Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is an old version of this entry, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Subjects:
Management
数字创新的概念最早由Yoo于2010年提出,他认为数字创新是将数字和物理组件相结合以产生新产品,服务和商业模式的创新过程。
- digital innovation intention
- digital innovation performance
- TOE framework
1. Introduction
A new round of scientific and technological revolution centered on digital technologies such as big data and cloud computing is accelerating its widespread application, triggering the reshaping of the global innovation economic system [1]. As a green, innovative, and sustainable high-quality economic paradigm [2], the digital economy has become a key theme for China’s economic growth. According to the “Digital China Development Report (2022)” released by the State Internet Information Office of China, the scale of China’s digital economy reached CNY 50.2 trillion in 2022, ranked second in the world in terms of total volume, and its proportion in GDP has increased to 41.5%, China’s digital industrialization and industrial digital development have achieved remarkable achievements. At the same time, according to the “Global Digital Economy Development Index Report” released by the Institute of Finance and Economics of the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences, although China’s digital economy has significant advantages in the digital market and digital infrastructure, ranking 2nd and 3rd in the world respectively, there is still a certain gap in digital technology and digital governance, ranking 15th and 41st in the world respectively, lacking development advantages. Compared with other advanced digital economy countries, the core competitiveness and the independent innovation ability of key core technologies of China’s digital industry still have a significant gap. Therefore, to accelerate the construction of digital China, it is more important to promote continuous innovation in the digital technology industry. As important micro-subjects of economic development, enterprises are explorers, organizers, and leaders of digital innovation, and play an important role in breaking through technological bottlenecks and tackling scientific and technological problems. In the wave of digital development, those companies that have seized the opportunities of digital technology have achieved curve overtaking, and companies that struggle to adapt to the development of digital transformation have been eliminated by the times. Therefore, how to promote enterprises to actively participate in digital innovation and improve digital innovation performance is of great significance for improving the international competitiveness and sustainable development capabilities of China’s digital industry and promoting the high-quality development of China’s digital economy.
The concept of digital innovation was first introduced by Yoo in 2010 [3], who thought digital innovation is an innovative process of combining digital and physical components to produce new products, services, and business models. Subsequently, it aroused widespread concern in academic circles. In terms of the connotation and measurement of digital innovation, some studies based on output theory proposed that digital innovation refers to the innovative results produced by applying digital technology in the innovation process, including the use of digital technology to bring new products, improving production processes, changing organizational models, creating and changing business models, etc. [4]. Based on process theory, some scholars proposed that digital innovation is the combination of digital technologies such as information, computing, communication, and connection used in the innovation process [1]. There are also studies based on the theory of synthesis, pointing out that digital innovation should combine the application of digital technology and the results, including both the efficiency in the innovation process and the generation of innovation results [5].
In terms of research on the driving factors of digital innovation, there are studies on resource, organizational, and environmental factors. Some studies have showed that digital innovation requires advanced human capital, human capital can be integrated and iterated with technological and organizational resources to accelerate digital innovation [6]; knowledge management can also promote digital process innovation [7,8]. Regarding organizational factors, some scholars have found that digital innovation is affected by organizational strategy and organizational change [9], digital innovation is driven by many organizational factors such as opportunity search, business intelligence, organizational change, and organizational adaptation [10]. For example, Beatrice et al. [11] used the cases of four multinational companies operating in different industries to explore how existing companies can adjust their business models to cope with digital innovation. Other scholars have further proved that the capabilities of young entrepreneurs during economic turmoil have different impacts on digital innovation in micro-, small-, and medium-sized enterprises [12]. Regarding environmental factors, some studies have found that government financial support and training can enhance enterprises’ understanding of digital innovation [13], while human capital such as economic level and population size have little effect on the development of digital industries, and regions with poor economic foundations can use information infrastructure construction to promote industrial development [14].
In terms of the role of digital innovation, due to the reprogrammability of digital technologies, which can be continuously embedded into the innovation process to increase the fault tolerance and unpredictability of products, firms can make continuous adjustments to the innovation strategies in a dynamic innovation environment [15,16]. Based on this, some scholars pointed out that digital innovation can enhance the ability of enterprises to perceive the threat of potential competitors and the direction of industrial change, strengthen the continuous monitoring and reconnaissance of changes in the market environment [17], and create prerequisites for enterprises to grasp the window of opportunity of digitization and realize pioneering development [18]. Some scholars proposed that enterprises with strong digital innovation capabilities generally have strong development resilience [19]. Enterprises can use intelligent data to build resource protection walls to help enterprises adapt to changes in the face of external uncertainties and corporate crises, and even build new competitive advantages, and use this as a lever to achieve disruptive development [20,21]. In addition, some studies have found that companies that actively participate in digital innovation can more actively undertake social responsibilities, improve social reputation [22], and build organizational culture, risk quality management, and other organizational capabilities necessary for sustainable development [23].
From the above research, it can be found that digital innovation is a core and effective way to achieve digital empowerment and promote enterprises to enhance their competitiveness and achieve sustainable development [24]. Scholars have conducted various studies on digital innovation, but there are still the following deficiencies: first, the current measurement of enterprise digital innovation is mostly based on result theory, considering that digital innovation is a new product or new income produced by the enterprise, ignoring the consideration of the initiative and enthusiasm of enterprises participating in digital innovation from the perspective of process theory; second, although the existing literature has initially explored the impact of resources, organizational, and environmental factors on digital innovation in enterprises, few studies have integrated the internal and external factors into a holistic and systematic framework; third, most of the existing research focused on the influence and effect of a single factor or single dimension on enterprise digital innovation and used regression analysis to confirm the net effect of a single variable, neglecting the comprehensive consideration of the combination and superposition effect of multiple factors, and failing to reveal the group effect of multi-factor interaction on enterprise digital innovation.
2. How Technological, Organizational, and Environmental Factors Drive Enterprise Digital Innovation
The TOE framework was initially applied to the research on factors affecting enterprise technology adoption, and the factors were summarized into three dimensions: technology, organization, and environment [25]. Among them, technological factors refer to characteristics related to technological innovation, such as technological advantages, technological compatibility, technological cost, and technological complexity, etc. [25,26]; organizational factors include organizational scale, organizational type, and organizational support [27]; and environmental factors refer to characteristics of the organization’s external environment, including political environment, economic environment, social environment, etc. [28]. As the framework is applied to different research scenarios, the framework connotations are continuously enriched. For example, Wang analyzed the impact of enterprise technology preparation, organizational preparation, and environmental preparation on the performance of green innovation based on the TOE framework [26]; Lei combined innovation environment to explore the impact of different types of digital technology and organizational characteristics on enterprise service diversification [27]; Lexutt used the TOE framework to investigate how technology transfer and geographical location affect regional economic growth [29]. Under the penetration of digital technology, enterprise innovation not only requires organizational resources as the basis for digital technology application but also requires strong support from the external environment, such as regional and industry influences, so as to release innovation vitality in the synergy of internal and external factors [30].
2.1. Technological Dimension
The TOE framework first focuses on the impact of the technological characteristics of the enterprise itself on the development and application of digital technology [31]. The dynamic and self-growth features of digital technology have increased the uncertainty of digital innovation. New technologies will not only bring new products and solutions but also may bring all-new changes or disruptions to industry, placing higher demands on the speed and quality of digital innovation [32]. As one form of internal resource allocation in enterprises, R&D investment represents the level of intention to digitally innovate and is an important condition for enterprises to start digital innovation [33]. The Chinese Internet company Alibaba’s total R&D investment in 2022 has exceeded CNY 120 billion. In the past three years, 60% of its patents have been concentrated in digital innovation fields such as artificial intelligence and cloud computing. Its Alibaba Cloud, which relies on its self-developed Feitian operating system, has the world’s leading market share and has achieved market share growth for six consecutive years. It can be seen that R&D investment can accelerate digital innovation output by helping enterprises to build digital resource systems.
In addition, the rapid development of emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, cloud computing, big data, and blockchain, which are characterized by digitization and intelligence, requires more high-level technological talents. As the core of the enterprise’s digital innovation capability, high level talents have strong digital technology learning ability can continuously focus on the connection between corporate resources, capabilities, and product markets, actively respond to dynamic changes in the company and the market, and help accelerate technology development and market expansion [34]. At the same time, in the process of digital innovation, high-level talents can better understand the user needs, actively conduct critical evaluation and improvement of product design and functions, and finally promote product landing.
2.2. Organizational Dimension
The TOE framework also pays attention to the influence of organizational structural characteristics and organizational strategy on the development of digital innovation [35]. Studies have shown that the size of the organization affects the digital innovation of enterprises [36]. Compared with medium-sized businesses (SMEs), large enterprises have more innovative resource advantages, stronger risk resistance, and easier to achieve cross-border operations. Dell’s IdeaStorm, Haier’s crowdsourcing platform, and Xiaomi Community all take advantage of the strong organizational scale to gather heterogeneous innovation groups, thus achieving benefit sharing and risk sharing of digital innovation. However, some scholars have also found that SMEs are more flexible in their organization and could seize technological opportunities promptly to achieve breakthroughs in the rapid iteration of digital technologies [37].
In addition, in the process of digital innovation, as the lead of the organization, the composition of the top management team also has a significant impact on the deployment of the company’s overall digital strategy and the development of innovation actions [38]. First of all, the greater the difference in the professional background of the executive team, the more channels and ways the organization can obtain information, the more quickly the company can perceive the changes in the external environment, and it is easier to identify innovation opportunities and potential risks to adjust the digital innovation strategy on time [39]; second, a more heterogeneous executive team has different knowledge backgrounds, decision-making styles and professional perspectives, which make the whole team more creative and inclusive, meaning it is easier to form an active digital innovation atmosphere and open up innovation boundaries through collective brainstorming [40].
2.3. Environmental Dimension
The TOE framework also focuses on the impact of the dynamically evolving external environment on digital innovation [41]. As digital technology triggers a “digital butterfly” in various economic sectors, more and more industries are recognizing the importance of digital innovation. Generally speaking, industries with faster development have a more advanced understanding of the R&D and application of digital technology. Based on the isomorphic effect, the improvement of the digitalization level in the industry promotes the formation of new competition rules, the survival of the fittest, and the elimination of the inferior [42]. To obtain quality suppliers and customers and increase the innovation efficiency of enterprises, enterprises need to have digital resources and capabilities that match the development of enterprises in the same industry, thus stimulating the motivation and innovative energy of digital innovation.
此外,数字技术系统和数字产业的进步与当地的数字基础设施和政策支持密不可分[14]。近年来,各地在数字经济领域持续发力,广泛建设数字基础设施,推动地方数字经济发展。政府高度重视区域数字创新活动,通过城市服务和城市治理总体规划开展数字创新区域布局[43]。通常,区域数字基础设施建设越好,地方数字政策治理体系越完善,就越能推动企业的数字创新活动。
2.4. 模型构建
上述分析表明,技术、组织、环境这六个先行条件中的每一个都对企业的数字化创新活动产生重要影响。但从配置上看,各种条件对企业数字化创新的影响并非相互独立,而是通过联动匹配协同发挥其效应。在这个过程中,数字技术的应用成为数字创新的基本媒介和变革者[44,45]。然而,数字技术必须与资本、设备、人才等传统创新资源紧密结合,才能充分发挥其创新赋能作用[46]。研发投入和高层次人才构成了数字化创新的资源基础,在很大程度上决定了组织应用数字化技术的可行性和适应性,可以进一步影响组织的具体技术需求。组织规模和高层管理团队异质性影响着企业组织资源的配置和互动效应,也影响着一定技术特征下创新成果的实现。同时,在内外部因素的相互作用下,企业需要不断从环境中吸收数字创新资源,识别、组织和应用有效信息,动态调整创新行为,促进资源整合,进而推进数字化创新活动。
综上所述,本研究以TOE框架为理论基础,建立企业数字化创新影响因素分析框架,从技术、组织、环境三个层面选取研发投入、高层次人才、组织规模、高层管理团队异质性、产业发展速度、区域数字化水平等六大影响因素。 探讨技术、组织、环境等多种因素如何通过相互联系、并行协同效应影响企业数字化创新活动。理论框架如图1所示。
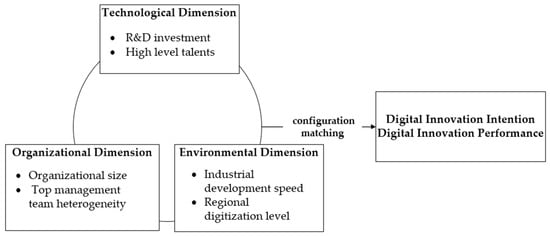
图1.理论框架。
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/su151612248
This entry is offline, you can click here to edit this entry!
