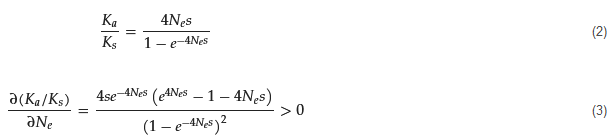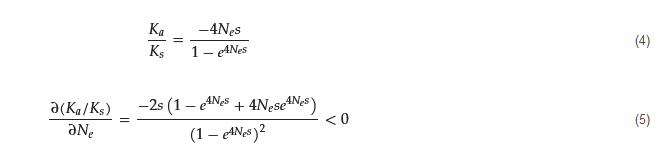Forest genetic conservation is typically species-specific and does not integrate interspecific interaction and community structure. It mainly focuses on the theories of population and quantitative genetics. This approach depicts the intraspecific patterns of population genetic structure derived from genetic markers and the genetic differentiation of adaptive quantitative traits in provenance trials. Phylogenetic β-diversity would assess the similarities and differences of a tree species across communities regarding ecological function, the strength of selection pressure, and the nature and extent of its interaction with other species.
1. Introduction
Forest genetic resources consist of primary and secondary gene pools [
1]. The primary gene pools are the undisturbed natural forests, and the secondary gene pools are the remaining forests after ecosystem disturbance (including breeding populations and provenance trials). Many believe that genetic diversity in the primary gene pools can be conserved without the need to maintain it. However, as natural areas become progressively modified by human and non-human interferences, maintaining the genetic diversity of natural forests and their ecosystems will increasingly depend on the knowledge of intraspecific population and interspecific community evolutionary processes under the community ecology framework.
A well-known fact is that forest trees are long-lived compared to crops, insects, and animal species. Trees often grow in heterogeneous habitats where the environmental conditions vary in time and space. They are sessile and are constantly under multi-year influences of the changes in the ecosystem and the pressure of either abiotic or biotic factors. The abiotic factors include natural environmental and physical habitats, such as rivers, mountains, climatic conditions, habitat fragmentation, and other barriers to species distribution. These factors interact with a tree species’ reproductive system (selfing, outcrossing, or a mixed system) to influence its population genetic structure [
2]. Except for a small proportion of species that reproduce asexually only, most tree species have their geographic distributions formed by restrictive seed dispersal or pollen dispersal via pollination with recipient populations to produce seeds, followed by seedlings and subsequent growth. The abiotic factors impede seed and pollen dispersal and create population genetic differentiation or phylogeographical variation [
3,
4,
5].
Biotic factors also influence species distribution, including intraspecific (e.g., density-dependent growth) and interspecific interactions [
6,
7]. A typical tree species distribution often covers diverse ecological communities and coexists with multiple species in its natural distribution. It may have positive, negative, or random associations with other species across communities. Such associations subsequently reduce genetic diversity if interspecific interactions produce directional selection acting on the tree species or maintain genetic diversity if balancing selection acting on the tree species is created.
In addition, natural hybridization and gene introgression frequently occur between closely related species in a forest community [
8,
9]. Hybridization occurs naturally in about 25% of plant species [
10,
11]. These hybrids contribute to species diversity, such as a hybrid zone as a barrier to isolating parental populations. Hybrids combined with recombination could generate transgressive segregation where extreme phenotypes that lead to speciation are formed [
12,
13]. These phenomena necessitate attention to hybrids in genetic conservation, which is not considered in species-based genetic conservation either.
Conventional forest genetic conservation is based on the theories of population and quantitative genetics [
14,
15,
16,
17]. Molecular markers are often applied to investigate population genetic structure (
𝐹𝑠𝑡) and the geographical pattern of genetic diversity and to infer potential routes of population formation and historical events [
18,
19,
20,
21]. Provenance trials, also known as common garden trials, are the planting experiments on multiple controlled field sites, with seedlings derived from seeds sampled from various locations in the natural distribution of a tree species [
22]. Provenance trials are employed to investigate population genetic differentiation (
𝑄𝑠𝑡, the same biological meaning as
𝐹𝑠𝑡) [
23] and the geographical variation of quantitative traits, to delineate seed zones, and to develop seed allocation guidelines. These two pieces of information, one for population structure/history and the other for adaptive population differentiation, are then combined to determine the strategy of genetic conservation [
4,
24,
25]. However, the results from both molecular markers and provenance trials do not provide information on species coexistence in natural forests. Provenance trials could examine site or genotype-by-environment effects and implicate conservation strategy in situ [
26,
27]. Because provenance trials are designed under controlled environmental conditions, the site effects imply the necessity of not protecting local habitats. Neither molecular marker-based nor provenance trials provide information on interspecific interactions and natural hybridization in natural forest communities.
The population genetic theory emphasizes the intraspecific interaction among genotypes, and its approach is widely applied to instructing genetic conservation [
3,
28]. The basic evolutionary processes that maintain genetic diversity involve selection, genetic drift, migration, and mutation at the population level [
29]. These are naturally connected to the evolutionary processes that maintain biodiversity at the community level, including species selection, ecological drift, dispersal, and speciation [
30,
31,
32,
33]. These two levels of ecological and evolutionary processes not only participate in forest community assembly and succession but also shape the genetic diversity and evolution of tree species in the forest community.
Community phylogeny effectively addresses interspecific interactions and natural hybridization, where community assembly can be characterized by lineage phylogenetic relationships [
34]. Few reports are available to analyze community ecological functions and biodiversity conservation from the perspective of community phylogeny [
35,
36]. For forest genetic resource management, the analysis of forest community phylogeny also helps to determine the taxonomic status of a species in its community and its association with other species. A species may have the same or different taxonomical positions across forest communities, depending upon the community assembly and the phase of community succession [
37,
38,
39]. Thus, it is interesting to integrate forest genetic conservation into the community ecology framework.
2. Community-Based Strategy of Genetic Conservation
2.1. Determining the Number of Communities
Scholars use β-diversity to characterize the degree of community differentiation in species assembly. This index can be calculated differently [
102,
103,
104,
105]. Many studies have used β-diversity to describe biodiversity [
106,
107,
108]. However, few studies have associated the community evolutionary processes with β-diversity. This line of work remains in its infancy but is of significance to better understand the mechanisms that maintain community differentiation [
109]. A straightforward case is under the neutrality assumption where the community size is fixed (
J) and other species equally compensate a decrease in one species’ abundance. All individuals in the community have the same birth and death rates [
31]. Suppose that there are an infinite number of local communities each with
J individuals, analogous to Wright’s island model in population genetics [
29]. Community differentiation (
𝐶𝑠𝑡) is derived below under an equilibrium of ecological drift (
1/𝐽) in any local community, the dispersal rate (m) to each local community, and the speciation rate (
𝑣) [
71]:

Dispersal across communities and speciation reduce β-diversity (𝐶𝑠𝑡) and tend to homogenize community assembly or community phylogenies. This relation may be used as a null hypothesis to test whether the selection process is broadly engaged in community differentiation.
With the conservation of forest genetic resources, β-diversity is used to design a network for protected communities. When a large proportion of the community differentiation (e.g., 95%) occurs, the community difference in species composition could be substantial. The protected area should cover multiple communities and more species. Heterogeneity in interspecific interaction could occur for a tree species with other species across the communities. In contrast, when there is a low level of community differentiation (e.g., less than 5%), only a few communities should be selected for conserving species diversity. This is analogous to the decision making on conserving genetic diversity based on
𝐹𝑠𝑡value for a single species [
18,
24]. A decision based on β-diversity focuses on the tree species diversity at the community level.
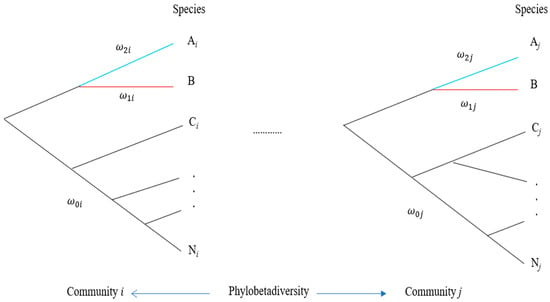
Apart from characterizing community differentiation by β-diversity, a further measurement is to combine β-diversity with phylogeny to define phylobetadiversity that measures community differentiation in terms of both community phylogeny and β-diversity (
Figure 2). This index is calculated by the distance (branch length differences) between phylogenetic trees of different communities. Several methods have been proposed to estimate this index. Graham and Fine [
110] discussed the application of phylobetadiversity in a biodiversity study, including an analysis of speciation, a combination with niche models, neutral theory, and global biodiversity patterns. However, the practical application of phylobetadiversity to conservation is rarely emphasized in the literature [
111]. In theory, phylobetadiversity can also be used to design the number of communities for conservation, analogous to the use of β-diversity. A slight difference in phylobetadiversity implies that a few communities are appropriate for conservation.
Figure 2. Determination of the number of communities based on the pattern of phylobetadiversity. A species of interest (species B) is indicated in red under hypothetical community phylogenies (communities i and j). Letters Ai, Ci, …, and Ni represent different species in community 𝑖. Letters Aj, Cj, …, and Nj represent different species in community 𝑗. All 𝜔 values on different branches can be estimated under different hypotheses of branch models in a community.
The practical analysis of community differentiation needs setting up forest plots, such as the forest census plots in Barro Colorado Island [
114] and multiple plots in China [
115,
116], to survey species richness and abundance for a given community. The ideal case is that entire plots are surveyed once a community boundary is set, but this forest census requires a high cost. Instead, multiple quadrats are often designed for forest surveys in each community. Community differentiation is then measured using some beta-diversity indices. Moreover, to identify hybrids of a species with other related species, large samples, such as more plots or quadrats, are preferred to improve the probability of capturing hybrids.
Accompanying community surveys by setting multiple plots or quadrats are the population samples of a species of interest. When the species is abundant in each community, a large sample size of the species per community, for example, >30 individuals, is recommended. When the species is less abundant in some communities, more quadrats are suggested to include the species as much as possible to assess the species’ population structure appropriately.
As mentioned above, the careful selection of orthologous genes or barcodes is needed to genotype all sampled individuals. High polymorphic markers, such as nuclear ITS markers, are recommended to identify hybrids or closely related subspecies. Chloroplast or mitochondrial DNA markers are appropriate to elucidate community phylogenetic relationships among distant species. Multiple orthologous nuclear gene sequences are relevant to examining genetic variation within and between species.
5.2. Detecting the Molecular Mechanism of Interspecific Interactions
The second step is to screen interspecific interaction for tree species in different forest communities. Various methods have been proposed to test species associations [
117], such as the method based on species presence/absence data among quadrats [
118] or the chi-square test using contingency tables [
119]. Cavender-Bares et al. [
34] reviewed species competitive interaction as a mechanism for phylogenetic relatedness.
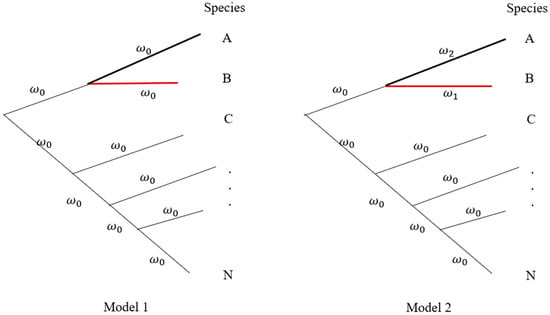
Figure 3 shows a hypothetical phylogenetic tree of a forest community. Suppose species B is the tree species of interest, and species A is its closely related species with interaction. We may set the branch model in the PAML (phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood) program [
120] to detect ω
and evaluate the relative selection pressure on different branches. For instance, two models are assumed in
Figure 3. The logarithm of likelihood ratio test (LRT),
, is applied to test whether the interacted species have significantly natural selection or not. With the analyses of multiple ecological communities, the change of ω on the branch of the target tree species signals different selection pressures or the difference of the target tree species interacting with different species across communities.
Figure 3. A hypothetical phylogeny in a forest community. Different species may have unequal branch lengths. Model 1 assumes that all branches have equal selection strength (𝜔0
). Model 2 assumes that species A (
𝜔2) is closely related to Species B (
𝜔1) under different selection intensities. All remaining species are set to have the same selection intensity (
𝜔0
). Letters A, B, C, …, and N represent different species in a forest community.
Besides the branch model, site or branch–site model analysis may also detect the positive or purifying selection of specific genes at the amino acid sites. This helps to screen particular genes involved in interspecific interaction in different communities.
It is essential to understand that disruptive selection facilitates speciation where alternative alleles tend to be fixed in different species. However, incompletely sorted lineages tend to occupy similar ecological niches and result in competition. This could vary in various communities. One prediction is that ecological drift (
1/𝐽) reduces the efficacy of species selection and weakens interspecific interaction in a small forest community. However, this benefits the species vulnerable to survival, which can be analogously implied from the population genetics theory [
121,
122,
123,
124]. Consider a diploid nuclear gene in a population with effective population size
𝑁𝑒. Under an equilibrium of selection and genetic drift effects, Kimura [
122] derived the fixation probability of a mutant allele. When the mutant allele is favorable (positive selection), the ratio of nonsynonymous to synonymous divergence among orthologous genes is
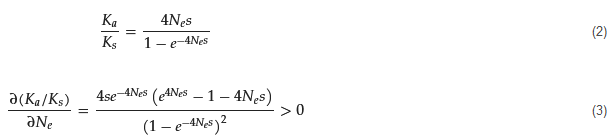
The product of the effective population size and selection coefficient,
𝑁𝑒𝑠, can be viewed as a scaled-selection coefficient and measures the strength of natural selection. An analogous expression to
𝑘𝑎⁄𝐾𝑠
for the fixation of a species relative to that under a neutral community in a local community of size J is not available yet. It is speculated that a large forest community could tend to facilitate the species with synergistic interacted effects (e.g., mutualism) on a species and improve species selection efficacy. A small forest community could impede such synergistic effects. However, population genetic theory implications need further theoretical confirmation in community ecology.
When the mutant allele is deleterious (purifying selection) in a population, the ratio of nonsynonymous to synonymous divergence is
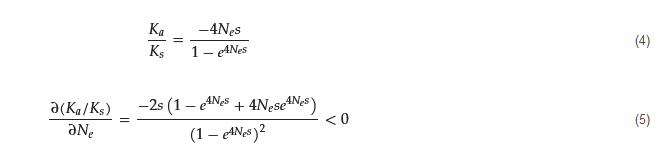
Similarly, it is speculated that a small forest community could weaken the purifying selection of the target tree species, while a large forest community could strengthen the purifying selection. This could likely weaken the antagonistic interacted effects on a species. Empirical evidence implicitly supports this theoretical prediction under communities of different sizes. Kapralov [
125] used 36 orthologous nuclear genes to estimate the
𝐾𝑎/𝐾𝑠 ratio of 27 species of the genus
Schiedea (Caryophyllaceae) sampled from the Hawaiian Islands and the mainland. The results showed that the
𝐾𝑎/𝐾𝑠
values were higher in the island group than in the mainland group. This was because the purifying selection in the island group was relaxed, and positive selection was more common than in the mainland group. Therefore, it is hypothesized that a tree species could undergo different intensities of natural selection in communities of different sizes. More evidence is needed to verify this prediction.
5.3. Integrating Two Levels of Evolutionary Processes into Genetic Conservation
The third step is integrating information from population genetic structure, community structure, and interspecific interactions into genetic conservation. Under the community framework, if the sampling sites are set in different forest communities, both community phylogeny and interspecific interactions help to interpret population genetic differentiation. When the effects of interspecific interactions are more significant than the effects of genetic drift, the following outcomes could be yielded:
-
When the given tree species has different patterns of selection across communities, e.g., a half number of communities with positive selection (𝐾𝑎/𝐾𝑠>1) and another half with purifying selection (𝐾𝑎/𝐾𝑠<1
-
), the effects of interspecific interactions can amplify population genetic differentiation. Population genetic differentiation is more significant than that under neutrality. Selection due to interspecific interactions would increase the genetic differentiation of the species at the population level, which is analogous to the outcome of genetic hitchhiking effects or background selection effects on genetic differentiation at a linked neutral site [
126,
127,
128].
-
When the given tree species has the same degree and pattern of interspecific interactions across communities, e.g., all communities with a similar extent of purifying/positive selection, population genetic differentiation may be smaller than that under neutrality.
-
When the given tree species has different extents and types of interspecific interactions in different communities, such as weak positive and purifying selection, population genetic differentiation may be close to that under neutrality. An appropriate number of community-based populations could be suggested for conservation from this array of patterns of the population genetic differentiation of a given species.
When interspecific interactions are ignorable, our suggested strategy reduces to the conventional
𝐹𝑠𝑡 and
𝑄𝑠𝑡 schemes that rely on population and quantitative genetics theories [
15,
25,
129].
One caution is that when the ecological drift effects are unequal and highly fluctuate across communities, a given tree species’ effective population size (
𝑁𝑒) may also be different among communities. The ecological drift (
1/𝐽) strengthens the genetic drift and amplifies population genetic differentiation. Other processes, such as species invasion or distinct speciation rate, could influence the genetic differentiation of a given tree species through species interactions [
71]. Therefore, it is necessary to consider the type of forest community, phylogeny, and interspecific interactions in genetic resource conservation, which provides complementary information to the conventional (
𝐹𝑠𝑡)-based genetic conservation.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/plants13030435