The rare earth elements (REEs) have unique and diverse properties that make them function as an “industrial vitamin” and thus, many countries consider them as strategically important resources. China, responsible for more than 60% of the world’s REE production, is one of the REE‐rich countries in the world. Most REE (especially light rare earth elements (LREE)) deposits are closely related to carbonatite in China. Such a type of deposit may also contain appreciable amounts of industrially critical metals, such as Nb, Th and Sc. According to the genesis, the carbonatite‐related REE deposits can be divided into three types: primary magmatic type, hydrothermal type and carbonatite weathering‐crust type. This paper provides an overview of the carbonatite‐related endogenetic REE deposits, i.e., primary magmatic type and hydrothermal type. The carbonatite‐related endogenetic REE deposits are mainly distributed in continental margin depression or rift belts, e.g., Bayan Obo REE‐Nb‐Fe deposit, and orogenic belts on the margin of craton such as the Miaoya Nb‐REE deposit. The genesis of carbonatite‐related endogenetic REE deposits is still debated. It is generally believed that the carbonatite magma is originated from the low‐degree partial melting of the mantle. During the evolution process, the carbonatite rocks or dykes rich in REE were formed through the immiscibility of carbonate-silicate magma and fractional crystallization of carbonate minerals from carbonatite magma. The ore‐forming elements are mainly sourced from primitive mantle, with possible contribution of crustal materials that carry a large amount of REE. In the magmatic-hydrothermal system, REEs migrate in the form of complexes, and precipitate corresponding to changes of temperature, pressure, pH and composition of the fluids. A simple magmatic evolution process cannot ensure massive enrichment of REE to economic values. Fractional crystallization of carbonate minerals and immiscibility of melts and hydrothermal fluids in the hydrothermal evolution stage play an important role in upgrading the REE mineralization. Future work of experimental petrology will be fundamental to understand the partitioning behaviors of REE in magmatic-hydrothermal system through simulation of the metallogenic geological environment. Applying “comparative metallogeny” methods to investigate both REE fertile and barren carbonatites will enhance the understanding of factors controlling the fertility.
- ore genesis
- fluid evolution
- REE enrichment
- carbonatite‐related REE deposit
1. Introduction
Rare earth elements (REEs) are a group of 17 chemically similar metallic elements (scandium, yttrium and lanthanide series in the periodic table IIIB). Scandium and yttrium are included in the REE group considering their comparable nature to the lanthanide elements and their common occurrence in a deposit [1][2]. The REE group is usually divided into two subgroups: light rare earth elements (LREEs, La‐Eu) and heavy rare earth elements (HREEs, Gd‐Lu and Y). Scandium is not included in the two subgroups because of its much smaller ion radius [3][4]. Rare earth elements are not at all rare in the Earth’s crust (especially LREEs), but are rather dispersed. The crustal abundance of REE is 0.017%, and the abundance of Ce, La and Nd is higher than that of W, Sn, Mo, Pb and Co. In comparison, heavy rare earth elements such as Tb and Tm are two to five times less abundant than Mo in the continental crust [5]. Under the upper mantle conditions, the trend of REE distribution into melts decreases with the decrease in ion radius from La to Lu (i.e., HREEs are generally more compatible with mantle peridotites). REEs are vital to modern technologies and society and are among the most critical of all raw materials. The demand for REE is constantly growing, driven particularly by their application in a range of modern and green technologies, including electric and conventional vehicles, communication technologies, and production and storage of renewable energy [6]. Supply of REE resources is largely restricted to China, along with a minor contribution from Brazil, Australia, the United States, Canada, India [7][8]. Although there is a substantial development on recycling of REE from end‐products [9], the majority of demand still depends on the production from natural source of REE. The major REE deposits that are economically exploitable are restricted to a few localities in the world (Table 1), while the economic potential of a REE deposit is strongly influenced by the mineralization processes and its mineralogy [8]. The most commercially important REE deposits are associated with magmatic processes and are found in, or related to, alkaline igneous rocks and carbonatites. The supergene REE deposits also represent a large REE resource such as placer‐type and ion adsorption‐type (IAR) deposits. The IAR deposits distributing over a wide area of southern China are usually rich in middle and heavy REE, which meet almost all the needs of HREE such as Gd, Tb, Dy in the development of emerging industries around the world and also having extremely high economic value [10]. The reserves, production scale, and export volume of rare earth resources in China rank first in the world, which has become the center of many economic and political controversies. Rare earth resources are widely distributed in China and relatively concentrated in the individual deposits. According to statistics, rare earth resources have been found in more than 2/3 of the provinces (regions) in China, among which the Bayan Obo in Inner Mongolia, Mianning in Sichuan province, the Gannan in Jiangxi province and northern Guangdong province are the major areas [11].
Table 1. Major economically exploitable rare earth element (REE) deposits in the world.
|
Country |
Deposit |
Deposit‐type |
|
|
China |
Bayan Obo (REE‐Nb‐Fe) |
Igneous carbonatite |
|
|
China |
Maoniuping (REE) |
Carbonatite |
|
|
China |
HREE‐enriched deposits in southern China |
Weathered crust elution |
|
|
Brazil |
Araxá、Catalão (REE) |
Weathered Carbonatite |
|
|
Brazil |
Mrro do Ferro (Th‐REE) |
Carbonatite |
|
|
Australia |
Mount Weld (REE) |
Weathered Carbonatite |
|
|
United States |
Mountain Pass (REE) |
Carbonatite |
|
|
Russia |
Tomtor (REE) |
Weathered Carbonatite |
|
|
Russia |
Lovozero (REE‐Nb) |
Alkaline igneous rock |
|
|
India |
Amba Dongar (REE) |
Carbonatite |
|
|
Vietnam |
Mau Sai (REE) |
Carbonatite |
|
|
Burundi |
Gakara (REE) |
Carbonatite |
|
|
Malawi |
Kangankunde (REE) |
Carbonatite |
|
|
South Africa |
Palabora (REE) |
Carbonatite |
|
|
South Africa |
Steenkampskraal (REE‐Th‐Cu) |
Alkaline igneous rock |
|
|
Turkey |
Aksu Diamas (REE) |
Placer |
|
|
Greenland |
Tanbreez (REE) |
Alkaline igneous rock |
|
|
Sweden |
Norra Kärr (REE) |
Alkaline igneous rock |
|
Worldwide, carbonatites are major sources of both REE and niobium, and are characterized by significant enrichment in the LREEs (La‐Gd) over the HREEs (Tb‐Lu). The Bayan Obo REE‐niobium‐iron deposit in Inner Mongolia, China, the world’s largest REE deposit, is an important example [12][13]. Whereas, the alkaline oversaturated rocks associated with REE deposits represent one of the most economically important resources of heavy REE and yttrium. Alkaline oversaturated rocks form from magma so enriched in alkalis that they crystallize sodium‐ and potassium‐bearing minerals (e.g., feldspathoids, alkali amphiboles). The source magma is usually mantle‐derived and highly differentiated. The world‐class Tanbreez REE deposit, which is hosted in the Ilímaussaq complex of southern Greenland, is a typical example [14][15].
Carbonatite usually refers to igneous rocks derived from the mantle with carbonate mineral volume > 50% and SiO2 < 20wt.% [16][17]. Based on wt.% ratios of the major elements (MgO, CaO, FeO, MnO, Fe2O3, etc.), carbonatites are subdivided into magnesiocarbonatites, ferrocarbonatites and calciocarbonatites (Table 2) by the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS) [12]. Two unique types of carbonatite are identified to occur locally: silicocarbonatite (carbonatite with more than 20% SiO2) existing in the Afrikanda of the Kola Peninsula (Russia), and natrocarbonatite in the Ol Doinyo Lengai volcano (Tanzania) mainly consisting of Na‐K‐Ca carbonates, such as nyerereite [(Na, K)2Ca(CO3)2] and gregoryite [(Na, K, Cax)2−x(CO3)] [18][19]. Recent works on the different types of carbonatite in the Bayan Obo REE‐Nb‐Fe deposit reveal that the evolutionary sequence of carbonatitic magma is from ferroan through magnesian to calcic in composition, accompanied with an increase in LREE enrichment [20].
Table 2. Classification of carbonatites (adapted from Simandl and Paradis [12] and Gou et al. [17]).
|
Classification |
Major Elements |
|
Calciocarbonatite |
CaO/(CaO + MgO + FeO + Fe2O3 + MnO) > 0.8 |
|
Magnesiocarbonatite |
CaO/(CaO + MgO + FeO + Fe2O3 + MnO) < 0.8 and MgO>(FeO + Fe2O3 + MnO) |
|
Ferrocarbonatite |
CaO/(CaO + MgO + FeO + Fe2O3 + MnO)<0.8 and MgO<(FeO + Fe2O3 + MnO) |
|
Natrocarbonatite |
High content of Na, K, Ca |
|
Silicocarbonatite |
SiO2 > 20% of the whole rock |
The types of REE deposits are complex and diverse, and the ones related to carbonatite–alkaline complexes are the most typical and abundant, including the Bayan Obo REE‐Nb‐Fe deposit in Inner Mongolia, Maoniuping REE deposit in Sichuan, Mountain Pass REE deposit in the USA and Araxá Nb‐P‐REE deposit in Brazil [21]. Carbonatite‐related REE deposits comprising the main source of LREE and Nb resources in the world refer to REE deposits that are closely related to a set of carbonatite or alkaline rocks (usually coexisting) in genesis and space. Although carbonatite‐related REE deposits are particularly crucial, there are still many debates and controversies about their geological background and genetic characteristics, and the detailed metallogenic process is not clear. Therefore, it is necessary to summarize the tectonic background, petrology and geochemical characteristics of carbonatite‐related REE deposits, so as to better understand the genesis of the deposits and provide guidance for mineral exploration.
This article first summarizes the geological characteristics of carbonatite‐related REE deposits, then summarizes and briefly introduces the typical carbonatite‐related REE deposits in China. In combination with previous studies, we present a full discussion of the genetic characteristics and the mechanism of massive REE enrichment of carbonatite‐related REE deposits. Ultimately, the existing problems are discussed and the future research directions are proposed to address the problems.
2. Types and Basic Geological Characteristics of Carbonatite‐Related REE Deposits
2.1. Types of Carbonatite‐Related REE Deposits
Carbonatite usually coexists with alkaline silicate igneous rocks to form carbonatite–alkaline (ring) complexes, but some appear in the form of isolated batholiths, dykes, intrusions, lava flows and pyroclastic overburdens [22]. Three types of carbonatite‐related REE deposits are recognized according to the varied characteristics of mineralization, namely primary magmatic type, hydrothermal type and carbonatite weathering‐crust type [23]. The former two types, collectively called carbonatite‐related endogenetic REE deposits, are mainly formed in relation to carbonatite magma and its derived hydrothermal fluids, forming REE mineral accumulation and mineralization. The mineralization of primary magmatic type REE deposits mainly occur in the magmatic stage. REE minerals such as bastnäsite, monazite, allanite, xenotime, parasite occur in carbonatite or magmatic phosphorite, and the entire rock body is mineralized. REE minerals of hydrothermal type deposits are formed by hydrothermal fluids that are evolved from magmas, which are usually associated with calcite, barite, fluorite, quartz and other minerals to form major or net veins. The mineralized veins frequently interpenetrate in the contact zone and surrounding rock of carbonatite complexes. The hydrothermal REE minerals can also occur as crack fillings superimposed on the minerals that are formed during the magmatic stage. This type of deposit is usually large in scale, and the REE minerals are relatively simple, mainly bastnäsite [24]. Carbonatite weathering‐crust type is secondary carbonatite REE deposits, which comprise laterite crust after long‐term weathering and fluid leaching under particular environmental conditions that are hot, humid and suitable for weathering crust preservation. REEs in the weathered crust section are remobilized, enriched, and adsorbed on the surface of clay minerals such as kaolinite in the form of ions. This type of REE deposit is usually HREE‐enriched due to the higher mobility of LREE during weathering [25].
2.2. Spatial and Temporal Distribution
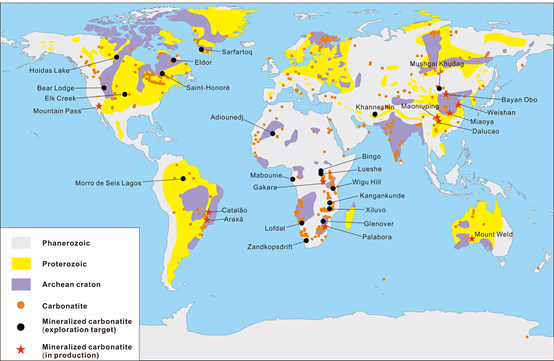
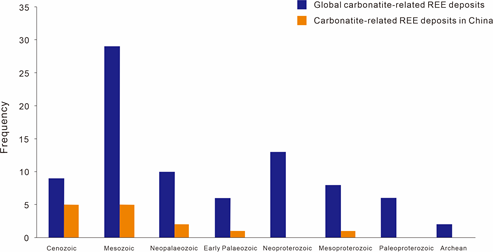
Worldwide there are more than 500 proven carbonatites, only a small proportion of which is fertile with REEs (Figure 1) [26][27]. The ages of carbonatites range from the Archean to Cenozoic. The mineralization of carbonatite‐related REE deposits occurs over a long period of time but is mostly concentrated in the Mesozoic. Carbonatite‐related REE deposits in China are formed during the Proterozoic to Mesozoic. Among those, two major mineralization events occurred in the Mesoproterozoic and Mesozoic (Figure 2), which are represented by the Bayan Obo REE deposit in Inner Mongolia (~1.32 Ga, [20]) and the Miaoya REE deposit in Hubei province (232 Ma, [28]), respectively.
Globally, carbonatite‐related REE deposits mostly occur in continental marginal depression belts and rift belts along craton margins controlled by large‐scale deep lithosphere faults (e.g., the Mountain Pass REE deposit in the USA). Subordinately, REE mineralization also occurs at stable geological structural units (platform or paraplatform) such as the Araxá Nb‐P‐REE deposit in Brazil and the Sarfartoq REE deposit in Greenland (Figure 1) [29][30]. The distribution of carbonatite‐related REE deposits in China is rather restricted to continental margin rifts or orogenic belts at the margin of cratons [21]. For example, the Bayan Obo and Weishan REE deposits are located on the northern and southeastern margins of the North China Craton, respectively; the Maoniuping REE deposit is located in the rift belt of the western margin of the Yangtze Craton; the Miaoya and Shaxiongdong REE deposits in Hubei Province are located in the Qinling orogenic belt [31][32][33][34][35].
2.3. Ore and Orebody Characteristics
The vast majority of carbonatite‐related REE deposits in China belong to endogenetic deposits including both the primary magmatic type and hydrothermal type REE deposits. Large and super large‐scale REE deposits often have both magmatic and hydrothermal features, reflecting an interplay of both processes in contribution to the ore genesis [23]. The Bayan Obo REE‐Nb‐Fe deposit is a great example [36]. Previous studies suggest that two major mineralization events occurred at 1400 Ma and 440 Ma, respectively, at the giant Bayan Obo REE‐Nb‐Fe deposit, which correspond to an early emplacement of large‐scale carbonatitic magma (1.4‐1.3 Ga) and a late intense hydrothermal activity (440 Ma). The early carbonatitic magma is fertile in REEs, and the REEs are captured in primary REE‐minerals such as bastnäsite and monazite. The late hydrothermal fluids released the REEs from its original host minerals, and upgraded the reserves, forming REE minerals such as secondary bastnäsite, parasite and cerianite, which are usually coarse‐grained and appear in veins [37][38][39][40].
Carbonatite‐related primary magmatic type REE deposits are mainly hosted in a set of ring‐shaped complexes composed of carbonatites and alkaline rocks. The entire carbonatite body is commonly mineralized, and mineralization tends to extend into the alkaline complexes appearing as lenticular or irregular lenses [23]. The occurrence of ore bodies is usually controlled by regional deep faults existing in the extensional lithosphere. In this context, the regional deep faults act as conduits for the migration of deeply seated and fertile magma [17]. For example, the Mountain Pass REE deposit, United States, is controlled by a large deep fault that crosses the west coast of North America. The Miaoya REE deposit in China occurs in an extensional tectonic setting derived from fault zones or orogenic belts [41][42][43]. The ores usually are fine‐grained and massive, disseminated, or striped in texture. The REE minerals are generally formed from crystallization in the late stage of magma evolution, mainly including bastnäsite, monazite, xenotime, parisite, allanite, and frequently in association with Nb‐containing minerals such as pyrochlore, aeschynite, niobite. Other existing minerals include magnetite, hematite, apatite, barite, calcite, dolomite, mica and zircon [23][25].
Figure 1. Distribution of carbonatites and carbonatite‐related REE deposits, including deposits in production and exploration targets discussed in this paper (modified from Woolley and Kjarsgaard [26], Liu and Hou [27] and Verplanck et al. [29]).
Figure 2. Age distribution histograms of major carbonatite‐related REE deposits in the world and China (based on data from Woolley and Kjarsgaard, with minor updates).
The orebodies of hydrothermal type REE deposits are usually in the form of veins or stockwork that occur near the contact zone between orebodies and host rocks or in the host rocks. The mineralization is also controlled by regional deep faults. For example, the Maoniuping REE deposit in Sichuan Province and Weishan REE deposit in Shandong Province are typical hydrothermal type REE mineralization. They are located in the Panxi Rift Valley and Tanlu Fault Zone, respectively [44][45]. Compared with REE deposits of primary magmatic type, the REE minerals in hydrothermal type deposits are mineralogically simpler, typically containing bastnäsite and parasite. The REE minerals appear either as filling in veins or disseminated or as overgrowth on the early magmatic minerals in carbonatite. The gangue minerals mainly comprise of fluorite, quartz, barite, calcite, apatite and aegirine‐augite. The hydrothermal fluids exsolved from the late stage magma tend to overprint early magmatic mineralization, a process that is crucial for the massive enrichment of REEs in carbonatite‐related REE deposits.
2.4. Geochemical Characteristics
The chemical composition of carbonatite varies greatly. Typical carbonatites are SiO2 unsaturated, rich in CO2 and CaO, and some are rich in Mg, Fe and alkalis [46]. Trace elements in carbonatite mainly include LREE, Nb, Ta, Th, Zr, Hf, Sr, Ba, F, and P. Carbonatite is one of the rocks with the highest REE content and the highest LREE differentiation on the Earth. It has become an essential prospecting indicator for large‐scale, high‐grade and LREE‐enriched REE deposits. As the most characteristic and significant elements in carbonatite, LREEs are enriched to a higher level than other trace elements as main ore‐forming elements in some carbonatite‐related REE deposits, e.g., Bayan Obo REE‐Nb‐Fe deposit . Niobium and Ta often appear as associated elements in the deposits and are enriched in the late petrogenic stage. The precipitation of Nb and Ta often forms pyrochlore, aeschynite, etc. Alkaline‐earth metals such as Sr, Ba also show enrichment and are incorporated in carbonates. Substantial accumulation of Fe can occur to a level that is economically exploitable (e.g., Bayan Obo REE‐Nb‐Fe deposit) [47]. The contents of F and Cl in carbonatite are higher compared to those of other magmatic rocks, which is essential for the efficient migration and precipitation of REEs in the fluids. Occasionally, F is highly enriched in carbonatite‐forming carbonatite‐type fluorite deposits [48][49][50]. Phosphorus is also one of the most characteristic trace element in carbonatite, and often occurs in the form of apatite.
2.5. Alteration Characteristics
In the process of ascending and emplacement of carbonatitic magma, the temperature and pressure of fluids decrease, along with release of volatiles (F, Cl, P and S) and elements such as REE, Na, K, and Fe. The fluids reach the upper crust and metasomatize surrounding rocks, forming a lithological belt of fenite with asymmetric zonal distribution in the orebody, which is called fenitization (Figure 3). Fenitization is an alkali metasomatism, which is caused by alkali‐rich fluids exsolved from igneous carbonatitic or alkaline magma. It is a typical and unique alteration phenomenon of carbonatite and alkaline igneous rocks [51][52][53]. McKie (1966) defined fenite as the rock produced by the metasomatism of igneous carbonatite with surrounding rocks, mainly composed of alkaline feldspar and alkaline mafic minerals [54]. During the metasomatism, a large amount of Si and substantial Al are released into the solution, while K, Na, Ca, and Fe are retained in the fenite forming new minerals. The degree of metasomatism varies according to the distance to the causative rocks, resulting in halo‐like patterns of fenitization. The main minerals of fenite include Na‐ and K‐amphiboles, Na‐pyroxene, aegirine‐augite, K‐feldspar, albite, perthite, nepheline and pale brown mica. The accessory minerals include apatite and REE minerals such as titanite, pyrochlore, monazite and bastnäsite.
According to the Na2O/K2O ratio of whole rock, fenitization can be divided into three main types: sodic, potassic, and sodic‐potassic. Potassic fenite is dominated by K‐rich feldspars (orthoclase or microcline). In some cases, there are also low‐Al phlogopite or biotite, which is usually developed near the upper part of intrusive calcite/dolomite carbonatite. Sodic fenite mainly consists of Na‐rich amphibole, sodic pyroxene, alkali feldspar or albite. Sodic‐potassic fenitization is an intermediate between the two endmembers [55]. In addition, sodic fenite usually occurs in the contact zones between carbonatite bodies and surrounding rocks in the early stage or deep emplacement, while potassic fenite is often found in the contact zones in the late stage or shallow emplacement [56]. Previous studies have suggested that the initial carbonatite contains a considerable amount of alkali, and the hydrothermal fluid rich in Na and K can be derived in the process of evolution and metasomatic reaction with surrounding rocks [46]. This initial carbonatite is named sodic carbonatite, such as Oldoinyo Lengai sodic carbonatite in northern Tanzania [57][58]. However, carbonatites exposed in nature are mostly ferroan, magnesian, and calcic carbonatites, rarely alkali in composition, although they spatially closely coexist with alkali‐rich fenite. In addition to Na and K, other elements such as Fe, Zr, V, Zn, Rb and Ba are incorporated into the fluids derived from carbonatite magma [59][60]. During the separation of fluid phase, REEs, especially LREEs, prefer to partition into the liquid and vapor phases. The fenitizing fluids derived from carbonatite magma are characterized by strong enrichment of LREEs. REE‐bearing minerals such as bastnäsite and monazite crystallize and accumulate from the fenitizing fluids during its auto‐metasomatism to carbonatite, which favors for the formation of large REE deposits.
Figure 3. Fenitization in the wallrock quartz sandstone from the Bayan Obo REE‐Nb‐Fe deposit.
References
- Loges, A.; Migdisov, A.A.; Wagner, T.; Williams‐Jones, A.E.; Markl, G. An experimental study of the aqueous solubility and speciation of Y(III) fluoride at temperatures up to 250 °C. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2013, 123, 403–415.
- Binnemans, K.; Jones, P.T.; Blanpain, B.; Van Gerven, T.; Yang, Y.; Walton, A.; Buchert, M. Recycling of rare earths: A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 51, 1–22.
- Jha, M.K.; Kumari, A.; Panda, R.; Rajesh Kumar, J.; Yoo, K.; Lee, J.Y. Review on hydrometallurgical recovery of rare earth metals. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 161, 77–77.
- Jordens, A.; Cheng, Y.P.; Waters, K.E. A review of the beneficiation of rare earth element bearing minerals. Miner. Eng. 2013, 41, 97–114.
- Chakhmouradian, A.R.; Wall, F. Rare Earth Elements: Minerals, Mines, Magnets (and More). Elements 2012, 8, 333–340.
- Kumari, A.; Panda, R.; Jha, M.K.; Kumar, J.R.; Lee, J.Y. Process development to recover rare earth metals from monazite mineral: A review. Miner. Eng. 2015, 79, 102–115.
- Zhang, S.J.; Zhang, L.W.; Zhang, Y.W.; Shang, L.; Li, J.B. Summarize on rare earth mineral resources and their distribution at home and abroad. Inorg. Chem. Ind. 2020, 52, 9–16. (In Chinese with English abstract)
- Li, Z.; Hu, J.Z. World rare earth resources survey and development utilization trend. Mod. Min. 2017, 33, 97–101+105. (In Chinese with English abstract)
- Li, F.Q.; Dai, T.; Wang, G.S. A review on recycling and reuse of rare earth metals. Conserv. Util. Min. Resour. 2019, 39, 84–89. (In Chinese with English abstract)
- Wang, D.H.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, Y.; Wang, C.H.; Dai, J.J.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, T.; Li, J.K.; Huang, F.; Chen, Z.Y.; al. A review of the achievements in the survey and study of ion‐absorption type REE deposits in China. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2017, 38, 317–325. (In Chinese with English abstract)
- Fu, T.Y.; Li, B.H.; Dong, X.Y.; Xu, L. Analysis on the distribution, classification and characteristics of rare earth deposits in China. J. Henan Sci. Technol. 2015, 14, 124–126. (In Chinese with English abstract)
- Simandl, G.J.; Paradis, S. Carbonatites: Related ore deposits, resources, footprint, and exploration methods. Appl. Earth Sci. 2018, 127, 123–152.
- Sun, J.; Zhu, X.K.; Chen, Y.L.; Fang, N.; Li, S.Z. Is the Bayan Obo ore deposit a micrite mound? A comparison with the Sailinhudong micrite mound. Int. Geol. Rev. 2014, 56, 1720–1731.
- Liu, Q.P.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Liu, C.H. REE resources potential in Greenland and the availability evaluation in favor of China. Geol. Bull. China 2019, 38, 1386–1395. (In Chinese with English abstract)
- Schonwandt, H.K.; Barnes, G.B.; Ulrich, T. Chapter 5—A Description of the World‐Class Rare Earth Element Deposit, Tanbreez, South Greenland. In Rare Earths Industry: Technological, Economic, and Environmental Implications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 73–85.
- Streckeisen, A. Classification and nomenclature of volcanic rocks, lamprophyres, carbonatites and melilitic rocks IUGS Subcommission on the Systematics of Igneous Rocks. Geol. Rundsch. 1980, 69, 194–207.
- Gou, R.T.; Zeng, P.S.; Liu, S.W.; Ma, J.; Wang, J.J.; Dai, Y.J.; Wang, Z.Q. Distribution characteristics of carbonatites of the world and its metallogenic significance. Acta Geol. Sin. 2019, 93, 2348–2361. (In Chinese with English abstract)
- Chakhmouradian, A.R.; Cooper, M.A.; Medici, L.; Abdu, Y.A.; Shelukhina, Y.S. Anzaite‐(Ce), a new rare‐earth mineral and structure type from the Afrikanda silicocarbonatite, Kola Peninsula, Russia. Mineral. Mag. 2018, 79, 1231–1244.
- Mattsson, H.B.; Balashova, A.; Almqvist, B.S.G.; Bosshard‐Stadlin, S.A.; Weidendorfer, D. Magnetic mineralogy and rock magnetic properties of silicate and carbonatite rocks from Oldoinyo Lengai volcano (Tanzania). J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2018, 142, 193–206.
- Yang, K.F.; Fan, H.R.; Pirajno, F.; Li, X.C. The Bayan Obo (China) giant REE accumulation conundrum elucidated by intense magmatic differentiation of carbonatite. Geology 2019, 47, 1198–1202.
- Yang, Z.M.; Woolley, A. Carbonatites in China: A review. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2006, 27, 559–575.
- Linnen, R.L.; Samson, I.M.; Williams‐Jones, A.E.; Chakhmouradian, A.R. Geochemistry of the Rare‐Earth Element, Nb, Ta, Hf, and Zr Deposits. In Treatise on Geochemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 543–568.
- Song, W.L.; Xu, C.; Wang, L.J.; Wu, M.; Zeng, L.; Wang, L.Z.; Feng, M. Review of the metallogenesis of the endogenetic rare earth elements deposits related to carbonatite‐alkaline complex. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Pekin. 2013, 49, 725–740. (In Chinese with English abstract)
- Weng, Z.H.; Jowitt, S.M.; Mudd, G.M.; Haque, N. A Detailed Assessment of Global Rare Earth Element Resources: Opportunities and Challenges. Econ. Geol. 2015, 110, 1925–1952.
- Kanazawa, Y.; Kamitani, M. Rare earth minerals and resources in the world. J. Alloy. Compd. 2006, 408–412, 1339–1343.
- Woolley, A.R.; Kjarsgaard, B.A. Carbonatite occurrences of the world: Map and database. Geol. Surv. Can. Open File 2008, 5796, 1–21.
- Liu, Y.; Hou, Z.Q. A synthesis of mineralization styles with an integrated genetic model of carbonatite‐syenite‐hosted REE deposits in the Cenozoic Mianning‐Dechang REE metallogenic belt, the eastern Tibetan Plateau, southwestern China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2017, 137, 35–79.
- Ying, Y.C.; Chen, W.; Lu, J.; Jiang, S.Y.; Yang, Y.H. In situ U–Th–Pb ages of the Miaoya carbonatite complex in the South Qinling orogenic belt, central China. Lithos 2017, 290–291, 159–171.
- Verplanck, P.L.; Mariano, A.N.; Mariano, A., Jr. Rare Earth Element Ore Geology of Carbonatites. In Rare Earth and Critical Elements in Ore Deposits; Verplanck, P.L., Hitzman, M.W., Eds.; Soc Economic Geologists, Inc.: Littleton, CO, USA, 2016; pp. 5–32.
- Xie, Y.L.; Hou, Z.Q.; Goldfarb, R.J.; Guo, X.; Wang, L. Rare Earth Element Deposits in China. In Rare Earth and Critical Elements in Ore Deposits; Verplanck, P.L., Hitzman, M.W., Eds.; Soc Economic Geologists, Inc.: Littleton, CO, USA, 2016; pp. 115–136.
- Lai, X.D.; Yang, X.Y. U‐Pb Ages and Hf Isotope of Zircons from a Carbonatite Dyke in the Bayan Obo Fe‐REE Deposit in Inner Mongolia: Its Geological Significance. Acta Geol. Sin. Engl. Ed. 2019, 93, 1783–1796.
- Xie, Y.L.; Li, Y.X.; Cooke, D.; Kamenetsky, V.; Chang, Z.S.; Danyushevsky, L.; Dominy, S.; Ryan, C.; Laird, J. Geochemical characteristics of carbonatite fluids at the Maoniuping REE deposit, Western Sichuan, China. Let’s Talk Ore Deposits. In Proceedings of the Eleventh Biennial SGA Meeting, Antofagasta, Chile, 26–29 September 2011; Volume 1, pp. 196–198.
- Zhu, J.; Wang, L.X.; Peng, S.G.; Peng, L.H.; Wu, C.X.; Qiu, X.F. U‐Pb zircon age, geochemical and isotopic characteristics of the Miaoya syenite and carbonatite complex, central China. Geol. J. 2017, 52, 938–954.
- Wang, C.; Liu, J.C.; Zhang, H.D.; Zhang, X.Z.; Zhang, D.M.; Xi, Z.; Wang, Z.X.; Wang, Z.J. Geochronology and mineralogy of the Weishan carbonatite in Shandong province, eastern China. Geosci. Front. 2019, 10, 769–785.
- Xu, C.; Campbell, I.H.; Allen, C.M.; Chen, Y.J.; Huang, Z.L.; Qi, L.; Zhang, G.S.; Yan, Z.F. U‐Pb zircon age, geochemical and isotopic characteristics of carbonatite and syenite complexes from the Shaxiongdong, China. Lithos 2008, 105, 118–128.
- Liu, S.; Fan, H.R.; Groves, D.I.; Yang, K.F.; Yang, Z.F.; Wang, Q.W. Multiphase carbonatite‐related magmatic and metasomatic processes in the genesis of the ore‐hosting dolomite in the giant Bayan Obo REE‐Nb‐Fe deposit. Lithos 2020, 354–355, 105359.
- Yang, X.Y.; Lai, X.Y.; Pirajno, F.; Liu, Y.L.; Ling, M.X.; Sun, W.D. Genesis of the Bayan Obo Fe‐REE‐Nb formation in Inner Mongolia, North China Craton: A perspective review. Precambrian Res. 2017, 288, 39–71.
- Song, W.L.; Xu, C.; Smith, M.P.; Chakhmouradian, A.R.; Brenna, M.; Kynický, J.; Chen, W.; Yang, Y.H.; Deng, M.; Tang, H.Y. Genesis of the world’s largest rare earth element deposit, Bayan Obo, China: Protracted mineralization evolution over ~1 b.y. Geology 2018, 46, 323–326.
- Hu, L.; Li, Y.K.; Wu, Z.J.; Bai, Y.; Wang, A.J. Two metasomatic events recorded in apatite from the ore‐hosting dolomite marble and implications for genesis of the giant Bayan Obo REE deposit, Inner Mongolia, Northern China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2019, 172, 56–65.
- Fan, H.R.; Yang, K.F.; Hu, F.F.; Liu, S.; Wang, K.Y. The giant Bayan Obo REE‐Nb‐Fe deposit, China: Controversy and ore genesis. Geosci. Front. 2016, 7, 335–344.
- Su, J.H.; Zhao, X.F.; Li, X.C.; Hu, W.; Chen, M.; Xiong, Y.L. Geological and geochemical characteristics of the Miaoya syenite‐carbonatite complex, Central China: Implications for the origin of REE‐Nb‐enriched carbonatite. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 113, 103101.
- Ying, Y.C.; Chen, W.; Simonetti, A.; Jiang, S.Y.; Zhao, K.D. Significance of hydrothermal reworking for REE mineralization associated with carbonatite: Constraints from in situ trace element and C‐Sr isotope study of calcite and apatite from the Miaoya carbonatite complex (China). Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2020, 280, 340–359.
- Xu, C.; Kynicky, J.; Chakhmouradian, A.R.; Campbell, I.H.; Allen, C.M. Trace‐element modeling of the magmatic evolution of rare‐earth‐rich carbonatite from the Miaoya deposit, Central China. Lithos 2010, 118, 145–155.
- Jia, Y.H.; Liu, Y. REE Enrichment during Magmatic‐Hydrothermal Processes in Carbonatite‐Related REE Deposits: A Case Study of the Weishan REE Deposit, China. Minerals 2019, 10, 25.
- Hou, Z.Q.; Tian, S.H.; Xie, Y.L.; Yang, Z.; Yuan, Z.S.; Yin, S.P.; Yi, L.S.; Fei, H.C.; Zou, T.R.; Bai, G.; al. The Himalayan Mianning‐Dechang REE belt associated with carbonatite‐alkaline complexes, eastern Indo‐Asian collision zone, SW China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2009, 36, 65–89.
- Woolley, A.R. A discussion of carbonatite evolution and nomenclature, and the generation of sodic and potassic fenites. Mineral. Mag. 1982, 46, 13–17.
- Liu, S.; Fan, H.R.; Yang, K.F.; Hu, F.F.; Rusk, B.; Liu, X.; Li, X.C.; Yang, Z.F.; Wang, Q.W.; Wang, K.Y. Fenitization in the giant Bayan Obo REE‐Nb‐Fe deposit: Implication for REE mineralization. Ore Geol. Rev. 2018, 94, 290–309.
- Migdisov, A.A.; Williams‐Jones, A.E. Hydrothermal transport and deposition of the rare earth elements by fluorine‐bearing aqueous liquids. Miner. Depos. 2014, 49, 987–997.
- Liu, Y.; Chen, Z.Y.; Yang, Z.S.; Sun, X.; Zhu, Z.M.; Zhang, Q.C. Mineralogical and geochemical studies of brecciated ores in the Dalucao REE deposit, Sichuan Province, southwestern China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 70, 613–636.
- Williams‐Jones, A.E.; Migdisov, A.A.; Samson, I.M. Hydrothermal Mobilisation of the Rare Earth Elements—A Tale of “Ceria” and “Yttria”. Elements 2012, 8, 355–360.
- Cooper, A.F.; Palin, J.M.; Collins, A.K. Fenitization of metabasic rocks by ferrocarbonatites at Haast River, New Zealand. Lithos 2016, 244, 109–121.
- Currie, K.L.; Ferguson, J. A Study of Fenitization Around the Alkaline Carbonatite Complex at Callander Bay, Ontario, Canada. Can. J. Earth Sci. 1971, 8, 498–517.
- Currie, K.L.; Ferguson, J. A Study of Fenitization in Mafic Rocks, with Special Reference to the Callander Bay Complex. Can. J. Earth Sci. 1972, 9, 1254–1261.
- McKie, D., Fenitization: In: Tuttle OF & Gittins J.(eds.) Carbonatites. New York: Interscience Publishers. 1966, 261-294.
- Le Bas, M.J. Fenites Associated with Carbonatites. Can. Mineral. 2008, 46, 915–932.
- Yang, X.M.; Yang, X.Y.; Fan, H.R.; Guo, F.; Zhang, Z.F.; Zheng, Y.F. Petrological characteristics of fenites and their geological significance. Geol. Rev. 2000, 46, 481–490. (In Chinese with English abstract)
- Potter, N.J.; Kamenetsky, V.S.; Simonetti, A.; Goemann, K. Different types of liquid immiscibility in carbonatite magma: A case study of the Oldoinyo Lengai 1993 lava and melt inclusions. Chem. Geol. 2017, 455, 376–384.
- Mitchell, R.H. Peralkaline nephelinite‐natrocarbonatite immiscibility and carbonatite assimilation at Oldoinyo Lengai, Tanzania. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2009, 158, 589–598.
- Kresten, P.; Morogan, V. Fenitization at the Fen complex, southern Norway. Lithos 1986, 19, 27–42.
- Kresten, P. The chemistry of fenitization: Examples from Fen, Norway. Chem. Geol. 1988, 68, 329–349.