Unlike in normal epithelium, dysregulated overactivation of various proteases have been
reported in cancers. Degradation of pericancerous extracellular matrix leading to cancer cell invasion
by matrix metalloproteases is well known evidence. On the other hand, several cell-surface proteases,
including type II transmembrane serine proteases (TTSPs), also induce progression through activation
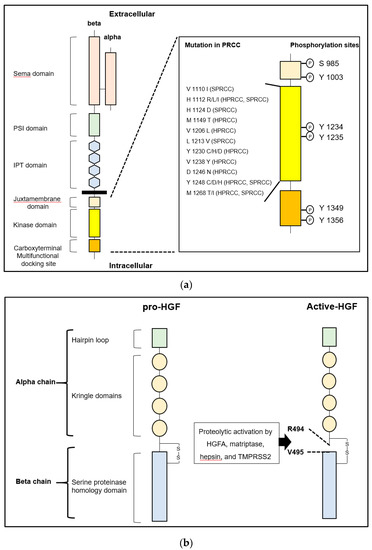
of growth factors, protease activating receptors and other proteases. Hepatocyte growth factor
(HGF) known as a multifunctional growth factor that upregulates cancer cell motility, invasiveness,
proliferative, and anti-apoptotic activities through phosphorylation of MET (a specific receptor of
HGF). HGF secreted as inactive zymogen (pro-HGF) from cancer associated stromal fibroblasts,
and the proteolytic activation by several TTSPs including matriptase and hepsin is required. The
activation is strictly regulated by HGF activator inhibitors (HAIs) in physiological condition. However,
downregulation is frequently observed in cancers. Indeed, overactivation of MET by upregulation of
matriptase and hepsin accompanied by the downregulation of HAIs in urological cancers (prostate
cancer, renal cell carcinoma, and bladder cancer) are also reported, a phenomenon observed in cancer
cells with malignant phenotype, and correlated with poor prognosis. In this review, we summarized
current reports focusing on TTSPs, HAIs, and MET signaling axis in urological cancers.
- matriptase
- hepsin
- hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)
- MET
- prostate cancer
- renal cell carcinoma
- bladder cancer
- HGF activator inhibitor (HAI)
HGF/MET and the Related Molecules
HGF and MET in Cancer
HGF/MET Signaling Axis
Cell Surface pro-HGF Activating Enzymes and the Regulators
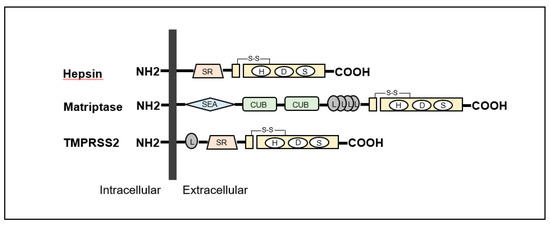
Type-II Transmembrane Serine Proteases (TTSP) in Cancers
| Subfamily | Protease |
|---|---|
| HAT/DESC | HAT |
| DESC1 | |
| TMPRSS 11A | |
| HAT-like 4 | |
| HAT-like 5 | |
| Hepsin/TMPRSS | Hepsin (TMPRSS1) |
| TMPRSS 2 | |
| TMPRSS 3 | |
| TMPRSS 4 | |
| TMPRSS 13 | |
| Enteropeptidase | |
| Spinesin | |
| Matriptase | Matriptase |
| Matriptase 2 | |
| Matriptase 3 | |
| Polyserase | |
| Corin | Corin |
Matriptase
Hepsin
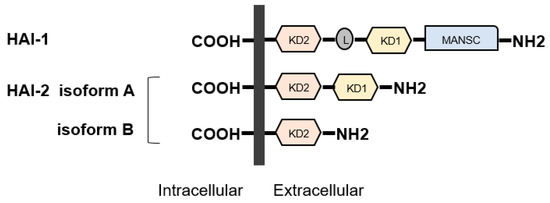
Regulators of TTSPs—HAIs
- Janetka, W.J.; Benson, M.R. Extracellular Targeting of Cell Signaling in Cancer; Strategies Directed at MET and RON Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Pathways; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1–154. [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka, H.; Miyata, S.; Uchinokura, S.; Itoh, H. Roles of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) activator and HGF activator inhibitor in the pericellular activation of HGF/scatter factor. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2003, 22, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazawa, K.; Shimomura, T.; Kitamura, N. Activation of hepatocyte growth factor in the injured tissues is mediated by hepatocyte growth factor activator. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 16, 3615–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimomura, T.; Kondo, J.; Ochiai, M.; Naka, D.; Miyazawa, K.; Morimoto, Y.; Kitamura, N. Activation of the zymogen of hepatocyte growth factor activator by thrombin. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 25, 22927–22932. [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka, H.; Kawaguchi, M. Hepatocyte growth factor activator (HGFA): pathophysiological functions in vivo. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 2230–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchhofer, D.; Peek, M.; Lipari, M.T.; Billeci, K.; Fan, B.; Moran, P. Hepsin activates pro-hepatocyte growth factor and is inhibited by hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitor-1B (HAI-1B) and HAI-2. FEBS Lett. 2005, 28, 1945–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, K.A.; Qiu, D.; Alves, J.; Schumacher, A.M.; Kilpatrick, L.M.; Li, J.; Harris, J.L.; Ellis, V. Pericellular activation of hepatocyte growth factor by the transmembrane serine proteases matriptase and hepsin, but not by the membrane-associated protease uPA. Biochem. J. 2010, 426, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.E.; List, K. Cell surface-anchored serine proteases in cancer progression and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2019, 38, 357–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, M.; Kataoka, H. Mechanisms of hepatocyte growth factor activation in cancer tissues. Cancers (Basel) 2014, 29, 1890–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, H.; Kawaguchi, M.; Fukushima, T.; Shimomura, T. Hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitors (HAI-1 and HAI-2): Emerging key players in epithelial integrity and cancer. Pathol. Int. 2018, 68, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentile, A.; Trusolino, L.; Comoglio, P.M. The Met tyrosine kinase receptor in development and cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2008, 27, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trusolino, L.; Bertotti, A.; Comoglio, P.M. MET signalling: Principles and functions in development, organ regeneration and cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, P.C.; Maulik, G.; Christensen, J.; Salgia, R. c-Met: structure, functions and potential for therapeutic inhibition. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2003, 22, 309–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tovar, E.A.; Graveel, C.R. MET in human cancer: germline and somatic mutations. Ann. Transl. Med. 2017, 5, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, L.M.; List, K. The role of type II transmembrane serine protease-mediated signaling in cancer. FEBS J. 2017, 284, 1421–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- List, K.; Bugge, T.H.; Szabo, R. Matriptase: potent proteolysis on the cell surface. Mol. Med. 2006, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.J.; Feng, X.; Lu, M.; Morimura, S.; Udey, M.C. Matriptase-mediated cleavage of EpCAM destabilizes claudins and dysregulates intestinal epithelial homeostasis. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, R.; Bugge, T.H. Membrane-anchored serine proteases in vertebrate cell and developmental biology. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2011, 27, 213–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlings, N.D.; Barrett, A.J.; Thomas, P.D.; Huang, X.; Bateman, A.; Finn, R.D. The MEROPS database of proteolytic enzymes, their substrates and inhibitors in 2017 and a comparison with peptidases in the PANTHER database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D624–D632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.F.; Huang, M.S.; Lin, C.S.; Lin, L.H.; Lee, H.S.; Jiang, J.C.; Hsia, K.T. Expression of matriptase correlates with tumour progression and clinical prognosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Histopathology 2014, 65, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, A.; Torres-Rosado, A.; Arai, T.; Le Beau, M.M.; Lemons, R.S.; Chou, S.H.; Kurachi, K. Hepsin, a cell membrane-associated protease. Characterization, tissue distribution, and gene localization. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 5, 16948–16953. [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi, M.; Nandana, S.; Yamashita, H.; Ganesan, R.; Kirchhofer, D.; Quaranta, V. Laminin-332 is a substrate for hepsin, a protease associated with prostate cancer progression. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 7, 30576–30584. [Google Scholar]
- Shimomura, T.; Denda, K.; Kitamura, A.; Kawaguchi, T.; Kito, M.; Kondo, J.; Kagaya, S.; Qin, L.; Takata, H.; Miyazawa, K.; et al. Hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitor, a novel Kunitz-type serine protease inhibitor. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 6370–6376. [Google Scholar]
- Kawaguchi, T.; Qin, L.; Shimomura, T.; Kondo, J.; Matsumoto, K.; Denda, K.; Kitamura, N. Purification and cloning of hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitor type 2, a Kunitz-type serine protease inhibitor. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 27558–27564. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marlor, C.W.; Delaria, K.A.; Davis, G.; Muller, D.K.; Greve, J.M.; Tamburini, P.P. Identification and cloning of human placental bikunin, a novel serine protease inhibitor containing two Kunitz domains. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 12202–12208. [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka, H.; Itoh, H.; Nuki, Y.; Hamasuna, R.; Naganuma, S.; Kitamura, N.; Shimomura, T. Mouse hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) activator inhibitor type 2 lacking the first Kunitz domain potently inhibits the HGF activator. Biochem. Biophy. Res. Commun. 2002, 290, 1096–1100. [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka, H.; Shimomura, T.; Kawaguchi, T.; Hamasuna, R.; Itoh, H.; Kitamura, N.; Miyazawa, K.; Koono, M. Hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitor type 1 is a specific cell surface binding protein of hepatocyte growth factor activator (HGFA) and regulates HGFA activity in the pericellular microenvironment. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 40453–40462. [Google Scholar]
- Kawaguchi, M.; Takeda, N.; Hoshiko, S.; Yorita, K.; Baba, T.; Sawaguchi, A.; Nezu, Y.; Yoshikawa, T.; Fukushima, T.; Kataoka, H. Membrane-bound serine protease inhibitor HAI-1 is required for maintenance of intestinal epithelial integrity. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 179, 1815–1826. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, H.; Nagaike, K.; Takeda, N.; Itoh, H.; Kohama, K.; Fukushima, T.; Miyata, S.; Uchiyama, S.; Uchinokura, S.; Shimomura, T.; et al. Hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitor type 1 (HAI-1) is required for branching morphogenesis in the chorioallantoic placenta. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 25, 5687–5698. [Google Scholar]
- Hoshiko, S.; Kawaguchi, M.; Fukushima, T.; Haruyama, Y.; Yorita, K.; Tanaka, H.; Seiki, M.; Inatsu, H.; Kitamura, K.; Kataoka, H. Hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitor type 1 is a suppressor of intestinal tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 2659–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, T.; Kawaguchi, M.; Fukushima, T.; Sato, Y.; Orikawa, H.; Yorita, K.; Tanaka, H.; Lin, C.Y.; Sakoda, S.; Kataoka, H. Loss of membrane-bound serine protease inhibitor HAI-1 induces oral squamous cell carcinoma cells’ invasiveness. J. Pathol. 2012, 228, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ning, T.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Deng, T.; Zhou, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, R.; Bai, M.; et al. miR-221 and miR-222 synergistically regulate hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitor type 1 to promote cell proliferation and migration in gastric cancer. Tumour. Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317701636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Kawaguchi, M.; Haruyama, Y.; Kanemaru, A.; Fukushima, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Lin, C.Y.; Kataoka, H. Loss of hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitor type 1 participates in metastatic spreading of human pancreatic cancer cells in a mouse orthotopic transplantation model. Cancer Sci. 2014, 105, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberst, M.D.; Johnson, M.D.; Dickson, R.B.; Lin, C.Y.; Singh, B.; Stewart, M.; Williams, A.; al-Nafussi, A.; Smyth, J.F.; Gabra, H.; et al. Expression of the serine protease matriptase and its inhibitor HAI-1 in epithelial ovarian cancer: Correlation with clinical outcome and tumor clinicopathological parameters. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 1101–1107. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, K.; Abarzua, F.; Hongo, A.; Kodama, J.; Nasu, Y.; Kumon, H.; Hiramatsu, Y. The role of hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitor-1 (HAI-1) as a prognostic indicator in cervical cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2009, 35, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Hongo, A.; Kodama, J.; Hiramatsu, Y. The role of hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitor (HAI)-1 and HAI-2 in endometrial cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 128, 2613–2624. [Google Scholar]
- Hamasuna, R.; Kataoka, H.; Meng, J.Y.; Itoh, H.; Moriyama, T.; Wakisaka, S.; Koono, M. Reduced expression of hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitor type-2/placental bikunin (HAI-2/PB) in human glioblastomas: Implication for anti-invasive role of HAI-2/PB in glioblastoma cells. Int. J. Cancer 2001, 93, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, B.E.; Moran, P.; Lipari, T.; Ganesan, R.; Corpuz, R.; Ludlam, M.J.; Gogineni, A.; Koeppen, H.; Bunting, S.; et al. Pegylated Kunitz domain inhibitor suppresses hepsin-mediated invasive tumor growth and metastasis. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 8395–8402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, T.; Kawaguchi, M.; Yamasaki, M.; Tanaka, H.; Yorita, K.; Kataoka, H. Hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitor type 1 suppresses metastatic pulmonary colonization of pancreatic carcinoma cells. Cancer Sci. 2011, 102, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betsunoh, H.; Mukai, S.; Akiyama, Y.; Fukushima, T.; Minamiguchi, N.; Hasui, Y.; Osada, Y.; Kataoka, H. Clinical relevance of hepsin and hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitor type 2 expression in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2007, 98, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Fukushima, T.; Takahashi, N.; Tanaka, H.; Kataoka, H. Hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitor type 1 regulates epithelial to mesenchymal transition through membrane-bound serine proteinases. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 1828–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaguchi, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Takeda, N.; Fukushima, T.; Yamashita, F.; Sato, K.; Kitamura, K.; Hippo, Y.; Janetka, J.W.; Kataoka, H. Hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitor-2 stabilizes Epcam and maintains epithelial organization in the mouse intestine. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, M.R.; Gentle, D.; Abdulrahman, M.; Maina, E.N.; Gupta, K.; Banks, R.E.; Wiesener, M.S.; Kishida, T.; Yao, M.; The, B.; et al. Tumor suppressor activity and epigenetic inactivation of hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitor type 2/SPINT2 in papillary and clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 4598–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Kim, H.E.; Min, M.; Raghunathan, R.; Panova, I.P.; Munshi, R.; Ryu, B. Epigenetic silencing of SPINT2 promotes cancer cell motility via HGF-MET pathway activation in Melanoma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 2283–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, D.; Fan, Q.; Chen, X.; Li, F.; Wang, L.; Huang, L.; Dong, W.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; et al. Epigenetic inactivation of SPINT2 is associated with tumor suppressive function in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Exp. Cell Res. 2014, 322, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Chen, X.; Xie, J.; Sun, P.; Wu, Y. Epigenetic inactivation and tumor suppressor activity of HAI-2/SPINT2 in gastric cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 1526–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.H.; Teng, C.H.; Tu, Y.T.; Cheng, T.S.; Wu, S.R.; Ko, C.J.; Shyu, H.Y.; Lan, S.W.; Huang, H.P.; Tzeng, S.F.; et al. HAI-2 suppresses the invasive growth and metastasis of prostate cancer through regulation of matriptase. Oncogene 2014, 18, 4643–4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roversi, F.M.; Olalla Saad, S.T.; Machado-Neto, J.A. Serine peptidase inhibitor Kunitz type 2 (SPINT2) in cancer development and progression. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 101, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Kawaguchi, M.; Shimomura, T.; Izumi, A.; Konari, K.; Honda, A.; Lin, C.Y.; Johnson, M.D.; Yamashita, Y.; Fukushima, T.; et al. Hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitor-2 (HAI-2)/SPINT2 contributes to invasive growth of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Oncotarget 2018, 8, 11691–11706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/ijms21082663
