Online reviews, also referred to as electronic word of mouth (eWOM) or user-generated content (UGC), are all similar concepts with minor differences. eWOM is all electronic communications between producers and consumers and between consumers themselves: emails, websites, consumer review sites, blogs, virtual communities, chat rooms, newsgroups, and instant messaging. UGC is data generated online by consumers, e.g., text (consumer reviews and blogs) and picture data.
- online reviews
- literature review
- VOSviewer
- Ucinet
- citation analysis
- thematic evolution
- bibliometric analysis
- co-word analysis
- conceptual structure
- science maps
Introduction
Tourism and hospitality relies very much on word of mouth among consumers [5]. Before the Internet, this word of mouth was usually obtained from friends and acquaintances, but has now moved to the Internet, with consumers overwhelmingly consulting the opinions of fellow consumers online [6,7]. Their decision-making and travel experience is shaped by the reviews they read, and this has been a significant development in the industry [8].
Consumers use online reviews at every stage of the travel process—pre-trip, during trip, and post-trip—to engage in information search, share experiences, and give feedback [5]. Companies use it for customer engagement, to build online presence, get consumers’ opinions, influence booking intentions, and earn revenue [9–11]. With its usefulness to both producers and consumers, it is no surprise that online reviews are a highly popular topic in tourism and hospitality for both researchers and managers [12].
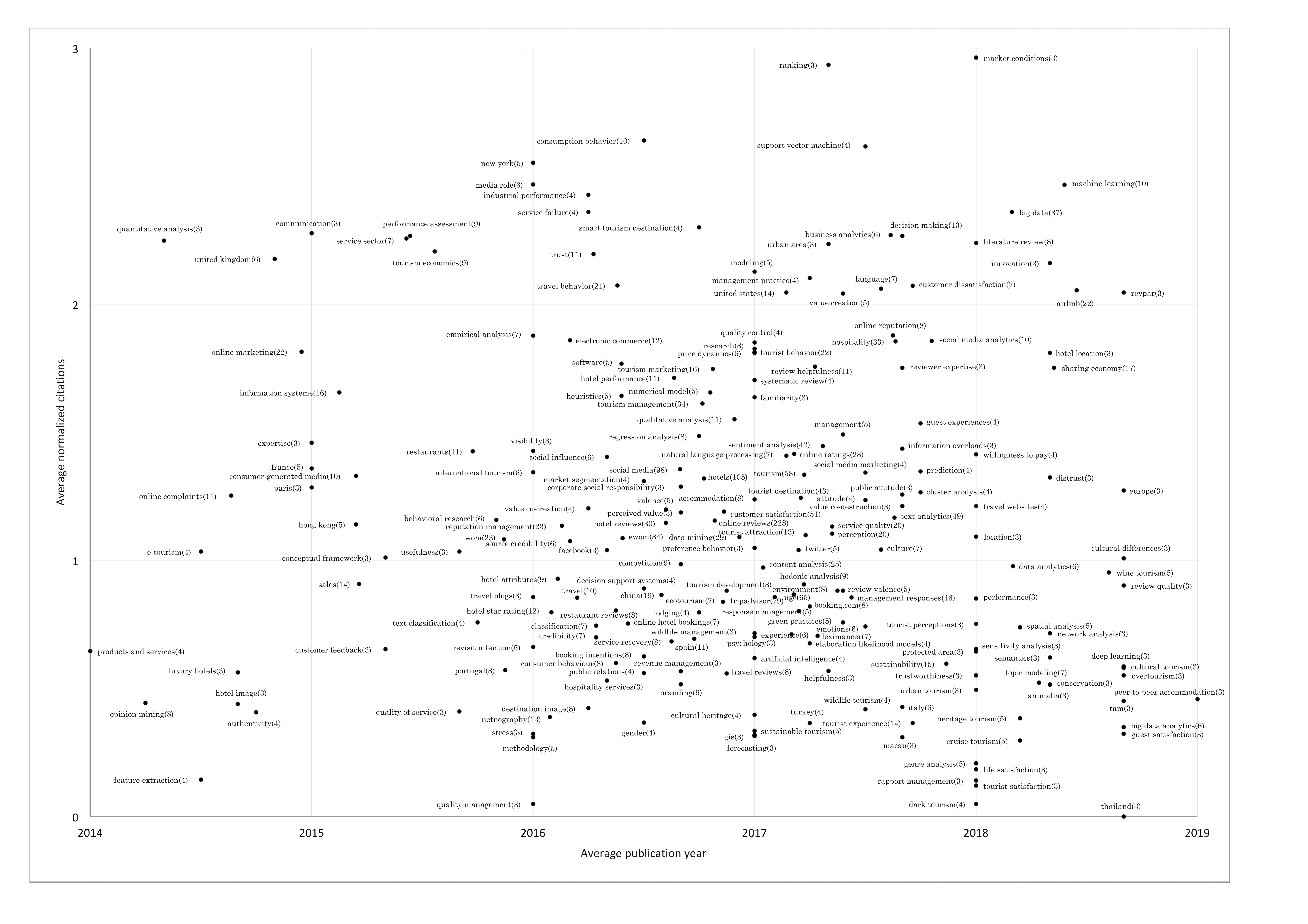
Evolution of Research Interests
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/su12239977