Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Clément Lemaitre and Version 2 by Rita Xu.
Atropisomers are fascinating objects of study by themselves for chemists but also find applications in various sub-fields of applied chemistry. Among these strategies, oxidative aromatization with central-to-axial conversion of chirality has gained increasing popularity. It consists of the oxidation of a cyclic non-aromatic precursors into the corresponding aromatic atropisomers.
- aromatic compounds
- atropisomers
- conversion of chirality
1. Introduction
1.1. Interest of Atropisomers and Synthetic Methods to Prepare Them
Described for the first time 100 hundred years ago [1], atropisomers are conformers that gained enough stability because of the hindered rotation around a single bond. They are, thus, considered configurational stereoisomers [2], in which the bond with hindered rotation becomes a stereogenic axis. A half time life higher than 103 s is usually set as the limit to claim their existence, corresponding to a barrier to rotation of 93 kJ·mol−1 at 300 K [2][3][2,3]. However, to be synthesized, stored, and used at ambient or biological temperature, higher barriers to rotation of ≥105 kJ·mol−1 are generally required. The most frequently encountered atropisomers are biaryl compounds bearing ortho substituents to prevent the rotation around the biaryl bond. However, non-biaryl based atropisomers also exist [4][5][6][4,5,6].
In view of their unique properties, atropisomers have received much attention from researchers in all sub-fields of chemistry (Figure 1) [7][8][9][7,8,9]. They are present in natural products [10][11][10,11], such as gossypol (1) [12], and bioactive compounds [13][14][15][16][17][13,14,15,16,17], such as HIV integrase inhibitor (2) [18] and kinase inhibitor (3) [19], but they also find applications as metal ligands, such as BINAP (4) [20], organocatalysts, such as chiral phosphoric acid (5) [21], in polymer science [22][23][22,23], etc.
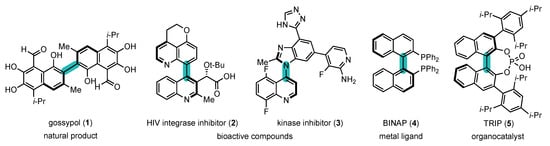
Figure 1. Atropisomers: examples and their fields of application.
Considering the importance of atropisomers and the fact that the two enantiomers are likely to have different behaviors when placed in a chiral environment (as is the case for biological applications), methods to obtain them in enantioenriched form have been actively pursued. While resolution of the racemate is often used, the development of enantioselective synthetic methods can be highly appealing since (i) they obviate the need to discard the unwanted enantiomer or recycle it by enantiomerization; and (ii) they stimulate the creativity of organic chemists.
Enantioenriched atropisomers can be synthesized by a variety of methods, which can be classified into six main categories (Scheme 1): [24][25][26][27][28][29][30][24,25,26,27,28,29,30]
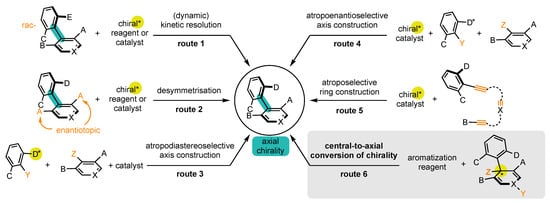
Scheme 1. Synthetic strategies to prepare atropisomers (presented on biaryl atropisomers for better readability).
- ]
- .
- Route 6:
It should be noted that routes 1 and 2 start from substrates where the bond of the stereogenic axis and the two aromatic rings already preexist. On the contrary, substrates where the bond does not exist are involved in routes 3 and 4, whereas routes 5 and 6 involve substrates where at least one aromatic ring has to be constructed.
1.2. Defining Conversion of Chirality
RWesearchers wish to define as conversions of chirality [50][51] all synthetic operations where a stereogenic element is forged in a molecule concomitantly with the destruction of a stereogenic element of a different type (Scheme 2a). The selection of this name requires an in-depth explanation:
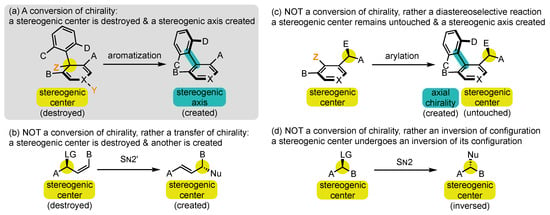
Scheme 2. What is and is NOT a conversion of chirality?
-
At first, chirality is used in a quite improper sense, as it is normally applied to a molecule or an object in its entirety, while the process discussed here falls within local stereochemistry discussions [51][52]. Conversion of stereogenicity should, in fact, be recommended, but it seems completely absent from the literature and perhaps more difficult to comprehend for those who are not specialists of this field.
-
Conversions of chirality are also referred to in the literature by several other denominations, which all appear to reusearchers as less suited. Transfer has long been the most frequently used term [52][53][54][53,54,55], but it brings the idea of relocation rather than transformation. For reusearchers, it should be restricted to reactions where the stereogenic element that is destroyed and the one that is created are of the same nature, such as in SN2′ reactions with allylic leaving groups (Scheme 2b) [55].Scheme 2b) Exchange[56]. [49][56] and Exchangeinterconversion [49,57] and [47]interconversion can also be encountered, but they evoke the idea of reversibility, which is generally not the case in those transformations.[47] can also be encountered, but they evoke the idea of reversibility, which is generally not the case in those transformations.
Having defined the conversion of chirality, rwesearchers now wish to point out which type of phenomenon should NOT be called so. Indeed, all the terms presented above are often misused to describe phenomena that are fundamentally different from conversion of chirality. Conversions/transfers/interconversions/exchanges of chirality are by nature potentially stereospecific processes and should be clearly distinguished from diastereoselective reactions. RWesearchers can, for example, cite those where the configuration of a stereogenic axis is controlled thanks to the presence of one or several stereogenic centers in the surroundings, which remain completely untouched during the transformation (Scheme 2c) [57][58][59][60][61][58,59,60,61,62]. Rather, they belong to the strategy exposed in Route 3 above. Sometimes these terms are even used for reactions that involve only an inversion of configuration, such as in a SN2 reaction (Scheme 2d) [62][63].
Being a phenomenon of enantiospecific nature, the efficiency of a conversion of chirality should be evaluated by comparing the relative enantioenrichment of the product and the substrate. In order to normalize this evaluation, Bressy, Bugaut, and Rodriguez introduced the notion of conversion percentage (cp) [63][64], which can be calculated as such and will be used throughout this review:
2. Historical Background
2.1. A surprisingly Early First Example!
From an historical point of view, it is quite amusing to realize that the first central-to-axial conversion of chirality was achieved in 1905 by Freund, even before the description of axial chirality, during reactivity studies on the natural product thebaine (6) (Scheme 3) [64][65]. Of course, it could not be identified at that moment, and it took almost half a century before the real explanation of what happened could be given by Robinson and Berson [65][66][67][66,67,68]. Treatment of 6 with phenylmagnesium bromide resulted in a complex rearrangement with aromatization to deliver biaryl atropisomer 9 as a mixture of two diastereomers. The reaction proceeds through the opening of the oxa-bridge with rearrangement of the carbon skeleton to afford 7, which can aromatize to 8. At this stage, the three initially present stereogenic centers have been destroyed with the concomitant installation of the stereogenic axis. The reaction terminates with trapping of the iminium ion by the Grignard reagent, giving rise to the formation of 9 as two diastereomers, which complicated the understanding of the transformation.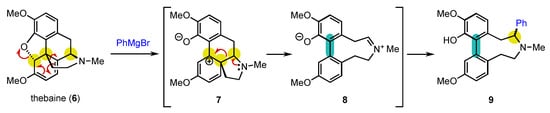
Scheme 3. Rearrangement of thebaine: the first example of central-to-axial conversion of chirality during aromatization.
2.2. Formulating Research Hypotheses to Achieve Conversion of Chirality
With the understanding of this phenomenon, Berson formulated three fundamental conditions that must be satisfied to allow the synthesis of atropisomers with central-to-axial conversion of chirality [50][51]:-
Centrally chiral non-aromatic precursors should be accessible in enantioenriched form;
-
Steric hindrance around the stereogenic axis should be sufficient to ensure its configurational stability;
-
Aromatization should occur with a preservation of the enantiopurity.
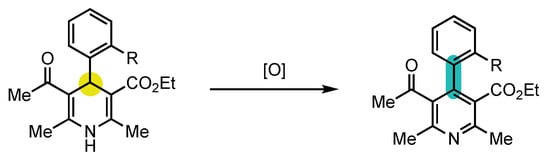
Scheme 4. Model proposed by Berson to study aromatization with central-to-axial conversion of chirality.
2.3. Verification of Berson’s Hypotheses by Meyers
Berson’s hypotheses were first confirmed by the explicitly designed central-to-axial conversion of chirality during aromatization proposed by the group of Meyers in 1984 (Scheme 5) [52][53]. Chiral oxazoline containing quinoline 10 underwent an efficient dearomatization by addition of naphthyllithium to obtain the corresponding dihydropyridine (S)-11 with a diastereomeric ratio of 88:12. The sequence went on with an oxidative rearomatization with DDQ, yielding 4-arylquinoline atropisomer (aS)-12 with a 84:16 dr, indicating a conversion percentage of 90%. In order to confirm that the enantioselectivity was not induced by the chiral oxazoline, it was deprotected to afford aldehyde (S)-13, which was oxidized in the same condition to obtain the pyridine (aS)-14 with an enantiomeric excess of 80%. Those experiments brought the first definitive evidence that central-to-axial conversion of chirality can be an efficient strategy for the preparation of enantioenriched atropisomers.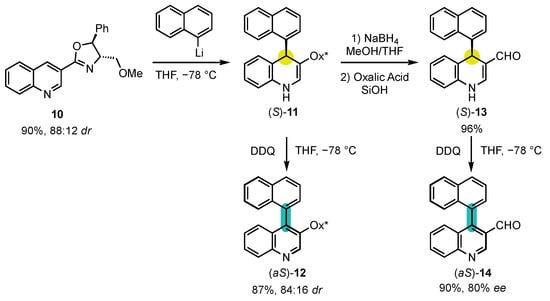
Scheme 5. First explicitly designed example of central-to-axial conversion of chirality during aromatization.
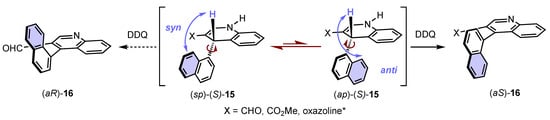
Scheme 6. Curtin–Hammett-type description of the stereochemical model during oxidative aromatization with central-to-axial conversion of chirality.
3. Synthesis of Pyridine Atropisomers
3.1. 4-Arylpyridineatropisomers
Following Meyer’s initial achievement, other research groups applied similar strategies to the synthesis of pyridine atropisomers. The group of Straub was the first one to expose the strong dependence of conversion of chirality’s efficiency on the choice of the oxidant in 1996 (Scheme 7) [73][110]. Indeed, starting from enantiopure (S)-17, obtained by preparative chiral HPLC on chiral stationary phase, they could convert it either to (aS)-18 with 94% ee using MnO2 or into its antipode (aR)-18, also with 94% ee using NOBF4 as the oxidant. This enantiodivergence is likely to arise from the difference in mechanisms and steric requirements between the two oxidants. It should also be noted that other oxidants gave moderately or poorly efficient conversion of chirality (for example: 83% ee in favor of the (aR) enantiomer for KMnO4 or 18% ee in favor of the (aS) enantiomer for Cu(NO3)2). Interestingly, electrochemical reduction of (aR)-18 with axial-to-central conversion of chirality could turn it into (R)-17 with 91% ee, achieving a formal inversion of configuration of the 1,4-dihydropyridine.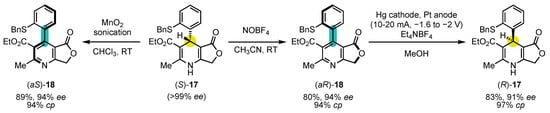
Scheme 7. Enantiodivergent oxidation of a 4-aryl-1,4-dihydropyridine in 4-arylpyridine atropisomer and subsequent inversion of configuration of the 1,4-dihydropyridine.
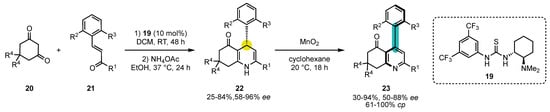
Scheme 8. Atroposelective Hantzsch pyridine synthesis by Takemoto’s thiourea catalysis to build chiral 1,4-dihydropyridines/oxidation sequence.
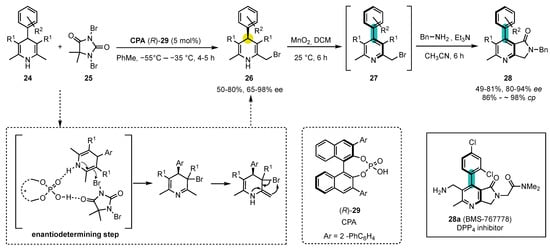
Scheme 9. Atroposelective synthesis of 4-arylpyridines from commercially available, symmetric 1,4-dihydropyridines by enantioselective phosphoric acid catalyzed desymmetrization–oxidation–substitution sequence.
3.2. Nicotinamide Atropisomers
In addition to 4-arylpyridine atropisomers, 3-carbamoylpyridine congeners, also known as nicotinamides, have also been the center of an intense attention, notably because of their structural similarity to NAD(P)H. Numerous contributions came from the research group of Ohno (Scheme 10). In 1986, they reported the synthesis of the enantioenriched 3-carbamoyl-1,4-dihydropyridine 30 containing a stereogenic center on the amide chain to facilitate analysis by the formation of diastereomers [76][113]. This substrate was oxidized using methyl phenylglyoxylate (31) as a hydride acceptor in presence of Mg(ClO4)2, delivering highly enantioenriched methyl (R)-mandelate (33) but with no diastereocontrol of the atropisomeric pyridinium salt 32 (Scheme 10a). This disappointing result was interpreted in terms of low configurational stability, which was confirmed by the fact that the subsequent reduction with Na2S2O4 afforded 3-carbamoyl-1,4-dihydropyridine 30 with 1:1 dr.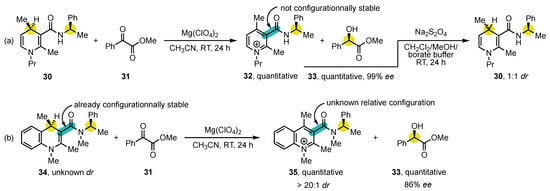
Scheme 10. Initial studies on the stereospecific oxidation of NAD(P)H mimics: (a) without diastereocontrol of atropisomeric salt 32, and (b) by employment of a configurationally stable substrate.
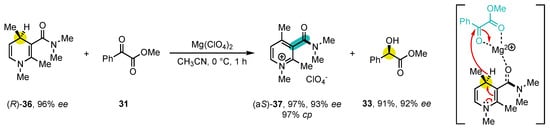
Scheme 11. Studies on the enantiospecific oxidation of NAD(P)H mimics.
