Vitamin D is a steroid hormone crucial for bone mineral metabolism. In addition, vitamin D has pleiotropic actions in the body, including anti-cancer actions. These anti-cancer properties observed within in vitro studies frequently report the reduction of cell proliferation by direct alteration of cell cycle regulators which induce cell cycle arrest. The most recurrent reported mode of cell cycle arrest by vitamin D is at the G1/G0 phase of the cell cycle. This arrest is mediated by p21 and p27 upregulation, which results in suppression of cyclin D and E activity which leads to G1/G0 arrest. In addition, vitamin D treatments within in vitro cell lines have observed a reduced C-MYC expression and increased retinoblastoma protein levels that also result in G1/G0 arrest.
- cancer
- vitamin D
- calcitriol
- anti-proliferation
- cell cycle arrest
- cyclin-dependent kinase
- cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor
1. Introduction
Vitamin D is a secosteroid hormone critical for bone and mineral metabolism in humans [1]. It is activated and inactivated by cytochrome-P450 (CYP-450) enzymes, and transduces its biological effects at an intracellular level by the vitamin D receptor (VDR) [1]. Activated vitamin D and its metabolites are able to induce biological effects by genomic and non-genomic pathways in a wide variety of human tissue [2]. Over the last four decades, observational, pre-clinical, and clinical studies have demonstrated anti-cancer properties of vitamin D [2][3]. The anti-cancer actions described are mediated by mechanisms which involve apoptosis, regulation of cell differentiation, and inhibition of cell invasion and metastasis[4][2][3][5][6][7]. In addition, vitamin D and its metabolites have demonstrated reduction of cell proliferation by the interruption of the cell cycle in cancer cell lines.
2. Vitamin D metabolism and the vitamin D metabolising system (VDMS)
The precursor vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) is formed from 7-dehydrocholesterol in the skin by exposure to ultraviolet B sunlight [1]. Cholecalciferol undergoes two sequential hydroxylation steps catalysed by cytochrome P450 (CYP-450) enzymes in the liver (mainly, CYP2R1 and CYP27A1) and kidney (CYP27B1) to form calcidiol (25(OH)D3) and calcitriol (1,25(OH)2D3), respectively [1][8]. In addition, dietary vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) follows a similar activation pathway. 1,25(OH)2D3 trimerises with retinoid X receptor (RXR) and vitamin D receptor (VDR) to regulate gene expression [1] by binding to vitamin D response elements (VDREs) in DNA [9]. Alternatively, vitamin D is biologically active through minor non-genomic pathways[10][11]. Vitamin D and its metabolites are catabolised by CYP24A1 to form predominantly inactive excretory products, and thus maintain vitamin D homeostasis [8]. Collectively, the activating and inactivating enzymes and receptor signalling system constitute the vitamin D metabolising system (VDMS). Notably, autocrine VDMS expression has been described in healthy and cancerous human tissue where it exerts autocrine/paracrine actions on cell growth and metabolism [3]. Epigenetic marks have also been shown to regulate various components of the VDMS and therefore potentially alter autocrine vitamin D metabolism [12].
3. The effects of vitamin D metabolites on the cell cycle
Vitamin D derivatives inhibit the progression of the cell cycle in various cell and tumor types. To date, the anti-proliferative action of vitamin D derivatives has been well established in malignant keratinocytes, and this action has also been well studied in breast and prostate cancer cells [2][6][7]. The best-described direct action of vitamin D on cell cycle regulators is the role of vitamin D in the G1/G0 cell cycle arrest. The G1/G0 cell cycle arrest is predominantly mediated by the upregulation of CDKIs p21 and p27 [2][6][7]. The mechanisms of p21 and p27 upregulation by calcitriol are varied. This section will explore the role of vitamin D and its metabolites on p21 and p27 expression. Furthermore, other mechanisms of G1/G0 cell cycle arrest, such as inducing pRB expression and inhibition of C-MYC expression, will also be explored. Lastly, the role of calcitriol in arresting the cell at the G2/M checkpoint will also be discussed.
3.1. Upregulation of p21 and p27 by 1,25(OH)2D3
The upregulation of cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKIs), p21 and p27, in numerous types of cells treated with vitamin D is frequently documented within in vitro studies (Table 1). Considering the importance of cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) in driving the cell cycle, it follows that an increase in CDKI targeting CDK2 (complexed to cyclin D, E, or A) halts the cell cycle.
Table 1. Mechanisms of cell cycle arrest induced by calcitriol and/or vitamin D analogues on cancer cell lines.
|
Tissue of Origin |
Author |
Cell Line/s |
Treatment (Concentration) |
Mechanism of Action |
Conclusion |
|
Breast cancer |
S. Jensen et al. [13] |
MCF-7 |
1,25(OH)2D3 (100 nM) |
1,25(OH)2D3 increased tumor suppressor pRB expression and decreased expression of CDK 4, 6 and 2 and increased expression of CDKI p21. 1,25(OH)2D3 treatment also decreased C-MYC oncoprotein expression. |
G0/G1 cell cycle arrest |
|
Chiang et al. [14] |
MCF-7 |
MART-10 (1 nM, 10 nM and 100 nM) 1,25(OH)2D3 (10 nM, 100 nM and 1000 nM) |
1,25(OH)2D3 and MART-10 induced p21 and p27 CDKI expression and induced G0/G1 cell cycle arrest. |
G0/G1 cell cycle arrest |
|
|
Wu et al. [15] |
MCF-7 E MCF-7 L BT20 T47D ZR75 |
EB1089 (0.01 nM, 0.1nM, 1 nM, 10 nM) |
EB1089 induced p21 expression and increased p21-CDK2 complex formation, which caused decreased DNA synthesis in all cell lines except EB1089-resistant MCF-7 L cell line. p27 was increased by EB1089 treatment in BT20 and ZR75 cell lines only. |
Cell-dependent G0/G1 cell cycle arrest |
|
|
Ovarian cancer |
Li et al. [16] |
2008 CAOV3 |
1,25(OH)2D3 (100 nM) |
1,25(OH)2D3 decreased the expression of cyclin E and Skp2, which resulted in decreased CDK2-cyclin E activity and decreased p27 phosphorylation, respectively. The decreased p27 phosphorylation prevents p27 protein degradation, allowing it to accumulate in the cell and induce G1/G0 cell cycle arrest. |
G0/G1 cell cycle arrest |
|
Li et al. [16] |
OVCAR3 |
1,25(OH)2D3 (100 nM) |
VDR stabilized intracellular p27 protein levels by decreasing the activity of the Skp2 proteosome, which is responsible for p27 degradation. |
G0/G1 cell cycle arrest |
|
|
Human head and neck squamous cells |
Akutsu et al. [17] |
SCC25 |
EB1089 (1 nM, 10 nM and 100 nM) |
Calcitriol analogue EB1089 upregulated growth repair damage factor GADD45α. |
G0/G1 cell cycle arrest |
|
Salehi-Tabar et al. [18] |
SCC25 |
1,25(OH)2D3 (100 nM) |
1,25(OH)2D3 decreased C-MYC expression and increased C-MYC repressor MAD1 levels. The increased MAD1 prevented C-MYC’s transcriptional regulation of target genes and inhibited cell proliferation. |
G0/G1 cell cycle arrest |
|
|
Thyroid cancer |
Liu et al. [19] |
PTC-1 NPA WRO |
1,25(OH)2D3 (0.1nM, 1 nM, 10 nM, 100 nM and 1000 nM) EB1089 (0.1 nM, 1nM, 10 nM, 100 nM and 1000 nM) |
1,25(OH)2D3 and EB1089 increased p27 expression and decreased Skp2 expression, which allowed p27 to accumulate and induce G0/G1 cell cycle arrest. |
G0/G1 cell cycle arrest |
|
Promyelocytic leukaemia |
Wang et al. [20] |
HL60 |
1,25(OH)2D3 (1 nM and 100 nM) |
1,25(OH)2D3 induced p12 and p27 mRNA and protein expression and induced G0/G1 cell cycle arrest. |
G0/G1 cell cycle arrest |
|
Prostate cancer |
Washington et al. [21] |
C4-2 |
1,25(OH)2D3 (100 nM) |
1,25(OH)2D3 decreased C-MYC expression and induced G1 cell cycle arrest in a pRB-independent manner. |
G0/G1 cell cycle arrest |
|
Bao et al. [22] |
LNCaP CWR22R PC-3 DU145 |
1,25(OH)2D3 (100 nM) |
1,25(OH)2D3 increased pRB and p27 expression and decreased CDK2 expression, thereby preventing entry into the S phase. |
G0/G1 cell cycle arrest |
|
|
Boyle et al. [23] |
LNCaP |
1,25(OH)2D3 (10 nM) |
Calcitriol upregulated the mRNA and protein expression of insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3, which resulted in increased expression of p21 and induced a G0/G1 cell cycle arrest. |
G0/G1 cell cycle arrest |
|
|
Flores et al. [24] |
LNCaP |
1,25(OH)2D3 (50 nM) |
1,25(OH)2D3 decreased CDK2 activity leading to hypophosphorylation of pRB, which prevented entry into the S phase. |
G0/G1 cell cycle arrest |
|
|
Rohan et al. [25] |
LnCaP C4-2 RWPE-1 |
1,25(OH)2D3 (10 nM) |
Downregulation of C-MYC mRNA and protein expression induced by 1,25(OH)2D3 treatment. |
G0/G1 cell cycle arrest |
|
|
Colorectal adenoma and carcinoma |
Diaz et al. [26] |
SW620 PC/JW HT29 |
1,25(OH)2D3 (0.1nM, 1 nM, 10 nM, 100 nM, 1000 nM) EB1089 (0.1 nM, 1nM, 10 nM, 100 nM, 1000 nM) |
Calcitriol and analogue EB1089 increased cells in G1 in a p53- dependent manner. |
G0/G1 cell cycle arrest |
|
Pancreatic cancer |
Li et al. [27] |
HPDE6-C7 Panc-1 |
1,25(OH)2D3 (1 nM, 5nM, 10 nM, 50 nM, 100 nM) |
p21 expression was significantly increased in HPDE6-C7 cells but not in metastatic Panc-1 cells. |
G0/G1 cell cycle arrest |
|
Petterson et al. [28] |
AsPc-1 BxPc-3 T3M-4 |
EB1089 (50 nM) CB1093 (50 nM) |
EB1089 and CB1093 induced cell cycle arrest in all cell lines investigated in this study. |
G0/G1 cell cycle arrest |
|
|
Schwartz et al. [29] |
BxPC-3 Hs700T Hs766T AsPC-1 |
1,25(OH)2D3 (100 nM) 25(OH)D3 (100 nM or 2µM) |
Increased expression of p21 and p27 proteins in BxPC-3, Hs700T and AsPC-1 cell lines only. |
G0/G1 cell cycle arrest |
|
|
Malignant pleural mesothelioma |
Gesmundo et al. [30] |
MeT-5A Msto-211H REN |
1,25(OH)2D3 (1 nM, 10 nM, 50 nM and 100 nM) |
Reduction in C-MYC expression and cyclin A, cyclin D1 and cyclin D2 which induced a G1/G0 cell cycle arrest. |
G0/G1 cell cycle arrest |
|
Malignant melanoma |
Reichrath et al. [31] |
IGR MelJuso MeWo SK-Mel-5 SK-Mel-25 SK-Mel-28 SM2 |
1,25(OH)2D3 (100 nM) 25(OH)D3 (100 nM) EB1089 (100 nM) |
Treatments induced a significant decrease in cell proliferation of MeWo, SK-Mel 28, and SM2 melanoma cell lines. In addition, IGR, MelJuso, SkMel5 and SK-Mel-25 cell lines demonstrated no significant change in cell growth. |
Cell cycle not investigated; however, a significant decrease in cell proliferation was observed in a cell-specific manner. |
|
Spath et al. [32] |
IR6 VAG 1007 |
1,25(OH)2D3 (50 nM) |
1,25(OH)2D3 induced G1/G0 cell cycle arrest in IR6 cell line by p21 and p27 upregulation, and cyclin D downregulation. 1,25(OH)2D3 induced G2/M arrest in VAG cell line by decreased cyclin B1 expression. In 1007 melanoma cell line, 1,25(OH)2D3 increased cells in the proliferative compartments of the cell cycle (S-phase plus G2 phase) by increased cyclin A1, p21 and p27 expression. |
Cell-specific cell arrest responses were observed to 1,25(OH)2D3 treatment. |
|
|
Liu et al. [33] |
U937 |
1,25(OH)2D3 (100 nM) |
1,25(OH)2D3 induced p21 mRNA expression in a p53-independent manner and 1,25(OH)2D3 induced p27 gene and protein expression. |
1,25(OH)2D3 arrested cell proliferation and induced cell surface markers of cell differentiation. |
Abbreviations: 1,25(OH)2D3, calcitriol; 25(OH)2D3, calcidiol; EB1089, Seocalcitol; CB1093, novel 20-epi-vitamin D3 analogue; MART-10 (19-nor-2α-(3-hydroxypropyl)-1α,25(OH)₂D₃; pRB, retinoblastoma protein.
3.1.1. Mechanisms of p21 upregulation by 1,25(OH)2D3
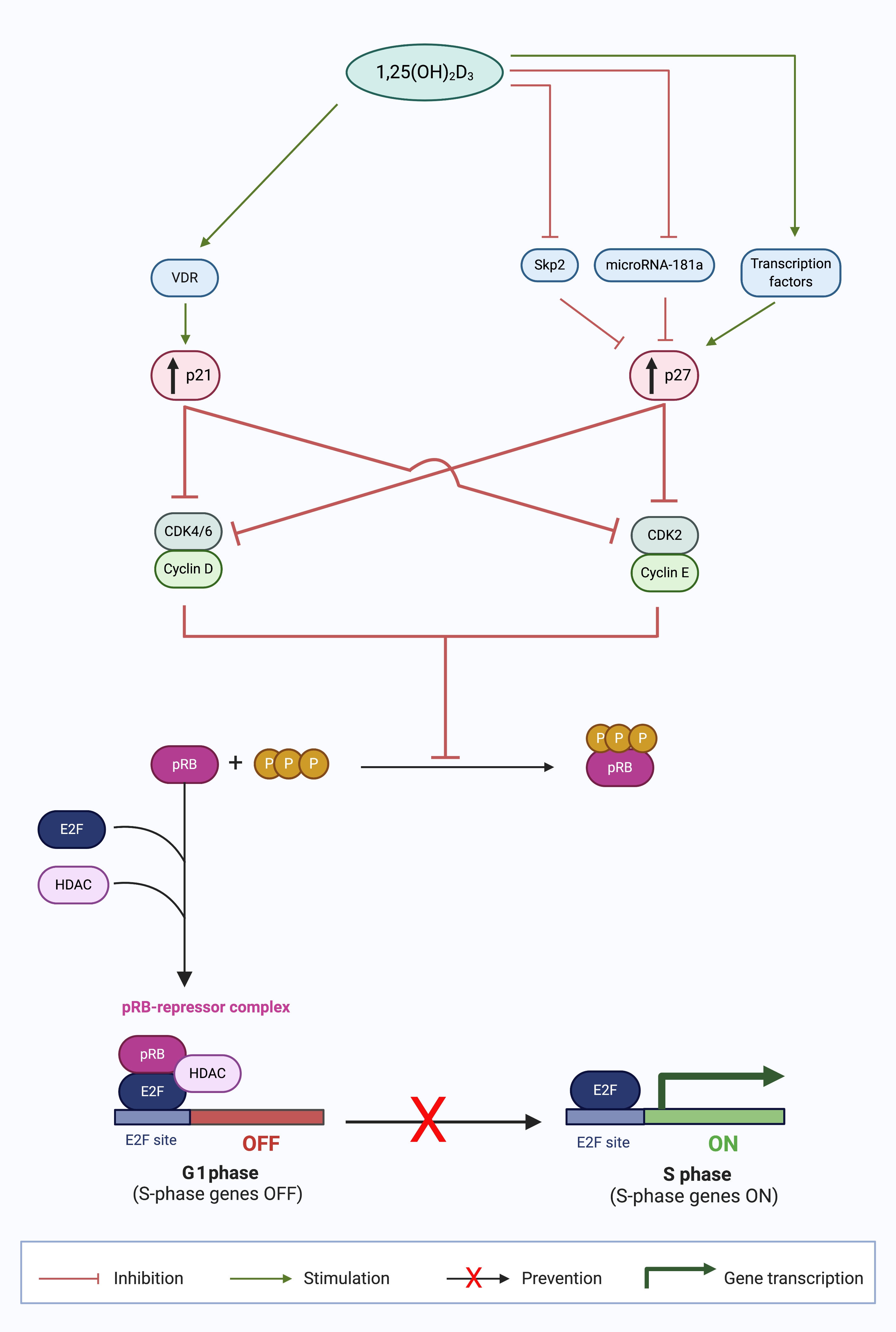
At a genomic level, 1,25(OH)2D3 increases the expression of p21 (Figure 1). A functional VDRE has been identified in the p21 promoter region. This enables direct regulation of p21 transcription by VDR. p21 is upregulated in cells treated with vitamin D metabolites [33]. Functional VDRE in the p21 promoter has been reported in prostate cancer [46,57], breast cancer [13][15][34], and parathyroid cancer cells [35]. Therefore, VDR binding to VDRE at the p21 promoter region enhances p21 transcription and induces cell cycle arrest at G1/G0.
Within in vitro cell differentiation models, such as myeloid leukemia HL60 and SCC cell lines, p21 showed variable response to calcitriol treatment. In addition to cell cycle arrest, p21 is also associated with cellular differentiation. Despite the presence of VDRE at the p21 gene promoter, studies on calcitriol treatment reveal cell-specific results. In HL60 cells, calcitriol increased p21 expression and induced G1/G0 cell cycle arrest [36]. However, in SCC cells, which are malignant counterparts of keratinocytes, 1,25(OH)2D3 inhibited cell growth but also decreased p21 expression [37]. In the myelomonocytic cell line, U937, p21 mRNA was significantly increased two hours after treatment with 1,25(OH)2D3, and this resulted in a G1 arrest [33]. However, assessment of the cell cycle 24 and 48 h after treatment identified that this initial quick response was not sustained [38]. The initial G1 arrest was followed by a “proliferative burst.” This may suggest that it is unlikely that p21 is solely responsible for the G1/G0 arrest in leukemia. These findings suggest that the role of vitamin D in p21 upregulation and subsequent cell cycle arrest or differentiation remains unclear in healthy and malignant keratinocytes.
In addition, p21 is also transcriptionally regulated by p53 protein [39]. This p53-p21 axis is regulated by multiple p53 binding regions located in the p21 promoter [40]. The p53 tumor-suppressor protein is activated by cellular stressors, for example, oncogene activation [39]. This transcription factor can activate or repress target genes directly by the recruitment of p53 tetramers to response elements on target gene promoter sites to cause tumor suppression by affecting cell cycling and apoptosis [39]. The direct activation of cell cycle arrest proteins by p53 include the upregulation of p21 CDKI [41]. In addition, indirect p53-mediated repression of other tumor-suppressor genes can be affected by the direct p53-dependent increase of p21 expression [42]. Thus, p53 can cause cell cycle disruption directly or indirectly via p21, which recruits E2F4 repression complexes to target promoters of genes involved in cell cycle progression. 1,25(OH)2D3 has been shown to regulate the p53-p21 axis. Cross-talk between VDR and p53 family members is important in tumor suppression [43]. For example, in gastric cancer cells, multiple sites for p53 binding are present in the promoter region of p21 and p53 co-operates with VDR to regulate the transactivation of p21 mRNA [44]. Mechanisms that are important in the cross-talk between vitamin D and p53 signaling include direct regulation of VDR by p53 [45]; the regulation of cutaneous vitamin D synthesis by p53 [46] and the binding of p53 to highly conserved intron sequences of the VDR gene [47]. Additionally, vitamin D metabolites can regulate murine double minute (MDM2) gene independent of p53 [48], which encodes an E3 ubiquitin ligase that degrades p53 by the 26S proteosome [49] which can regulate p53-induced cell death. Cell cycle arrest in cancer cell lines has demonstrated p53 dependent and p53 independent mechanisms.
3.1.2. Mechanisms of p27 upregulation by 1,25(OH)2D3
In contrast to the genomic regulation of p21, calcitriol regulates p27 at a protein level. In 1996, Wang et al. were the first to report an increase in p27 and subsequent G1 block after 1,25(OH)2D3 treatment in HL60 cells [20]. In later experiments, the same group demonstrated reduced Cdk6 and Cdk2 kinase activity and p27 upregulation [50] which induced a G1 cell cycle arrest. In addition, p27 silencing by siRNA reversed the G1 block in HL60 cells [51]. Taken together, these findings demonstrate that p27 has a crucial role in G1/G0 cell cycle arrest in HL60 cells. To date, several different mechanisms of 1,25(OH)2D3 regulation of p27 have been reported (Figure 1).
The dominant mechanism of p27 regulation by vitamin D is by proteosome-dependent protein degradation. For example, in both ovarian [16] and prostate [52] cancer cell lines, 1,25(OH)2D3 treatment did not change p27 mRNA levels, but reduced mRNA expression of p45/Skp2 and Cks1 which are responsible for p27 protein ubiquitinylation and degradation [53]. The net effect is that there is decreased ubiquitin tagging of p27 protein and subsequent protein degradation, ultimately leading to increased p27 stabilization [53][54]. This mechanism of p27 stabilization was also observed in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells [55] and human hepatoma cells [56]. By protein stabilization, 1,25(OH)2D3 may increase p27 expression and sustain the G1 cell cycle block as p27 regulates cyclin E-CDK2 activity [57].
In addition to the aforementioned post-translational mechanism of p27, 1,25(OH)2D3 also mediates p27 by two transcriptional mechanisms. Firstly, VDR enhanced the expression of transcription factors responsible for the increase in p27 gene expression, Sp1, and NFY, in SW620 colon cancer cell line and LNCaP prostate cancer cell line [58]. Secondly, calcitriol has been observed to induce Akt expression and thereby indirectly regulate p27 gene expression [59]. Akt promotes forkhead transcription factors, such as AFX (FOXO4), which is required for p27 gene expression [60][61]. Therefore, VDR indirectly increases p27 expression at the genomic level by several key transcription factors.
Furthermore, 1,25(OH)2D3 regulates p27 expression by decreasing microRNA 181a expression, and it has been reported in myeloid cells [62]. MicroRNAs repress protein expression at the post-transcriptional level by binding to mRNA transcripts and blocking access to protein synthesis machinery [63]. Wang et al., reported a decrease in expression of miRNA 181a in HL60 and U937 cells when treated with 1,25(OH)2D3 in a dose- and time-dependent manner [62] which decreased p27 mRNA whereas cells transfected with pre-miR181a constructs abrogated the 1,25(OH)2D3-induced upregulation of p27 [62].
Hence, several mechanisms of p27 regulation have been reported, and data suggests a cell-specific response to calcitriol treatment. Additional studies on p27 regulation by vitamin D metabolites in other cell lines and cancer cell types are needed to fully elucidate the mechanism of p27 upregulation by vitamin D metabolites in cancer.
Figure 1. Calcitriol upregulates p21 and p27 expression in the G1 phase and prevents cell cycle progression to the S phase [3]. Calcitriol (1,25(OH)2D3) increases the expression of CDK inhibitors (CDKIs), p21 and p27, by numerous mechanisms. p21 expression is increased by stimulation of liganded VDR signaling. p27 expression is increased by signaling transcription factors; inhibition of p27 protein degradation by S-phase kinase-associated protein 2 (Skp2); and enhanced p27 translation by abrogated microRNA-181a expression. The collective outcome of the increased CDKI expression is suppression of cyclin-CDK complex formation, which inhibits the formation of hyperphosphorylated retinoblastoma protein (pRB). The unphosphorylated pRB thus is able to form a repressor complex with histone deacetylase (HDAC) and E2F transcription factor (E2F), which prevents the progression of cancer cells in the G1 phase to the S phase, inhibiting S phase gene expression, and thus causing G0/G1 cell cycle arrest. (Source: personal collection; image created with BioRender.com)
3.2. The effect of 1,25(OH)2D3 on pRB expression
By increasing CDKIs p21 and p27, 1,25(OH)2D3 directly decreases the action of downstream targets, cyclin D-CDK4/6, and cyclin E-CDK2 complexes, respectively. The result of these perturbations of cell cycle regulatory proteins is that pRB remains in a hypophosphorylated state complexed to E2F [64]. In this way, 1,25(OH)2D3 prevents the transcriptional activity of E2F transcription factors and denies entry into the S phase of the cell cycle. In addition to this indirect role of 1,25(OH)2D3 on E2F expression, 1,25(OH)2D3 can increase the expression of pRB in myeloid leukemia cells approximately 10 h after vitamin D treatment [65], although the mechanism of pRB upregulation is currently unknown. The increased abundance of pRB sequesters any free E2F factors and inhibits E2F, which results in a G1/G0 cell cycle arrest [64].
3.3. Downregulation of C-MYC by 1,25(OH)2D3
In addition to its regulation of pRB, 1,25(OH)2D3 has demonstrated downregulation of the prominent pRB target gene, C-MYC. Several studies have demonstrated a significant reduction of C-MYC expression after 1,25(OH)2D3 treatment in colon [66][67] and prostate cancer cell lines [25][68]. These studies collectively demonstrate that decreased C-MYC expression is associated with G1/G0 arrest, followed by cell differentiation.
The mechanism for C-MYC repression by calcitriol seems to be cell-specific. In prostate cancer C4-2 cells, 1,25(OH)2D3 treatment reduced C-MYC mRNA by 50% and resulted in a significant reduction in C-MYC protein [25]. In SW480 colon cancer cells, 1,25(OH)2D3 promoted VDR/β-catenin interaction and prevented the β-catenin translocation into the nucleus [69]. β-catenin is important for C-MYC gene transcription. Thus, 1,25(OH)2D3 may indirectly inhibit C-MYC gene transcription via the APC/β-catenin pathway. C-MYC, therefore, appears to be an important target of calcitriol in policing cancer cells to cause G1/G0 arrest.
3.4. Role of 1,25(OH)2D3 in G2/M cell cycle arrest
Currently, there is limited evidence of the induction of G2/M arrest by 1,25(OH)2D3, with the general consensus that G1/G0 cell cycle arrest is the primary target of vitamin D metabolites. However, there are a selected number of studies that have shown G2/M cell cycle arrest in cells treated with 1,25(OH)2D3. In HL60 myeloid leukemia cells treated with 1,25(OH)2D3, a G2/M arrest was evident in cell cycle analyses [70][71]. Only one study identified a mechanistic link in 1,25(OH)2D3-induced G2/M cell cycle arrest. In ovarian cancer cell lines, 1,25(OH)2D3 increased GADD45α (Growth arrest and DNA-Damage-Inducible alpha) and subsequently induced cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase [72]. Interestingly, a functional VDRE was identified in an exonic enhancer region of the GADD45α gene [72]; however, no additional studies exploring GADD45α, and this VDRE in other cancer cell lines, have been identified.
4. Epigenetic marks of the VDMS in cancer cell lines may alter cell arrest
The autocrine VDMS controls genes that regulate cell proliferation and cell death. CpG islands span the promoters of CYP2R1, CYP24A1, and VDR, while a CpG island is located within the CYP27B1 gene locus [73].
Liganded VDR signaling has been shown to be attenuated in cancer [96]. Epigenetic silencing of the vitamin D receptor (VDR) can be mediated by hypermethylation in various types of cancerous cells, including breast and choriocarcinoma tumor cell lines [74]. The pattern of hypermethylation of the VDR promoter region is inconsistent in cancer cell lines; for example, colonic cancer cells do not reveal a hypermethylated status in the VDR promoter region [75][76]. Therefore, the decreased sensitivity to calcitriol may be caused by epigenetic corruption of the VDR in cancer cell lines. In addition, epigenetic marks can reduce sensitivity to vitamin D metabolites in clinical trials [77] by increased methylation of VDR promoter and associated VDR expression in cancer [78].
In addition, expression of CYP27B1 is often downregulated in cancer which may be accounted for by CpG islands also present in the gene locus. In breast cancer cell lines, the CYP27B1 gene showed reversible DNA hypermethylation which caused CYP27B1 silencing. Similarly, Novakovic et al. [79] demonstrated hypermethylation of the CYP27B1 gene promoter region in the choriocarcinoma cell lines, BeWo and JAR. Inhibitors of methylation in prostate cancer cell lines increased CYP27B1 expression [80] supporting the importance of epigenetic marking of CYP27B1 in autocrine calcitriol synthesis. Hypermethylation of CYP27B1, therefore, may be associated with the decreased local synthesis of calcitriol from calcidiol substrate, and potentially decreased cell growth, differentiation, and perturbed cell cycling.
The regulation of CYP24A1 by DNA methylation demonstrates cell-specificity. Hypermethylation of the CYP24A1 promoter region, with associated epigenetic silencing of CYP24A1 expression, has been identified in prostate cancer cell line PC3 [81] and tumor-derived endothelial cells (TDEC) [82]. The hypomethylation of the CYP24A1 promoter in colon adenocarcinoma associated with significantly elevated CYP24A1 expression [83] has also been observed. The catabolic role of CYP24A1 in these studies may support the disruption of calcitriol-mediated cell arrest in tumorigenic cell lines.
Collectively, these studies demonstrate that the epigenetic regulation of gene expression of the VDMS is altered in cancer mainly by DNA hypermethylation. This altered state leads to abnormal protein expression levels, which may favor carcinogenesis in a cell-specific manner. Therefore, autocrine regulation of the VDMS may impact G1/G0 and G2/M cell cycle arrest in cell lines and in clinical studies. Epigenetic alteration of the VDMS may also provide insight into the discordant alignment between in vitro cancer studies and clinical studies. Exploration of epigenetic marks of the VDMS on cell cycle regulators may thus provide a possible explanation of the inhibition of cell arrest in cancer patients. Future studies can also target altered autocrine activation of vitamin D precursors, autocrine catabolism of activated vitamin D hormone, and abrogated signaling of liganded VDR, and their collective association with perturbations of vitamin D-induced cell cycle arrest.
5. Conclusion
Vitamin D metabolites and synthetic analogues demonstrate cell cycle arrest in a cell-specific manner in cancer cell line models at cell cycle phases, G1/G0 and less commonly G2. Vitamin D induces cell arrest by upregulation of CDKIs (p21, and p27); decreased C-MYC expression; and increased pRB expression. Studies exploring the autocrine epigenetic regulation of the VDMS can provide further insight into vitamin D metabolism and cell arrest in cancer.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/ijms21239296
References
- Holick, M.F. Vitamin D Deficiency. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 266–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, D.; Krishnan, A.V.; Swami, S.; Giovannucci, E.; Feldman, B.J. The role of vitamin D in reducing cancer risk and progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 342–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleet, J.C.; DeSmet, M.; Johnson, R.; Li, Y. Vitamin D and cancer: A review of molecular mechanisms. Biochem. J. 2012, 441, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhoora, S.; Pather, Y.; Marais, S.; Punchoo, R. Cholecalciferol Inhibits Cell Growth and Induces Apoptosis in the CaSki Cell Line. Med. Sci. 2020, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trump, D.; Aragon-Ching, J. Vitamin D in prostate cancer. Asian J. Androl. 2018, 20, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, M.J.; Trump, D.L. Vitamin D Receptor Signaling and Cancer. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 46, 1009–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkinson, C. The vitamin D metabolome: An update on analysis and function. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2019, 37, 408–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- K Ozono; J Liao; S A Kerner; R A Scott; J W Pike; The vitamin D-responsive element in the human osteocalcin gene. Association with a nuclear proto-oncogene enhancer.. Journal of Biological Chemistry 1990, 265, 21881-21888, .
- Igor N. Sergeev; 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 and type 2 diabetes: Ca2+-dependent molecular mechanisms and the role of vitamin D status. Hormone Molecular Biology and Clinical Investigation 2016, 26, 61-65, 10.1515/hmbci-2015-0069.
- Jiaxuan Chen; Rene Olivares-Navarrete; Yun Wang; Tyler R. Herman; B.D. Boyan; Zvi Schwartz; Protein-disulfide Isomerase-associated 3 (Pdia3) Mediates the Membrane Response to 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3in Osteoblasts. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2010, 285, 37041-37050, 10.1074/jbc.m110.157115.
- Irfete S. Fetahu; Julia Hã¶baus; Enikå‘ Kã¡llay; Vitamin D and the epigenome. Frontiers in Physiology 2014, 5, 164, 10.3389/fphys.2014.00164.
- Jensen, S.S.; Madsen, M.W.; Lukas, J.; Binderup, L.; Bartek, J. Inhibitory effects of 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3) on the G(1)-S phase-controlling machinery. Mol. Endocrinol. 2001, 15, 1370–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, K.-C.; Yeh, C.-N.; Chen, S.-C.; Shen, S.-C.; Hsu, J.-T.; Yeh, T.-S.; Pang, J.-H.S.; Su, L.-J.; Takano, M.; Kittaka, A.; et al. MART-10, a New Generation of Vitamin D Analog, Is More Potent than 1α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 in Inhibiting Cell Proliferation and Inducing Apoptosis in ER+ MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 310872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Fan, R.S.; Li, W.; Ko, T.C.; Brattain, M.G. Modulation of cell cycle control by vitamin D3 and its analogue, EB1089, in human breast cancer cells. Oncogene 1997, 15, 1555–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, C.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, X.; Nicosia, S.V.; Bai, W. p27(Kip1) stabilization and G(1) arrest by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3) in ovarian cancer cells mediated through down-regulation of cyclin E/cyclin-dependent kinase 2 and Skp1-Cullin-F-box protein/Skp2 ubiquitin ligase. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 25260–25267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akutsu, N.; Lin, R.; Bastien, Y.; Bestawros, A.; Enepekides, D.J.; Black, M.J.; White, J.H. Regulation of gene Expression by 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and Its analog EB1089 under growth-inhibitory conditions in squamous carcinoma Cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 2001, 15, 1127–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi-Tabar, R.; Nguyen-Yamamoto, L.; Tavera-Mendoza, L.E.; Quail, T.; Dimitrov, V.; An, B.-S.; Glass, L.; Goltzman, D.; White, J.H. Vitamin D receptor as a master regulator of the c-MYC/MXD1 network. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 18827–18832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Asa, S.L.; Fantus, I.G.; Walfish, P.G.; Ezzat, S. Vitamin D arrests thyroid carcinoma cell growth and induces p27 dephosphorylation and accumulation through PTEN/akt-dependent and -independent pathways. Am. J. Pathol. 2002, 160, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.M.; Jones, J.B.; Studzinski, G.P. Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27 as a mediator of the G1-S phase block induced by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in HL60 cells. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 264–267. [Google Scholar]
- Washington, M.N.; Kim, J.-S.; Weigel, N.L. 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 inhibits C4-2 prostate cancer cell growth via a retinoblastoma protein (Rb)-independent G1 arrest. Prostate 2011, 71, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, B.Y.; Hu, Y.C.; Ting, H.J.; Lee, Y.F. Androgen signaling is required for the vitamin D-mediated growth inhibition in human prostate cancer cells. Oncogene 2004, 23, 3350–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyle, B.J.; Zhao, X.Y.; Cohen, P.; Feldman, D. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 mediates 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin d(3) growth inhibition in the LNCaP prostate cancer cell line through p21/WAF1. J. Urol. 2001, 165, 1319–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, O.; Wang, Z.; Knudsen, K.E.; Burnstein, K.L. Nuclear targeting of cyclin-dependent kinase 2 reveals essential roles of cyclin-dependent kinase 2 localization and cyclin E in vitamin D-mediated growth inhibition. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 896–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohan, J.N.; Weigel, N.L. 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 reduces c-Myc expression, inhibiting proliferation and causing G1 accumulation in C4-2 prostate cancer cells. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 2046–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, G.D.; Paraskeva, C.; Thomas, M.G.; Binderup, L.; Hague, A. Apoptosis is induced by the active metabolite of vitamin D3 and its analogue EB1089 in colorectal adenoma and carcinoma cells: Possible implications for prevention and therapy. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 2304–2312. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Shang, F.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Sudi, R.S. Modulation of VDR and Cell Cycle-Related Proteins by Vitamin D in Normal Pancreatic Cells and Poorly Differentiated Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Nutr. Cancer 2019, 71, 818–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, F.; Colston, K.W.; Dalgleish, A.G. Differential and antagonistic effects of 9-cis-retinoic acid and vitamin D analogues on pancreatic cancer cells in vitro. Br. J. Cancer 2000, 83, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, G.G.; Eads, D.; Rao, A.; Cramer, S.D.; Willingham, M.C.; Chen, T.C.; Jamieson, D.P.; Wang, L.; Burnstein, K.L.; Holick, M.F.; et al. Pancreatic cancer cells express 25-hydroxyvitamin D-1 alpha-hydroxylase and their proliferation is inhibited by the prohormone 25-hydroxyvitamin D3. Carcinogenesis 2004, 25, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gesmundo, I.; Silvagno, F.; Banfi, D.; Monica, V.; Fanciulli, A.; Gamba, G.; Congiusta, N.; Libener, R.; Riganti, C.; Ghigo, E.; et al. Calcitriol Inhibits Viability and Proliferation in Human Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Cells. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichrath, J.; Rech, M.; Moeini, M.; Meese, E.; Tilgen, W.; Seifert, M. In vitro comparison of the vitamin D endocrine system in 1,25(OH)2D3-responsive and -resistant melanoma cells. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2007, 6, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spath, L.; Ulivieri, A.; Lavra, L.; Fidanza, L.; Carlesimo, M.; Giubettini, M.; Narcisi, A.; Luciani, E.; Bucci, B.; Pisani, D.; et al. Antiproliferative Effects of 1α-OH-vitD3 in Malignant Melanoma: Potential Therapeutic implications. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Lee, M.H.; Cohen, M.; Bommakanti, M.; Freedman, L.P. Transcriptional activation of the Cdk inhibitor p21 by vitamin D3 leads to the induced differentiation of the myelomonocytic cell line U937. Genes Dev. 1996, 10, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verlinden, L.; Verstuyf, A.; Convents, R.; Marcelis, S.; Van Camp, M.; Bouillon, R. Action of 1,25(OH)2D3 on the cell cycle genes, cyclin D1, p21 and p27 in MCF-7 cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1998, 142, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzolino, M.; Lu, Y.; Finch, J.; Slatopolsky, E.; Dusso, A.S. p21WAF1 and TGF-alpha mediate parathyroid growth arrest by vitamin D and high calcium. Kidney Int. 2001, 60, 2109–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hager, G.; Kornfehl, J.; Knerer, B.; Weigel, G.; Formanek, M. Molecular analysis of p21 promoter activity isolated from squamous carcinoma cell lines of the head and neck under the influence of 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D3 and its analogs. Acta Otolaryngol. 2004, 124, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershberger, P.A.; Modzelewski, R.A.; Shurin, Z.R.; Rueger, R.M.; Trump, D.L.; Johnson, C.S. 1,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol (1,25-D3) inhibits the growth of squamous cell carcinoma and down-modulates p21(Waf1/Cip1) in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 2644–2649. [Google Scholar]
- Rots, N.Y.; Iavarone, A.; Bromleigh, V.; Freedman, L.P. Induced differentiation of U937 cells by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 involves cell cycle arrest in G1 that is preceded by a transient proliferative burst and an increase in cyclin expression. Blood 1999, 93, 2721–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vousden, K.H.; Prives, C. Blinded by the Light: The Growing Complexity of p53. Cell 2009, 137, 413–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saramäki, A.; Banwell, C.M.; Campbell, M.J.; Carlberg, C. Regulation of the human p21(waf1/cip1) gene promoter via multiple binding sites for p53 and the vitamin D3 receptor. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laptenko, O.; Prives, C. Transcriptional regulation by p53: One protein, many possibilities. Cell Death Differ. 2006, 13, 951–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, E.K.; Mungamuri, S.K.; Attie, O.; Kracikova, M.; Sachidanandam, R.; Manfredi, J.J.; Aaronson, S.A. p53-dependent gene repression through p21 is mediated by recruitment of E2F4 repression complexes. Oncogene 2014, 33, 3959–3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichrath, J.; Reichrath, S.; Heyne, K.; Vogt, T.; Roemer, K. Tumor suppression in skin and other tissues via cross-talk between vitamin D- and p53-signaling. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, L.; Zhang, L.; Hu, W.; Shen, J.; Xiao, Z.; Wu, X.; Chan, F.L.; Cho, C.H. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D(3) suppresses gastric cancer cell growth through VDR- and mutant p53-mediated induction of p21. Life Sci. 2017, 179, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, R.; Aoki, F.; Toyota, M.; Sasaki, Y.; Akashi, H.; Mita, H.; Suzuki, H.; Akino, K.; Ohe-Toyota, M.; Maruyama, Y.; et al. Comparative genome analysis identifies the vitamin D receptor gene as a direct target of p53-mediated transcriptional activation. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 4574–4583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Hearing, V.J. Physiological factors that regulate skin pigmentation. Biofactors 2009, 35, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kommagani, R.; Payal, V.; Kadakia, M.P. Differential regulation of vitamin D receptor (VDR) by the p53 Family: p73-dependent induction of VDR upon DNA damage. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 29847–29854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Marechal, V.; Levine, A.J. Mapping of the p53 and mdm-2 interaction domains. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1993, 13, 4107–4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roemer, K. Notch and the p53 clan of transcription factors. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2012, 727, 223–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.M.; Luo, X.; Studzinski, G.P. Cyclin-dependent kinase 6 is the principal target of p27/Kip1 regulation of the G1-phase traverse in 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3-treated HL60 cells. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 2851–2855. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.M.; Chen, F.; Luo, X.; Moore, D.C.; Flanagan, M.; Studzinski, G.P. Lowering of p27Kip1 levels by its antisense or by development of resistance to 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 reverses the G1 block but not differentiation of HL60 cells. Leukemia 1998, 12, 1256–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, E.S.; Burnstein, K.L. Vitamin D Inhibits G1 to S Progression in LNCaP Prostate Cancer Cells through p27Kip1 Stabilization and Cdk2 Mislocalization to the Cytoplasm. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 46862–46868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsvetkov, L.M.; Yeh, K.H.; Lee, S.J.; Sun, H.; Zhang, H. p27(Kip1) ubiquitination and degradation is regulated by the SCF(Skp2) complex through phosphorylated Thr187 in p27. Curr. Biol. 1999, 9, 661–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrano, A.C.; Eytan, E.; Hershko, A.; Pagano, M. SKP2 is required for ubiquitin-mediated degradation of the CDK inhibitor p27. Nat. Cell Biol. 1999, 1, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, R.; Wang, T.T.; Miller, W.H., Jr.; White, J.H. Inhibition of F-Box protein p45(SKP2) expression and stabilization of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27(KIP1) in vitamin D analog-treated cancer cells. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 749–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Chen, Y.; Liu, M.; Du, K.; Zheng, G.; Cai, T.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, F.; Yao, T.; Yang, R.; et al. EB1089 Induces Skp2-Dependent p27 Accumulation, Leading to Cell Growth Inhibition and Cell Cycle G1 Phase Arrest in Human Hepatoma Cells. Cancer Investig. 2009, 27, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moller, M.B. P27 in cell cycle control and cancer. Leuk. Lymphoma 2000, 39, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.C.; Chen, J.Y.; Hung, W.C. Vitamin D3 receptor/Sp1 complex is required for the induction of p27Kip1 expression by vitamin D3. Oncogene 2004, 23, 4856–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Studzinski, G.P. AKT pathway is activated by 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and participates in its anti-apoptotic effect and cell cycle control in differentiating HL60 cells. Cell Cycle 2006, 5, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medema, R.H.; Kops, G.J.; Bos, J.L.; Burgering, B.M. AFX-like Forkhead transcription factors mediate cell-cycle regulation by Ras and PKB through p27kip1. Nature 2000, 404, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahl, M.; Dijkers, P.F.; Kops, G.J.; Lens, S.M.; Coffer, P.J.; Burgering, B.M.; Medema, R.H. The forkhead transcription factor FoxO regulates transcription of p27Kip1 and Bim in response to IL-2. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 5024–5031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Gocek, E.; Liu, C.G.; Studzinski, G.P. MicroRNAs181 regulate the expression of p27Kip1 in human myeloid leukemia cells induced to differentiate by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malumbres, M. 4-Control of the Cell Cycle. In Abeloff’s Clinical Oncology, 6th ed.; Niederhuber, J.E., Armitage, J.O., Kastan, M.B., Doroshow, J.H., Tepper, J.E., Eds.; Content Repository Only: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2020; pp. 56–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Kutner, A.; Verstuyf, A.; Verlinden, L.; Studzinski, G.P. Derivatives of vitamins D2 and D3 activate three MAPK pathways and upregulate pRb expression in differentiating HL60 cells. Cell Cycle 2002, 1, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eelen, G.; Verlinden, L.; Bouillon, R.; De Clercq, P.; Muñoz, A.; Verstuyf, A. CD-ring modified vitamin D3 analogs and their superagonistic action. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 121, 417–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.J.; Velcich, A.; Arango, D.; Kurland, A.R.; Shenoy, S.M.; Pezo, R.C.; Levsky, J.M.; Singer, R.H.; Augenlicht, L.H. Novel detection and differential utilization of a c-myc transcriptional block in colon cancer chemoprevention. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 6006–6010. [Google Scholar]
- Washington, M.N.; Weigel, N.L. 1{alpha},25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 inhibits growth of VCaP prostate cancer cells despite inducing the growth-promoting TMPRSS2:ERG gene fusion. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 1409–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, H.G.; Gonzalez-Sancho, J.M.; Espada, J.; Berciano, M.T.; Puig, I.; Baulida, J.; Quintanilla, M.; Cano, A.; de Herreros, A.G.; Lafarga, M.; et al. Vitamin D(3) promotes the differentiation of colon carcinoma cells by the induction of E-cadherin and the inhibition of beta-catenin signaling. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 154, 369–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studzinski, G.P.; Rathod, B.; Rao, J.; Kheir, A.; Wajchman, H.J.; Zhang, F.; Finan, J.B.; Nowell, P.C. Transition to tetraploidy in 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3-resistant HL60 cells is preceded by reduced growth factor dependence and constitutive up-regulation of Sp1 and AP-1 transcription factors. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 5513–5521. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Godyn, J.J.; Xu, H.; Zhang, F.; Kolla, S.; Studzinski, G.P. A dual block to cell cycle progression in HL60 cells exposed to analogues of vitamin D. Cell Prolif. 1994, 27, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, F.; Li, P.; Fornace, A.J., Jr.; Nicosia, S.V.; Bai, W. G2/M arrest by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in ovarian cancer cells mediated through the induction of GADD45 via an exonic enhancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 48030–48040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetahu, I.S.; Höbaus, J.; Kállay, E. Vitamin D and the epigenome. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marik, R.; Fackler, M.; Gabrielson, E.; Zeiger, M.A.; Sukumar, S.; Stearns, V.; Umbricht, C.B. DNA methylation-related vitamin D receptor insensitivity in breast cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2010, 10, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habano, W.; Gamo, T.; Terashima, J.; Sugai, T.; Otsuka, K.; Wakabayashi, G.; Ozawa, S. Involvement of promoter methylation in the regulation of Pregnane X receptor in colon cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höbaus, J.; Fetahu, I.S.; Khorchide, M.; Manhardt, T.; Kallay, E. Epigenetic regulation of the 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 24-hydroxylase (CYP24A1) in colon cancer cells. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 136, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamshchikov, A.; Desai, N.; Blumberg, H.; Ziegler, T.; Tangpricha, V. Vitamin D for Treatment and Prevention of Infectious Diseases: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Endocr. Pract. 2009, 15, 438–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandel, N.; Husain, M.; Goel, H.; Salhan, D.; Lan, X.; Malhotra, A.; McGowan, J.; Singhal, P.C. VDR hypermethylation and HIV-induced T cell loss. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2013, 93, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novakovic, B.; Sibson, M.; Ng, H.K.; Manuelpillai, U.; Rakyan, V.; Down, T.; Beck, S.; Fournier, T.; Evain-Brion, D.; Dimitriadis, E.; et al. Placenta-specific methylation of the gitamin D 24-gydroxylase gene implications for feedback autoregulation of active vitamin d levels at the fetomaternal interface. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 14838–14848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorchide, M.; Lechner, D.; Cross, H.S. Epigenetic regulation of Vitamin D hydroxylase expression and activity in normal and malignant human prostate cells. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2005, 93, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, W.; Karpf, A.R.; Deeb, K.K.; Muindi, J.R.; Morrison, C.D.; Johnson, C.S.; Trump, D.L. Epigenetic Regulation of Vitamin D 24-Hydroxylase/CYP24A1 in Human Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 5953–5962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, C.S.; Chung, I.; Trump, D.L. Epigenetic silencing of CYP24 in the tumor microenvironment. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 121, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höbaus, J.; Hummel, D.M.; Thiem, U.; Fetahu, I.S.; Aggarwal, A.; Müllauer, L.; Heller, G.; Egger, G.; Mesteri, I.; Baumgartner-Parzer, S.; et al. Increased copy-number and not DNA hypomethylation causes overexpression of the candidate proto-oncogene CYP24A1 in colorectal cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 133, 1380–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]