1. Phytochemicals of Essential Oil
Plants from the
Lavandula genus are valuable raw materials for cosmetics and perfumes as well as aromatherapy and household products. Their essential oils are especially valued and most research on lavender phytochemicals is related to this material. Lavender essential oils are usually produced through steam distillation or hydrodistillation of fresh or dried flowering tops gathered during the flowering season. As previously stated,
L. × intermedia is a particularly important lavender crop for the essential oil industry due to its higher yield as opposed to
L. angustifolia [1][2][14,55]. The EO content in LI plant material has been analyzed multiple times. Various parts of the plants were analyzed, such as fresh and dried flowers, flowering tops, and dried leaves (
Table 14). The percentage of oil content in fresh flowers from different world regions ranged from 0.9% to 3.3%. In dried flowers, the oil yield was higher and varied from 3.6% to 9.9%, except for Spain with reported lower yields (1.3% or lower)
[2][3][4][5][6][7][8][9][2,6,55,59,60,61,62,63]. Kaloustian et al.
[9][63], and Bajalan and Pirbalouti
[10][16], analyzed the yield of essential oil produced from dried leaves and found that this part of the plant contains significantly less oil than the flowering parts (0.4–1.5%). A comparison of the EO content in LI plant material shows that the oil content is significantly higher than in
L. angustifolia. As reported by Walasek-Janusz et al.
[11][64], the oil yield of lavandin grown in Poland was 4.4–8.1%, whereas the yield of LA was only 3.1–3.6%.
Table 14.
L. × intermedia
essential oil yield from different plant materials.
‘Abrial’ essential oil compositions from different countries.
Even though
L. × intermedia is native to the Mediterranean area, lavandin is cultivated in many places and oils from different world regions have been obtained and analyzed, e.g., Spain
[2][17][55,70], France
[18][19][71,72], Australia
[20][73], Norway
[7][61], Turkey
[1][8][16][14,62,69], Greece
[6][60], United Kingdom
[21][74], Italy
[22][23][75,76], Croatia
[5][59], USA
[24][77], Romania
[25][78] and Iran
[10][16]. Many different cultivars of this plant have already been investigated. However, the cultivars ‘Grosso’, ‘Abrial’, ‘Provence’, and ‘Super’ are the most popular, best-known, and studied. Regardless of the plant cultivar or origin, over the years, more than 100 different volatile organic compounds have been identified in
L. × intermedia oil
[1][2][7][10][16][17][18][19][20][24][26][14,16,55,61,69,70,71,72,73,77,79].
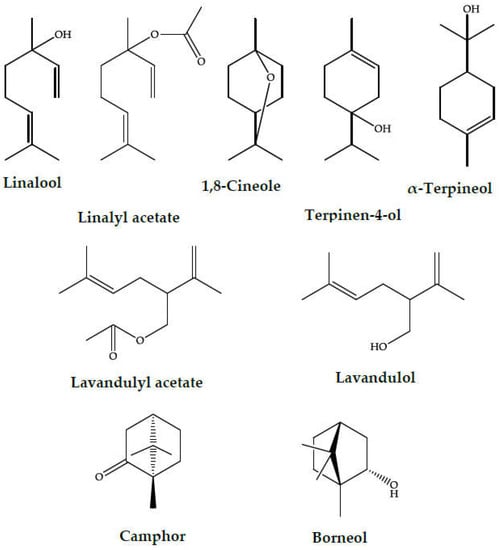
Lavandin essential oil, similar to the oils from the parent species—LA and LL, is characterized by a high content of polar terpenoids, especially oxygenated monoterpenes. 1,8-Cineole, linalool, camphor, borneol, terpinene-4-ol, linalyl acetate, lavandulol, and lavandulyl acetate are the most characteristic compounds in these oils (the structures are given in
Figure 14). Other compounds, such as monoterpene and sesquiterpene hydrocarbons were also present, e.g., α-and β-pinene, myrcene, sabinene, 3-carene, α-terpinene, α-santalene, germacrene D, (E)-β-caryophyllene, and trans-α-bergamotene, but the levels of these compounds were much lower than those of the polar constituents. The most abundant components of LI essential oils are linalool and linalyl acetate, which can occur from a few percent to exceeding 50%, but usually over 20%. The presence of high levels of linalool and linalyl acetate is desirable because it results in a more pleasant floral aroma and desired pharmaceutical quality. Other dominant terpenoids found in lavandin EO include camphor (ranging from 2–33%, but most frequently occurring at levels from 5–10%), borneol (1–26%, typically a few percent), and 1,8-cineole (2–49%, usually a few percent). Additionally, significant volatile compounds in the EO include terpinen-4-ol (0.4–16%) and α-terpineol (2–10%), which typically contribute up to 5% of the EO. LI essential oil also contains characteristic terpenoids: lavandulol and its ester, lavandulyl acetate. These are present in the EO at levels ranging from a fraction of a percent to 3%. As with linalool-linalyl acetate, the presence of lavandulol and lavandulyl acetate is desirable as it gives the oil a beneficial herbal-rosy scent
[3][4][2,6].
Figure 14.
The characteristic monoterpenoids in lavandin essential oil.
The essential oil composition of plants of the same species varies due to different factors such as the place of cultivation, weather conditions, harvesting time, etc. The plant variety or cultivar is considered one of the most prominent factors in essential oil chemistry
[27][28][29][4,23,80]. The chemical composition of EO produced from the most popular lavandin cultivars, such as ‘Super’, ‘Grosso’, and ‘Abrial’.
The qualitative composition of lavandin essential oil from different cultivars is comparable. Across all EOs analyzed, the same group of oxygenated compounds was dominant. The slight differences concerned the content of individual components. The EO of ‘Super’ (Table 2) revealed a higher content of 1,8-cineole (2.6–15.9%) and borneol (1.3–4.2%) than the ‘Grosso’ and ‘Abrial’ cultivars (Table 3 and Table 4) [2][7][18][19][20]. The ‘Super’ essential oil was also generally recognized as containing a high linalyl acetate percentage (35–37%) among the other cultivars, which also results in a scent that is more similar to that of L. angustifolia essential oil [4]. It should be noted that this is not an absolute principle, as the examination of Table 2 with examples of ‘Super’ EO compositions illustrates; this varies significantly depending on the location of cultivation.
Table 25. Exemplary L. × intermedia ‘Super’ essential oil compositions from different countries. Values over 3% are bolded (this rule also applies to the following tables concerning chemical composition).
Mill. ×
Lavandula latifolia Medik.), French type”
[38][87]. This is noteworthy, as lavandin EO dominates the lavender oil market. However, the lack of a general norm for lavandin EO is not necessarily detrimental. Despite being authentic, due to natural variability, some EOs obtained from lavender have a substantially different chemical profile and do not meet the specifications set by the standard-setting organizations. This would exclude many new or unique cultivars or new farmers from other than traditional countries and locations.
Table 58.
WHO and European pharmacopeia (Ph. Eur.) standards for a chromatographic profile of
Lavandula
sp. essential oils.
2. Phytochemicals of Other Lavandin Products
Essential oils are valued raw materials obtained through the process of steam distillation or hydrodistillation of plant material. The water byproduct of this process, known as hydrolate or hydrosol (H), is also considered a valuable product. From a chemical perspective, hydrolates are volatile organic compounds, mainly polar oxygenated mono- and sesquiterpenes, dispersed in an aqueous phase. They are used as ingredients in the cosmetic and beverage industry
[39][40][41][42][88,89,90,91]. The chemical composition of
L. × intermedia hydrolates has been investigated multiple times.
Table 69 presents the exemplary summarized test results.
Table 69.
Exemplary
L. × intermedia
hydrolate compositions (and their corresponding EOs) from different countries.
Table 36.
Exemplary
L. × intermedia
‘Grosso’ essential oil compositions from different countries.
Table 47.
Exemplary
L. × intermedia
The
qualitative
s composition of lavandin essential oil
s produced fr from different cultivars is comparable. Across all EOs analyzed, the same group of oxygenated compounds was dominant. The slight differences concerned the content of individual components. The EO of ‘Super’ (Table 5) revealed a higher co
ntent of 1,8-cineole (2.6–15.9%) and borneol (1.3–4.2%) than the ‘Grosso’ and ‘Abrial’ cultivars (Table 6 and Table 7) [55,61,71,72,73]. The ‘Super’ essential oil was also generally recognized as containing a high linalyl acetate percentage (35–37%) am
ong the
other cultivars, which also results in a scent that is more similar to that of L. angustifolia essential oil [6]. It should be noted that this is not an absolute principle, as the examination of Table 5 with examples of ‘
Super’ EO compositions illustrates; this varies significantly depending on the location of cultivation.The essential oils produced from the ‘Grosso’ cultivar (
Table 36) are relatively richer in linalool (22.5–51.3%), terpinen-4-ol (1.5–5.3%), camphor (6.0–12.2%), and lavandulyl acetate (1.5–3.5%)
[2][7][18][19][20][55,61,71,72,73].
Table 47 presents the qualitative and quantitative composition of the ‘Abrial’ cultivar, which revealed the highest content of camphor, relatively, than the other two varieties. The content of the other main ingredients in ‘Abrial’ EO was in the middle range, between the other two cultivars.
As seen in Table 25, Table 36 and Table 47, individual chemical compositions provided by various authors differ in detail. Some authors provide a more detailed analysis and also present minor components. Other authors do not investigate the content of minor terpenes. Key components are commonly thought to be the main compounds responsible for the EO’s biological effects. However, even minor components can contribute to the activity. They could be neutral or interact with other constituents, to produce either synergistic or antagonistic effects.
The chemical composition of
L. × intermedia EO is similar in nature to that of
L. angustifolia and
L. latifolia. However, some quantitative differences in the concentrations of the key components are observed. Lavandin essential oil contains a similar or slightly lower content of linalool and linalyl acetate than true lavender, but it contains a significantly higher level of 1,8-cineole, camphor, and borneol
[1][2][3][6][18][19][20][30][2,14,55,60,71,72,73,81]. These monoterpenoids are camphoraceous, resulting in sharper notes in the LI aroma and reduced value in the perfume industry when compared to true lavender oil. On the other hand, an LI oil richer in camphor can be beneficial in aromatherapy. When comparing LI essential oil to the second parent species—LL, it has significantly less 1,8-cineole, less or similar quantities of camphor, and much more linalyl acetate
[3][4][2,6].
True lavender and lavandin essential oils have a similar chemical composition and corresponding aromas. On the other hand, due to the divergent productivity of the plants, they differ significantly in price—lavandin EO is several times cheaper. Therefore, it is often used as a replacement for true lavender oil or even used to adulterate it
[3][31][32][2,7,9]. The oil adulterations along with the natural variability of the chemical compositions of the oils pose a significant challenge when performing replicable scientific research on lavender oils, their reliable and safe applications, and the whole essential oil industry. To address these challenges, various industry standards have been established. The most recognized are the standards of the European Pharmacopeia (Ph. Eur.) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
Table 58 presents the existing specification for the chromatographic profile of different lavender oils (the ISO ranges are not presented due to copyright issues). As opposed to spike or true lavender oil, lavandin EO is not considered a pharmacopeial material. There is no specification in the Ph. Eur. for the oil of
L. × intermedia [33][82]. Inconsistent with the entries in the Ph. Eur., the World Health Organization (WHO) monographs on selected medicinal plants define lavender oil (
aetheroleum lavandulae) as essential oil obtained by steam distillation from the fresh flowering tops of
L. angustifolia Mill. or of
L. × intermedia [34][83]. In this context, the WHO has a different approach compared to other regulating bodies, as it permits the use of lavandin as a source of lavender oil and establishes one common specification. The ISO 3515:2002 standard specifies more terpenes in the chromatographic profile of LA oils
[35][84]. It also gives different acceptable ranges for components from different oil origins. These ranges vary depending on the origin and sometimes they exclude each other, which suggests that compliance with the standard does not determine the quality of the oil, but regulates and gives guidelines for the producers of the main oil-producing countries. The ISO also established a general norm for
L. latifolia—ISO 4719:2012
[36][85]. However, it did not publish any overall norm for
L. × intermedia. Bastard lavender only received standards for two cultivars: ‘Grosso’ and ‘Abrial’, namely “ISO 8902:2009 Oil of lavandin Grosso (
Lavandula angustifolia Mill. ×
Lavandula latifolia Medik.), French type”
[37][86], and “ISO 3054:2017 Essential oil of lavandin Abrial (
Lavandula angustifoliaLinalool (19.0–68.5%), borneol (1.4–31.8%), 1,8-cineole (t–28.9%), camphor (0.8–17.5%), terpinen-4-ol (2.3–14.0%), and α-terpineol (1.8–9.0%), cis- and trans-linalool oxide (0.8–6.0% and 0.6–4.2%, respectively) were the major constituents identified in LI hydrolate. These components were also present in corresponding EOs. Quantitative differences in composition between these two products were observed. Lavandin hydrolates were significantly richer in alcohols, e.g., 1,8-cineole, linalool, borneol, terpinen-4-ol; ketones, such as camphor; and oxides, e.g., cis- and trans-linalool oxides. On the other hand, the content of esters, such as lavandulyl and linalyl acetate, was much lower than in corresponding essential oils, or these two compounds were even absent.
According to the literature, some relationships between essential oil and hydrolate produced in the same distillation process can be observed. When EO contains a lot of polar compounds (e.g., alcohol, diols, esters), the qualitative composition of EO and hydrolates is similar, but they differ in the levels of individual components. However, if the essential oil consists of predominately nonpolar constituents, as in the case of
Pinus silvestris L., significant qualitative differences between EO and H occur
[40][41][89,90]. The same relationship was observed for
L. × intermedia products. As it produces a relatively polar essential oil rich in oxygenated monoterpenes, the hydrolate contains similar constituents to the EO.
Most studies of the composition of lavandin have focused on the essential oil and hydrolate. However, some other secondary metabolites other than terpenoids were also investigated. Dobros et al.
[44][93] determined the presence of phenolic acids (rosmarinic acid, ferulic acid glucoside, caffeic acid, ellagic acid), flavonoids (morin, isoquercitrin, vanillin), and coumarins (herniarin and coumarin) in flower ethanolic macerates. The composition of phenolic acids, glucosides, and flavonoids in lavandin was consistent with the findings of Torras-Calveria et al.
[45][94] who analyzed essential oil distillation waste products. They found other phytochemicals, such as chlorogenic and rosmarinic acids, coumaric acid-
O-glucoside isomers, and 3,4,5-trihydroxycinnamic acid-
O-glucoside. The rosmarinic and chlorogenic acid content was 124 and 215 mg/100 g dry matter, respectively. Lavandin was found to have a higher content of coumarin than true lavender. However,
L. angustifolia flower extracts had higher concentrations of flavonoids and phenolic acids compared to lavandin
[44][93].