Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is an old version of this entry, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Subjects:
Cardiac & Cardiovascular Systems
轻至中度肺动脉高压 (PH) 是慢性阻塞性肺疾病 (COPD) 的常见并发症。已发现前列腺素 E2 (PGE2) 及其下游信号转导在各种生物过程中发挥重要作用。新出现的证据表明,PGE2 及其受体(即 EP1-4)参与肺血管稳态和重塑的调节。
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- pulmonary hypertension
- prostaglandin E2
1. 引言
PGE2 由 PGES 催化,通过与 EP1、EP2、EP3 和 EP4 等 EP 受体结合发挥其生物学功能。EP1 增加细胞内 Ca2+主要通过与Gq蛋白偶联来水平。EP3 通常与 Gi 蛋白偶联以抑制细胞内 cAMP 水平和 PKA 活性。由于存在多种亚型,EP3 可以与 Gs 偶联以刺激 cAMP 的产生,并与 Gq 偶联以刺激细胞内 Ca2+水平。EP2 和 EP4 通过偶联 Gs 蛋白和激活 PKA 通路来增加细胞内 cAMP 水平。一般来说,PGE2在血压调节中起着关键作用。其降压作用主要通过EP2和EP4实现,而EP1和EP3的激活会使全身血压升高[71]。研究表明,COX/mPGES/PGE2/EPs系统对血压调节和血管重塑至关重要[72,73,74,75,76,77]。研究发现,IP、EP3和EP4在正常肺动脉中高表达,而EP2主要位于肺静脉[72]。在3种EP受体中,EP4和EP2与PGE1的亲和力最高(Kd < 1 nM),而EP2和EP2与PGE10的亲和力较低(Kd > 73 nM)[2]。已经发现 PGI2 类似物既能激活 IP 又作用于 EP 受体(表 2)。许多研究表明,不同的PGE2受体参与PH的发生和发展(图<>)。
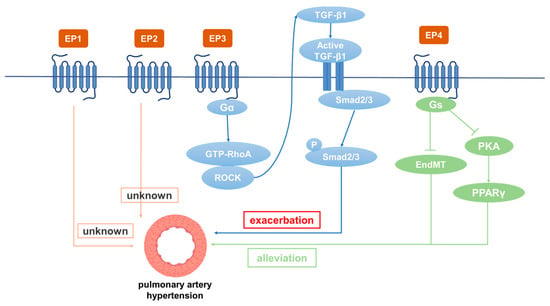
图2.不同PGE2受体在PAH发生发展中的作用。
表 2.IP 和 EP1-4 对人和小鼠中 PGI2 类似物的结合亲和力 (Ki)。放射性配体结合数据(Ki,单位为nM)来自PGI2类似物的原始研究参考文献[73,74,75,76]。空白表示 Ki 值> 3 μM,ND 表示未完成,YES 表示功能活性的证据。
| PGI2 类似物 | 知识产权 | EP1系列 | EP2系列 | EP3系列 | EP4系列 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 伊洛前列素 | 人 | 4 | 1 | 1172 | 203 | 212 |
| 鼠 | 11 | 21 | 1600 | 27 | 2300 | |
| 曲前列尼尔 | 人 | 32 | 212 | 3.6 | 2505 | 826 |
| 鼠 | 是的 | ND型 | 是的 | ND型 | ND型 | |
| 贝前列素 | 人 | 39 | 680 | |||
| 鼠 | 16 | 110 | ||||
| 卡前列素 | 人 | 17 | >1340 | >1340 | 255 | 44 |
| 鼠 | 10 | 1300 | 170 | |||
2. EP1在PH中的作用
据报道,口服EP1拮抗剂SC51322可降低自发性高血压大鼠的血压。此外,EP1基因敲除小鼠的收缩压明显低于野生型小鼠,表明EP1具有收缩血管和升高血压的作用[77]。在重度高血压模型中,敲除EP1能够降低血压并减轻器官损伤[78]。在肺静脉中,EP1抵消PG诱导的松弛[79]。伊洛前列素对不同受体的选择性较差,其激活IP和EP1的作用基本相同[80]。伊洛前列素的临床疗效较差,因为它也靶向EP1[81]。EP1拮抗剂SC-19220抑制内源性大麻素花生四烯基乙醇酰胺(anandamide)诱导的肺动脉压升高[82]。研究表明,PDGF和VEGF促进EC和SMCs的异常增殖和迁移,促进血管重塑,酪氨酸激酶抑制剂伊马替尼可以剂量依赖性逆转[83]。阻断EP1/3和TP或抑制MAP2K、p38MAPK、PI3K-α/γ和AKT/PKB信号通路可阻止PDGF诱导的收缩[84]。由于肺静脉床对肺血管阻力的贡献很大,PDGF-BB诱导的肺静脉曲张收缩增强[85]。免疫组化研究表明,EP1主要在人肺静脉中表达[86]。然而,在PH患者和缺氧诱导的PH小鼠中,EP1表达没有显著变化[87]。目前,EP1对PH的影响尚未见报道。
3. EP2在PH中的作用
在PH患者中,PASMC中EP2的表达上调[88]。曲前列尼尔是一种目前用于治疗PH的药物,对EP2和IP具有高亲和力[74],并通过激活巨噬细胞中的EP2来增加cAMP含量[23]。它是唯一能有效结合EP2的PGI2类似物,EP2拮抗剂PF-04418948(1μM)显著降低了曲前列尼尔的抗增殖作用[88]。此外,研究发现EP2与SMC的增殖和迁移增加有关,所有这些都表明EP2受体在血管重塑中具有保护作用[89,90]。曲前列尼尔可显著减少缺氧PH中血管重塑部位成纤维细胞的募集,成纤维细胞在血管的炎症期和增殖期发挥作用[91]。有趣的是,在MCT诱导的大鼠PH模型中,PASMC中EP2的表达不受影响[92]。目前,EP2对PH的影响有待进一步探讨。
4. EP3在PH中的作用
EP3在小鼠全身组织中广泛表达[93]。EP3激动剂对离体人肺动脉有很强的收缩作用[94]。发现EP3敲除小鼠的平均动脉压低于野生型小鼠,表明EP3具有收缩血管和升高血压的功能[95]。贝前列素作为首个稳定的口服PGI2类似物,主要用于PH、动脉闭塞性疾病、外周血管疾病、肾功能衰竭等的临床治疗[96]。研究显示,贝前列素可改善运动能力和血流动力学,从而缓解PH症状[97]。其他结果表明,除了与IP结合外,贝拉前列素在大鼠中与EP3(Ki 110 Nm)具有很强的结合亲和力[23]。许多研究提供了证据,证明PGI2类似物的收缩作用是通过EP3受体介导的[75,98,99]。在接受贝前列素治疗但未接受 selexipag(一种前列腺素受体选择性激动剂)治疗的 PH 患者中,由于肺动脉中 EP3 激活引起的收缩,血管扩张剂疗效降低。此外,贝拉前列素的一个常见副作用是由于EP3受体的激活而导致股动脉的反常收缩。因此,接受PGI2类似物治疗的PH患者会出现腿痛,而司来帕不太可能引起这种副作用[100]。依巴前列素是贝拉前列素的一种亚型,在大鼠肺动脉血管舒张方面比贝拉前列素强五倍。Esuberaprost 促进 cAMP 产生并抑制人 PASMC 的增殖,其抑制作用是贝前列素 (EC40 50 nM 和 EC3 50 nM) 的 120 倍。EP3拮抗剂L-798106可显著降低高浓度依巴前列素的肺动脉收缩作用。了解EP3在收缩反应中的作用很重要,因为这可能会限制治疗用PGI2类似物的剂量,并可能引起不良副作用[101]。此外,EP3在肺血管重塑中发挥作用。EP3的过表达,尤其是其α和β亚型,促进血管SMC的增殖和迁移,EP3敲除可显著改善股动脉导丝应变引起的血管重塑[102]。此外,已发现 EP3 表达在缺氧处理的 PASMC 中上调。EP3 拮抗剂 L-798106 改善了 MCT 和缺氧诱导的 PH,并抑制了肺动脉中 ECM 的沉积。SMC中的EP3(主要是EP3α和EP3β)敲除通过抑制Rho/TGF-β1信号转导来缓解PH[87]。然而,EP3缺陷小鼠的出血倾向增加[103]。研究发现,从肺动脉(外径:1mm)分离的远端人PASMC(外径:2mm)比从近端肺动脉(外径:0.8mm)分离的PASMC更容易受到PGI104类似物诱导的增殖抑制[3]。与对照组相比,MCT处理组大鼠IP、EP0、FP和TP的表达均降低(p < 05.0或p < 01.104)[3]。因此,EP<>参与PH的发生,其拮抗剂具有治疗潜力。
5. Role of EP4 in PH
EP4 plays a critical role in the closure of the ductus arteriosus at birth [105]. EP2 and EP4 have been reported to be the major mediators causing pulmonary vasodilation in rabbits [82]. The expression of IP, EP3, and EP4 in normal pulmonary arteries is much higher than EP1 and EP2. Patients treated with beraprost exhibited less disease progression at 6 months [106]. Additionally, it binds to EP4 and results in AC activation at lower affinity [107]. Levels of both PGI2 and PGE2 in plasma were dramatically depressed in experimental PH rats compared with controls. However, these depressed levels were elevated by beraprost treatment. Furthermore, both the dilatation response of vascular rings and the magnitude of the Kv channel response to beraprost were shown to be attenuated by the EP4 selective antagonist GW 627368X, suggesting involvement of EP4 in mediating the effects of PGI2 on O2-sensitive Kv channels and vasomotion [72]. While further studies are required to directly prove the interaction of beraprost and EP4, studies have reported that IP expression is significantly decreased in PH patients and rats, while the expression of EP4 is decreased slightly. The EP4 antagonist AH23848 can inhibit intracellular cAMP accumulation induced by iloprost in a dose-dependent manner, indicating that iloprost may mediate the diastolic function caused by EP4 instead of IP in PASMCs [92]. Cicaprost elevated cAMP in PASMCs four-fold compared with control, while iloprost only caused a one-fold increase [108]. This is probably because cicaprost has strong binding affinity to EP4 [23]. The PGE2-EP4 signal transduction pathway aggravates chronic inflammation and various autoimmune diseases. Therefore, specific antagonists for EP4 are expected to be effective therapeutic drugs for acute and chronic inflammation as well as for autoimmune diseases in non-pregnant adults [109]. Results have shown that reduced EP4 expression in macrophages can alleviate bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis [110]. An increase in perivascular macrophages is essential in the development of hypoxia-induced PH in experimental animals [111]. Another study showed that EP4 knockout in mice increased airway inflammation induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and cigarette smoke, while PGE2 inhibited the production of TNF-α and IL-6 in human lung macrophages by binding with EP4 [112,113]. SMC-specific EP4 knockout exacerbated angiotensin II-induced aortic dissection by increasing vascular inflammation [114]. PGE2 exerted anti-inflammatory effects by binding to EP4 to regulate macrophage and T lymphocyte functions, which are essential in innate and adaptive immunity as well as in tissue remodeling and repair. Evaluation of respiratory function is essential for patients with PH. For PH caused by COPD, inducing bronchial relaxation and reducing hypoxia may bring benefits to patients [115]. It has been found that EP4 agonists have a 10-fold to 50-fold greater bronchorelaxing effect than IP receptor agonists, and that PGE2-induced bronchiectasis is attenuated due to decreased expression of EP4 in PH associated with lung disease and/or hypoxia. Restoration of EP4 expression may be an effective way to improve the respiratory function of patients [116]. PGE2 inhibited PDGF-BB-induced proliferation and migration of human airway SMCs through EP4 to improve airway remodeling and improve COPD [117]. EP4 may be a new effective target for the treatment of PH. In addition, EP4 plays an important role in physiological and pathological vascular remodeling [114]. It was subsequently demonstrated that the expression of PPARγ in PAECs is decreased in PH patients [117] and that the loss of PPARγ in PASMCs or PAECs can cause pulmonary vascular remodeling, leading to PH and distal pulmonary artery muscularization [118]. L-902688, a selective EP4 agonist, has been reported to inhibit MCT-induced PASMC proliferation and migration as well as pulmonary vascular remodeling through PKA/PPARγ activation, which can ameliorate right ventricular fibrosis and TGF-β-induced endothelial–mesenchymal transition (EndMT) in PAH models [119,120]. Therefore, EP4 can inhibit the proliferation of PASMCs, improve pulmonary vascular remodeling, and suppress human lung macrophage inflammation, which is an important target for the treatment of PH [121].
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/metabo13111152
This entry is offline, you can click here to edit this entry!
