Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Shashi Kant Bhatia and Version 2 by Sirius Huang.
Microbial exopolysaccharides (EPSs), e.g., xanthan, dextran, gellan, curdlan, etc., have significant applications in several industries (pharma, food, textiles, petroleum, etc.) due to their biocompatibility, nontoxicity, and functional characteristics. Exopolysaccharides are produced by diverse microorganisms, including yeasts, fungi, and bacteria, utilizing various raw materials.
- biopolymers
- exopolysaccharides
- EPS composites
1. Introduction
Exopolysaccharides (EPSs) are natural biopolymers synthesized by microorganisms and are secreted for various respective functions, such as defense, biofilm formation, pathogenicity, structure, adhesion, etc. [1]. EPSs are long-chain biomolecules with molecular weights ranging from 10 to 30 kD, and are produced during the late exponential and or stationary phase of microbial growth. EPSs are produced in response to environmental stress conditions, such as pH and temperature, and exposure to heavy metals or inhibitors, etc. [2][3][2,3]. Biochemically, EPSs are carbohydrate polymers composed of glucose, galactose, and rhamnose, accompanied by non-carbohydrate moieties such as proteins, enzymes, nucleic acid, etc. The exact composition may vary with microorganisms and growth conditions.
Based on the biochemical structure and composition, EPSs can be categorized into homo-exopolysaccharides (HOEPSs) and hetero-exopolysaccharides (HEEPSs) [4]. HOEPSs are composed of one type of monosaccharide, such as α-D-glucans, β-D-glucans, fructans, and polygalactans, interlinked with α-1-6, α-1-3, β-1-2, β-1-3, β-2-6, and β-2-1 linkage among the subunits, depending upon the monomeric units. Dextran is one of the well-known examples of HOEPSs, which is made of glucose interlinked with α-1-6 glucoside linkage. In contrast, HEEPSs are comprised of different sugar monomers, along with their respective derivatives and non-carbohydrate moieties. Succinoglycan is one of HEEPSs present in bacterial biofilm. It is comprised of saccharide-based oligomers in which sugar molecules are derivatized with acyl, pyruvate, and succinic acid [4][5][6][4,5,6]. Both classes are further recognized as subgroups based on the dominant sugar residues [4]. In recent years, EPSs have gained wide attention for their cost-effective production and diverse applications as pharma and healthcare products, cosmeceutical, nutraceutical, functional food, and biocontrol agents in agriculture [7], oil recovery in petroleum industries [8], heavy metal removal [9], drug delivery, and tissue regeneration and repair [10]. Microbial exopolysaccharides have applications in various sectors, as depicted in Figure 1.
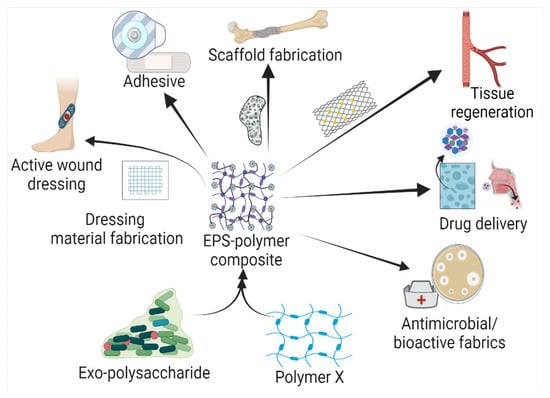
Figure 1.
Exopolysaccharide composites with natural and synthetic polymers and their application in the health sector.
2. Microbes Producing Exopolysaccharides
Exopolysaccharides are produced by diverse microorganisms, including yeasts, fungi, and bacteria, utilizing various raw materials (Figure 2). Besides the native physiological role, microbial EPSs also have diverse applications in many industries. Several efforts have been made by various researchers for the production of EPSs (Table 1). In comparison to yeasts and other fungi, probiotic bacteria are commonly used due to non-pathogenicity and categorization of generally regarded as safe (GRAS) [11][25]. It has been found that carbon source has a direct relation with EPS production and composition. A study on 20 strains of Lactobacillus paracasei revealed that with a change in carbon source, not only does EPS yield, but it also influences the monosaccharide composition. The yield of EPS was increased by 115% with optimized carbon sources, including fructose, glucose, galactose, lactose, mannose, and trehalose [12][26]. Among different carbon sources, including sucrose, maltose, lactose, glycerol, and sorbitol, maximum EPS production has been achieved with maltose by Candida guilliermondii and Candida famata (0.505 and 0.321, respectively) [13][27]. Among 156 lactic acid bacteria isolated from healthy young children’s feces, the maximum EPS production, i.e., 59.99 g/L, was reported from Weissella confusa VP30 after 48 h in growth media containing 10% sucrose [14][28].
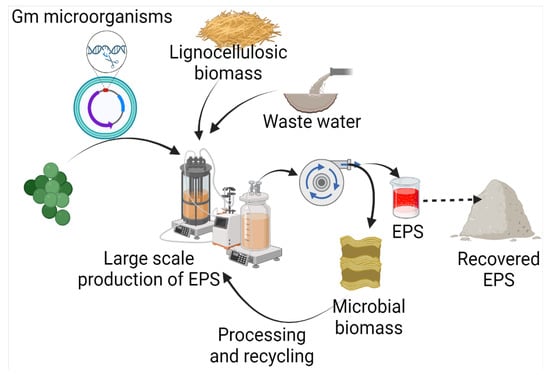
Figure 2.
Microbial production of EPS using waste, and its recovery.
The use of commercial-grade sugars/substrates has a direct impact on product cost, and is one of the factors responsible for high production costs. Hence low-cost waste materials, such as lignocellulosic residues and wastewater, are preferred as raw materials for EPS production. The carbohydrate and organic fractions present in the waste can be used by microorganisms. It opens up the opportunity to reduce product costs, along with waste management. Da Silva et al. [15][29] have compared coconut shells, cocoa husks, and sucrose for xanthan gum production by Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris IBSBF 1866 and 1867. The study revealed that xanthan gum yields were higher, i.e., 4.48 g/L and 3.89 g/L, in the case of cocoa husk by Xanthomonas strains 1866 and 1867, respectively, but the apparent viscosity was higher than sucrose, i.e., 181.88 mPas over cocoa husk, with a viscosity of 112.06 mPas.
Choi et al. [16][30] used spent media wastewater (originated from kimchi fermentation) for EPS production using Leuconostoc mesenteroides WiKim32. Under optimal conditions, the maximum EPS productivity was 7.7–9.0 g/L, with a conversion of 38.6–45.1%. The EPSs were nontoxic and exhibited thermal tolerance and antioxidant activity. Pan et al. [17][31] optimized dextran production from Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides XG5 using an L9 (33) orthogonal test. Under optimal conditions (sucrose 100 g/L, pH 7.0, 25 °C, at 100 rpm for 36 h), the maximum dextran yield of 26.02 g/L and 40.07 g/L were recorded at a laboratory scale and fed-batch fermentation, respectively. The EPS was also exhibiting water-holding capacity and antioxidant activity. It reduced the chewiness and hardness of yogurt, but the resilience increased during the 14 days of storage. Product cost is one of the main obstacles in commercialization, hence process economics is one of the major factors that must be assessed. Integration of multiple processes might improve process economics, as well as environmental adaptability. Sphingobium yanoikuyae was evaluated for the coproduction of EPS and polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) using lignocellulosic hydrolysate. Hydroxymethyl furfural (HMF), one of the hydrolysis byproducts, improved the consumption of glucose and xylose during fermentation. The optimum C/N ratio of 5 resulted in the maximum EPS production of 3.24 ± 0.05 g/L, however, a further increase in the C/N ratio (30) favored PHB accumulation (38.7 ± 0.08% w/w) [18][32]. Biomass hydrolysate is usually accompanied by phenolics, furfurals, and HMF, which also act as fermentation inhibitors and hinder microbial action. Some of the methods, including activated carbon-based adsorption and membrane filtration, have been proposed for hydrolysate detoxification [19][20][33,34]. Removal of inhibitors might improve microbial action and product yield. Bhatia et al. [18][32] have compared the potential of various raw and detoxified hydrolysates for EPS production. In comparison to raw hydrolysate, detoxified biomass hydrolysate showed increased EPS production and maximum EPS production was reported with detoxified pine biomass hydrolysate, i.e., 2.83 ± 0.03 g/L. Table 1 summarizes the recent efforts for EPS production using various microbes (yeasts, bacteria, and fungi), utilizing various pure carbon and organic waste materials.
Table 1.
Microbial production of EPS from various substrates.
| EPS | Organism | Substrate | Growth Conditions | Working Volume | EPS Yield | Key Achievements | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dextran (α-D-gluco pyranosyl moieties interlinked with α-(1,6) linkage and have α-(1,2)/α-(1,3)/α-(1,4) branching) 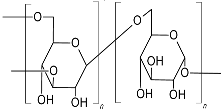 |
Leuconostoc mesenteroides SF3 | 10% sucrose | Temp 25 °C; pH 6; incubation period 16 h; inoculum 24 h old, 10% inoculum with cell concentration of 108 cells/mL. | 100 mL | 23.8 ± 4 g/L | Water absorption capacity 361.8% ± 3.1; oil absorption capacity 212.0% ± 6.7; emulsion activity 58.3% ± 0.7. | [21][35] |
| Lactobacillus spp. | 15% sucrose | Temp 30 °C; pH 7; incubation period 24 h; inoculum 24 h old 4%, growth conditions aerobic. | 100 mL | 5.8 mg/mL | Lactobacillus strains were isolated from the human vagina and infant stool. | [22][36] | |
| Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides DSM20193 | Brewers’ spent grain | Initial cell concentration 6.0 Log cfu/g; temp 25 °C; period 24 h. | 1000 g | 1.2 g/100 g | EPS production is accompanied by mannitol; no dextran production without a starter (commercial granulated sugar). | [23][37] | |
| Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides XG5 | 100 g/L sucrose | Temp 25 °C; pH 7.0; mixing rate 20 rpm; time period 60 h; inoculum 2%. | 35 L | 26.02 g/L dextran | Protein content in EPS reduced when extracted with EDTA or NaOH+formal-dehyde. | [17][31] | |
| Weissella confusa A16 | Brewers’ spent grain | Initial cell concentration 6.0 log cfu/g; temp 25 °C; period 24 h. | 1000 g | 1.1 g/100 g | No mannitol production was observed, but a starter was required for EPS production. | [23][37] | |
| Curdlan (Type HOEPS, unbranched; molecular weight 5.3 × 104–2 × 106 Da; components glucosyl residues inter-connected with β-D-(1→3) bonds) 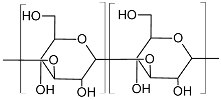 |
Agrobacterium sp. IFO 13140 | 50 g/L | Synthetic medium; temp 30 °C; mixing rate 150 rpm; period 5 d; pH 7. | 100 mL | - | Water holding capacity and oil holding capacity 64% and 98% higher in comparison to commercial curdlan. | [24][38] |
| Bacillus cereus PR3 | 10% starch | Synthetic medium; period 96 h. | 100 mL | 20.88 g/L | Anti-oxidant activity increased with curdlan. | [25][39] | |
| Agrobacterium sp. ATCC 31749 | Asparagus spear bottom part juice | Synthetic medium; temp 30 °C; mixing rate 200 rpm; period 168 h. | 100 mL | 40.2 g/L | Curdlan production is higher with sucrose in comparison to mineral salt. | [26][40] | |
| Xanthan (Type HEEPS; components backbone made of D-glucose unit linked with β-1,4-glycosidic bonds and side chain trisaccharide; side chain comprised of mannose, glucuronic acid, and mannose, terminal mannose with pyruvic acid residues; molecular weight 2.0 × 106–2.0 × 107 Da) 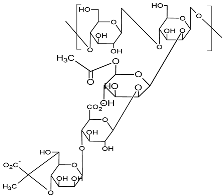 |
Xanthomonas campestris | 20 g/L glucose | Stainless steel supported biofilm reactor; period 27 h; synthetic medium; mixing rate 180 rpm. | 150 mL | 3.47 ± 0.71 g/L | Use of biofilm reactor increased the xanthan recovery. | [27][41] |
| Xanthomonas campestris | 20 g/L glucose | Polyethylene supported biofilm reactor; period 78.5 h; synthetic medium; mixing rate 180 rpm. | 150 mL | 3.21 ± 0.68 g/L | Biofilm reactor increased the glucose consumption. | [27][41] | |
| Gellan gum (Type HEEPS; components backbone made up of β-d-glucose, l-rhamnose, and d-glucuronic acid along with acetate and glycerate attached to glucose) 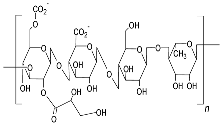 |
Sphingomonas pseudosanguinis (Accession No. GI:724472387) | 80 g/L biodiesel-derived waste glycerol | pH 7; synthetic medium; temp 30 °C; mixing rate 200 rpm; inoculum 10%; period 7 days; 0.5 vvm. | 3 L | 51.6 g/L | At lower concentrations, glycerol is consumed completely at all pHs, but at a higher concentration, it is not exhausted completely. | [28][42] |
| Sphingomonas yabuuchiae (GI:724472388) | 52.6 g/L | [28][42] | |||||
| EPS Br42 was found to be a heteropolysaccharide consisting of glucose and galacturonic acid with a molecular weight of about 286 kDa. | Brevibacillus borstelensis M42 | 2% glucose | Period 60 h. | - | 1.88 g/L | Water-holding capacity 510 ± 0.35%, oil-holding 374 ± 0.12% and swelling capacities 146.6 ± 5.75%. | [29][43] |
| EPS K1T-9 (EPS type HEEPS; components glucose and galacturonic acid; molecular weight 207 kDa. |
Neorhizobium urealyticum sp. nov. | Glucose 5 g/L | Zobell’s marine broth; pH 7; temp 28 °C; mixing rate 150 rpm; inoculum size 5 mL/100 mL; period 72 h. | Working volume 400 mL | 3.38 g/L | Water holding 356 ± 0.8%, oil holding 697 ± 1% (coconut oil); 317 ± 1.3% (olive oil), swelling capacity 200 ± 1.1%. | [30][44] |
Preparation of composites for healthcare applications needs high purity, therefore the downstream processing becomes an inseparable part of processing after fermentation. After production recovery, the identification of structural and chemical characteristics is necessary for further applications. The characterization of EPSs is quantitative, as well as qualitative. EPSs are mainly comprised of carbohydrates conjugated with other biomolecules, hence the basic characterization techniques employed are a colorimetric estimation and use spectrophotometry [31][45]. For carbohydrate estimation ‘Dinitrosalicylic Acid Reagent’ is one of the common methods which quantify the reducing sugars [32][46]. Similarly, for protein, Bradford’s dye-binding method [33][47] and Lowry’s method [34][48] are used. Besides basic characterization with colorimetric methods, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) is employed to detect the available functional groups and structural functionalities of EPSs. For the detailed structures of EPSs, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and mass spectra are used. In NMR, the sample is dissolved in deuterated solvents for quantification with respect to internal standards [35][36][49,50]. The mass spectrum of EPS provides a monosaccharide composition. For analysis, EPSs are hydrolyzed with acid hydrolysis, followed by silylation derivatization. The derivatives are detected and identified by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry [35][49]. The biological potential of EPS has followed the general procedure for antimicrobial, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and other activities [31][45].
