al.’s study [33] showed that VR could be effectively employed in telerehabilitation settings, particularly for stroke rehabilitation. Patients using VR systems showed improved physical activity compared to those who underwent conventional therapy.
DRL has been employed in various healthcare applications. For example, Peng et al. [34], utilized DRL for dose optimization in radiation therapy. Another application of DRL is in optimizing treatment plans for patients with chronic conditions such as diabetes, where Prasad et al. [35] used DRL to create personalized insulin plans. One recent development is using artificial intelligence (AI) in telerehabilitation. Wade et al. [36] highlighted AI’s role in enhancing telerehabilitation outcomes. By incorporating AI algorithms, it is possible to analyze patients’ data to create personalized rehabilitation plans that can dynamically change as per their progress. Table 1 describes different published research work with respective technologies and advantages and disadvantages.
Table 1. Comparison of different published works of related fields.
| Research Paper | Technology Used | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| [1] | Telehealth robotic system |
|
|
| [5] | Telehealth swallowing assessment tool |
|
|
| [6] | Robotic gait therapy |
|
|
| [7] | Robotic exoskeleton |
|
|
| [16] | Deep reinforcement learning for dose optimization |
|
|
| [17] | Deep reinforcement learning for insulin optimization |
|
|
| [This Study] | Telepresence robot with mechanical arm |
|
|
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/s24041273
This entry is offline, you can click here to edit this entry!
