1. 基于SPA的复杂网络建模
集合对分析[
62](简称SPA)最早由中国学者赵克勤于1989年提出。它是一种新的数学分析方法,它使用连接度来处理模糊和不确定的信息。集合对分析与复杂网络集成的研究始于2011年。首先由张春英教授[
17]提出构建集合对社交网络分析模型,并进行了一系列研究。
1.1. 复杂网络集合对建模的理论基础
1.1.1. 集合对分析的基础
集合对是由具有一定关系的两个集合组成的基本单元;它是由这两组组成的对。集合对的现象普遍存在,系统中任何两个部分,如医生和病人或图像和方程,在一定条件下都可以形成集合对。
假设根据问题 W 的需要分析由集合 A 和集合 B 组成的集合对 H。总共得到集合对 H 的 N 个特征。其中,S是集合对H中的两个集合共有的,两个集合在P性质上是相反的,在其余的F = N-S-P性质中它们既不对立也不相同。然后,设定对连接度u
两组是:
在公式中,S N、FN 和 PN 缩写为 a、b 和 c.然后,连接度的公式表示为:
这里,i 是差分标记,它在区间 [−1, 1] 中取不同的值。当 i 的值在 [0, 1] 中时,不同的部分趋于相同,当它在 [−1, 0] 中时,不同的部分趋于相反。| 的值越大i|,则转换概率越大。j
仅充当标记。集合对需要处理的问题是任意两个集合之间的不确定性引起的差异,连接程度用于表示两个集合之间的关联程度。例如,在评价问题中,待评价样本的评价指标的测量值与评价指标的标准可以形成一对。然后,相同的度a表示测量值达到标准;差异度b表示测量值与指标标准相差一级;矛盾C表示实测值与指标标准之差大于一级[
63,
64]。
显然,在上面的定义下,b和c满足规范化条件,即它们满足关系表达式:
1.1.2. 设置复杂网络顶点之间的对相似性度量
节点相似度度量是学习复杂网络结构模型的重要研究点。传统的全局相似性度量需要考虑网络的整体结构关系。虽然精度高,但也伴随着高时空复杂度;局部相似性度量仅考虑最近邻顶点,时间复杂度相对较低,但低估了直连顶点之间和路径连接的顶点之间的相似度。将集合对分析理论应用于复杂网络中节点间关系的描述,不仅可以充分考虑整体结构信息对节点的影响,还可以有效降低时空复杂度。
顶点之间的相似性测量方法是复杂网络研究的一个重要方面。2013年,文献[
15,
65]提出了基于集合对理论和公共邻居的顶点之间的相似性度量,并将其应用于静态和动态α关系社区挖掘。[
15] 中的源给出了顶点之间连接度的定义。
在复杂网络中,任意两个节点 vk
和 v s 具有对象属性和关系属性,即 A(vk)={xk1,xk2,...,} 和 A(xkn1vs)={xs1,xs2,...、xsn2} 和 |A(vk)|=n1, |A(vs)|分别 =n2。两个节点的对象总共有 N=|A(vk)∪A(vs)|属性。因此,两个节点在一定时间的连接度可以表示为:
在这里,一个 ks(t)
是节点 v k 和 v s 在时间 t 处的相同程度,bks(t) 是节点 v 之间的差异程度时间 t 处的 k 和 v s,c k s(t) 是节点 vk 之间的对立程度和 VS
在时间 T.
因此,集合对连接度可用于描述复杂网络中两个节点的相似性。
顶点之间的相似性度量是网络结构研究中的一个重要问题。张春英[
15,
65]曾经定义过顶点之间的相似性度量。然而,这些定义只考虑了共同邻居数量对顶点间相似度的影响,而不考虑不同网络密度和顶点度对顶点间相似度的影响,因此不能更好地反映网络群落结构。因此,陈晓[
16]提出了一个新的度量,即加权聚类系数连接度WCCD,并将传统复杂网络中的顶点相似度表示为:
这里,(1)1×S 和 1×P 分别表示相同属性和(1)相反属性的行向量,向量值均为 1。(∗)1×F 表示不同属性的行向量。w(vi)G 表示相应顶点的权重。i(vi) 表示相应顶点的差值。
陈晓应用指数链接传统复杂网络的预测,通过实验证明了指标的有效性。
1.1.3. 复网络集对关系矩阵
集合对关系矩阵由集合对连接度组成。集合对关系矩阵可以确定集合对复杂网络中每个节点的关系连接程度。
表示节点 v k 和 vs 在时间 t 处的集合对关系矩阵,表示为:
With a constant change in time t, the nodes in the network may change with it, resulting in a constant change in the relationship matrix. When time t is not considered, the matrix is a static relationship matrix. By analyzing the relationship matrix at different times, the changing trend of the complex network can be obtained.
1.1.4. Set Pair Relationship Community Description
A complex network can be regarded as a dataset of individuals and relationships. Its nodes represent individuals to be studied, and edges represent possible relationships between individuals. Based on the theory of set pair analysis, the complex network can be regarded as a complex system of sameness, difference, and antithesis. The source in [
17] buildt a SPA-based set pair social network analysis model for the attribute graph of a social network, and the static and dynamic forms of the set pair social network analysis model are discussed [
18,
19]. Based on this model, the literature proposed a set pair complex network α-relationship community as well as static and dynamic mining algorithms [
15,
66].
The definition of the α-relationship community is given by the authors of [
15]:
According to different practical problems, a threshold α∈[0,1]
is set, and when the identity ak of the set pair connection degree of nodes in the network is greater than the threshold, the node is divided into the minimum community; when the uncertainty of a node is transformed into the same degree, that is, ak+bk>α
, the node is merged into the largest community. A community pair is thus formed, which is called an α-relational community.
At time t, the community pair composed of the α-minimum relationship community and the α-maximum relationship community is called the α-relationship community at time t, and the formula is expressed as:
1.2. SPA-Based Complex Network Modeling and Application
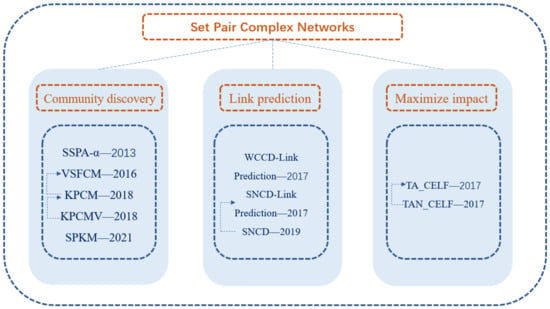
Modeling research on complex networks based on set pair analysis mainly includes research on community discovery, link prediction and influence maximization. Figure 1 lists the main algorithms in the three areas and their proposed time, and the dashed lines with arrows are used to indicate the update and improvement between the algorithms. For example, in the research of “Community discovery”, the algorithm KPCMV is proposed on the basis of the algorithm KPCM, which is an improvement to the algorithm.
Figure 1. Main algorithms of set pair complex networks and their relations.
1.2.1. Community Discovery
Community structure is a common feature in complex networks. A community consists of a group of similar interconnected nodes. Nodes within the same community are closely connected, whereas connections between different communities are sparse [
67]. Community discovery is the process of finding disjoint community structures that exist in the network.
In recent years, aiming at the uncertain information in community discovery, some scholars have used the set pair connection degree to measure the similarity between vertices in the community, and they proposed a series of new models and algorithms, which provide a new direction for complex network research.
The research on SPA-based complex network community discovery focuses on static community discovery, dynamic community discovery and overlapping community discovery.
- (1)
-
Static community discovery
The source in [
20] used the similarity, difference and inversion relationship in set pair analysis to propose a similarity measurement method between vertices based on the weighted clustering coefficient connection degree, and based on this method, a new similarity-based hierarchical clustering algorithm VSFCM was proposed. The similarity, difference and inverse relationship between vertices is weighted to achieve the purpose of distinguishing the contribution of paths between different vertices. On the basis of the existing set pair social network research, the unsigned network and the symbolic network were studied, respectively. For the symbolic network, a similarity measurement method between the vertices of the symbolic network based on the set pair connection degree was proposed, which can effectively describe the close relationship between the vertices in the symbolic network. The source in [
21] aimed at the problem of the premature merging of vertices in the initial aggregation stage of the independent community in the VSFCM algorithm, introduced the edge aggregation coefficient and similarity together as the community merging criteria and proposed an improved VSFCM algorithm, which effectively improved the accuracy of community merging at this stage. In order to alleviate the problem of excessive time complexity in the original algorithm, the k-shell decomposition method and set pair analysis are combined, the algorithm KPCM and algorithm KPCMV are proposed, and the algorithm is applied to community discovery.
The source in [
22] integrated set pair analysis into a complex network with uncertain information, used the set pair connection degree to describe the similarity, difference and reverse relationship between vertices and proposed a similarity measurement method between vertices with a weighted aggregation coefficient connection degree. Then, scholars re-characterized the similarity between network vertices with the set pair connection degree [
16] and proposed a new measure of similarity between vertices, WCCD, and weighted it. Aiming at problems such as the high complexity of the global index and the inaccurate estimation of the local index in the index of measuring the similarity between vertices in the symbolic network, a new measurement index SNCD was proposed, which effectively improves the accuracy of measuring the similarity between vertices and lays a good foundation for follow-up research.
The topic-attention model is a new complex network model that has been proposed in recent years. The vertices in the network are composed of entities and topics. Chen Xiao et al. [
16,
23] considered the social relationship and interest relationship together, constructed a topic-attention model, used the set pair connection degree to describe the similarity between the vertices of the model and set different weights according to different topics and users’ contributions to similarity. The community discovery problem of the topic-attention model is transformed into an agglomerative clustering problem based on the connection degree, and a corresponding algorithm is given. According to the characteristics of the topic-focused network, a new measure of similarity between vertices, TANCD, was proposed, and a topic community discovery algorithm based on TANCD was proposed, so as to achieve the purpose of accurately dividing topic-centered communities. In order to deal with large-scale topic-focused networks, the source in [
25] integrated deep-learning technology into natural language processing, used the set pair connection degree to describe the transition probability of vertices in the network and proposed a topic community discovery algorithm based on representation learning. Compared with previous community discovery algorithms, this algorithm takes into account the information of network structure and semantics, which is more comprehensive and has more practical application value.
To solve the problem of the soft clustering of incomplete datasets, the source in [
26] introduced set pair information granules into traditional clustering and constructed a three-way clustering algorithm, SPKM, based on set pair information granules. The author proposed a distance calculation method based on the set pair connection degree and then applied it to the CURE algorithm, proposing a set pair three-way hierarchical clustering algorithm, SPGCURE, and the set pair three-way clustering algorithm was then applied to community discovery in a complex network. Compared with other algorithms, this algorithm can handle both complete and incomplete datasets and can maintain good accuracy in both datasets.
- (2)
-
Dynamic community discovery
In [
17], in the process of exploring the relationship between individuals in a social network, it was found that the information in this process is uncertain, and the social network is constantly dynamically changing. Aiming at these problems, the author first applies set pair analysis to the social network, proposes a set pair analysis model of the social network and gives the relevant properties of the model.
In [
15], aiming at the existence of definite and uncertain relations in a Web social network, the concept of α-relationship community with a given threshold was proposed to be applied to a set pair social network, and a SPA-based dynamic α relationship community mining (DSPA-α) algorithm is given. Experiments prove that the α-relationship community is able to better reflect the dynamic changes of the community. Compared with previous algorithms, this algorithm fully considers the uncertainty of relations. It can figure out the largest relational community and the smallest relational community at the same time and obtain different ranges of communities by adjusting the threshold. The algorithm provides a new idea for further research on community dynamic mining.
- (3)
-
Overlapping community discovery
The modeling research into set pair analysis in complex networks has also been extended to the discovery of overlapping communities. In [
68], aiming at the problem of various types of vertices in the social Internet of Things, the author used the idea of set-pair information granule computing and clustering, and the set pair connection degree was used to analyze the similarities, differences and opposites of neighbor vertices. A set pair three-way overlapping Community Discovery Algorithm is proposed. In addition, considering the different connection strengths of vertices and edges and the degree of vertices, the aggregation strength of vertices is defined, and an improved k-means initial value selection algorithm is proposed. Each vertex has different set pair similarities for different communities, and the vertices are assigned into three-way community structures consisting of positive similitude, a border domain and a negative domain.
1.2.2. Link Prediction
Link prediction refers to predicting the possibility of a connection between two nodes that are not connected temporarily in the network by analyzing the known node information in the network and the network structure. This prediction includes predictions for both unknown links and future links [
27].
There are few studies on fusion set pair analysis for link prediction in a complex network. Only the source in [
16] defines the similarity metrics WCCD and SNCD between vertices for the link prediction problem in a traditional social network and a symbolic network, respectively. In view of the idea of connection degree, a WCCD-Link Prediction algorithm and an SNCD-Link Prediction algorithm were put forward. Experiments showed that the two algorithms can effectively reduce the time complexity and have high accuracy for their corresponding network, which provides a new direction for future research on link prediction problems.
For the deterministic and uncertain information in the symbolic network, considering the local and global characteristics comprehensively, combined with set pair analysis theory, the symbolic network is regarded as a kind of system of sameness, difference and antithesis. For the link prediction problem, a new method is proposed. This method improves the accuracy of predicting positive and negative edges at the same time and has certain stability in networks of different sizes and densities [
28].
1.2.3. Maximizing Impact
One of the main tasks of influence maximization research is to think about how to select a set of “seed” vertices with a certain strategy in a complex network and use it as the initial disseminator of information in the network. These “seed” vertices are capable of cascading effects throughout the network to maximize the spread of information [
69]. Traditional influence maximization algorithms are mainly based on greedy strategy [
70], and heuristic algorithms are based on central strategy [
71]. The algorithm based on the greedy strategy has high time complexity, and the effect is not good when dealing with a large-scale complex network. Meanwhile, the heuristic algorithm based on the centrality strategy has its own limitations, resulting in a low solution quality of the algorithm.
The source in [
16] used the path relationship and the Markov model to describe the object’s preference for the topic, considering the scope of the topic’s influence. The object’s preference for topic
tkis determined, the topic’s influence within the scope is described, and the influence maximization algorithm is implemented to discover the user group with the greatest influence in a certain topic. In addition, Chen Xiao used the set pair connection degree and random walk model to describe the user’s preference for topics according to the characteristics of a topic-attention network and proposed a topic-based influence maximization algorithm [
24]. This is the first attempt toward achieving impact maximization research in the topic-attention network and has achieved good results.
1.2.4. Other Problems
In addition to community discovery, link prediction and influence maximization studies, set pair social networks are also applied in the study of some other problems [
72,
73].
In the literature [
73], Zhao Guanghua combined the concept of sameness, difference and antithesis in set pair analysis theory with information entropy, which describes the degree of information confusion. For the uncertainty problem in text sentiment analysis, he proposed the set pair information entropy SP-IE algorithm. Guanghua divided text sentiment into five categories by analyzing the difference coefficient
iand calculated the set pair information entropy to judge the polarity and intensity of tendentious texts. The research on this topic can be extended to many fields, such as psychological counseling, public opinion analysis, etc. and has great research potential.
Since the complex network was proposed, it has received extensive attention from scholars. As a new research method proposed in recent years, the complex network has been continuously developed, and its modeling research and application fields need to be further expanded.
2. Complex Network Modeling Based on RS
Using the upper and lower approximations of rough sets to describe the uncertainty of graphs, the source in [
74] proposed the concept of rough graphs for the first time, but rough graphs were not extended to an actual complex network. The sources in [
65,
75] introduced rough set theory into the attribute graph model and analyzed its rough characteristics, concluding that the finer the edge set division degree of the rough attribute graph, the higher the accuracy of the obtained graph. For a complex network with incomplete information, the source in [
29] proposed the concept of a rough complex network and offered static geometric characteristics, which provides a theoretical basis for future research on uncertain complex networks.
2.1. Basics of RS Modeling Complex Network
2.1.1. Basic Theory of RS
In the early 1980s, Pawlak [
76] proposed the concept of a rough set for G. Frege’s boundary line area thought. Those individuals that cannot be identified belong to the boundary area, and this boundary area is defined as the difference set between the upper approximation set and the lower approximation set. Here, according to the existing knowledge R, the lower approximate set is defined as the set composed of objects that must belong to the set
Xin the domain of discourse U, that is:
The upper approximate set is defined as the set of objects that must belong to and may belong to the set X in the universe U, that is:
Here, [x]R indicates the equivalence class containing the element x under the equivalence relation R.
One of the main advantages of rough set theory is that it does not require any preliminary or additional data information.
2.1.2. RS Complex Network
Rough complex networks [
35] are composed of rough vertex complex networks and rough edge complex networks:
Rough vertex complex network RCNV: In the complex network, for vertex set UV, there are XV and RV, where XV is a subset of vertex set UV, and RV is an equivalence relation of UV. When XV is the rough set of RV, the vertex set of the complex network is said to have rough characteristics, and the complex network is called the rough vertex complex network RCNV;
Rough edge complex network RCNE: In the complex network, for edge set UE, there are XE and RE, where XE is a subset of the edge set UE, and RE is an equivalence relationship of the UE. When XE is the rough set of RE, it is said that the edge set of the complex network has rough characteristics, and the complex network is the rough edge complex network RCNE;
Rough vertex complex network RCNV and rough edge complex network RCNE are collectively referred to as rough complex networks.
2.1.3. Rough Complex Network Accuracy Metrics
As in rough sets, the uncertainty and incompleteness of information in complex networks is caused by the existence of boundary domains of vertex sets and edge sets. The larger the boundary domain, the lower the accuracy. In order to express this more accurately, the concepts of precision and roughness of rough complex networks are introduced:
Let the ratio of the measure of the lower approximate complex network CN¯¯¯¯¯¯V(R−−(XV),E) (or CN¯¯¯¯¯¯E(R−−(XE))) of the rough complex network RCNV (or RCNE) to the measure of the upper approximate complex network ¯) be the precision of the rough vertex (or edge) complex network, denoted as:
The accuracy of the rough complex network RCN is the product of the precision of the rough vertex complex network RCNV and the rough edge complex network RCNE precision, namely:
That is called:
This is the roughness of the rough complex network.
2.1.4. Coarse Clustering Coefficients for Rough Complex Network
The clustering coefficient measures the degree of interconnection between a vertex and its neighbors in a network. It can be divided into the overall clustering coefficient and the local clustering coefficient.
Here, ki is the number of edges connected to the vertex Vi, ki(ki−1)2 is the maximum number of edges that may exist between the ki vertices, and Mi is the actual number of edges between the ki
vertices.
The source in [
35] gives a definition of the coarse clustering coefficient:
In the rough complex network, assuming that the clustering coefficient of the lower approximate complex network is C−−, and the clustering coefficient of the upper approximate complex network is C¯¯¯, then it is called:
This is the coarse clustering coefficient of the rough complex network.
2.2. Rough Set Modeling Method for Complex Networks
The research on rough complex networks mainly focuses on the discussion of rough decision-making problems and overlapping community discovery problems. This section will mainly review the literature on these two aspects.
2.2.1. Rough Decision-making Model
As a mathematical research method to characterize incomplete information and uncertainty, rough set theory has applications in many fields.
Decision science is an ancient and emerging discipline, which was born in the 1920s and 1930s and developed rapidly after the 1950s. The source in [
31] proposed a decision analysis model based on an extended rough set based on a rough set, obtained the rough approximate relationship of decision-making classes under the new feature relationship, and gave classification decision rules. However, scholars have not used rough sets to solve decision-making problems on complex networks. Since then, some scholars have started research on rough and complex network modeling.
- (1)
-
Rough path and defensive decision making
Cyber defense decisions receive a lot of attention. The source in [
30] comprehensively considers network-based remote attacks and host-based local attacks, establishes a construction method that can clearly describe network attack models, defines rough attack paths on the top-level network and then proposes a rough path generation algorithm. On this basis, the ant colony algorithm is used to further mine k key vulnerable paths to the attack target. These vulnerable paths have the highest attack efficiency and are most likely to be taken by the attacker. Finally, by comprehensively considering the rough path and the precise path, an evaluation method for the risk of each vertex and the vulnerability threat is proposed. The construction of this model provides an important basis for network defense decision making.
- (2)
-
Rough and complex network decision-making method
The literature [
29,
35] combined the rough set and complex network, proposing the concept of a rough complex network, and the positive domain, negative domain and boundary domain of the rough complex network are given. The source in [
32] established a rough and complex third-party payment network for practical problems. The research found that the average distance interval of the network is too large, and the rough clustering coefficient is too small, indicating that the network does not have the characteristics of a small-world network, and the network structure is relatively scattered. In addition, scholars have also constructed a scale-free benefit risk assessment model [
36] to assess risk levels. Combining this with the thought of game theory, the author conducted a game analysis on the risk of the rough network operation of a third-party payment.
The literature [
33,
34] has analyzed the risk problems in the network, discussing the various possibilities for the actual situation of third-party payment risk evaluation and management under Internet finance and establishing a relatively complete risk evaluation system. Then, by defining the network basis of the rough and complex network, a decision-making method for the rough and complex network is given, and it is used to solve the operational risk decision analysis of the rough and complex network for third-party payment. By establishing a two-tier risk decision-making model, quantitative decision-making analysis results are given.
2.2.2. Community Discovery
Community discovery is a significant research direction in complex networks. Many scholars have researched and modeled the problem of community discovery from many different angles and applied it to real networks. However, the research in this field still has plenty of deficiencies. For example, the research on the problem of community discovery in uncertain complex networks still needs to be deepened, the accuracy and efficiency of overlapping community discovery algorithms still need to be improved [
77], etc. Community discovery includes overlapping community discovery and non-overlapping community discovery.
- (1)
-
Non-overlapping community discovery
In the 1990s, Yao proposed a Rough Set–Decision Rough Set based on the probability inclusion relationship [
78]. The three-way decision theory connects the positive domain, negative domain and boundary domain in the rough set to the acceptance, rejection and delay decision rules in decision making [
79]. Later, some scholars applied three-way decision-making theory to the community discovery problem. The source in [
37] divides the affiliation relationship between communities into three types: complete belonging, not completely belonging and incomplete belonging, and then the three-way decision-making idea is used to propose a community discovery algorithm.
The literature [
38,
39] introduced the three-way decision idea into granular community division. Scholars divide the overlapping communities in the granulation process in three ways to obtain non-overlapping communities. The source in [
40] aimed at the problem of community merging in the process of hierarchical clustering and proposed a community discovery method based on variable granularity hierarchical clustering. Aiming at the division of boundary domain vertices, a community discovery method based on random walk boundary domain processing is proposed, which effectively divides overlapping communities into non-overlapping communities.
The source in [
41] constructs a network community structure discovery model based on rough set theory for the problem of network community structure discovery. This method uses information centrality to measure the relationship between vertices and uses the concept of upper and lower approximations in a rough set to divide community boundaries. The ideal community structure is then determined by modularity. The number of communities finally obtained by the algorithm does not need to be given manually but is automatically given by the algorithm. The algorithm introduces rough set theory into community division. It has higher accuracy than general algorithms in dealing with boundaries, and the algorithm can realize community structure discovery without knowing the number of communities and the number of vertices in the community.
Since Pawlak put forward the idea of “knowledge is classification” and established a granular computing model based on rough set theory in 1982, rough sets have been widely used in various fields, such as machine learning and data mining. The source in [
42] constructed a community mining algorithm based on granular computing of a rough set model. The article defines the granularity in the network structure and discusses the method of granularity conversion. The core of the algorithm is to construct the granularity criterion of the network structure based on the granular computing model based on rough set theory, to generate the network granularity space under the criterion and to convert the problem of community mining into the problem of granularity transformation in different granularity spaces. The algorithm achieves the purpose of community mining through layer-by-layer abstraction with granularity ranging from fine to coarse.
Samrat Gupta [
46] proposed a new algorithm based on rough set theory considering the complexity in a real-world network. The algorithm detects disjointed, overlapping and hierarchically nested communities in a network by constructing the granularity of neighborhood vertices and representing them as a rough set. A new metric based on relative connectivity is also introduced, which is used as a measure of merged ensembles. The method has a good competitive advantage for the community detection problem.
The source in [
48] combined rough set theory with a complex network, gave a definition of the rough network and proposed a new quality measurement method for exploratory analysis of the community structure in a single network and in multiple networks. The network is able to evaluate detected communities without the need for reference structures. Furthermore, the proposed new method for evolutionary estimation and discovery of interactions among communities enables experts to gain a deep understanding of real systems. Applying rough network theory to community detection analysis shows that the algorithm has huge potential.
- (2)
-
Overlapping community discovery
The source in [
43] proposed an overlapping community discovery algorithm, OCDRD, based on rough set theory and density peaks. The algorithm combines the idea of a density peak with a rough set, and it can automatically determine the number of communities, avoiding the subjective influence of humans. This method uses the idea of a rough set to divide the uncertainty area of the community, so as to excavate overlapping vertices in the uncertainty area and obtain a community structure with a better division effect. Later, scholars [
44,
45] proposed an overlapping community discovery algorithm, OCDRDD, based on rough set theory and distance dynamic models. This method considers that the distance between vertices in the network changes with time. This method takes into account the fact that the distance between vertices in the network is constantly changing over time. According to the network topology, K initial core vertices are determined in combination with the degree centrality, the approximate set and boundary domain of the community are initialized, and the optimal overlapping community structure division is obtained through iterative adjustment of the distance dynamic model.
2.2.3. Other Problems
The biological transmission network is one of the common complex networks. The source in [
80] applied a rough complex network to the problem of malaria parasite transmission. Using a complex network as the underlying model for the spread of Plasmodium parasites in the Phytophthora machine, the vertices in the network are interpreted as the set of origin points for Plasmodium, the set of attractants and the set of repellents. A variable precision rough set model-based measurement method is defined to quantitatively evaluate the cohesion of Plasmodium connections between different regions of interest.
In order to solve the problem that compound faults are difficult to identify in the fault diagnosis of diesel generator sets, scholars [
81] proposed a fault diagnosis method based on a neighborhood rough set. The method uses the variational mode decomposition method to decompose the collected acoustic signal and forms an initial feature set, and then the optimized neighborhood rough set is used for feature screening, and the community structure in the complex network is used to establish a fault diagnosis network. The model uses the community distinguishing criterion function to figure out the community structure and achieve the purpose of fault diagnosis and classification.
The source in [
82] transformed the multi-granularity rough set attribute reduction problem into a discrete multi-objective optimization problem. The study uses the idea of swarm intelligence as a framework and realizes the precision of attribute reduction by designing a population topology structure with excellent individual information interaction functions and genetic operators that maintain good population diversity. The population topological space has a complex network topology structure, and the spatial structure of the complex network is used to represent the interactional relationship between individuals in the population. The network structure with specific information dissemination performance can improve the transmission efficiency of excellent individuals. The attribute appointment optimization algorithm can obtain more comprehensive and higher-quality reduction results, and it has better feasibility and practical significance.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/math11051212