High-order aberrations (HOAs) are optical defects that degrade the image quality. They change with factors such as pupil diameter, age, and accommodation. The changes in optical aberrations during accommodation are mainly due to lens shape and position changes. Primary spherical aberration (Z(4.0)) is closely related to accommodation and some studies suggested that it plays an important role in the control of accommodation. Furthermore, central and peripheral HOAs vary with refractive error and seem to influence eye growth and the onset and progression of myopia. The variations of central and peripheral HOAs during accommodation also appear to be different
depending on the refractive error. Central and peripheral high-order aberrations are closely related to accommodation and influence the accuracy of the accommodative response and the progression of refractive errors, especially myopia.
- aberrations
- accommodation
- refractive error
1. Introduction
2. Central HOAs and Accommodation
The quality of the retinal image change with accommodation has been already verified [7,8,9,10,11,12][7][8][9][10][11][12]. Atchison et al. [13] investigated in detail the changes of ocular aberrations of the eye as a function of accommodation. Monochromatic aberrations were analyzed in 15 subjects in 3 different levels of accommodation (0D, 1.50D, and 3.00D). Although the spherical aberration (Z(4,0)) became more negative with accommodation in eight subjects, there was not a clear trend in the amount and direction of changes for other aberrations. The sample size and substantial variability in aberrations between individuals may influence the results. Further studies were carried out and, although the variability between individuals was verified in several studies [8[8][9][12][14],9,12,14], it was shown that aberrations tend to become larger for a high level of accommodation (Figure 1) [8,9,10,11,12][8][9][10][11][12]. Some studies analyzed these variations only between the relaxed state and for a given accommodative demand, whereas others investigated different accommodative levels (Table 1). Root-mean-square (RMS) reaches a minimum close to a relaxed state, remaining constant from 0D to 3.00D of accommodation, and increases for high accommodative demands (Figure 1) (p < 0.05). [6,8,9,10,12][6][8][9][10][12]. In the relaxed state, most wavefront aberrations are approximately 0, except Z(4,0) (which is usually positive), and increase gradually for higher accommodative levels (from 3.00D) [6,8,9,10,12][6][8][9][10][12] with a relevant increase at 5.00D of accommodation (Figure 1) [10].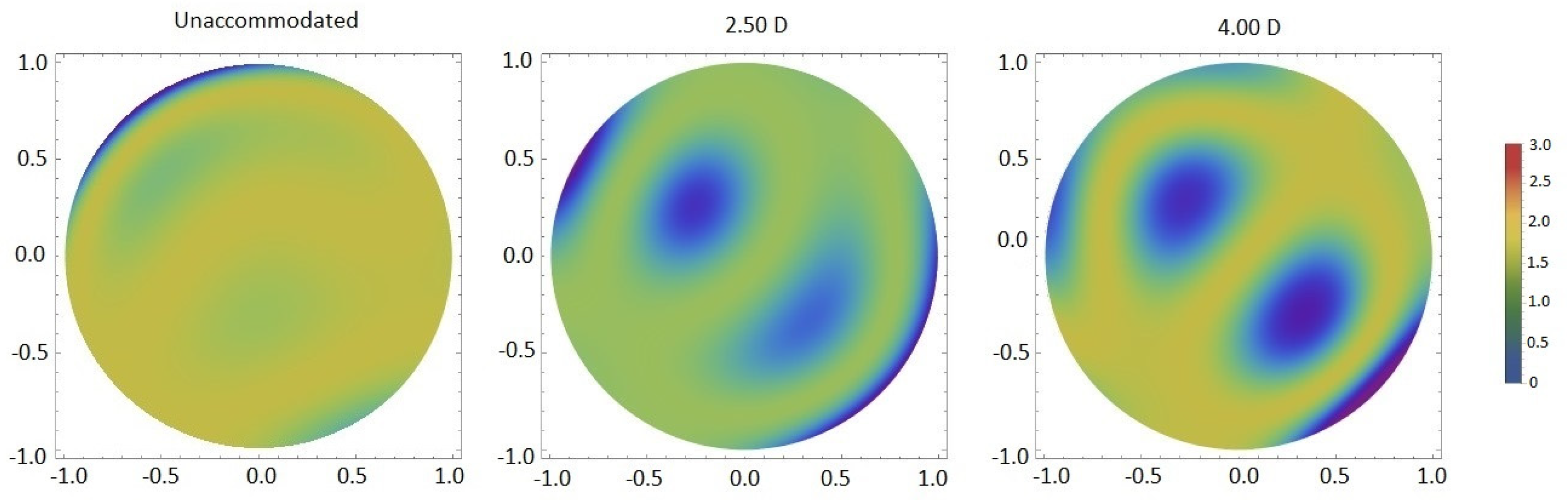
| Author (Year) | Eyes | Age (Years) | Refractive State (D) | Accommodative Stimulus (D) | Accommodation Stimulation Method | Measurement Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atchison et al. (1995) [13] | 15 | 0D, 1.5D and 3.00D | Aberroscope | |||
| He et al. (2000) [8] | 8 | 24–38 | SEQ: −2.00D–−5.56D | Between 0 and 6.00D in steps of 1.00D | Spatially resolved refractometer | |
| Ninomiya et al. (2002) [14] | 33 | 28.7 ± 4.4 | 0 and 3.00D | TDV | S-H | |
| He et al. (2003) [15] | 12 | 23–32 | SEQ: 0–−3.00D; Cil ≤ 0.25D | 0.25D and 5.00D | TDV | CTS |
| Hazel et al. (2003) [16] | 30 | 18–27 | SEQ: +0.50D–−6.00D; Cil < 0.50D | Between 0 and 4.00D in steps of 1.00D | NSL | S-H |
| Cheng et al. (2004) [9] | 76 | 21–40 | Sphere: +1.25D–−8.25D; Cil: −0.25D–−2.75D | 0, 3.00D and 6.00D | TDV | S-H |
| Gicquel et al. (2005) [17] | 28 | 20–25 | SEQ: −2.00D–+1.00D | Between 1.00D and 5.00D in steps of 0.50D | TDV | S-H |
| Plainis et al. (2005) [6] | 7 | 23–33 | Emmetropes; Myopes with sphere: −2.00D–−2.50D | Between 0D and 8.00D in steps of 1.00D | TDV | S-H |
| Buehren et al. (2006) [10] | 10 | 22–36 | Sphere: emmetropes +0.05D ± 0.19D; myopes −2.25D ± 0.85D Cil for both: −0.30D ± 0.45D |
0.17D, 1.00D, 2.00D, 3.00D, 4.00D and 5.00D | TDV | S-H |
| Wang et. al (2007) [18] | 20 | 18–32 | Sphere: −6.00D–+3.00D | Between 0 and −4.00D in steps of 1.00D | TDV | S-H |
| López-Gil et al. (2008) [19] | 24 | 19–29 | Sphere: −3.00D–+3.00D; Cil <1.00D | Between 0 and 5.00D in steps of 0.50D | TDV | S-H |
| López-Gil et al. (2010) [20] | 15 | 20–38 | Sphere: 0.38D–−3.06D; Cil: −0.38D ± 0.25D | Between 0.50D and 9.50D in steps of 0.50D | Badal | S-H |
| Fritzsch et. al (2011) [21] | 25 | 15–27 | Emmetropes | 0.22D and 5.00D | TDV | S-H |
| Yuan et al. (2013) [22] | 35 | 20–33 | SEQ: +0.50D–−2.38D; Cil <0.75D | 0.25D and 3.00D | TDV | S-H |
| Zhou et al. (2015) [12] | 22 | 18–28 | Sphere: 0D–−1.00D; Cil: −0.75D and 0D | Between 1.00D and 6.00D in steps of 1.00D | NSL | S-H |
| Wang et al. (2015) [11] | 10 | 0 and 3.00D | TDV | S-H |
2.1. Z(4,0), Z(6,0) and Accommodation
Z(4,0) is the aberration that shows the clearest trend with accommodation. When the accommodative system is relaxed, Z(4,0) is usually positive, and when accommodation is stimulated, it becomes less positive or more negative (Figure 2) [6,7,8,9,10,12,14,19,20][6][7][8][9][10][12][14][19][20]. However, the change from positive to negative values is not observed in every subject, because some individuals already present negative Z(4,0) in the relaxed state [6,8][6][8]. Moreover, the amount of this change varies between individuals [6,8,9,12,14,20][6][8][9][12][14][20]. The reason for these differences has not been explored but is likely due to the lens’s natural shape, which may not be the same for all subjects. Age also affects this tendency of Z(4,0) to become more negative with accommodation, being more evident in older subjects [19].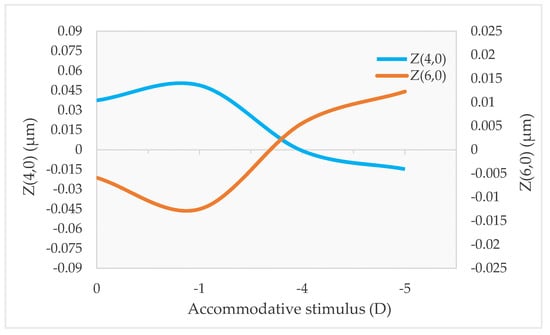
2.2. Other Zernike Terms and Accommodation
Other Zernike terms may change with accommodation and affect vision during near tasks and influence the accuracy of the accommodative response. Although the variability of aberrations among individuals is large, studies have shown that some Zernike terms also have a trend. Vertical and horizontal coma (Z(3,−1) and Z(3,1), respectively) seem to change to more positive values with accommodation, with Z(3,1) being more evident [6]. Vertical secondary astigmatism (Z(4,2)) and Z(7,−7) also showed a tendency to more negative values with increasing accommodative demand [12]. On the other hand, other studies found significant changes in oblique and vertical astigmatism (Z(2,−2) and Z(2,2), respectively), Z(3,−1), Z(3,1), vertical and oblique trefoil (Z(3,−3) and Z(3,3), respectively), vertical-pentafoil (Z(5,−5)), Z(6,−4), vertical-secondary-coma (Z(5,−1)), Z(7,−5), Z(7,−3), Z(7,3), and Z(7,5) with accommodation. However, since they change in different directions, there is no clear trend [7,8,9,12][7][8][9][12]. It appears that some other Zernike terms do undergo changes with accommodation, but the direction of these changes is not the same in all subjects.2.3. Z(4,0), Z(6,0) and Accommodative Lag
An interesting aspect is the relationship between spherical aberration and accommodative lag. A positive Z(4,0) causes a lead for far targets, while a negative Z(4,0) causes a lag for near targets [6]. On the other hand, Z(6,0) tends to increase the accommodative response regardless of whether it is positive or negative. The effect of Z(4,0) is greater than the effect of Z(6,0) [20]. A previous study [24] examined the effect of changing Z(4,0) on the accommodative response using contact lenses with controlled amounts of Z(4,0). When positive Z(4,0) was added, the slope of the accommodative stimulus–response function decreased, increasing the accommodative lag, whereas when negative Z(4,0) was added, the slope of the accommodative stimulus–response function increased, decreasing the accommodative lag. However, the same authors did not observe a relationship between RMS and accommodative lag. According to some authors [10,20][10][20], Z(4,0) is responsible for the most accommodative leads and lags. When it is present, some amount of defocus (lead/lag) could be helpful in improving retinal image quality. Therefore, lead/lag during the accommodative response may be a method to reduce the effects caused by changes in Z(4,0) and Z(6,0) during accommodation. As mentioned earlier, since Z(4,0) is responsible for most of the accommodative leads and lags, a different tendency of Z(4,0) during accommodation due to the shape of the lens could result in excess or insufficiency of accommodation. This may explain why, under the same conditions (e.g., visual ergonomics and hours of near viewing), some subjects develop accommodative dysfunction and others do not.2.4. Total, Corneal, and Internal HOAs during Accommodation
As previously noted, the shape and position of the crystalline lens change during ocular accommodation. The changes in ocular aberrations observed during accommodation are a result of these changes in the crystalline lens. Corneal wavefront aberrations do not change during accommodation [7]. Shi et al. [25] combined ultra-long-scan-depth spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (UL-SDOCT) and a Shack–Hartmann wavefront sensor to simultaneously analyze wavefront aberrations and anterior segment parameters, such as lens thickness and anterior and posterior lens curvature radii, during accommodation. Changes in lens dimensions occurred with changes in wavefront aberrations. It is the anterior surface of the lens that is most responsible for the variations in ocular aberrations during accommodation [11]. According to Norberto López-Gil and Vicente Fernández-Sánchez [20], 86% of the changes in wavefront aberrations with accommodation are due to the alterations in the anterior surface of the lens and 14% in its posterior surface. Another study [12] suggested that the changes in central Z(4,0) with accommodation are caused by the flattening of the peripheral portion of the lens, and other aberrations around this region are also changed. In the relaxed state, there is a balance between corneal and internal aberrations [26]. One partially compensates for the aberrations of the other, and this decreases with accommodation [27]. The loss of this compensation during accommodation, i.e., during near vision tasks [27], could lead to symptoms. The impact of this loss on the development of near-related problems should be investigated. In addition, refractive surgery must preserve this compensation as much as possible to improve visual quality for both distance and near vision.References
- Collins, M.J.; Wildsoet, C.F. Monochromatic aberrations and myopia. Vis. Res. 1995, 35, 1157–1163.
- Hiraoka, T.; Kakita, T.; Okamoto, F.; Oshika, T. Influence of ocular wavefront aberrations on axial length elongation in myopic children treated with overnight orthokeratology. Ophthalmology 2015, 122, 93–100.
- Osuagwu, U.L.; Suheimat, M.; Atchison, D.A. Peripheral aberrations in adult hyperopes, emmetropes and myopes. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2017, 37, 151–159.
- Valentina, B.S.; Ramona, B.; Speranta, S.; Calin, T. The influence of optical aberrations in refractive surgery. Rom. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 59, 217–222.
- López-Gil, N.; Rucker, F.J.; Stark, L.R.; Badar, M.; Borgovan, T.; Burke, S. and Kruger, Effect of third order aberrations on dynamic accommodation. Vis. Res. 2007, 47, 755–765.
- Plainis, S.; Ginis, H.S.; Pallikaris, A. The effect of ocular aberrations on steady-state errors of accommodative response. J. Vis. 2005, 5, 7.
- Li, Y.J.; Choi, J.A.; Kim, H.; Yu, S.Y.; Joo, C.K. Changes in ocular wavefront aberrations and retinal image quality with objective accommodation. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2011, 37, 835–841.
- He, J.C.; Burns, S.A. Monochromatic aberrations in the accommodated human eye. Vis. Res. 2000, 40, 41–48.
- Cheng, H.; Barnett, J.K.; Vilupuru, A.S.; Marsck, J.D.; Kasthurirangan, S.; Applegate, R.A.; Roorda, A. A population study on changes in wave aberrations with accomodation. J. Vis. 2004, 4, 272–280.
- Buehren, T.; Collins, M.J. Accommodation stimulus-response function and retinal image quality. Vis. Res. 2006, 46, 1633–1645.
- Wang, Y.; Shao, Y.; Yuan, Y. Simultaneously measuring ocular aberration and anterior segment biometry during accommodation. J. Innov. Opt. Health Sci. 2015, 8, 1550005.
- Zhou, X.Y.; Wang, L.; Zhou, X.T.; Yu, Z.Q. Wavefront aberration changes caused by a gradient of increasing accommodation stimuli. Eye 2015, 29, 115–121.
- Atchison, D.A.; Collins, M.J.; Wildsoet, C.F.; Christensen, J.; Waterworth, M.D. Measurement of monochromatic ocular aberrations of human eyes as a function of accommodation by the howland aberroscope technique. Vis. Res. 1995, 35, 313–323.
- Ninomiya, S.; Fujikado, T.; Kuroda, T.; Maeda, N.; Tano, Y.; Oshika, T.; Hirohara, Y.; Mihashi, T. Changes of ocular aberration with accommodation. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2002, 134, 924–926.
- He, J.C.; Gwiazda, J.; Thorn, F.; Held, R.; Huang, W. Change in corneal shape and corneal wave-front aberrations with accommodation. J. Vis. 2003, 3, 456–463.
- Hazel, C.A.; Cox, M.J.; Strang, N.C. Wavefront aberration and its relationship to the accommodative stimulus-response function in myopic subjects. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2003, 80, 151–158.
- Gicquel, J.J.; Nguyen-Khoa, J.L.; Lopez-Gil, N.; Legras, R.; Dighiero, P.; Lebuisson, D.A.; Gargasson, J.F. Optical Aberrations Variations of the Human Eye During Accommodation. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2005, 46, 1993.
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.Q.; Guo, H.Q.; Wang, Y.; Zuo, T. Wavefront aberrations in the accommodated human eye based on individual eye model. Optik 2007, 118, 271–277.
- López-Gil, N.; Fernández-Sánchez, V.; Legras, R.; Montés-Micó, R.; Lara, F.; Nguyen-Khoa, J.L. Accommodation-related changes in monochromatic aberrations of the human eye as a function of age. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 1736–1743.
- López-Gil, N.; Fernández-Sánchez, V. The change of spherical aberration during accommodation and its effect on the accommodation response. J. Vis. 2010, 10, 12.
- Fritzsch, M.; Dawczynski, J.; Vollandt, R.; Strobel, J. Aberrationen höherer Ordnung bei Akkommodation. Ophthalmologe 2011, 108, 553–560.
- Yuan, Y.; Shao, Y.; Tao, A.; Shen, M.; Wang, J.; Shi, G.; Chen, Q.; Zhu, D.; Lian, Y.; Qu, J.; et al. Ocular Anterior Segment Biometry and High-Order Wavefront Aberrations During Accommodation. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 10.
- Moreno-Barriuso, E.; Merayo Lloves, J.; Marcos, S.; Navarro, R.; Llorente, L.; Barbero, S. Ocular aberrations before and after myopic corneal refractive surgery: LASIK-induced changes measured with laser ray tracing. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2001, 42, 1396–1403.
- Theagarayan, B.; Radhakrishnan, H.; Allen, P.M.; Calver, R.I.; Rae, S.M.; O’Leary, D.J. The effect of altering spherical aberration on the static accommodative response. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2009, 29, 65–71.
- Shi, G.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Wei, L.; Lv, F.; Zhang, Y. Measurement of ocular anterior segment dimension and wavefront aberration simultaneously during accommodation. J. Biomed. Opt. 2012, 17, 120501.
- Tabernero, J.; Benito, A.; Alcón, A.; Artal, P. Mechanism of compensation of aberrations in the human eye. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2007, 24, 3274.
- Franco, S.; Gomes, J.; Gonçalves, A. Compensation effect between corneal and internal ocular aberrations during a computer task. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Applications of Optics and Photonics, Lisbon, Portugal, 31 May–4 June 2019; p. 11207.
