Sigma-1 and sigma-2 receptor have different pharmacological profiles. In the past two decades, the biological and pharmacological properties of the sigma-1 receptor has been well studied, however, little is known about the sigma-2 receptor. The molecular identity of Sigma-2 receptor has been proposed as TMEM97, but more work has to been done to address questions regarding our current knowledge of Sigma-2 pharmacology. Recently, the sigma-2 receptor is recognized as a novel regulator influencing cellular cholesterol homeostasis. Additionally, cholesterol homeostasis was disrupted in tumors and Alzheimer’s disease, and the sigma-2 receptor ligands have showed promise to treat tumors and AD.
- Sigma-2 receptor
- Cholesterol
- Alzheimer's Disease
Note:All the information in this draft can be edited by authors. And the entry will be online only after authors edit and submit it.
1. Introduction
The sigma receptors were identified in 1976 and initially recognized as a member of the opiate receptors; later studies revealed that they were different receptors [1]. The sigma receptors were classified into sigma-1 and sigma-2 receptors based on their different pharmacological profiles [2]. The sigma-1 receptor acts as a molecular chaperon and primarily localizes at the mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membrane (MAM) [3]. Upon stimulation by its ligands, the sigma-1 receptor translocates from MAM to plasma membrane (PM) [3], where it interacts with ion channels and G protein coupled receptors (GPCRs). The sigma-1 receptor plays important roles in many CNS diseases including drug addiction, depression, schizophrenia, Parkinson’s disease (PD), and Alzheimer’s disease (AD) [4][5][6][7][4–7]. The structure of the sigma-1 receptor has been recently reported, which exists as a trimer with one single transmembrane topology for each protomer [8]. In contrast, the molecular identity of the sigma-2 receptor was only recently revealed [9]. In 2006, Colabufo et al. proposed that sigma-2 receptors are histone proteins, since a specific sigma-2 ligand PB28 could pull down histone proteins [10]. However, this hypothesis was discarded. It showed that fluorescent ligands of the sigma-2 receptor are not found in the nucleus, which was not consistent with this histone hypothesis [11].
1.1. PGRMC1/Sigma-2 Receptor
In 2011, Xu et al. identified the sigma-2 receptor as a component of the progesterone receptor membrane component 1 (PGRMC1), because PGRMC1 could directly link to WC-21, which is a photoaffinity ligand for the sigma-2 receptor. PGRMC1 knockdown cells abolished this ligand binding to the sigma-2 receptor, while PGRMC1 overexpression increased the interaction between ligand and sigma-2 receptor [12].
However, later-accumulated evidence has suggested that the sigma-2 receptor is distinct from PGRMC1 [13]. The knockdown of PGRMC1 using siRNA or the overexpression of this protein using its cDNA in MCF7 cells did not alter the binding of [3H]-1,3 di-ortho-tolylguanidine ([3H]-DTG)to the sigma-2 receptor [14]. Knocking out PGRMC1 using CRISPR/Cas9 techniques in NSC34 cells also drew the same conclusion [15]. Furthermore, the molecular size of PGRMC1 is different from that of the sigma-2 receptor. Using photoaffinity labeling technique, the labeling with [3H] DTG in rat livers reveals that the sigma-2 receptor is about 21.5 kDa, while the molecular size of PGRMC1 is 25 kDa [16]. In addition, the sigma-2 receptor could still be detected by the photolabeling using [125I]-iodoazido-fenpropimorph ([125I]-IAF) in the PGRMC1 knockout cells [14]. Fluorescent sigma-2 ligands still have ability to bind to their receptor without the expression of PGRMC1 [17].
1.2. TMEM97/Sigma-2 Receptor
Recently transmembrane protein 97 (TMEM97) was identified as a sigma-2 receptor identity using mass spectrometry after affinity purification from the liver [9]. TMEM97 is an ER-resident transmembrane protein, also known as meningioma-associated protein (MAC30) [18]. The reduction in TMEM97 expression using siRNA decreased the binding of the sigma-2 receptor to its ligand [3H] DTG. In addition, the overexpression of TMEM97 in cells lacking the sigma-2 receptor demonstrated a similar sigma-2 receptor binding profile. The affinity of ligands for TMEM97 is identical to the sigma-2 receptor binding affinity [9]. Moreover, TMEM97 ligands bind sigma-2 receptors: Asp29 and Asp56 are identified as ligand binding sites [9].
TMEM97 is expressed in many cell types and play important functions in neurons and cancer cells [19][20][21][22][19–22]. It has been shown that TMEM97 is involved in alcohol withdrawal behaviors. JVW-1034 (a TMEM97 ligand) prevented withdrawal-induced behavioral impairments in worms and blunted withdrawal-induced excessive alcohol drinking in rats [21]. TMEM97 is also involved in neuropathic pain: the TMEM97 receptor agonist, UKH-1114, reduces mechanical hypersensitivity in an animal model of neuropathic pain [20]. CM398, a selective sigma-2 ligand, also showed anti-inflammatory analgesic effects in formalin model of inflammatory pain in mice [23]. Further, the activation of the sigma-2 receptor is neuroprotective: a novel sigma-2 receptor/TMEM97 modulator, DKR-1677, protects neurons from death and cognitive impairment after blast-mediated traumatic brain injury (TBI) [22]. Additionally several compounds with sigma-1/sigma-2 mixed selectivity were able to counteract the neurotoxicity induced by oxidative stress [24]. These evidences indicate that the sigma-2 receptor/TMEM97 may be a promising target for the treatment of neurological diseases. TMEM97 is also involved in cancer: its agonist, PB221, significantly inhibited the migration and invasion of ALTS1C1 cells (a murine brain tumor cell line). In addition, a high dose of PB221 induced cell death of ALTS1C1 cells; these effects all involved mitochondrial oxidative stress. Consistent with this notion, PB221 effectively retarded tumor growth in tumor models [19]. Using CRISPR/Cas9 technology to remove TMEM97 in HeLa cells, one recent study has found that TMEM97 does not mediate cytotoxicity induced by the sigma-2 ligand [25]. It is possible that this cytotoxicity might be caused by sigma-2-ligand-induced lysosomal dysfunction and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, but whether it relies on sigma-2 receptor remains unstudied.
1.3. The Complex of Sigma-2 Receptors
In fact, TMEM97/sigma-2 receptor forms a trimeric complex with PGRMC1 and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor (LDLR), which is responsible for the efficient uptake of LDL into the cells [26]. This complex is also necessary for the internalization of apolipoprotein E (ApoE) and Aβ monomers and oligomers [27]. These findings explain why PGRMC1 could be still photoaffinity tagged with a sigma-2 ligand, although PGRMC1 is not the sigma-2 receptor [12].
Consistently the activation of TMEM97 by its ligands could affect PGRMC1-dependent cell processes [21][28][21,28]. For example, JVW-1034 reduces withdrawal-induced impairments in ethanol-treated worms via PGRMC1/VEM-1 (a PGRMC1 ortholog in worms), although whether JVW-1034 binds directly to PGRMC1 is not studied [21]. The Sigma-2/TMEM97 ligand, SAS-0132, modulates PGRMC1-dependent mechanisms to reduce cell death, cognitive deficits, and neuroinflammation in AD mice [28].
2. Sigma-2 Receptor—A Novel Regulator of Cholesterol Homeostasis
2.1. Cholesterol Synthesis
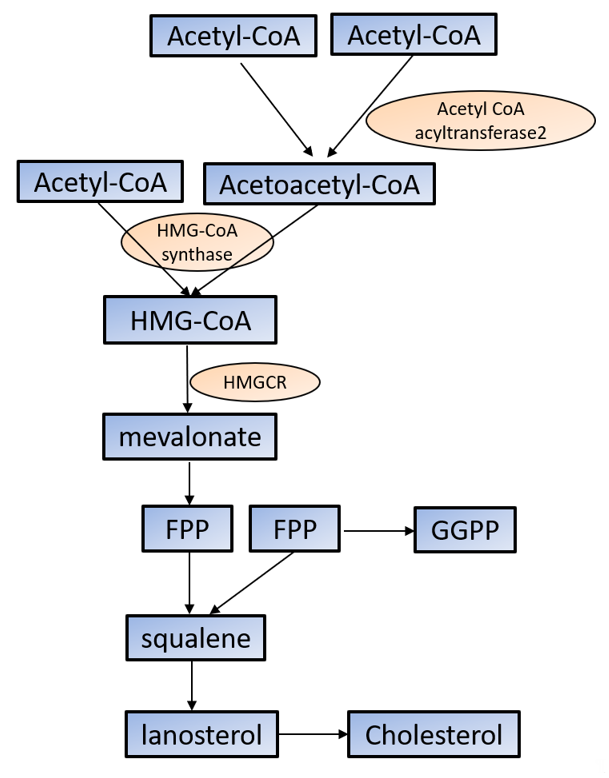
Cholesterol is required for not only membrane integrity and fluidity but also the production of hormones including steroids and vitamins [29][30][45,46]. Cholesterol biosynthesis begins with acetyl-CoA in the cytoplasm. Acetoacetyl-CoA is produced from two acetyl-CoA using acetyl-CoA acyltransferase 2 and then reacts with the third acetyl-CoA by the HMG-CoA synthase to produce 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA). HMG-CoA reductase (HMGCR) reduces HMG-CoA to mevalonate, which is the primary rate-limiting step in cholesterol synthesis [29][30][45,46]. Mevalonate is converted to farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP) by a series of enzymatic reactions, then two FPPs are condensed to squalene, which commits to sterol production. Most of squalene is converted to lanosterol, and through several additional enzymatic reactions, lanosterol is converted to cholesterol. FPP is also converted to geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP); both FPP and GGPP modify oncogenic proteins, such as Ras, via enzymatic prenylation and activate them [29][30][45,46] (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Cholesterol synthesis in the cytoplasm. Cholesterol biosynthesis begins with acetyl-CoA. See the text for the detailed information. HMG-CoA: 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA; HMGCR: HMG-CoA reductase; FPP: farnesyl pyrophosphate; GGPP: geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate.
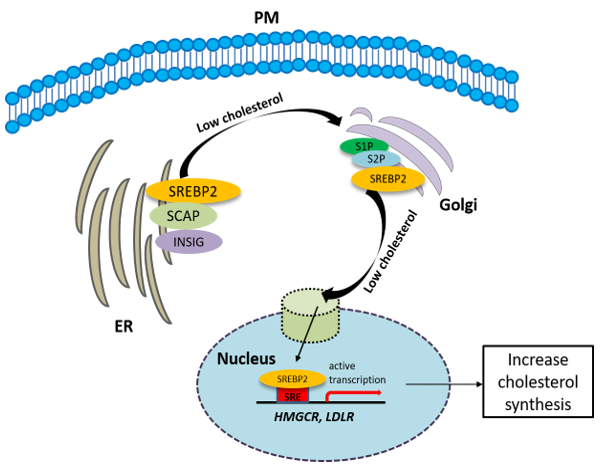
The synthesis of cholesterol is regulated by feedback control involving sterol regulatory element-binding protein 2 (SREBP2). SREBP is an ER membrane-bound protein, where it interacts with SREBP cleavage-activating protein (SCAP) [31][47]. When the sterol level at the ER is low, the conformation of SCAP is changed, allowing SREBP2 to translocate from the ER to the Golgi. At the Golgi, SREBP2 undergoes two sequential cleavages by site 1 protease (S1P) and site 2 protease (S2P), liberating the active soluble fragment of SREBP2 from the membrane. The processed SREBP2 enters the nucleus and increases expressions of many genes involving sterol biosynthetic pathway including HMGCR. Conversely the accumulation of cholesterol in the ER inactivates the SREBP2 pathway via insulin-induced genes (INSIGs). INSIGs interact with SCAP and promote the ER retention of SCAP, which blocks the ER-to-Golgi transportation of SREBP2 and reduces cholesterol biosynthesis [31][47] (Figure 2). In addition to SREBP2, liver X receptors (LXRs) [32][33][48,49] and nuclear factor erythroid 2 related factor-1 (NRF1) [34][50] are also involved in the regulation of cholesterol synthesis. High cholesterol levels activate LXRs, resulting in cholesterol synthesis inhibition [32][33][48,49].
Figure 2. The synthesis of cholesterol is regulated by feedback control involving sterol regulatory element-binding protein 2 (SREBP2). See the text for the detailed information.
2.2. Cholesterol Transport
In addition to de novo cholesterol synthesis, cells can acquire cholesterol from an external source. Cholesterol can be obtained from LDL, which is the major cholesterol-carrier in the blood via the clathrin-mediated endocytosis of LDLR. In the brain, neurons acquire their cholesterol mainly from apolipoprotein E (ApoE), the major lipoprotein in the CNS, via multiple ApoE receptors including LDLR, LDLR-related protein 1 (LRP1), and the very-low-density lipoprotein receptor (VLDLR) [35][51]. Once in the late endosomes/lysosomes in the cytosol, LDL is released from LDLR, then LDLR is recycled back to the cell surface, while LDL is degraded in the lysosome, and cholesterol is released. When the cell’s cholesterol demand is no longer high, proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) is secreted, which directs LDLR to the lysosome for degradation [36][37][52,53]. After cholesterol is released, it is then transported to the destined membranes to meet the need of cells [38][54]. When intracellular cholesterol is in excess, it is either exported out of cells by ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters including ABCA1 and ABCG1 or becomes esterified to form cholesteryl esters (CE) by acyl-coenzyme A: cholesterol acyltransferases (ACATs) [29][45]. Extracellularly high-density lipoproteins (HDL) remove excess cholesterol from tissues to the liver through reverse cholesterol transport (RCT), where it is subsequently eliminated with bile [39][55].
Cholesterol can also be oxidized via enzymatic or non-enzymatic reactions to produce oxysterols [40][56]. Cholesterol yields 7-ketocholesterol (7KC) and 7β-hydroxycholesterol (7βHC) by autoxidation, which does not need the help of enzymes. Other oxysterols are produced enzymatically by members of the cytochrome P450 family; for example, 25-hydroxycholesterol (25-HC) is produced by cholesterol 25-hydroxylase (CH25H), 24-hydroxycholesterol (24-HC) by CYP46A1, and 27-hydroxycholesterol (27-HC) by CYP27A1, respectively [41][57]. These oxysterols could act as ligands to activate LXRs, which regulate lipid metabolism and efflux [42][58]. In addition, oxysterols also have roles in immunity and inflammation. In particular, oxysterols, such as 25-HC, have been shown to have both pro- and anti-inflammatory effects on immune response. On the one hand, it can act as a signaling molecule to amplify inflammatory activation in macrophages [43][59]: 25-HC increases the production of many pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokine including IL-6 and IL-8 [44][60]. On the other hand, the production of 25-HC can prevent absent in melanoma 2 (AIM2) inflammasome activation in macrophages [45][61]. In conclusion, the roles of 25-HC in inflammation is quite complex, and further studies are strongly required.
Lipoprotein LDL can also be modified by oxidation. This modified LDL (oxLDL) is a ligand for Toll-like receptors (TLRs) in macrophages, which directly activates pro-inflammatory signaling pathways [46][62]. Further, macrophages also engulf oxLDL and cause the accumulation of cellular cholesterol in macrophages, resulting in the amplification of TLR signaling [47][48][63,64].
2.3. The Involvement of the Sigma-2 Receptor in Cholesterol Homeostasis
Substantial evidence has shown that the sigma-2 receptor/TMEM97 is involved in the synthesis of cholesterol. It was reported that, after treatment with progesterone, TMEM97 and cholesterol biosynthesis genes are coordinately upregulated in normal ovarian surface epithelial cells [49][65]. TMEM97 shares EXPERA functional domain with other cholesterol-related genes including transmembrane 6 superfamily member 2 (TM6SF) and emopamil binding protein (EBP) [18], implicating that TMEM97 is a cholesterol synthesis gene. Consistently, using an RNAi screening technique, TMEM97 was identified as a regulator of cholesterol homeostasis. The knockdown of TMEM97 reduced cholesterol contents as well as the internalization of LDLR. Furthermore, under sterol-depleted conditions, TMEM97 mRNA is upregulated, indicating TMEM97 plays a very important role in the regulation of cholesterol homeostasis [50][66].
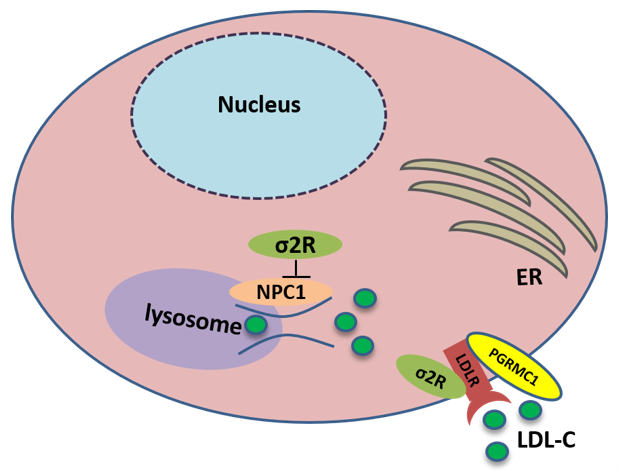
TMEM97 also controls the trafficking of cholesterol. TMEM97 could form a trimeric complex with PGRMC1 and LDLR and mediate cholesterol uptake via its interaction with PGRMC1 and LDLR: the loss or inhibition of either one of these proteins results in a decreased uptake of cholesterol [26]. In addition, TMEM97 is a Niemann-Pick C1 (NPC1) binding protein, which is required for transporting cholesterol out of lysosomes [50][66]. The loss of this protein results in NPC, a fatal lysosomal storage disorder. In NPC cellular model, TMEM97 knockdown upregulates NPC1 expression, reduces cholesterol accumulation, and restores the trafficking of cholesterol out of the lysosome [51][67] (Figure 3).
Figure 3. Sigma-2 receptor controls the trafficking of cholesterol. TMEM97 forms a trimeric complex with progesterone receptor membrane component 1 (PGRMC1) and low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR), which is responsible for the internalization of LDL. In addition, TMEM97 is a Niemann-Pick C1 (NPC1) binding protein and controls the trafficking of cholesterol out of lysosomes.
References
- Walker, J.M.; Bowen, W.D.; Walker, F.O.; Matsumoto, R.R.; De Costa, B.; Rice, K.C. Sigma receptors: Biology and function. Rev. 1990, 42, 355–402.
- Hellewell, S.B.; Bowen, W.D. A sigma-like binding site in rat pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells: Decreased affinity for (+)-benzomorphans and lower molecular weight suggest a different sigma receptor form from that of guinea pig brain. Brain Res. 1990, 527, 244–253, doi:10.1016/0006-8993(90)91143-5.
- Hayashi, T.; Su, T.P. Sigma-1 receptor chaperones at the ER-mitochondrion interface regulate Ca(2+) signaling and cell survival. Cell 2007, 131, 596–610, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.08.036.
- Aguinaga, D.; Casanovas, M.; Rivas-Santisteban, R.; Reyes-Resina, I.; Navarro, G.; Franco, R. The sigma-1 receptor as key common factor in cocaine and food-seeking behaviors. Mol. Endocrinol. 2019, 63, R81–R92, doi:10.1530/JME-19-0138.
- Hashimoto, K. Activation of sigma-1 receptor chaperone in the treatment of neuropsychiatric diseases and its clinical implication. Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 127, 6–9, doi:10.1016/j.jphs.2014.11.010.
- Ryskamp, D.A.; Korban, S.; Zhemkov, V.; Kraskovskaya, N.; Bezprozvanny, I. Neuronal Sigma-1 Receptors: Signaling Functions and Protective Roles in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 862, doi:10.3389/fnins.2019.00862.
- Yang, K.; Wang, C.; Sun, T. The Roles of Intracellular Chaperone Proteins, Sigma Receptors, in Parkinson’s Disease (PD) and Major Depressive Disorder (MDD). Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 528, doi:10.3389/fphar.2019.00528.
- Schmidt, H.R.; Zheng, S.; Gurpinar, E.; Koehl, A.; Manglik, A.; Kruse, A.C. Crystal structure of the human sigma1 receptor. Nature 2016, 532, 527–530, doi:10.1038/nature17391.
- Alon, A.; Schmidt, H.R.; Wood, M.D.; Sahn, J.J.; Martin, S.F.; Kruse, A.C. Identification of the gene that codes for the sigma2 receptor. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 7160–7165, doi:10.1073/pnas.1705154114.
- Colabufo, N.A.; Berardi, F.; Abate, C.; Contino, M.; Niso, M.; Perrone, R. Is the sigma2 receptor a histone binding protein? Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 4153–4158, doi:10.1021/jm0600592.
- Zeng, C.; Vangveravong, S.; Jones, L.A.; Hyrc, K.; Chang, K.C.; Xu, J.; Rothfuss, J.M.; Goldberg, M.P.; Hotchkiss, R.S.; Mach, R.H. Characterization and evaluation of two novel fluorescent sigma-2 receptor ligands as proliferation probes. Imaging 2011, 10, 420–433.
- Xu, J.; Zeng, C.; Chu, W.; Pan, F.; Rothfuss, J.M.; Zhang, F.; Tu, Z.; Zhou, D.; Zeng, D.; Vangveravong, S.; et al. Identification of the PGRMC1 protein complex as the putative sigma-2 receptor binding site. Commun. 2011, 2, 380, doi:10.1038/ncomms1386.
- Hiranita, T. Identification of the Sigma-2 Receptor: Distinct from the Progesterone Receptor Membrane Component 1 (PGRMC1). Alcohol. Drug Depend. 2016, 4, 1–7, doi:10.4172/2329-6488.1000e130.
- Abate, C.; Niso, M.; Infantino, V.; Menga, A.; Berardi, F. Elements in support of the ‘non-identity’ of the PGRMC1 protein with the sigma2 receptor. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 758, 16–23, doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.03.067.
- Chu, U.B.; Mavlyutov, T.A.; Chu, M.L.; Yang, H.; Schulman, A.; Mesangeau, C.; McCurdy, C.R.; Guo, L.W.; Ruoho, A.E. The Sigma-2 Receptor and Progesterone Receptor Membrane Component 1 are Different Binding Sites Derived From Independent Genes. EBioMedicine 2015, 2, 1806–1813, doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2015.10.017.
- Hellewell, S.B.; Bruce, A.; Feinstein, G.; Orringer, J.; Williams, W.; Bowen, W.D. Rat liver and kidney contain high densities of sigma 1 and sigma 2 receptors: Characterization by ligand binding and photoaffinity labeling. J. Pharmacol. 1994, 268, 9–18, doi:10.1016/0922-4106(94)90115-5.
- Pati, M.L.; Groza, D.; Riganti, C.; Kopecka, J.; Niso, M.; Berardi, F.; Hager, S.; Heffeter, P.; Hirai, M.; Tsugawa, H.; et al. Sigma-2 receptor and progesterone receptor membrane component 1 (PGRMC1) are two different proteins: Proofs by fluorescent labeling and binding of sigma-2 receptor ligands to PGRMC1. Res. 2017, 117, 67–74, doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2016.12.023.
- Sanchez-Pulido, L.; Ponting, C.P. TM6SF2 and MAC30, new enzyme homologs in sterol metabolism and common metabolic disease. Genet. 2014, 5, 439, doi:10.3389/fgene.2014.00439.
- Liu, C.C.; Yu, C.F.; Wang, S.C.; Li, H.Y.; Lin, C.M.; Wang, H.H.; Abate, C.; Chiang, C.S. Sigma-2 receptor/TMEM97 agonist PB221 as an alternative drug for brain tumor. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 473, doi:10.1186/s12885-019-5700-7.
- Sahn, J.J.; Mejia, G.L.; Ray, P.R.; Martin, S.F.; Price, T.J. Sigma 2 Receptor/Tmem97 Agonists Produce Long Lasting Antineuropathic Pain Effects in Mice. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2017, 8, 1801–1811, doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.7b00200.
- Scott, L.L.; Sahn, J.J.; Ferragud, A.; Yen, R.C.; Satarasinghe, P.N.; Wood, M.D.; Hodges, T.R.; Shi, T.; Prakash, B.A.; Friese, K.M.; et al. Small molecule modulators of sigma2R/Tmem97 reduce alcohol withdrawal-induced behaviors. Neuropsychopharmacology 2018, 43, 1867–1875, doi:10.1038/s41386-018-0067-z.
- Vazquez-Rosa, E.; Watson, M.R.; Sahn, J.J.; Hodges, T.R.; Schroeder, R.E.; Cintron-Perez, C.J.; Shin, M.K.; Yin, T.C.; Emery, J.L.; Martin, S.F.; et al. Neuroprotective Efficacy of a Sigma 2 Receptor/TMEM97 Modulator (DKR-1677) after Traumatic Brain Injury. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 1595–1602, doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.8b00543.
- Intagliata, S.; Sharma, A.; King, T.I.; Mesangeau, C.; Seminerio, M.; Chin, F.T.; Wilson, L.L.; Matsumoto, R.R.; McLaughlin, J.P.; Avery, B.A.; et al. Discovery of a Highly Selective Sigma-2 Receptor Ligand, 1-(4-(6,7-Dimethoxy-3,4-dihydroisoquinolin-2(1H)-yl)butyl)-3-methyl-1H-benzo[d]im idazol-2(3H)-one (CM398), with Drug-Like Properties and Antinociceptive Effects In Vivo. AAPS J. 2020, 22, 94, doi:10.1208/s12248-020-00472-x.
- Franchini, S.; Linciano, P.; Puja, G.; Tait, A.; Borsari, C.; Denora, N.; Iacobazzi, R.M.; Brasili, L.; Sorbi, C. Novel Dithiolane-Based Ligands Combining Sigma and NMDA Receptor Interactions as Potential Neuroprotective Agents. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 1028–1034, doi:10.1021/acsmedchemlett.0c00129.
- Zeng, C.; Weng, C.C.; Schneider, M.E., Jr.; Puentes, L.; Riad, A.; Xu, K.; Makvandi, M.; Jin, L.; Hawkins, W.G.; Mach, R.H. TMEM97 and PGRMC1 do not mediate sigma-2 ligand-induced cell death. Cell Death Discov. 2019, 5, 58, doi:10.1038/s41420-019-0141-2.
- Riad, A.; Zeng, C.; Weng, C.C.; Winters, H.; Xu, K.; Makvandi, M.; Metz, T.; Carlin, S.; Mach, R.H. Sigma-2 Receptor/TMEM97 and PGRMC-1 Increase the Rate of Internalization of LDL by LDL Receptor through the Formation of a Ternary Complex. Rep. 2018, 8, 16845, doi:10.1038/s41598-018-35430-3.
- Riad, A.; Lengyel-Zhand, Z.; Zeng, C.; Weng, C.C.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Mach, R.H. The Sigma-2 Receptor/TMEM97, PGRMC1, and LDL Receptor Complex Are Responsible for the Cellular Uptake of Abeta42 and Its Protein Aggregates. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 3803–3813, doi:10.1007/s12035-020-01988-1.
- Yi, B.; Sahn, J.J.; Ardestani, P.M.; Evans, A.K.; Scott, L.L.; Chan, J.Z.; Iyer, S.; Crisp, A.; Zuniga, G.; Pierce, J.T.; et al. Small molecule modulator of sigma 2 receptor is neuroprotective and reduces cognitive deficits and neuroinflammation in experimental models of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem. 2017, 140, 561–575, doi:10.1111/jnc.13917.