Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is an old version of this entry, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Subjects:
Oncology
Neuroblastoma is a common childhood tumor that mainly affects young children, especially toddlers, and, with a survival rate in high-risk patients of less than 50%. Treatment for high-risk neuroblastoma involves a combination of induction chemotherapy, most commonly doxorubicin, surgical tumor resection, stem cell transplantation, radiotherapy, and immunotherapy.
- high-risk neuroblastoma
- immunotherapy
- tumor microenvironment
1. Immunosuppressive Pathways in Neuroblastoma
The pediatric immune system has a wide variety of efficient mechanisms in place to detect and destroy foreign pathogens and malignancies that pose a threat to the host. Many cancers, including neuroblastoma, have developed unique abilities to suppress and/or evade the host immune system. The type of tumor and the extent of its infiltration into the immune cells has been associated with prognosis [12,30]. High-risk (HR) neuroblastoma tumors are characterized as immunologically “cold” and devoid of antitumor immune cells and/or have been infiltrated by immune-suppressive T-regulatory cell types rather than being “hot” and thus infiltrated by effector immune cells such as cytotoxic T cells and natural killer (NK) cells, which can kill tumors cells, and dendritic cells (DC), which are antigen-presenting and activate T cells [31,32,33]. HR neuroblastoma tumors have less tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes [34] than low-risk (LR) and medium-risk (MR) tumors [9]. These findings are supported by studies that show that HR tumors display lower levels of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL), NK and DC genetic signatures; higher levels of T-regulatory cells; and worse patient outcomes compared with LR tumors [35]. Importantly, LR patients, characterized by higher TIL density, have demonstrated higher disease-free survival (DFS), event-free survival (EFS) and overall survival (OS) [7].
Neuroblastoma tumors employ a variety of methods in which they suppress TILs and NK and DC cells while increasing the levels of regulatory T cells (Tregs). The immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME) comprises myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), stromal cells, tumor-associated macrophages [8] and neuroblastoma cancer cells [36]. MDSCs induce several immunoregulatory mechanisms including disialoganglioside (GD2), transforming growth factor (TGF-B), and the transcriptional coactivator TAZ (transcriptional coactivator with PDZ-binding motif) [1,36].
GD2 suppresses DC antigen presentation and the expression of MHC-I and MHC-II molecules, rendering neuroblastoma tumor cells invisible to cytotoxic CD8+ T lymphocytes, and repressing the ability of CD4+ helper T lymphocytes to mount an immune response via cytokine signaling inhibition [12,36]. Neuroblastoma tumors also express reduced levels of interferon (IFNγ), interleukin (IL-6), IL-8, IL-10, IL-12, and IL-21 [12,36,37]. Table 1 summarizes few of the cytokines and there interactions with the ICIs. Under normal conditions, these cytokines function by amplifying the host’s immune responses against pathogens and cancerous cells [38]. Their reduction in neuroblastoma tumors impedes TIL activation and infiltration, contributing to the low immunogenicity of the neuroblastoma TME [12,36,37]. Treatments that target GD2, such as the anti-GD2 antibody dinutuximab, have been developed and have undergone phase trials in neuroblastoma patients with promising results [7]. This discovery has marked an important breakthrough in pediatric solid tumor research and represents promising potential for further investigation in immunotherapy treatments in oncology.
Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) is responsible for cell growth, proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis [37] in various cancers. Although it has been shown that TGF-β plays an inhibitory, anti-tumor role in early cancer stages, recent studies have revealed that TGF-β also displays cancer-promoting properties, including the impairment of NK function, which in turn enhances tumorigenesis and metastasis while inducing immunosuppression and drug resistance [12,37]. This makes TGF-β a promising target in the development of novel immunotherapies.
Additionally, TAZ has a major impact on the NB TME’s immunosuppressive environment. Increased TAZ expression induces the expression of immune checkpoint programmed death-1 (PD-1) in both T lymphocytes and NK cells. It has been established that the interaction between programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) and PD1 is linked to decreased lymphocyte proliferation, downregulation of NK function, and the survival of cancer cells [36,39]. Importantly, studies have shown that higher expression of PD-1 and PDL-1 is related to poor prognosis [24]. From a therapeutic point of view, it would be beneficial to silence TAZ expression with Food and Drug Administration-approved drugs that target TAZ signaling [36]. Further, inhibition of the PD-1/PD-L1 immunomodulatory checkpoints molecule (ICMS) mechanism has been used to successfully treat some chemotherapy-resistant cancers in adults [36]. Neuroblastoma cells may not be recognized by CTL due to their poor MHC-I expression, but they should be vulnerable to NK cells as a result [40,41]. NK cells can kill neuroblastoma cells, though in some circumstances pre-activation of isolated NK cells is necessary [42]. Nonetheless, neuroblastoma appears to be shielded from NK-mediated death in patients by additional escape mechanisms that adjust the harmony between activating and inhibitory impulses on NK cells. For instance, the ligands (PVR, nectin-2, MICA, MICB, and ULBPs) for the NK cell activating receptors DNAM-1 and NKG2D are not expressed at high levels in neuroblastoma tumors. Thus, NK cell therapies may prove useful in both stand-alone and combination treatments for NB [43].
Table 1. The neuroblastoma tumor microenvironment, its immunologic function and interaction with immune checkpoint inhibitors.
| Cytokine | Immunologic Function | Interaction with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor (ICI) |
|---|---|---|
| TNFα | A proinflammatory cytokine primarily produced by activated macrophages, T lymphocytes, and NK cells. TNF plays major roles in bone remodeling, infection control, and leukocyte trafficking [37]. | TNF has been shown to induce resistance to immunotherapies and acts as a negative biomarker for prognosis. TNFα increases the expression of PD-L1 in tumor cells. Studies have also shown that a TNF-β blockade combined with ICI, such as anti-PD1, has a better therapeutic effect than ICI therapy alone [37]. |
| IFNγ | A proinflammatory cytokine primarily produced by NK cells, activated T lymphocytes, B-cells, and antigen presenting (AP) cells. IFNγ has many immunomodulatory roles including antiviral and antitumor functioning [37]. | IFNγ has an antitumor mechanism targeted by ICIs. It increases tumor immunogenicity, suppresses cancer cell proliferation, increases NK cell cytotoxic functioning, and recruit’s tumor-reactive T cells [37]. Clinic studies have reported increased IFNγ levels following anti-PD-1 ICI therapy and improved prognosis. Further, IFNγ has been shown to be a positive biomarker for successful ICI therapy [37]. |
| IL-6 | IL-6 has pro and anti-inflammatory properties. Its function is involved in cell survival and growth, immune system regulation, and carcinogenesis. Importantly, it has been shown to promote tumor transmission [44]. | IL-6 has been shown to have a negative role in immunotherapy. It has been reported that increased levels of IL-6 induce the production of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), which promote an immunosuppressive TME. Studies have shown that combining anti-IL6 with ICI treatment, such as anti-PD-1 immunotherapy, fosters increased anti-tumor activity and improved prognosis [44]. |
| IL-8 | A proinflammatory cytokine produced by macrophages. Its primary roles are to activate neutrophils stimulated by cellular stresses and stimulate endothelial cell proliferation. IL-8 levels have been shown to reflect tumor burden [44]. | The interaction between IL-8 and ICI therapy is unclear. However, studies have reported that increased levels of IL-8 are correlated with longer overall survival (OS) in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients treated with nivolumab, and anti-PD-1 ICI [44]. |
| TGF-β | A proinflammatory cytokine produced by leukocytes and stromal cells. It serves many functions, including driving the differentiation of T helper 17 (Th17) cells and regulating cell growth, proliferation, and apoptosis [32,45]. | TGF-β inhibits early cancer cells by inducing cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis. However, TGF-β has been shown to have cancer-promoting properties in later stages. Mouse models used to study urothelial cancer have demonstrated that combining anti-PD-1 therapy with the TGF-β antibody reduced the TGF-β pathway and induced tumor infiltration by cytotoxic T cells, resulting in tumor suppression. Similarly, another study has shown that combing ICI therapy with the TGF-β antibody resulted in improved prognosis compared with monotherapy [37]. |
| IL-17 | IL-17 has pro- and anti-inflammatory properties. It induces neutrophil-mediated inflammation while also suppressing autoimmune diseases [46,47]. Importantly, studies investigating colorectal cancer have shown that IL-17 exhibits protumoral properties, especially during the early stages [47]. | IL-17 signaling has been shown to promote carcinogenesis. Further, studies have shown that inhibiting signaling from this cytokine slows down oncogenesis initiation, suggesting that IL-17 inhibition may be used to halt the early stages of tumor growth. Importantly, studies utilizing mouse models have found that increased IL-17 levels were correlated with high PD-L1 expression. Further, combining IL-17 and a PD-1 blockade induced higher levels of cytotoxic T cells and tumor regression [48]. |
| Il-21 | IL-21 has pro- and anti-inflammatory properties. It regulates various immune cells such as NK and cytotoxic T cells while hindering the pro-inflammatory mechanisms of macrophages. IL-21 also exhibits anti-tumor properties [49]. | Studies have found that IL-21 hinders tumor development, especially during early stages [50]. Additionally, more recent studies using mouse models have demonstrated that combining an immune checkpoint blockade, such as anti PD-L1, with IL-21 administration increased antitumor activity, characterized by increased CD8+ T cell proliferation and by increased infiltration by, and memory of, effector T cells [50]. |
As previously mentioned, the combined immunosuppressive mechanisms of neuroblastoma cancer cells create an immunologically “cold” environment devoid of activated T lymphocytes and NK cells, with T-regulatory cells upregulated. Under normal circumstances, NK cells and cytotoxic T cells play a prominent role in preventing tumor progression and metastasis by inducing tumor cell lysis and inflammation [12]. T-regulatory (Tregs) cells function to modulate the immune system by inhibiting other immune effector cells to prevent the over activation of the immune system. The overexpression of Tregs further inhibits the already immunologically inactive TME by suppressing NK and cytotoxic T cell functioning [51,52]. This is especially seen in high-risk neuroblastoma tumors where there are increasingly higher levels of immunosuppressive stromal cancer cells, MDSCs and Tregs [36,52].
2. Immunotherapy Targets in Neuroblastoma
Immunotherapy can fall into two different types (Figure 1), one being active immunotherapy and the other being passive. Active immunotherapy relies on directly attacking cancer cells through the stimulation of the immune system [53]. Passive immunotherapy utilizes the acceptance of an organism’s immune system of antibodies, cytokines, and transformed immune cells to act directly on tumor cells [54]. Immunotherapy treatments that can target neuroblastoma cells have been in development over the course of recent decades.
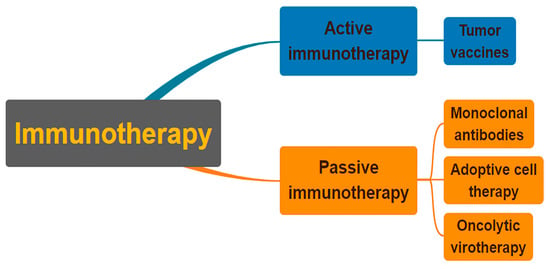
Figure 1. Classification of immunotherapies as either active or passive. In order to combat cancer cells, active immunotherapy stimulates the immune system of the cancer patient. Patients who cannot naturally make immune molecules are given them through passive immunotherapy. Both strategies may utilize a specific or a general strategy.
Cancer immune surveillance is a mechanism by which immune cells recognize and eliminate tumor cells. Neuroblastomas produce a highly immunosuppressive environment that has an effect on the body as well as locally in the tumor. Neuroblastomas employ indirect immunoregulatory mechanisms by chartering immune suppressive agents to dampen the activity of immune system. TGF, galectin-1, MIF, soluble GD2 (sGD2), and arginase-2 are some of the soluble mediators that neuroblastoma cells produce, and which have the ability to inhibit lymphocyte activation [55]. Neuroblastoma cancer cells also produce several other immunosuppressive molecules such as, sMICA, sB7-H6, sHLA-E, sHLA-G, IL-10 and HMGB1 [56]. Neuroblastoma tumors are intermixed with myeloid and stromal cell populations with defective activating functions or enhanced suppressive functions, which can prevent TIL from effectuating an anti-tumor response.
One of the areas in which immunotherapies have become focused is that associated with the passive invocation of the immune system to respond to a tumor in ways that would not occur without outside intervention. These therapies target the activation of immune cells such as T-cells to assist in the aim to provide an anti-tumor effect through the infiltration of the immune cells in the tumor. High-risk neuroblastoma with higher T cell infiltration has been associated with improved survival [57]. Increasing the levels of T cell infiltration into the tumor cells must be a goal for the improvement of patient outcomes.
A form of passive treatment for immunotherapy that has shown promising results is the use of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). One of these immune therapies focuses on the use of mAbs in order to recognize GD2, which is overexpressed relative to a control in neuroblastoma. GD2 is a disialoganglioside that is ubiquitously expressed on the surface of all neuroblastoma cells (source) [29]. This makes GD2 an appealing target due to its specificity for the disease. Adoption of mAbs such as anti-GD2 in both upfront and relapse treatment protocols has dramatically increased survival rates and altered the landscape for children with high-risk neuroblastoma [28]. Even in patients with relapsed disease, dinutuximab may have a treatment value [58]. The success of dinutuximab has sparked investigations into combination therapy with cytotoxic compounds, as well as cellular immunotherapy with (haploidentical) donor NK cells [59,60,61].
Recent technological advancements have made it feasible to analyze the immune response to patient-specific neoantigens that result from tumor-specific mutations. New evidence suggests that clinical immunotherapies may be more effective when these neoantigens are recognized. However, children probably have few, if any, actionable, mutation-generated, immunogenic tumor neoantigens because most juvenile cancers have a very low tumor mutation burden [62,63]. Cancer-testis antigens, as well as other embryonic or differentiation antigens expressed during development and on children’s cancers but not on normal postnatal tissues, may fall under this category [64]. Studies have shown a correlation between the use of these neoantigens and an increase in T cell activity [65]. Recently researchers have identified PHOX2B, a peptide displayed on the surface of neuroblastoma cells, by their MHC molecules [66]. The oncofetal proteins, expressed during embryonic development, though silenced after birth, may be ideal targets for T cell-based immunotherapies in NB due to their restricted expression outside of the tumor. While the comparatively low tumor mutational burden of neuroblastoma may limit neoantigen expression, developmental antigens may be the target of T cell-based immunotherapy. Given the high sensitivity and efficacy of some of these receptors, as has previously been seen with certain modified TCRs, researchers will need to be cautious of the possibility for antigen cross-reactivity. By administering immunomodulating agents that improve the tumor’s immunogenicity, stimulate antigen presentation, increase the patient’s endogenous tumor-reactive T cells, and suppress the tumor’s immunosuppressive microenvironment, it may also be possible to trigger endogenous tumor-reactive T cells in a patient [67,68,69,70]. Tumor-specific neoantigens lead to personalized immunotherapies for patients. Future development of technology involved in the recognition of these neoantigens can help provide an efficient and rapid response.
Cytokines released by cancer cells or cells in the tumor microenvironment support angiogenesis, tumor cell migration and metastasis, and the development of an immunosuppressive microenvironment. These tumor-promoting effects of cytokines also apply to NB, as depicted in Table 2. IL-6 and VEGF have been further characterized as cytokines that stimulate tumor growth and metastasis, while others, such as IFN-γ, can exert anti-NB activity by inducing tumor cell apoptosis and by inhibiting angiogenesis (Figure 2 and Table 2).
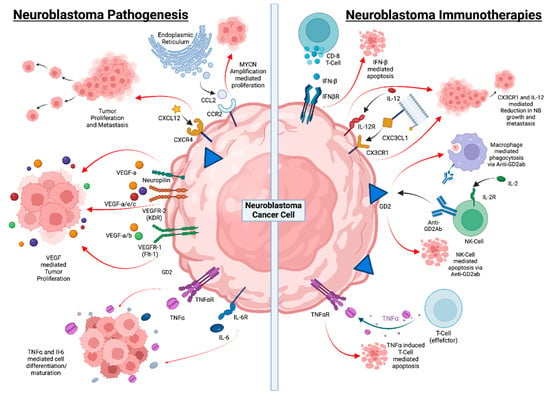
Figure 2. Neuroblastoma progression and underlying mechanisms behind immunotherapy. Neuroblastoma pathogenesis is marked with low MHC-I expression, which makes it difficult for T lymphocytes to recognize neuroblastomas, and low levels of activating ligand expression inhibit immune cell function. T and NK cell activity is further inhibited by soluble immunoregulatory mediators found in TME. However, with a potential immunotherapy, bispecific antibodies may cause T cell tumor reactivity, while anti-GD2 antibodies can activate NK cells, checkpoint inhibition can restore T cell function, and MSC and MDSC can be depleted. Soluble mediators’ immunosuppressive effects can be lessened, which will also boost DC’s ability to co-stimulate. IFN- β has been shown to sensitize NB cells to the cytotoxic effects of chemotherapy drugs such as TMZ. CX3CL1 is another chemokine that is highly expressed on the cell surface of NB tumor cells and combination with IL-12 has been shown to reduce NB growth and eliminate metastasis. Macrophage-mediated phagocytosis and NK-cell-mediated apoptosis using anti-GD2 have been shown to be effective treatments. TNFα induces T-cell-mediated apoptosis of NB cells.
Table 2. Cytokines and chemokines in neuroblastoma pathogenesis and preclinical therapy.
| Cytokine | Function | Role in Neuroblastoma |
|---|---|---|
| VEGF | VEGF acts as a pro-inflammatory cytokine by increasing endothelial cell permeability, by inducing the expression of endothelial cell adhesion molecules, and via its ability to act as a monocyte chemo-attractant [71]. | Studies looking at the expression of several markers in NB xenografts have shown that some angiogenic factors including VEGF-A, -B and -C are associated with advanced NB stage [72]. |
| CCL2 | Chemokine CCL2 (also known as monocyte chemo-attractant protein-1, MCP-1) is one of the vital chemokines that control the migration and infiltration of monocytes/macrophages [73]. | The infiltration of neuroblastoma cells by invariant NKT (iNKT) cells was found to correlate with the expression of the chemokine CCL2 by the tumor [74]. |
| CXCL12 | CXCL12 acts through its receptors CXCR4 and CXCR7. CXCR4 stimulation leads to the activation of numerous signaling pathways depending on the associated cell types, while CXCR7 has mainly been shown to be involved in scavenging CXCL12, although it can activate a MAP kinase pathway through β-arrestin in several systems [75]. | CXCL12 and CXCR4 have been demonstrated to be overexpressed in NB cell lines in addition to primary metastatic NB. This hints at the role of CXCL12 in its connection to autocrine/paracrine signaling of tumor growth instead of the development of metastatic pathways [76]. |
| CXC3CL1 | CXC3CL1 is an unusual chemokine expressed on the cell surface and acting as adhesion molecule by binding to its receptor CX3CR1.7 and is also expressed in a variety of human tissues and cell lines, where it mediates leukocyte migration and adhesion [77]. | It has been shown in animal models that CX3CL1 is able to inhibit NB growth and eradicate metastasis when used in combination with IL-12 through the attraction of immune cells to the tumor site [78]. |
| IL-6 | IL-6 and VEGF are the best characterized cytokines to stimulate tumor growth and metastasis, while others, such as IFN-γ, can exert anti-NB activity by inducing tumor cell apoptosis and inhibiting angiogenesis [79]. | IL-6 is introduced into the bone marrow by the bone marrow stromal cells (BMSC) which promotes the growth and survival of neuroblastoma cells [80]. |
| IL-7 | IL-7 is a cytokine that stimulates proliferation of all cells in the lymphoid lineage (B, T and NK cells) [81]. | A study using a humanized mouse model of metastatic NB showed that the combinatory therapy of human γδ T cells, hu14.18 anti-GD2 antibody, and Fc-IL-7 was able to increase the survival rate of the subject animals [82]. |
| IL-10 | IL-10 is an immunosuppressive cytokine consistently expressed in the tumor microenvironment. Studies carried out in different tumor models have demonstrated that blocking the IL-10R relieves immunosuppression in the tumor microenvironment and reinstates immune response directed at malignant cells [83]. | This response was observed in an NB model wherein an antibody targeting the IL-10 receptor was used in combination with liposomal oligonucleotides to enhance the immune response. The observed immune response was larger compared with the use of oligonucleotides alone [84]. |
| IFN-β | Interferon-beta reduces myeloid dendritic concentrations in peripheral blood. It also alters the function of dendritic cells and other APCs to downregulate antigen presentation and the ability of APCs to stimulate T cell responses [85]. | IFN-β was found to increase the sensitivity of NB cells to the cytotoxic effects of the chemotherapy drug temozolomide (TMZ) through the mitigation of DNA repair enzyme (MGMT) expression [86]. |
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/ijms24108470
This entry is offline, you can click here to edit this entry!
