Solid–lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers are delivery systems for the delivery of drugs and other bioactives used in diagnosis, therapy, and treatment procedures. These nanocarriers may enhance the solubility and permeability of drugs, increase their bioavailability, and extend the residence time in the body, combining low toxicity with a targeted delivery. Nanostructured lipid carriers are the second generation of lipid nanoparticles differing from solid lipid nanoparticles in their composition matrix. The use of a liquid lipid together with a solid lipid in nanostructured lipid carrier allows it to load a higher amount of drug, enhance drug release properties, and increase its stability. Therefore, a direct comparison between solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers is needed.
- lipid nanoparticle
- NLC
- nanocarrier
- nanoparticle characterization
1. Introduction
2. Structural Features of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers

| Compound | Classification | Source | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1-Tetradecanol (myristyl alcohol) | Straight chain saturated fatty alcohol | Myristica fragrans | Solid lipid |
| Beeswax | Wax ester | Honey bees (Apis mellifera) | Solid lipid |
| Caprylic/capric triglyceride | Triglyceride | Coconut oil | Liquid lipid |
| Castor oil | Fatty acid composed | Castor beans | Liquid lipid |
| Cetyl palmitate | Wax ester | Stony corals, Psidium guajava | Solid lipid |
| Cholesteryl myristate | Cholesterol ester | Trachyrhamphus serratus | Solid lipid |
| Cholesterol | Modified steroid | Animal, vegetable fat | Solid lipid |
| Compritol® 888 ATO | Mixture of mono-, di- and triglycerides of behenic acid (C22) | - | Surfactant |
| 1,2-dioleoyl-3-dimethylammonium propane (DODAP) | Ionizable cationic lipid | - | Solid lipid |
| Dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC) | Phospholipid | Pulmonary surfactant | Solid lipid |
| 1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine (DSPE) | Amine phospholipid | Escherichia coli | Solid lipid |
| Gelucire® 50/13 | Mixture of fatty acids (C16 and C18), esters of glycerol, PEG esters and free PEG | - | Surfactant |
| Glyceryl monostearate | Glycerol ester of a saturated fatty acid | Aristolochia cucurbitifolia, Lobelia longisepala | Surfactant |
| Labrafac™ CC | Mixture of medium chain triglycerides, mainly from caprylic (C8) and capric (C10) acids | - | Liquid lipid |
| Lecithin | Mixture of phospholipids in oil | Soybean, egg | Surfactant |
| Miglyol® 812 N | Glycerol triester of caprylic and capric acid (triglyceride esters) | Coconut, palm kernel oil | Liquid lipid |
| Myristylmyristate | Tetradecanoate ester | Coconut, palm kernel oil | Solid lipid |
| Oleic acid | Middle chain triglyceride | Olive oil | Liquid lipid |
| Palmitic acid | Saturated fatty acid | Palm oil | Solid lipid |
| Phosphatidylcholine | Phospholipid | Soybeans, eggs | Solid lipid |
| Poloxamer 407/Pluronic® F-127 | Triblock copolymer | - | Surfactant |
| Precirol® ATO-5 | Mixtures of diesters of glycerin and stearic acid | - | Solid lipid |
| Polyvinylalcohol (PVA) | Synthetic polymer of vinyl alcohol | - | Surfactant |
| Sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS) | Ethoxylated lauryl alcohol | Coconut, palm kernel oil | Surfactant |
| Squalene | Triterpenoid | Olive, wheat germ, and rice bran oils | Liquid lipid |
| Steric acid | Saturated fatty acid | Animal, vegetable fat | Solid lipid |
| Tricaprin | Triglyceride | Milkfat, palm kernel oil, and coconut oil | Solid lipid |
| Tripalmitin | Triglyceride | Lysiphlebia japonica, Tagetes erecta | Solid lipid |
| Tristearin | Triglyceride | Lysiphlebia japonica, Sciadopitys verticillata | Solid lipid |
| Tween® | Mixture of sorbitol, ethylene oxide, and oleic acid | - | Surfactant |
2.1. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles

| Solid–Lipid | Surfactant | Drug | Production Method | Therapeutic Purpose | Delivery Route | Characteristics | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gelucire® 50/13 | Tween® 85 | Grapeseed-derived proanthocyanidins | Melt Emulsification Technique | Chronic Respiratory Diseases | Spray Instillation | Size: 243 ± 24 nm PdI: 0.41 Zeta: −14.5 ± 1.0 mV EE: NA |
[33] |
| Palmitic Acid/Cholesteryl Myristate (68,5/31,5%) (w/w) | Sodium Lauryl Sulfate (SLS) | Rifampicin | Melt Emulsification Technique | Tuberculosis | NA | Size: 400 ± 20 nm PdI: 0.43 ± 0.09 Zeta: −35.3 ± 0.29 mV EE: 56.48% (w/w) |
[34] |
| Compritol 888 ATO, cholesterol, and Tf-PEG-OA | 1% Polyvinylalcohol (PVA) | Paclitaxel (PTX) | Solvent Evaporation Method | Leukemia | NA | Size: 176 nm PdI: NA Zeta: −22.5 ± 1.56 mV EE: 92.5 ± 1.35% |
[35] |
| Tripalmitin/Hydrogenated soybean phosphatidylcholine (HSPC) (80/20%) (w/w) | Polyethylene glycol monostearate (PGM) | Apomorphine | NA | Parkinson’s Disease | Oral | Size: 63.20 ± 0.98 nm PdI: 0.31 ± 0.02 Zeta: 7.3 ± 0.25 mV EE: NA |
[36] |
| Compritol® 888 ATO | Tween® 80 | Quercetin | NA | Alzheimer’s Disease | Oral | Size: 0.42 to 4.62 µm PdI: NA Zeta: −23.6 to −5.13 mV EE: 85.7% |
[37] |
| Beeswax | Tween® 80 Poloxamer 407 |
NA | Hot melt microemulsion | Skin Hydration | Topical | Size: 95.72 ± 9.63 nm PdI: 0.323 ± 0.03 Zeta: −9.85 ± 0.57 mV EE: NA |
[38] |
| Stearic Acid | Poloxamer 407 Soybean Phosphatidylcholine |
Resveratrol | Sonication | Anti-tumoral | Topical | Size:155.50 ± 0.26 nm PdI: 0.140 ± 0.02 Zeta: −2.60 ± 1.27 mV EE: NA |
[39] |
| Poly Lactic-co-Glycolic Acid (PLGA) | 1% polyoxyethylenepolyoxypropylene | Apigenin | Nanoprecipitation | Cosmetic | Topical | Size: 102.19 ± 0.002 nm PdI: 0.258 Zeta: 12.1 ± 0.0 mV EE: 87.2 ± 0.005 |
[40] |
| Tricaprin | Cetyl Palmitate, Tween® 60 Tego Care 450 Amphisol K, 1-Tetradecanol | Resveratrol | Hot melt homogenization | Cosmetic | Topical | Size: 102.190 ± 0.002 nm PdI: 0.258 Zeta: 12.1 ± 0.0 mV EE: 52.45% |
[41] |
2.2. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers
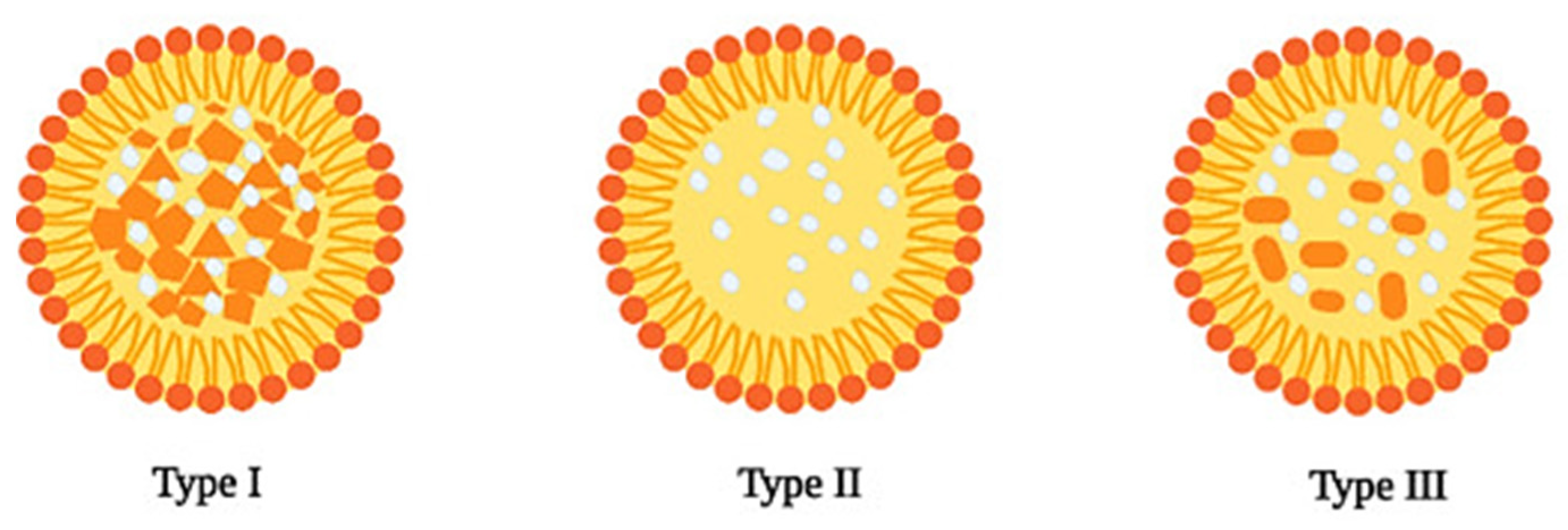
| Solid Lipid | Liquid Lipid | Surfactant | Drug | Production Method | Therapeutic Purpose | Delivery Route | Characteristics | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stearic acid | Oleic acid | Soya Lecithin Glyceryl Monostearate | Docetaxel (DTX) | Modified film ultrasonication–dispersion method | Murine Malignant Melanoma | Parenteral | Size: 203.67 ± 4.15 nm PdI: NA Zeta: −31.17 ± 2.20 mV EE: 89.39 ± 0.99% |
[46] |
| Precirol® ATO-5 | Squalene | Myverol | Lovastatin | Hot melt homogenization | Cholesterol | Oral | Size: 278.8 ± 0.6 nm PdI: ≤0.25 Zeta: −32.4 ± 0.4 mV EE: 83.8 ± 2.5 |
[47] |
| Comprito® 888 ATO | Miglyol 812N | Lecithin | Vinpocetin (VIN) | High-pressure homogenization | Brain Disorders | Oral | Size: 177 ± 5.4 nm PdI: NA Zeta: −24.7 ± 1.4 mV EE: 95.3 ± 1.4 |
[48] |
| Precirol® ATO-5 | Oleic Acid | Tween® 80 | 1-carbaldehyde-3,4-dimethoxyxanthone (LEM2) | Ultrasonication | Melanoma | Topical | Size: 219.67 ± 5.26 nm PdI: ≤0.3 Zeta: −24.88 ± 1.78 mV EE: 72% |
[49] |
| Cetyl Palmitate | Miglyol 812N | Tween® 60 | Curcumin | Modified hot homogenization | Brain Disorders | Oral/Intravenous | Size: 183 ± 12 nm PdI: 0.13 ± 0.01 Zeta: −21 ± 2 mV EE: 82 ± 15% |
[50] |
| Glyceryl Tribehenate | Oleic acid | P 407 | Raloxifene hydrochloride (RLX) | Hot homogenization | Osteoporosis | Oral | Size: 120 ± 3 nm PdI: 0.293 Zeta: 14.4 ± 0.5 mV EE: 91.71 |
[51] |
| Precirol ATO-5 | Miglyol 812N | Tween® 80 | Rifapentine (RPT) | Hot ultra-sonication | Tuberculosis | Oral/Pulmonary | Size: 242 ± 9 nm PdI: 0.17 ± 0.01 Zeta: −22 ± 2 mV EE: |
[52] |
| Glycerol monostearate (GMS) | Medium chain triglyceride (MCT) | Poloxamer 188 Soybean lecithin |
Amoitone B | Emulsion-evaporation and low temperature-solidification | Tumor Therapy | NA | Size: 241.2 ± 4.4 nm PDI: NA Zeta: 18.4 ± 0.2 mV EE: 71.5 ± 1.1% |
[53] |
| Myristyl Myristate |
Crodamolt GTCC-LQ | Pluronic F128 | Metvan | Sonication | Bone Cancer | NA | Size: 230.8 ± 3.1 nm PdI: 0.235 ± 0.010 Zeta: −7.9 ± 0.8 mV EE: 77.6 ± 4.8% |
[54] |
| Stearic acid or beeswax | Carvacrol | Kolliphor188® | Carvacrol | Warm microemulsion oil in water (o/w) | Leishmaniasis | Parenteral | Size: 98 ± 0.80 nm PdI: 0.166 ± 0.04 Zeta: −25 ± 5 mV |
[55] |
2.3. Comparison between Solid Lipid Nanoparticles and Nanostructured Lipid Carrier
| SLN | NLC | |
|---|---|---|
| Lipids | Use of physiological lipids; however, there is a lower stability comparatively with other materials | |
| Solvents | Absence of organic solvents | |
| Application | Application in different industries (food, cosmetic, pharmaceutical) | |
| Bioavailability | Improved bioavailability of drugs | |
| Drugs loaded | Loads both lipophilic and hydrophilic drugs; however, has difficulty in loading therapeutic proteins | |
| Drug delivery | Targeted drug delivery and enhanced drug permeation | |
| Scale-up | Cheaper and easier to scale up than polymeric nanoparticles | |
| Protection | Protection of drug molecules from enzymatic activity, harsh pH, and moisture | |
| Cytotoxicity | Cytotoxicity concerns due to the nature and concentration of matrix lipids | |
| Drug loading capacity | Limited drug loading capacity | Improved drug loading capacity |
| Controlled drug release profile | Difficulty in adjusting the drug release profile | Better controlled drug release profile |
| Polymorphic transitions | Prone to polymorphic transitions | No polymorphic transition takes place |
| Release during storage | Unwanted drug release during storage | Minimal drug release during storage |
| Physical stability | Possible particle aggregation or fusion during storage | Better physical stability during storage |
| Water content | High water content | Low water content |
3. Production Methods of Solid–lipid Nanoparticles and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers
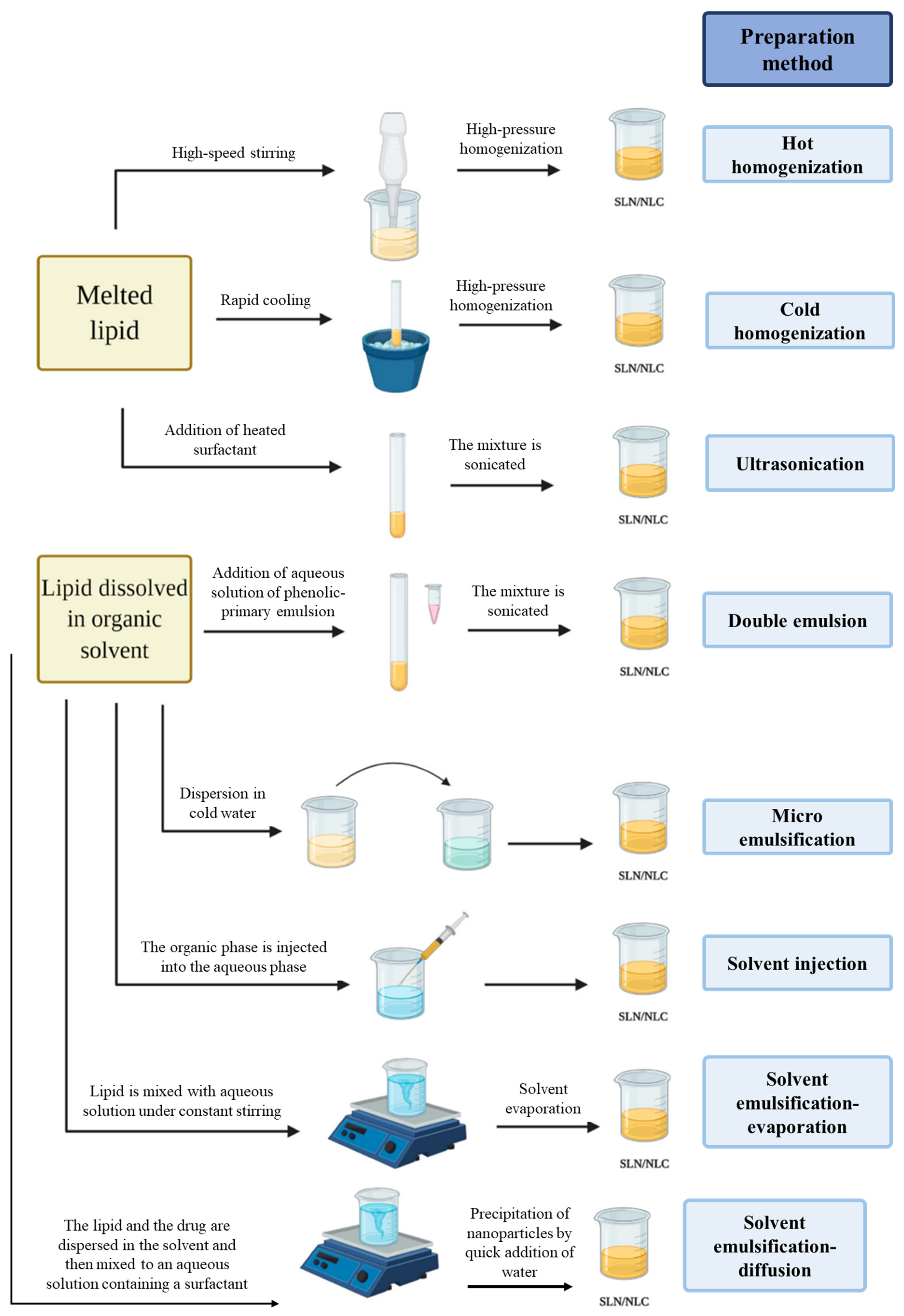
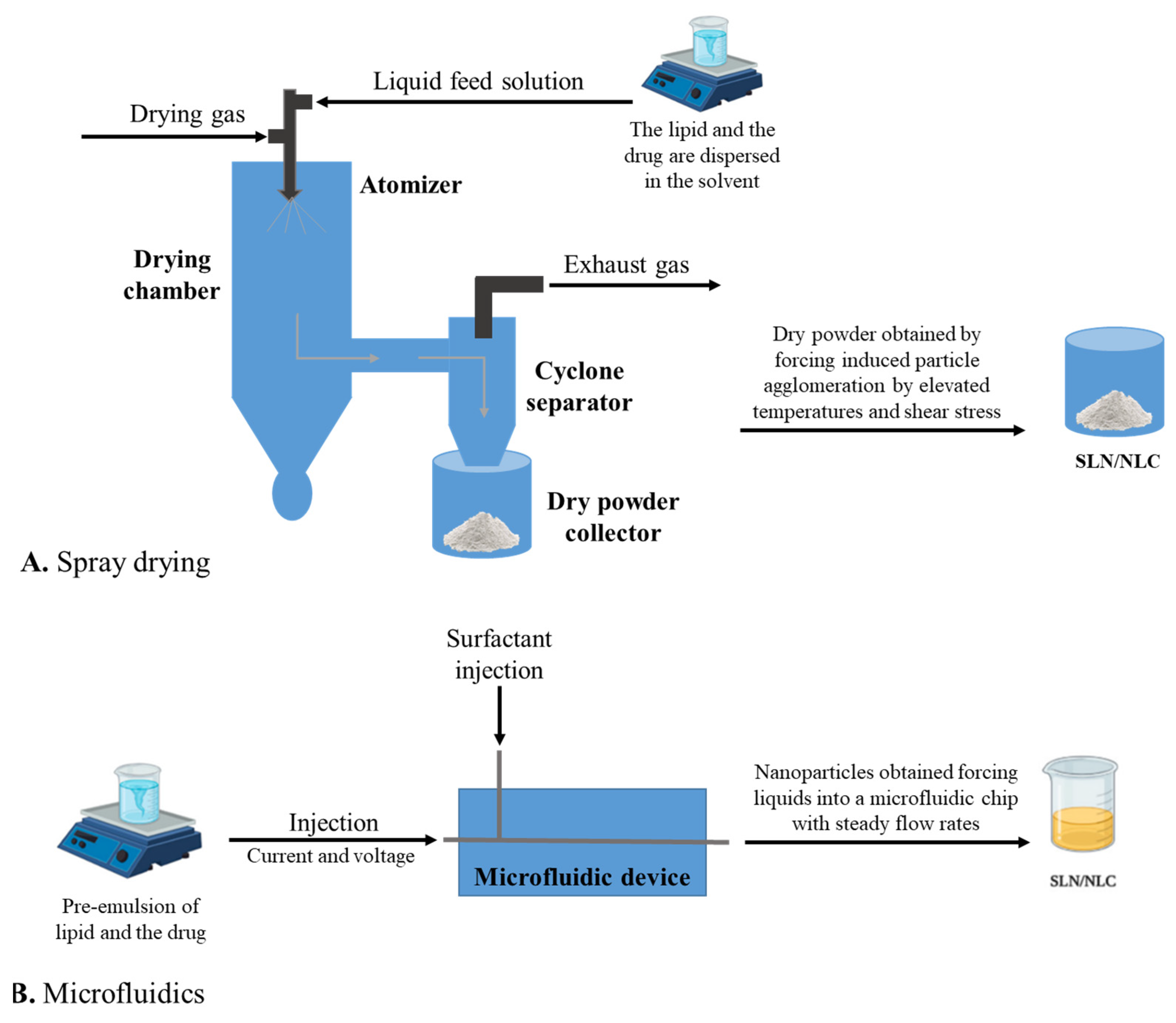
3.1. High-Pressure Homogenization
3.2. Ultra-Sonication or High-Speed Homogenization
3.3. Double Emulsion
3.4. Microemulsion Method
3.5. Solvent Injection
3.6. Solvent Emulsification-Evaporation
3.7. Solvent Emulsification-Diffusion
3.8. Spray Drying
3.9. Microfluidics
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/pharmaceutics15061593
References
- Soares, S.; Sousa, J.; Pais, A.; Vitorino, C. Nanomedicine: Principles, Properties, and Regulatory Issues. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 360.
- Patra, J.K.; Das, G.; Fraceto, L.F.; Campos, E.V.R.; del Pilar Rodriguez-Torres, M.; Acosta-Torres, L.S.; Diaz-Torres, L.A.; Grillo, R.; Swamy, M.K.; Sharma, S.; et al. Nano based drug delivery systems: Recent developments and future prospects. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 71.
- Jaiswal, P.; Gidwani, B.; Vyas, A. Nanostructured lipid carriers and their current application in targeted drug delivery. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2016, 44, 27–40.
- Alexis, F.; Rhee, J.-W.; Richie, J.P.; Radovic-Moreno, A.F.; Langer, R.; Farokhzad, O.C. New frontiers in nanotechnology for cancer treatment. Urol. Oncol. 2008, 26, 74–85.
- ud Din, F.; Aman, W.; Ullah, I.; Qureshi, O.S.; Mustapha, O.; Shafique, S.; Zeb, A. Effective use of nanocarriers as drug delivery systems for the treatment of selected tumors. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 7291–7309.
- Akel, H.; Ismail, R.; Katona, G.; Sabir, F.; Ambrus, R.; Csóka, I. A comparison study of lipid and polymeric nanoparticles in the nasal delivery of meloxicam: Formulation, characterization, and in vitro evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 604, 120724.
- Ghasemiyeh, P.; Mohammadi-Samani, S.J.R.i.p.s. Solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers as novel drug delivery systems: Applications, advantages and disadvantages. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 13, 288.
- Khosa, A.; Reddi, S.; Saha, R.N. Nanostructured lipid carriers for site-specific drug delivery. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 103, 598–613.
- Sgorla, D.; Bunhak, É.J.; Cavalcanti, O.A.; Fonte, P.; Sarmento, B. Exploitation of lipid-polymeric matrices at nanoscale for drug delivery applications. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2016, 13, 1301–1309.
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Hou, X.; Xie, X.; Shi, J.; Shen, J.; He, Y.; Wang, Z.; Feng, N. Functional lipid polymeric nanoparticles for oral drug delivery: Rapid mucus penetration and improved cell entry and cellular transport. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2019, 21, 102075.
- Sgorla, D.; Lechanteur, A.; Almeida, A.; Sousa, F.; Melo, E.; Bunhak, É.; Mainardes, R.; Khalil, N.; Cavalcanti, O.; Sarmento, B. Development and characterization of lipid-polymeric nanoparticles for oral insulin delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2018, 15, 213–222.
- Hallberg, D.; Holm, I.; Obel, A.L.; Schuberth, O.; Wretlind, A. Fat emulsions for complete intravenous nutrition. Postgrad. Med. J. 1967, 43, 307–316.
- Bangham, A.D.; Standish, M.M.; Watkins, J.C. Diffusion of univalent ions across the lamellae of swollen phospholipids. J. Mol. Biol. 1965, 13, 238–252, IN26–IN27.
- Bulbake, U.; Doppalapudi, S.; Kommineni, N.; Khan, W. Liposomal formulations in clinical use: An updated review. Pharmaceutics 2017, 9, 12.
- Muller, R.H.; Radtke, M.; Wissing, S.A. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) and nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) in cosmetic and dermatological preparations. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54 (Suppl. S1), S131–S155.
- Dudhipala, N.; Janga, K.Y.; Gorre, T. Comparative study of nisoldipine-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers and solid lipid nanoparticles for oral delivery: Preparation, characterization, permeation and pharmacokinetic evaluation. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 616–625.
- Fonte, P.; Andrade, F.; Araújo, F.; Andrade, C.; das Neves, J.; Sarmento, B. Chitosan-coated solid lipid nanoparticles for insulin delivery. Methods Enzymol. 2012, 508, 295–314.
- Müller, R.H.; Maaβen, S.; Weyhers, H.; Specht, F.; Lucks, J.S. Cytotoxicity of magnetite-loaded polylactide, polylactide/glycolide particles and solid lipid nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 1996, 138, 85–94.
- Eldem, T.; Speiser, P.; Hincal, A. Optimization of spray-dried and -congealed lipid micropellets and characterization of their surface morphology by scanning electron microscopy. Pharm. Res. 1991, 8, 47–54.
- Domb, A.J. Long acting injectable oxytetracycline-liposphere formulations. Int. J. Pharm. 1995, 124, 271–278.
- Jahangirian, H.; Lemraski, E.G.; Webster, T.J.; Rafiee-Moghaddam, R.; Abdollahi, Y. A review of drug delivery systems based on nanotechnology and green chemistry: Green nanomedicine. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 2957–2978.
- Barroso, L.; Viegas, C.; Vieira, J.; Ferreira-Pêgo, C.; Costa, J.; Fonte, P. Lipid-based carriers for food ingredients delivery. J. Food Eng. 2021, 295, 110451.
- Mueller Rainer Prof, D.R.; Lucks, J.-S. Arzneistofftraeger Aus Festen Lipidteilchen-Feste Lipidnanosphaeren (SLN). DE4131562A1, 18 September 1991.
- Parhi, R.; Suresh, P. Preparation and characterization of solid lipid nanoparticles-a review. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 2012, 9, 2–16.
- Morales, J.O.; Valdés, K.; Morales, J.; Oyarzun-Ampuero, F. Lipid nanoparticles for the topical delivery of retinoids and derivatives. Nanomedicine 2015, 10, 253–269.
- Naseri, N.; Valizadeh, H.; Zakeri-Milani, P. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers: Structure, Preparation and Application. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 5, 305–313.
- Kumar, S.; Randhawa, J.K. High melting lipid based approach for drug delivery: Solid lipid nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2013, 33, 1842–1852.
- Souto, E.B.; Almeida, A.J.; Müller, R.H. Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN®, NLC®) for Cutaneous Drug Delivery:Structure, Protection and Skin Effects. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2007, 3, 317–331.
- Viegas, C.; Seck, F.; Fonte, P. An insight on lipid nanoparticles for therapeutic proteins delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 77, 103839.
- zur Mühlen, A.; Schwarz, C.; Mehnert, W. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) for controlled drug delivery—Drug release and release mechanism. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 1998, 45, 149–155.
- Üner, M.; Yener, G. Importance of solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) in various administration routes and future perspectives. Int. J. Nanomed. 2007, 2, 289–300.
- Borges, A.; De Freitas, V.; Mateus, N.; Fernandes, I.; Oliveira, J. Solid lipid nanoparticles as carriers of natural phenolic compounds. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 998.
- Castellani, S.; Trapani, A.; Spagnoletta, A.; Di Toma, L.; Magrone, T.; Di Gioia, S.; Mandracchia, D.; Trapani, G.; Jirillo, E.; Conese, M. Nanoparticle delivery of grape seed-derived proanthocyanidins to airway epithelial cells dampens oxidative stress and inflammation. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 140.
- Maretti, E.; Costantino, L.; Buttini, F.; Rustichelli, C.; Leo, E.; Truzzi, E.; Iannuccelli, V. Newly synthesized surfactants for surface mannosylation of respirable SLN assemblies to target macrophages in tuberculosis therapy. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2019, 9, 298–310.
- Dai, Y.; Huang, J.; Xiang, B.; Zhu, H.; He, C. Antiproliferative and apoptosis triggering potential of paclitaxel-based targeted-lipid nanoparticles with enhanced cellular internalization by transferrin receptors—A study in leukemia cells. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 271.
- Tsai, M.-J.; Huang, Y.-B.; Wu, P.-C.; Fu, Y.-S.; Kao, Y.-R.; Fang, J.-Y.; Tsai, Y.-H. Oral Apomorphine Delivery from Solid Lipid Nanoparticles with Different Monostearate Emulsifiers: Pharmacokinetic and Behavioral Evaluations. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 547–557.
- Dhawan, S.; Kapil, R.; Singh, B. Formulation development and systematic optimization of solid lipid nanoparticles of quercetin for improved brain delivery. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2011, 63, 342–351.
- Souza, C.; de Freitas, L.A.P.; Maia Campos, P.M.B.G. Topical formulation containing beeswax-based nanoparticles improved In Vivo skin barrier function. AAPS PharmSciTech 2017, 18, 2505–2516.
- Rigon, R.; Fachinetti, N.; Severino, P.; Santana, M.; Chorilli, M. Skin Delivery and In Vitro biological evaluation of trans-resveratrol-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for skin disorder therapies. Molecules 2016, 21, 116.
- Das, S.; Das, J.; Samadder, A.; Paul, A.; Khuda-Bukhsh, A.R. Efficacy of PLGA-loaded apigenin nanoparticles in Benzopyrene and ultraviolet-B induced skin cancer of mice: Mitochondria mediated apoptotic signalling cascades. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 62, 670–680.
- Carlotti, M.E.; Sapino, S.; Ugazio, E.; Gallarate, M.; Morel, S. Resveratrol in solid lipid nanoparticles. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2012, 33, 465–471.
- Beloqui, A.; Solinís, M.Á.; Rodríguez-Gascón, A.; Almeida, A.J.; Préat, V. Nanostructured lipid carriers: Promising drug delivery systems for future clinics. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2016, 12, 143–161.
- Doktorovova, S.; Souto, E.B. Nanostructured lipid carrier-based hydrogel formulations for drug delivery: A comprehensive review. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2009, 6, 165–176.
- Gaba, B.; Fazil, M.; Ali, A.; Baboota, S.; Sahni, J.K.; Ali, J. Nanostructured lipid (NLCs) carriers as a bioavailability enhancement tool for oral administration. Drug Deliv. 2015, 22, 691–700.
- Pathak, K.; Keshri, L.; Shah, M. Lipid nanocarriers: Influence of lipids on product development and pharmacokinetics. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 2011, 28, 357–393.
- Liu, D.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, N. Nanostructured lipid carriers as novel carrier for parenteral delivery of docetaxel. Colloids Surf. B 2011, 85, 262–269.
- Chen, C.-C.; Tsai, T.-H.; Huang, Z.-R.; Fang, J.-Y. Effects of lipophilic emulsifiers on the oral administration of lovastatin from nanostructured lipid carriers: Physicochemical characterization and pharmacokinetics. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2010, 74, 474–482.
- Zhuang, C.-Y.; Li, N.; Wang, M.; Zhang, X.-N.; Pan, W.-S.; Peng, J.-J.; Pan, Y.-S.; Tang, X. Preparation and characterization of vinpocetine loaded nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) for improved oral bioavailability. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 394, 179–185.
- Malta, R.; Loureiro, J.B.; Costa, P.; Sousa, E.; Pinto, M.; Saraiva, L.; Amaral, M.H. Development of lipid nanoparticles containing the xanthone LEM2 for topical treatment of melanoma. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102226.
- Neves, A.R.; van der Putten, L.; Queiroz, J.F.; Pinheiro, M.; Reis, S. Transferrin-functionalized lipid nanoparticles for curcumin brain delivery. J. Biotechnol. 2021, 331, 108–117.
- Murthy, A.; Rao Ravi, P.; Kathuria, H.; Malekar, S. Oral Bioavailability Enhancement of Raloxifene with Nanostructured Lipid Carriers. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1085.
- Magalhães, J.; Chaves, L.L.; Vieira, A.C.; Santos, S.G.; Pinheiro, M.; Reis, S. Optimization of rifapentine-loaded lipid nanoparticles using a quality-by-design strategy. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 75.
- Luan, J.; Zhang, D.; Hao, L.; Li, C.; Qi, L.; Guo, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q. Design and characterization of Amoitone B-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers for controlled drug release. Drug Deliv. 2013, 20, 324–330.
- Cacicedo, M.L.; Ruiz, M.C.; Scioli-Montoto, S.; Ruiz, M.E.; Fernández, M.A.; Torres-Sanchez, R.M.; Baran, E.J.; Castro, G.R.; León, I.E. Lipid nanoparticles—Metvan: Revealing a novel way to deliver a vanadium compound to bone cancer cells. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 17726–17734.
- Galvão, J.G.; Santos, R.L.; Silva, A.R.S.T.; Santos, J.S.; Costa, A.M.B.; Chandasana, H.; Andrade-Neto, V.V.; Torres-Santos, E.C.; Lira, A.A.M.; Dolabella, S.; et al. Carvacrol loaded nanostructured lipid carriers as a promising parenteral formulation for leishmaniasis treatment. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 150, 105335.
- Shidhaye, S.S.; Vaidya, R.; Sutar, S.; Patwardhan, A.; Kadam, V.J. Solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers—Innovative generations of solid lipid carriers. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2008, 5, 324–331.
- Domingo, C.; Saurina, J. An overview of the analytical characterization of nanostructured drug delivery systems: Towards green and sustainable pharmaceuticals: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 744, 8–22.
- Pardeike, J.; Hommoss, A.; Müller, R.H. Lipid nanoparticles (SLN, NLC) in cosmetic and pharmaceutical dermal products. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 366, 170–184.
- Mehnert, W.; Mäder, K. Solid lipid nanoparticles Production, characterization and applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 47, 165–196.
- Li, Q.; Cai, T.; Huang, Y.; Xia, X.; Cole, S.P.C.; Cai, Y. A review of the structure, preparation, and application of NLCs, PNPs, and PLNs. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 122.
- Das, S.; Ng, W.K.; Tan, R.B.H. Are nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) better than solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs): Development, characterizations and comparative evaluations of clotrimazole-loaded SLNs and NLCs? Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 47, 139–151.
- Abdelbary, G.; Haider, M. In vitro characterization and growth inhibition effect of nanostructured lipid carriers for controlled delivery of methotrexate. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2013, 18, 1159–1168.
- Esposito, E.; Drechsler, M.; Cortesi, R.; Nastruzzi, C. Encapsulation of cannabinoid drugs in nanostructured lipid carriers. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 102, 87–91.
- Fang, C.L.; Al-Suwayeh, S.A.; Fang, J.Y. Nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) for drug delivery and targeting. Recent Pat. Nanotechnol. 2013, 7, 41–55.
- Jaganathan, K.S.; Rao, Y.U.; Singh, P.; Prabakaran, D.; Gupta, S.; Jain, A.; Vyas, S.P. Development of a single dose tetanus toxoid formulation based on polymeric microspheres: A comparative study of poly(D,L-lactic-co-glycolic acid) versus chitosan microspheres. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 294, 23–32.
- Utada, A.S.; Lorenceau, E.; Link, D.R.; Kaplan, P.D.; Stone, H.A.; Weitz, D.A. Monodisperse double emulsions generated from a microcapillary device. Science 2005, 308, 537–541.
- Gasco Maria, R. Method for Producing Solid Lipid Microspheres Having a Narrow Size Distribution. U.S. Patent 5,250,236A, 2 August 1991.
- Igartua, M.; Saulnier, P.; Heurtault, B.; Pech, B.; Proust, J.E.; Pedraz, J.L.; Benoit, J.P. Development and characterization of solid lipid nanoparticles loaded with magnetite. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 233, 149–157.
- Schubert, M.A.; Muller-Goymann, C.C. Solvent injection as a new approach for manufacturing lipid nanoparticles-evaluation of the method and process parameters. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2003, 55, 125–131.
- Shahgaldian, P.; Da Silva, E.; Coleman, A.W.; Rather, B.; Zaworotko, M.J. Para-acyl-calix-arene based solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs): A detailed study of preparation and stability parameters. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 253, 23–38.
- Hu, F.Q.; Hong, Y.; Yuan, H. Preparation and characterization of solid lipid nanoparticles containing peptide. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 273, 29–35.
- Trotta, M.; Chirio, D.; Cavalli, R.; Peira, E. Hydrophilic microspheres from water-in-oil emulsions by the water diffusion technique. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 1445–1449.
- Kaur, P.; Mishra, V.; Shunmugaperumal, T.; Goyal, A.K.; Ghosh, G.; Rath, G. Inhalable spray dried lipidnanoparticles for the co-delivery of paclitaxel and doxorubicin in lung cancer. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 56, 101502.
- Freitas, C.; Müller, R.H. Spray-drying of solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNTM). Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 1998, 46, 145–151.
- Zhang, X.; Pan, W.; Gan, L.; Zhu, C.; Gan, Y.; Nie, S. Preparation of a Dispersible PEGylate Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC) Loaded with 10-Hydroxycamptothecin by Spray-Drying. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2008, 56, 1645–1650.
- Xia, D.; Shrestha, N.; van de Streek, J.; Mu, H.; Yang, M. Spray drying of fenofibrate loaded nanostructured lipid carriers. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 11, 507–515.
- Zhong, Q.; Zhang, L. Nanoparticles fabricated from bulk solid lipids: Preparation, properties, and potential food applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 273, 102033.
- Marante, T.; Viegas, C.; Duarte, I.; Macedo, A.S.; Fonte, P. An Overview on Spray-Drying of Protein-Loaded Polymeric Nanoparticles for Dry Powder Inhalation. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1032.
- Lababidi, N.; Sigal, V.; Koenneke, A.; Schwarzkopf, K.; Manz, A.; Schneider, M. Microfluidics as tool to prepare size-tunable PLGA nanoparticles with high curcumin encapsulation for efficient mucus penetration. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 2280–2293.
- Lopes, C.; Cristóvão, J.; Silvério, V.; Lino, P.R.; Fonte, P. Microfluidic production of mRNA-loaded lipid nanoparticles for vaccine applications. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2022, 19, 1381–1395.
- Garg, S.; Heuck, G.; Ip, S.; Ramsay, E. Microfluidics: A transformational tool for nanomedicine development and production. J. Drug Target. 2016, 24, 821–835.
- Haider, M.; Abdin, S.M.; Kamal, L.; Orive, G. Nanostructured lipid carriers for delivery of chemotherapeutics: A review. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 288.
- Chen, S.; Liu, W.; Wan, J.; Cheng, X.; Gu, C.; Zhou, H.; Chen, S.; Zhao, X.; Tang, Y.; Yang, X. Preparation of Coenzyme Q10 nanostructured lipid carriers for epidermal targeting with high-pressure microfluidics technique. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2013, 39, 20–28.
