White holes are regions of space-time that although matter may come out, no matter is able to enter; or in other words, they have gravitational features opposite to those of black holes. White holes exist in the solutions to Einstein's general theory of relativity and the maximal extension of the Schwarzschild metric. The term "white hole" was coined by Soviet cosmologist Igor Novikov in 1965 after his theorization on the existence.
- white hole
- general relativity
- black hole
- wormhole
1. History
The possibility of the existence of white holes was theorized by Soviet cosmologist Igor Novikov in 1964 [1]; not realizing the significance of his work, mathematician Martin David Kruskal extended Schwarzchild's black hole description in 1960 to cover all domains of space and time and the work was later rediscovered [2][3]. According to Roger Penrose's account, Igor's theory was not greeted with much scientific interests from the community for general trust issues from the Cold War, but he and Steven Hawking were one of the few who took the theory seriously [4][5].
Another reason for the scientific community's indifference or disbelief in white holes is the lack of the physics knowledge basis and cosmological framework that can fully explain the prerequisites for their existence. Therefore, white holes are often studied alongside with black holes and cosmology. There have been four major hypotheses on the origins of white holes: 1) the Big Bang itself creating primordial black hole and white hole; 2) from the black hole even horizon, believed by Igor Novikov and later Stephen Hawking; 3) multiverse theories with wormholes (Einstein-Rosen Bridge) included; and 4) other theories typical of star collisions and mergers, such as from physicist Nikodem Poplawski [5][6][7].
The more one seeks to theorize the possible explanations for the formation of white holes, however, the more questions appear that shake the foundation of modern physics. For the multiplication of Big Bang explanations, Constantinos Challoumis provided the plausibilities of mathematical solutions, but the origins of the energies required for multiple Big Bangs remain unanswered [8]. Multiverse theories along with string theories structure the same mathematics from an opposite end, and are often constructed with wormholes and loop quantum gravity [9][10]. While collision and merger theories currently lack significant evidence to be supported, there have been thin evidence for black hole event horizon theory from Steven Hawking's observations and insights on the antimatter distribution and concentration around black holes.
2. Theoretical Development
Mathematical physicist Roger Penrose is one of the leading figures in the later development of white hole metaphysics. His perspective is founded upon one of his early works in the 1960s from the inquiries on the asymptotic questions with general relativity [11]. From the basis of Schwarzschild metric, Penrose further developed the Penrose diagram, reconciling Einstein-Rosen Bridge with Schwarzschild radius [12]. While sticking to the singular Big Bang framework, in 2006 Penrose proposed the time element "before the Big Bang" in the European Particle Accelerator Conference [13]. Afterwards, the antithetic theory Conformal Cyclic Cosmology was put forth by Roger Penrose with regard to the instrumentation limitations in furthering the inquiries [14]. The cosmological insights of Roger Penrose are commented by Yang I. Pachankis as falsification of the Big Bang theory by contradiction [15][16].
3. Applications
There has been no applications directly attributed to white hole science, but white holes have incentivized much progress in quantum physics along with the astronomical developments in black holes. Since the determination of causality in white hole physics rely on relativity theories, apart from other relativistic theories such as Lorentz transformation, issues of determinism in quantum mechanics and causal inference in relativistic theories started to shape the fundaments in modern physics [17][18]. Findings in nonperturbative quantum mechanics helped easing the tensions between general relativity and quantum indeterminacy, but have not closed the gaps between theory and application [19][20].
What brought temporary truce to the scientific and theoretical disputes between relativistic theories and quantum mechanics was Turing machines, with both disciplines' dependence on mathematics. In the early 1950s, roughly half the cycles of MANIAC were devoted to the first stellar evolution codes, and later came simulation models for astrophysics, computer-controlled and information-based observatories, etc. [21]
One of the most eminent application-driven developments in the direction is the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT), utilizing the rotation of our earth to the spins in the universe [22]. The EHT project, directored by Sheperd S. Doeleman, produced the first visual evidence of the black hole on M87 in 2019, which has been phenomenally known as the black hole shadow ignited by the emission region [23][24]. Image 1 outlines the EHT collaboration's empirical observations [25][26].

Image 1. Summary of the calibration and telescope arrangements of EHT [25].
Based on the negative cosmological constant, Yang I. Pachankis conducted the observational cosmology experiment that detected white holes [27]. The data calibration, along with the multispectral data calibration on the ergoregion from the experiment series with multi-mission space-based telescope data, depends on the ergodic hypothesis in quantum mechanics [17][28][29][30]. The imaging not only proved the ergodic hypothesis, but also proved the thermonuclear binding of black hole and white hole regarding the antimatter concentration around black holes in Hawking's observations [31][17]. Image 2 is the most visible white hole from the observations [27].
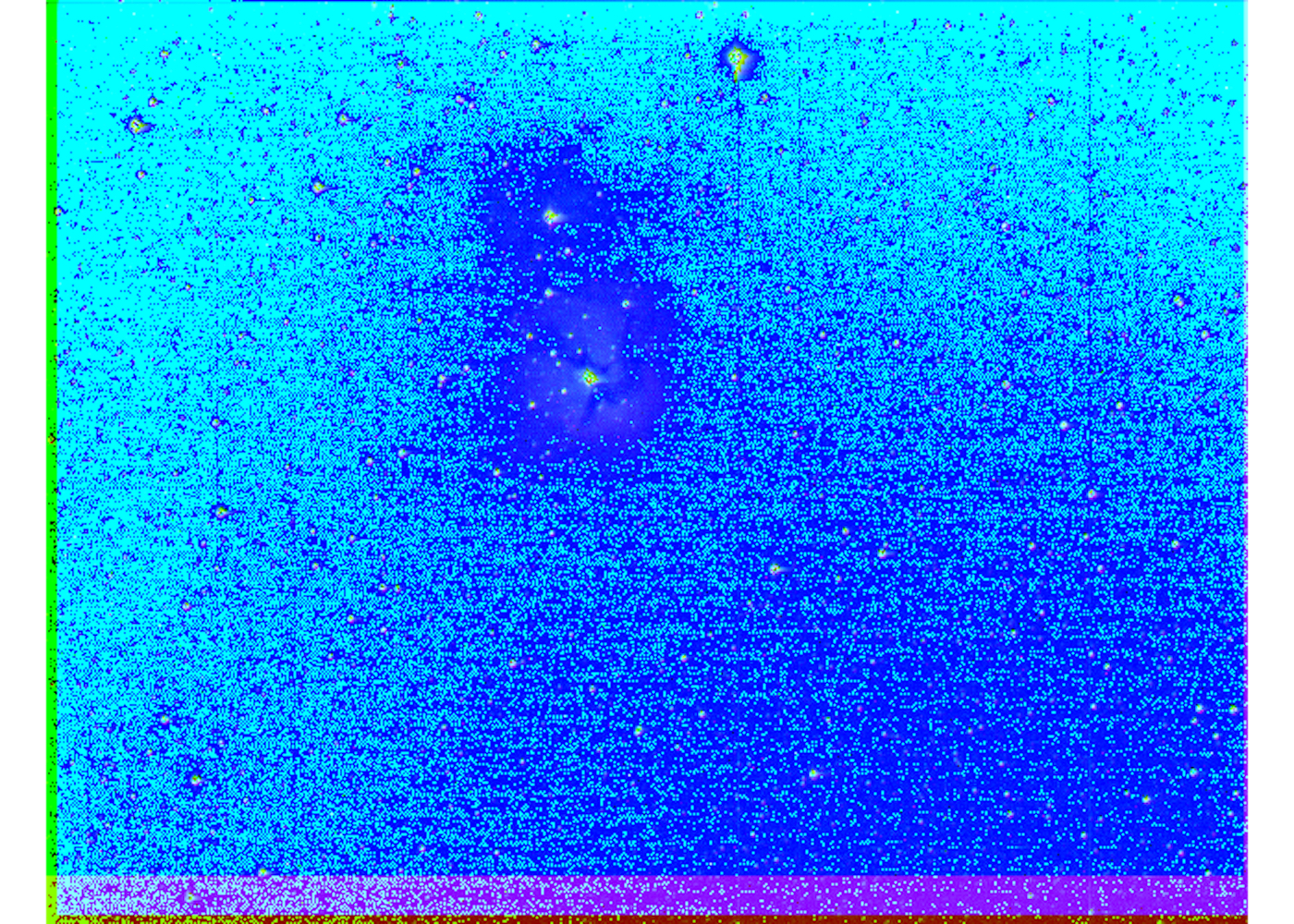
Image 2. White hole observed on Triffid Nebula M20 [27].
4. New Progress
Albeit no scientific literature has reported the detection of white hole gravitational signatures, white hole physics have progressed with the observations and data analysis. The relativistic particle recombinations indicate to antimatter component bremsstrahlung phenomenon, with the fifth cosmic force mediating the process [16][32][33]. It is induced that antimatter Van Der Waals force determined the non-imaging in gravitational recombination and antimatter imaging plates are necessary [34]. The holistic phenomena of the Kerr-Newman black hole and white hole compact on NGC 3034 together with the one on M20 seen in Image 2 suggest exotic metal insulator is formed with the black hole seed and white hole seed collision momenta, and the compulsion force produces Hawking points [34]. Contrary to the previous causal inferences, however, Yang Pachankis believes that black holes are decay products from white holes, instead of vice versa, in the asymptotic structure with cold fusion and hot fission [16].
The falsification of the Big Bang theory came with the observational evidence of white holes, even though the Big Bang theory is still the predominant consensus in cosmology. One of the competing theory is Klein-Alfvén cosmology, focused on the plasma contents of the universe [35][36]. Contemporary to Klein-Alfvén cosmology was string and superstring theory, which Roger Penrose and Stuart Hameroff seek to differentiate from conscious phenomena [37][38]. It is also considered that Conformal Cyclic Cosmology proposed by Roger Penrose may have the best extensibility in theoretical developments among the competing theories [15][39].
References
- White holes: Hunting the other side of a black hole . New Scientist. Retrieved 2023-10-8
- White holes: What we know about black holes' neglected twins . Space.com. Retrieved 2023-10-8
- M. D. Kruskal; Maximal Extension of Schwarzschild Metric. Phys. Rev. 1960, 119, 1743-1745, .
- Roger Penrose at the 2021 The Science and Roger Penrose webinar.
- The Antipode Of Black Hole: Is There A White Hole In Space? . Orbital Today. Retrieved 2023-10-8
- Alon Retter; Shlomo Heller; The revival of white holes as Small Bangs. New Astron. 2012, 17, 73-75, .
- Why cutting-edge braneworld theories say our universe began in a white hole . Big Think. Retrieved 2023-10-8
- Constantinos Challoumis. Creation Theory - The Light Space, the Dimensional Space and the Bounded Infinities – Where Comes the Energy of Multiple Big Bangs?; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, NX, Netherlands, 2019; pp. 3473000.
- String Theory: Travel through a Wormhole . Dummies. Retrieved 2023-10-8
- Francesca Vidotto: The Quantum Properties of Space-Time . JSTOR Daily. Retrieved 2023-10-8
- Penrose, R.; Asymptotic Properties of Fields and Space-Times. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1963, 10, 66-68, .
- Chunduru, A.P.; Cosmological Environment and Penrose Diagram of Axisymmetric Static Black Hole for Extended Schwarzschild Manifold. Gradiva Review Journal 2023, 9, 25-34, .
- Penrose, R.; Before the Big Bang: An Outrageous New Perspective and Its Implications for Particle Physics. European Particle Accelerator Conference 2006, 2006, 2759-2762, .
- Roger Penrose; The Big Bang and its Dark-Matter Content: Whence, Whither, and Wherefore. Found. Phys. 2018, 48, 1177-1190, .
- Yang Pachankis. Before or After -- the Big Bang Paradox; Yeap, K.H.; Chieh, T.H., Eds.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2023; pp. 1001964.
- Pachankis, Y.I.. The Lenses of Quantum Physics on Earth to the Cosmos: From the Humanities to the Apocalyptic Inevitability; Eliva Press: Moldova, Europe, 2022; pp. 397.
- Pachankis, Y.I.; A Multi-wavelength Data Analysis with Multi-mission Space Telescopes. International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology 2022, 7, 701-708, .
- R. P. Feynman; Space-Time Approach to Non-Relativistic Quantum Mechanics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1948, 20, 367-387, .
- Raphael Aronson; Nonperturbative Proof of Some Results in Classical Nonequilibrium Statistical Mechanics. Phys. Rev. 1966, 145, 46-54, .
- Belal E. Baaquie. Quantum Indeterminacy; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Dordrecht, GX, Netherlands, 2012; pp. 115-143.
- National Research Council. The Decade of Discovery in Astronomy and Astrophysics; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, United States, 1991; pp. 91.
- Locations of the telescopes that make up the EHT array . European Southern Observatory. Retrieved 2023-10-9
- Press Release (April 10, 2019): Astronomers Capture First Image of a Black Hole . Event Horizon Telescope. Retrieved 2023-10-9
- The Event Horizon Telescope Collaboration; et al.; First M87 Event Horizon Telescope Results. I. The Shadow of the Supermassive Black Hole. The Astrophysical Journal Letters 2019, 875, L1, .
- The Wobbling Shadow Of The M87* Black Hole . Science Blog. Retrieved 2023-10-9
- Maciek Wielgus; Kazunori Akiyama; Lindy Blackburn; Chi-Kwan Chan; Jason Dexter; Sheperd S. Doeleman; Vincent L. Fish; Sara Issaoun; Michael D. Johnson; Thomas P. Krichbaum; et al. Monitoring the Morphology of M87* in 2009–2017 with the Event Horizon Telescope. Astrophys. J. 2020, 901, 67, .
- Pachankis, Y.I.; White Hole Observation: An Experimental Result. International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology 2022, 7, 779–790, .
- Leandro A. Oliveira; Luis J. Garay; Luís C. B. Crispino; Ergoregion instability of a rotating quantum system. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 97, 124063, .
- Boltzmann’s Work in Statistical Physics . Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Retrieved 2023-10-10
- Pachankis, Y.I.; Some Concepts of Space, Time, and Lengths in Simplified Chinese* — An Analytical Linguistics Approach. International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology 2022, 7, 550-662, .
- Pachankis, Y.I.; Research on the Kerr-Newman Black Hole in M82 Confirms Black Hole and White Hole Thermonuclear Binding. Acad. Lett. 2021, AL, 3199, .
- Lightman, A.P.; Rybicki, G.B.. Radiative Processes in Astrophysics; WILEY-VCH GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2004; pp. 155-166.
- Pachankis, Y.I.; Physical Signals and Their Thermonuclear Astrochemical Potentials — A Review on Outer Space Technologies*. International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology 2022, 7, 669–674, .
- Pachankis, Y.I.; Neutron Number Asymmetry in Proton Decay Momentum. Journal of Agricultural, Earth & Environmental Sciences 2022, 1, 1-9, .
- Johan Hansson; The Klein-Alfvén cosmology revisited. J. Phys. Commun. 2019, 3, 115001, .
- Hannes Alfvén; Cosmology in the Plasma Universe. Laser Part. Beams 1988, 6, 389-398, .
- Edward W. Kolb. Cosmology and Extra Dimensions; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Dordrecht, GX, Netherlands, 1988; pp. 225-256.
- Stuart Hameroff; Roger Penrose; Consciousness in the universe. Phys. Life Rev. 2014, 11, 39-78, .
- Pachankis, Y.I.; Holographic Phenomenon of the Fifth Cosmic Force. Global Journal of Science Frontier Research - A 2023, 6, 37-43, .
