Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is an old version of this entry, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Subjects:
Engineering, Manufacturing
The potential of the metaverse as a tool to connect people has been increasingly recognized. The opportunities offered by the metaverse seem enormous in many sectors and fields of application. The metaverse presents a promising opportunity for educational innovation, particularly in fields that require hands on experience and practical training.
- metaverse
- education
- virtual reality
1. Introduction
1.1. The Historical Origins of the Metaverse
The origins of the metaverse go back to Neal Stephenson, who in his novel published in 1992 [1], described the metaverse as a sort of shared virtual reality [2]. The term “metaverse” is formed by the prefix meta, which means “with, behind, beyond, after”, and the noun (uni)verse [3]. The notion of the metaverse has existed for decades [4]. However, only after thirty years does the term “metaverse” begin to have more defined contours. In fact, in 2021 Mark Zuckerberg, with the transition from Facebook to Meta, brought the term and the concept of “metaverse” back to the center of public discussion [5]. From a technological point of view, interest in the metaverse has been accelerated by the recent advancements in virtual and augmented reality technologies [6]. The metaverse is a digital universe resulting from multiple technological elements including video, virtual reality, and augmented reality [7]. In the metaverse, users access using 3D viewers and live virtual experiences. Users can create realistic avatars, meet other users, create virtual objects or properties, go to concerts, conferences, travel, and more [8]. There are several platforms to access the metaverse [9] (i.e., Second Life, Decentraland, Sandbox, Stageverse, etc.) [10]. Recent advances in virtual reality technology have made it more feasible to create the metaverse. Leading tech companies, including Facebook, Google, and Microsoft, have invested heavily in developing virtual reality and augmented reality technologies [11]. At present, the metaverse is considered to be a promising area for online technology, with capability to revolutionize interactions, education, employment, and recreation [12]. It is an all-encompassing, interactive, and collaborative environment that combines the features of augmented reality, virtual reality, and the Internet [13]. Figure 1 shows the evolution that led to the birth of the metaverse.
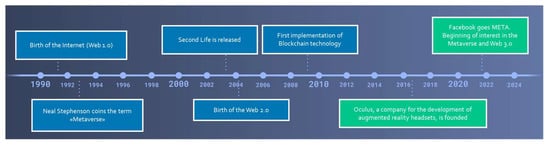
Figure 1. Evolution of the metaverse.
1.2. Technologies behind the Metaverse
Metaverse technologies are the essential tools utilized in constructing and managing virtual worlds. These encompass virtual reality (VR)/augmented reality (AR), blockchain, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence (AI) [14]. With these technologies, users can interact and experience virtual environments, generate digital assets, operate virtual worlds, and augment user experiences through intelligent, tactile feedback and motion tracking [15]. For example, virtual reality (VR) provides an immersive experience by simulating a complete digital environment, while augmented reality (AR) blends digital elements with the real world [16]. In addition, blockchain technology can secure and make transactions within the metaverse transparent. Cloud computing enables users to access metaverse experiences from anywhere with internet connectivity [17], and artificial intelligence (AI) can help to create more realistic and responsive virtual environments [18]. The metaverse is still under development; however, many companies are already exploring its potential. Big companies such as Microsoft, Nvidia, and Meta are making efforts in this direction, and with the technological advancement [19]. The continuous evolution of these technologies is critical as the metaverse continues to advance and expand [20]. As shown in Figure 2, the trend of “interest over time” is increasing. The development of the metaverse is connected with them. It is expected that the metaverse will use augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR) in combination with artificial intelligence and blockchain to create scalable and accurate virtual worlds.
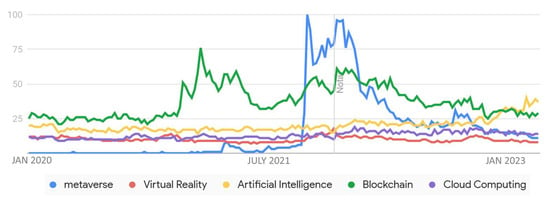
Figure 2. Trend of technologies related to the metaverse (source Google Trends—April 2023).
1.3. Exploring the Potential of the Metaverse
The metaverse has already become widely used in various technological fields. For example, it is being used in medicine to simulate surgical procedures and provide training for medical professionals [21]. Through artificial intelligence (AI), it is possible to improve medical diagnoses by connecting medical teams worldwide [22]. It is predicted that thanks to artificial intelligence, healthcare facilities will be able to quickly find timely and accurate information for the health of patients. It will be possible to make the most of resources, increasing efficiency and improving the flow performance of clinical and operational work. In finance, it is being used for virtual conferences and meetings, and even for conducting virtual trade shows and exhibitions. The metaverse has the potential to generate novel economic prospects by offering a platform for virtual commerce, advertising, and business transactions. Additionally, it could spawn new job openings in domains such as virtual reality development and design, contributing to the growth of the digital economy [23]. The metaverse holds promise in revolutionizing the work environment by providing new opportunities for remote teamwork, virtual conferencing, and skill development.
2. Role of Metaverse in Education
2.1. Red Cluster “Knowledge”
The Red Cluster is associated with a high importance score. The red cluster contains keywords related to the concepts: artificial intelligence, augmented reality, knowledge, pandemic/COVID-19. Traditionally, learning takes place in a physical classroom setting, whereas with metaverse technology, learning activities are conducted within a 3D virtual world [40]. As discussed by several authors, leveraging metaverse technology for learning has the potential to transform the way people acquire and process information [41]. This allows them to adapt and refine their knowledge as needed [42]. The analysis of the documents has highlighted that the need to imagine different ways and worlds to socialize [43], to study, and to work emerged essentially in the period of the pandemic/COVID-19 [44,45]. In fact, due to this catastrophe, companies have begun to understand the need to develop new technologies (i.e., the metaverse) [46,47]. In this way, new knowledge and skills can be developed [48]. Innovation makes it possible to implement effective and efficient processes to support the process of changing society worldwide [49]. Thanks to artificial intelligence in the metaverse, it will be possible to create increasingly similar users with a realistic appearance [50]. It will allow them to interact with others and share experiences and knowledge [51]. Furthermore, for the metaverse, as in other fields, artificial intelligence makes it possible to automate software development processes, reducing the time to create new applications and solutions in the metaverse [52]. Therefore, after years in which cloud computing, virtual reality, and artificial intelligence have dominated media interest and attention from organizations, a new trend is now making its way to innovate how people and companies will work, communicate, and have fun [53].
The studies analyzed highlight that realizing the metaverse as the next immersive internet requires overcoming several unprecedented technological challenges [54]. The metaverse has the potential to transform education by creating immersive, interactive, and collaborative learning environments that can enhance employee/student engagement and facilitate active learning [55]. In the era of Industry 4.0 and virtual reality, the industrial metaverse takes shape [56]. Enabled by artificial intelligence, it promotes digital twin technology to help decision-makers make timely informed decisions [57]. However, the success of the metaverse will greatly depend on the integration of technologies and the data that are transmitted by sensors installed in the real world [58]. Figure 11 shows an example of training through the metaverse.

Figure 11. Metaverse experience integrated with a digital twin (elaboration by the authors).
In the experience, a photo-realistic digital twin is integrated into the industrial metaverse, offering a potential to transform a real supply chain into a virtual world in which people can interact and collaborate. A svupply chain of a manufacturing company is simulated.
2.2. Green Cluster “Technologies”
The Green Cluster is characterized by a medium importance score. The keywords are: blockchain, deep learning, digital twins, extended reality, I4.0, IoT, and machine learning. As highlighted by several authors, from a technological point of view, there are several technologies that today contribute to the creation of metaverses [59,60]. These technologies include virtual reality, mixed reality, artificial intelligence, blockchain, and finally the internet infrastructure and device processors [61,62]. In this regard, it emerges that the various industrial sectors have long been looking for new ways to increase productivity, efficiency, and resilience [63,64]. Thus, digitization has become one of the main methods to achieve this goal [65,66]. COVID-19 has required and enabled companies to accelerate their digital transformation journey, opening up multiple opportunities that many did not think possible before [67]. As a result, the need for digital skills of the future will become ever more critical [68]. Emerging technologies that enable Web3, the cloud, and perhaps one of the greatest ICT innovations of all, the metaverse, will be essential [69,70]. A lot of research shows that the biggest and most impactful opportunities will come from other forms of this virtual and augmented environment, such as the industrial and corporate metaverse [71]. These applications will allow organizations to blur the lines between physical and digital environments and to reshape the world, defined as “digital twins” [72]. In practice, it means that projects can be built virtually before being replicated in the real world [73]. For example, using augmented reality and virtual reality (AR/VR), factory employees will be able to design and test equipment before implementing it in a real production line, thereby limiting risk and more accurately predicting production volumes [74]. Figure 12 shows an example of training through the metaverse for interactive learning using VR and AR.

Figure 12. Industrial metaverse for interactive learning (elaboration by the authors).
2.3. Blue Cluster “Platform”
The Blue Cluster contains keywords related to the concepts: avatar, e-learning, education, training, platforms, virtual worlds, and virtual learning environment. Analysis of the documents highlights that the metaverse is seen as the next big evolution in online interaction, moving from today’s text-based websites and often closed ecosystems to shared, interconnected spaces where users interact via avatars [75,76]. However, many authors point out that today the technology of the metaverse is only in its infancy [77,78]. Despite the existence of various virtual worlds, many of them are still in fact far from becoming truly interconnected with each other [79,80]. However, studies show that there is no doubt about its potential. The metaverse at the moment is like the internet of the 1990s; it needs several leaps of development before it gains widespread use [81]. The metaverse represents a new means of communication [82]. It radically evolves social interactions between users, overcoming the limits of 2D technology, and therefore offers the possibility of relating in an innovative and immersive way, as pointed out by several authors [83]. It is reasonable to think that the metaverse is not only a virtual universe, but also an innovative means of communication [84]. Probably it is the most inclusive space currently existing, both online and offline [85]. This undoubtedly represents a strong point of the metaverse, which characterizes it and distinguishes it from all the rest, fully demonstrating its innovative character that everyone is talking about [86,87].
2.4. Yellow Cluster “Academic”
The Yellow Cluster contains keywords related to the concepts: human experiment, university, sustainability, teaching, internet, and student. From this point of view, many authors agree in stating that the metaverse and training is a winning combination because AR, VR, and MR experiences increase student involvement, promoting memory and understanding [88,89]. Associating the words metaverse and formation may seem precocious [90]. However, the academic and training world is witnessing an unstoppable evolution. In fact, on the one hand, traditional teaching methods make it possible to achieve the desired learning objectives [91]. On the other hand, however, the younger generations (digital natives) require the adoption of tools and methodologies beyond the traditional frontal lesson [92]. Therefore, from the analysis it emerges that especially in academies (places of excellence of knowledge) it is worth exploring what technology offers today for education, because Web3, even more than Web2, presents great opportunities for those who want to learn [93,94]. In fact, students can follow the lesson wherever they are, but without losing the perception of being in the place assigned to learning [95]. The metaverse makes travel not only in space, but also in time. This means that the study of history can take place by visiting the still intact ancient Rome, or that of astronomy by traveling to the moon, and so on [96]. Many authors point out that, for example, another typical activity of the metaverse and training (above all corporate) is the simulation of risky or difficult actions to try firsthand in reality [97]—an activity from which technical-scientific professions can especially benefit, making up for the possible scarcity of physical means with digital technology and avoiding the risk of accidents [98,99]. In addition, it should be noted that virtual worlds can also support intellectual learning (for example, languages can be learned by dialoguing and interacting with chatbot avatars, guided by artificial intelligence) [100,101]. Finally, the metaverse can support the implementation of teamwork activities in the classroom or in the company. In fact, students in the virtual space can work more easily on a common project by sharing a desktop without limitations [102,103].
2.5. Purple Cluster “Ecosystems”
The Purple Cluster is associated with the following keywords: ecosystems, learning systems, and technology acceptance. From this point of view, most of the authors agree in stating that the world is heading towards a “great reversal” [104,105,106]. It means a new ecosystem composed of 5G and related key technologies such as edge cloud infrastructure, software, augmented intelligence/machine learning, advanced sensors, and robotics [107,108,109,110]. Thanks to the combination of these capabilities the technologies operating in the physical and digital industries will find the necessary solutions to address the much-needed digital transformation in the next ten years [111,112]. In other words, the metaverse is a complex ecosystem made up of different tools and digital tools [113,114,115,116,117,118]. The digital transition in the health system is revolutionizing medicine. For example, many researchers predict that it will be possible to amplify the curative efficacy of rehabilitation treatments (both at home and post-operative in specialized centers) [119,120,121,122]. Without doubt, many researchers believe that metaverse-related opportunities will grow as long as they are balanced by long-term plans to support economic needs and social and environmental transformations [123,124,125,126].
3. Conclusions
The metaverse is a concept that has been in development for several years. The metaverse presents a promising opportunity for educational innovation, particularly in fields that require hands on experience and practical training. In fact, the economy of the metaverse is predicted to reach over $824 billion by 2030. Organizations investing in this technology now are the ones that will win the innovation race. However, the metaverse can only reach its full potential if organizations themselves work together to create an open, safe, environmentally sustainable, and all-encompassing environment that encourages innovation and translates into value for all involved. This will require huge technological investments and adaptations, sophisticated content creation tools, and large servers to maintain system stability and create a truly immersive experience.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/app13095682
This entry is offline, you can click here to edit this entry!
