Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 3 by Vicky Zhou and Version 2 by Vicky Zhou.
Mozambique is a Southern African tropical country; it forms a 4330 km coastline on the Indian Ocean side. It is one of the continent’s five former Portuguese colonies, with the economy relying mainly on agriculture and mining.
- Mozambique
- country
- profile
Land and Society
Geography
The Republic of Mozambique (Figure 1) is a developing country located on the southeastern coast of Southern Africa [1][2][3], occupying 801,590 km2 [4][5] (13,000 km2 comprising inner water such as rivers and lakes [6]).
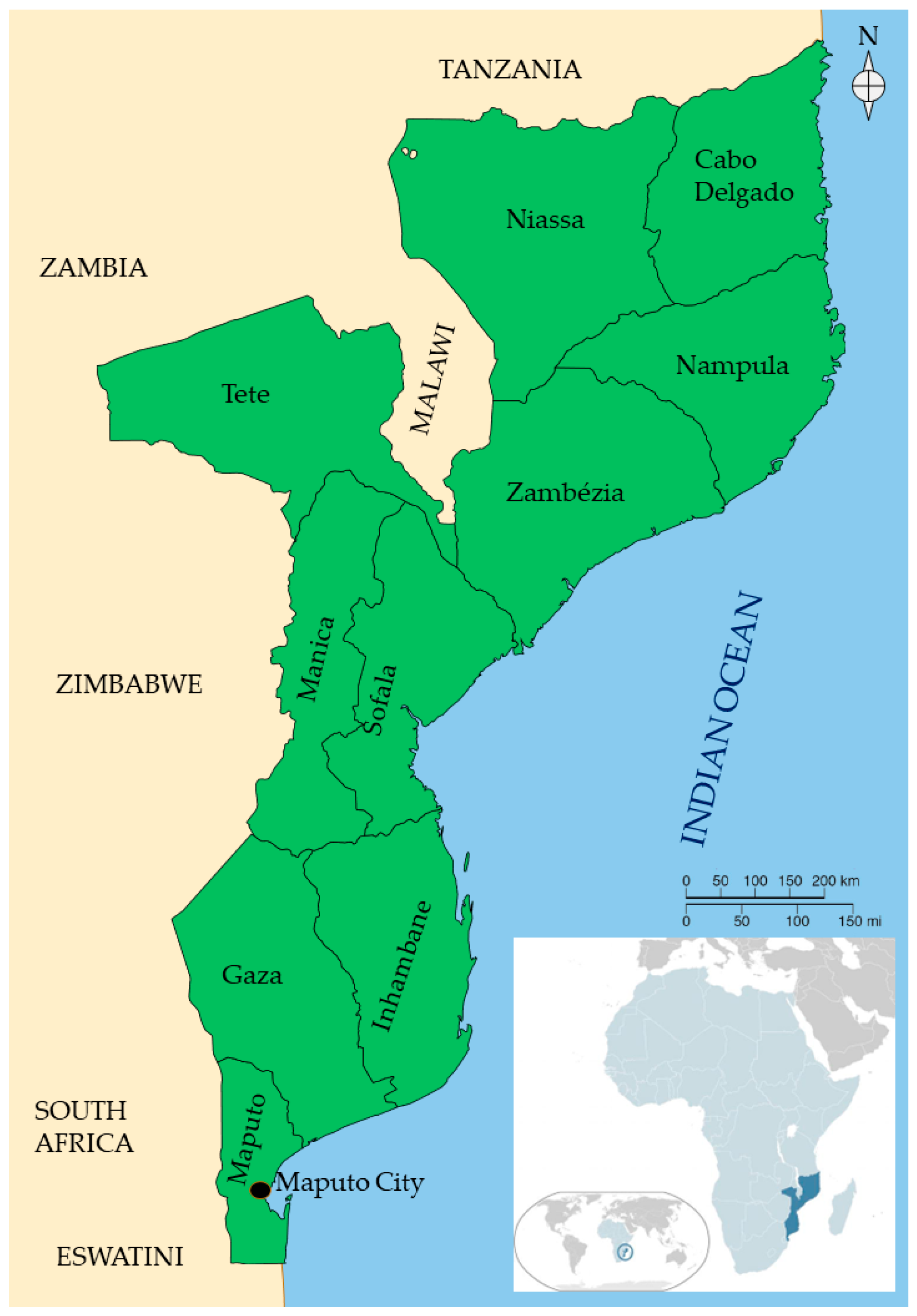
Figure 1. Map of Mozambique.
The Indian Ocean forms its eastern coastline (4330 km) [6] and shares its southwestern border with South Africa and Eswatini (former Swaziland), western with Zimbabwe and Zambia, northwestern with Malawi, and northern with Tanzania [4][7][8]. Its temperatures are higher nearby the coast (25–27 °C during summer and 20–23 °C during winter) and reduce as one enters the continent [6].
Mozambique has eleven provinces, including the capital Maputo City [8][9]. The country’s southern region comprises Maputo City, Maputo province, Gaza, and Inhambane [10]. Maputo City, with 1,122,607 inhabitants [9], is the country’s busiest and most developed area and is relatively multicultural due to the increasing number of people from other provinces who study or find work opportunities [11]. The central region comprises Manica, Sofala, Tete, and Zambézia provinces, and the northern region encompasses Nampula, Cabo Delgado, and Niassa provinces [8].
The climate is tropical and humid [4]. Mozambique has a dry and rainy season [12]. The locals frequently describe the dry season as winter because the temperature decreases steadily from mid-April to mid-July and rises until mid-September [5][13]. The rainy season has a peak temperature between December and January [13] and floods might occur in some areas (e.g., Chokwe district) [14].
The rural areas frequently lack pipe water, electricity, and access roads [15]. According to Census 2017, 35% of Mozambican households have at least one radio and 21.8% have a TV, which is the primary media to disseminate information and spread awareness throughout the population [3][16]. The statistics presented show disturbing disparity, not only regarding access to media but also regarding real estate ownership.
Only 26.4% of the population has cell phones, 4.4–5.3% have personal computers, and 5.8–7% have access to the internet [3][9]. Most people with cell phones can hardly afford the prices from the providers [9]. Internet and information technologies are scarce and irregularly distributed in terms of availability and quality [9][17]. However, recent statistics show that internet users are increasing, especially in the Maputo province [9].
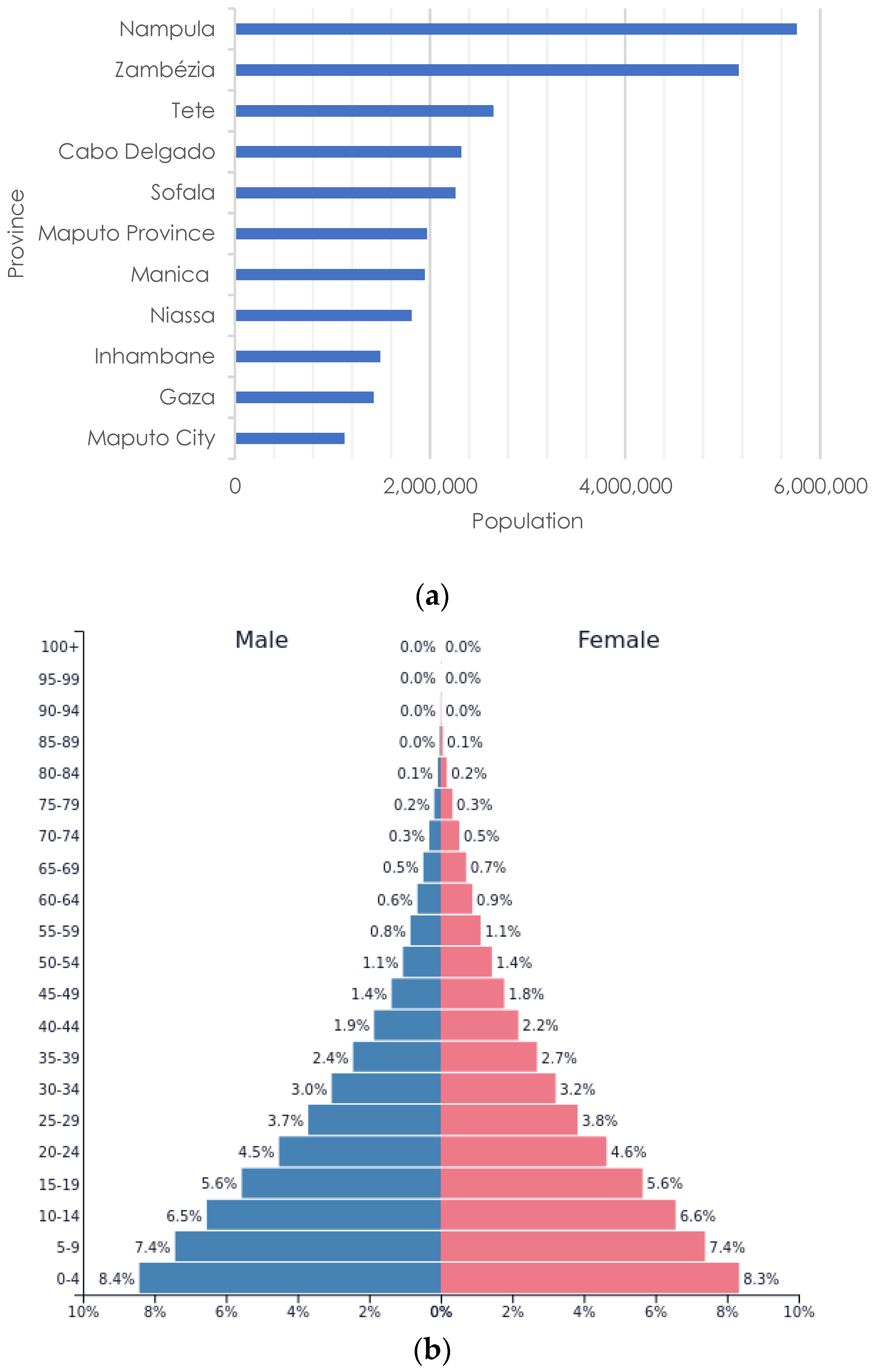
 The General Population and Housing Census of 2017 [50] indicated 27,909,798 inhabitants (density: 39 inhabitants/km2 [34]), but projections from the National Institute of Statistics [51] estimated 30,832,244 inhabitants by 2021, 65% living in rural areas (67.2% of the private households), almost equally divided between men (14,885,787) and women (15,946,457). The northern and central areas are the most populated (Figure 3). The country’s southern area (Maputo City, Maputo, Gaza, and Inhambane provinces) has approximately 4 million people [10]. There are 6.3 million households [17]. The steady increase in the population is a significant reason why family planning is essential in Mozambique [52].
The population pyramid is typical of a developing country, considerably narrowing as one moves bottom–up. The population is predominantly young [10][53], with 16.6–17.6 years as the average age [10][53][54][55], 53% under 17, and a life expectancy of 60 years (in 2018) [56]. As for the main age groups: children and adolescents below 15 years old comprise 46.7% of the population, the group 16–45 years old is 38.5%, followed by 10.2% comprising the 45–59-year old, the cluster above 60 years old is 4.6% [55], and above 64 years comprise 3% [34]. The population is growing partly because of low adherence to family planning [57]. Countrywide, the use of contraceptives decreased from 17% in 2003 to 11.5% in 2011 and increased to 35% in 2019 [57][58]. If the trend remains, population growth will stabilize.
The General Population and Housing Census of 2017 [50] indicated 27,909,798 inhabitants (density: 39 inhabitants/km2 [34]), but projections from the National Institute of Statistics [51] estimated 30,832,244 inhabitants by 2021, 65% living in rural areas (67.2% of the private households), almost equally divided between men (14,885,787) and women (15,946,457). The northern and central areas are the most populated (Figure 3). The country’s southern area (Maputo City, Maputo, Gaza, and Inhambane provinces) has approximately 4 million people [10]. There are 6.3 million households [17]. The steady increase in the population is a significant reason why family planning is essential in Mozambique [52].
The population pyramid is typical of a developing country, considerably narrowing as one moves bottom–up. The population is predominantly young [10][53], with 16.6–17.6 years as the average age [10][53][54][55], 53% under 17, and a life expectancy of 60 years (in 2018) [56]. As for the main age groups: children and adolescents below 15 years old comprise 46.7% of the population, the group 16–45 years old is 38.5%, followed by 10.2% comprising the 45–59-year old, the cluster above 60 years old is 4.6% [55], and above 64 years comprise 3% [34]. The population is growing partly because of low adherence to family planning [57]. Countrywide, the use of contraceptives decreased from 17% in 2003 to 11.5% in 2011 and increased to 35% in 2019 [57][58]. If the trend remains, population growth will stabilize.
History
Mozambique has a distinctive cultural identity [18], with a unique and rich culture [1] inherited from early Bantu settlers with Arab merchants, Portuguese colonizers, and Indian immigrants, among others. Although secondary orality (written or graphic records) is the main form of the perpetuation of the population’s collective memory, a significant part of the cultural identity passes across generations through primary orality (spoken information), using, for instance, proverbs, poems, nursery rhymes, folk tales, and songs [2]. The scarcity of written records before Portuguese colonialism causes it to be difficult for scientists to fully grasp the extent of the population’s historical and cultural heritage [2][19]. The oldest written records about Mozambique belong to al-Masud, who described the markets of Sofala as a source of gold [20]. The country’s name came from Mussa ibn Biki, a wealthy merchant and sheik on Mozambique Island [21]. The first contact between the local population and Portuguese colonizers occurred at the end of the 15th century when Vasco da Gama stopped in Inhambane while going to India [22]. Then, the visits became more frequent until the Portuguese finally settled to strengthen the commercial relationship with the locals. Notable explorers include Lourenço Marques and António Caldeira [23]. Before Mozambique’s unification, there were empires such as Mutapa [24] and Gaza [25], with many accounts of prosperity, treason, and war. Portugal occupied Mozambique effectively after the Berlin Conference (1884–1885), when European countries claimed ownership of the African territory [26][27] and when Mouzinho de Albuquerque captured Gaza’s emperor Ngungunhane, the last before Mozambique became a Portuguese Province [27][28]. According to Magalhães [29], when Portugal occupied Mozambique, António Enes ordered Portuguese officers to replace the traditional leaders and the colony adopted, in 1907, the Minute of the Administrative Reform of Mozambique, which was initially adopted in the South and later colony-wide. Mozambique had a Governor-General and District Governors with authority over Administrators. The lowest administrative position was the regulo (small king), a native who dealt directly with the population. Portugal colonized Mozambique and other territories for longer than other European countries partly because it assumed the position of the metropolis of a multicontinental country rather than the image of a colonizer. The war for independence between the Front for Liberation of Mozambique (FRELIMO) and the Portuguese lasted from 1964 to 1974 [30]. After the proclamation of independence on 25 June 1975 [8][10], few Portuguese stayed and changed their nationality to Mozambican. However, most engineers, scientists, and highly skilled people returned to Portugal or migrated to areas such as Rhodesia (now Zambia and Zimbabwe) or South Africa [31][32]. The economy struggled because there was very little qualified labor [33]. For the following post-independence years (1975–1989), the new government adopted a Marxist–Leninist orientation, with a single party and centralized rule [27]. However, a 16-year civil war (1976–1992), mostly in rural areas, created a political–economic destabilization [10][34] and production crises until the peace treaty in 1992, when Mozambique transitioned from state socialism to an increasingly neoliberalist regime [33]. The then rebels, known as the Mozambican National Resistance (RENAMO), had support from Ian Smith’s Southern Rhodesian and the South African apartheid regime. RENAMO was primarily dissatisfied with the communist government, in which no citizen could have private property. From their perspective, it was unfair to live in such conditions after the struggle for independence. Despite the problematic post-independence situation, the population was highly motivated to help consolidate the nation’s pride and sovereignty, primarily due to the charismatic leadership of President Samora Machel [35][36]. For instance, the country adhered to the Green Revolution’s agricultural movement, intensifying production, adopting modern machinery, and using chemical pesticides and fertilizers [37][38]. Mozambique’s economy changed from communist to market-oriented, introducing the so-called Economic and Social Rehabilitation Program (PRES) in 1987 [27][39]. Sponsored by the International Monetary Fund (IMF), this program included the regime change to democratic multiparty, modernization of the economy and the mode of production, mass privatization of the government’s assets, voluminous foreign investment, urban expansion, and improvements in the healthcare system [33][39]. According to Langa [40], other political transitions were post-conflict, after the Peace Treaty in 1992, the multiparty elections in 1994, and the following political decentralization. The regime change affects social relations, shifting from a closed to an open society [18]. However, Sambo and Guambe [41] criticized that despite several Constitution amendments, they aimed to consolidate the new State’s sovereignty, not necessarily the will of the different social classes. For instance, tribalism and social inequality are still frequent [42][43], and civic space, inclusiveness, and freedom of speech are deteriorating [44]. Aliança Moçambicana da Sociedade Civil C-19 [45] stated that economic disparity is increasing in Mozambique and worldwide, resulting from an economic system based on the development and accumulation of capital reliant on the exploration of workers and nature. Since the millennium started, Mozambique became increasingly aligned with international policies, pursuing the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs), followed by the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), reflected in the country’s policies, such as the Plan of Activities to Reduce Poverty [27]. Mozambique thrives after a long history of severe disease outbreaks, geopolitical tension, economic crises, and natural disasters [14]. The Mozambican Constitution has a specific protocol for an Emergency State [46], but nobody expected to use it due to a worldwide pandemic.Population
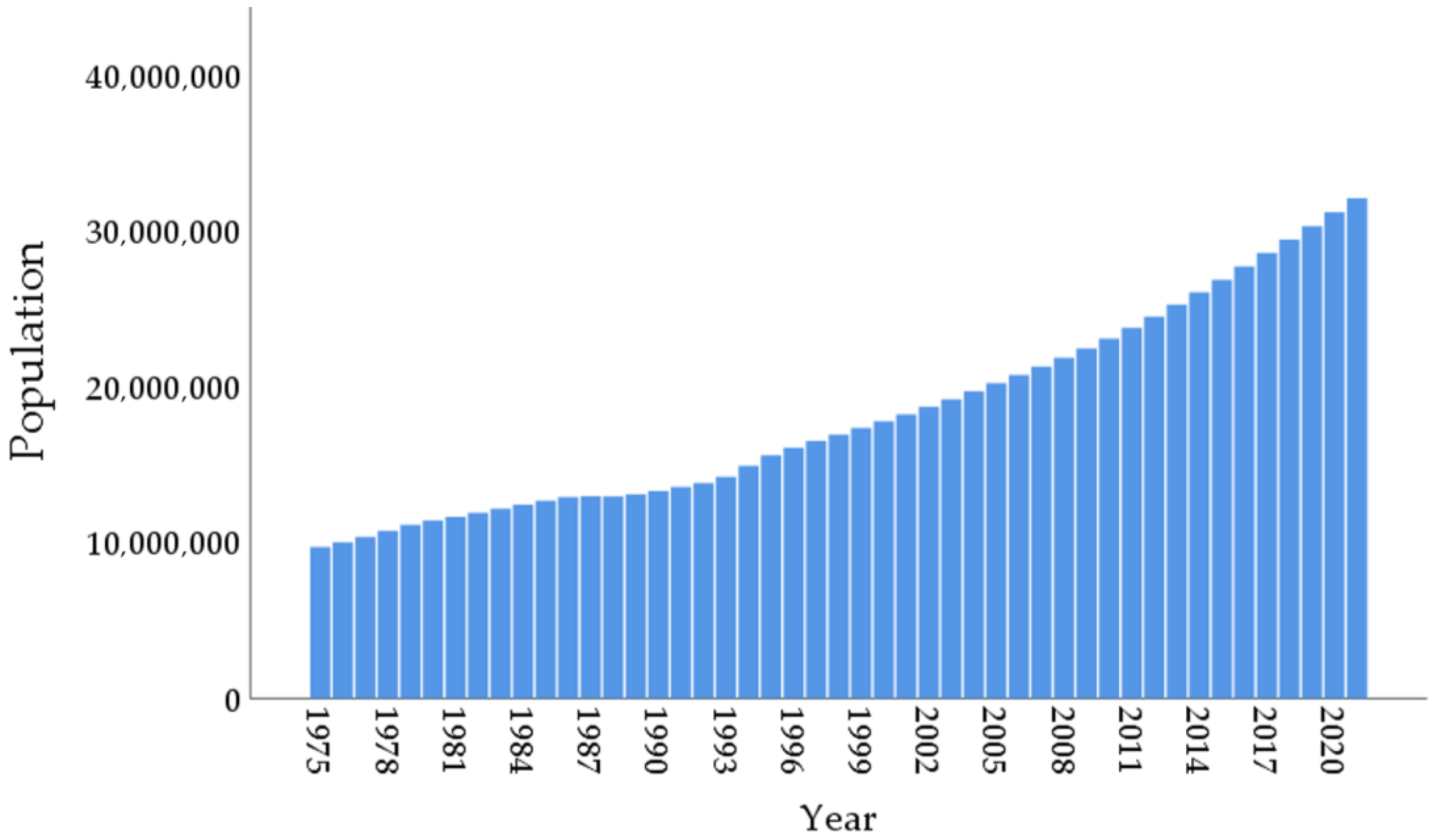
Figure 2 shows the population of Mozambique from 1990 to 2020. The period presented a constant arithmetic growth from approximately 12.5 million to almost 30 million citizens [47].
Culture and Religion
Besides being multicultural, Mozambique is multilingual [2][59]. It is among the five African countries with Portuguese as its official language [3], spoken by 37.7% of the population [2][8], used in the anthem, all official documents and communications, and the National Educational System (SNE) [8], except in international interactions or specific educational programs. There are 19 other national languages (Bantu) [59][60] (43 considering dialects [8]), which are spoken daily in informal settings. Local languages include Makwa, Swahili, Yao, Nyanja, Chuabo, Ndau, Sena, Bitonga, Changana, and Ronga. According to da Câmara [59], the language policy inherited from colonialism disadvantages people who communicate primarily through non-official languages, considered only a cultural and educational heritage to distinguish the population’s identity as Mozambican. According to the author and general knowledge, the Portuguese “assimilated” some natives with their language and culture in late colonialism, distinguishing them as a privileged class.
Figure 3. Mozambican population (a) per province (Made by the author based on the data from INAGE [61]) and (b) age pyramid (source: PopulationPyramid.net [62], under a Creative Commons license CC BY 3.0 IGO). According to the 2017 General Census, the estimated population is 29,496,008 [63].
Mozambicans are familiar with English because Mozambique is a member of the Commonwealth of Nations [64], all bordering countries are English-speaking, the SNE includes basic English classes from 8th to 12th grade, and there is a high exposure to songs and other multimedia content in English. Most imported products from South Africa have English labels. French is not as frequent but is also present in Mozambique and Spanish is also present due to its similarity with Portuguese and the strong relationship between Mozambique and Cuba and other Spanish-speaking countries. Minor groups speak other European languages such as Italian, Russian, and Deutsche; Asian languages such as Arabic, Hindu, Gujarati, Urdu, and Mandarin; and local languages from Nigeria, Somalia, Sudan, the Democratic Republic of Congo, and Rwanda [59].
There are matriarchal and patriarchal communities, depending on areas and ethnic groups [18]. The country seems predominantly patriarchal, but the northern provinces are mainly matriarchal [65][66]. Post-independence factors such as migration—especially inter-regional—and interethnic or intertribal marriages probably affect these social systems.
According to Mutiua [67], since the early 1990s, the existing religions have expanded substantially in infrastructure and there have been new congregations or other religious institutions. Table 1 shows that the number of believers between 2007 and 2017 increased, especially the followers of Pentecostal evangelic churches [68][69], with a 2.4% increase. However, the Catholic church suffered a reduction in the percentage of followers. These trends are not surprising, considering their approaches to faith. Pentecostal churches frequently promise prosperity to their followers as a divine reward for their offers to the congregation; such offers are enough to reinvest in their infrastructures and communication channels and attract more followers and resources [70].
Table 1. Percentage of followers of different religions in Mozambique in 2007 and 2017. Source: Adapted from Mutiua [67].
| Religion | Percentage of Followers (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| 2007 | 2017 | |
| Catholic | 28.8 | 27.2 |
| Islam | 17.9 | 18.9 |
| Evangelic | 10.9 | 15.3 |
| Other * | 18.7 | 13.9 |
* Hindus, atheists, agnostics, followers of local traditional religions, and more.
Regarding Islam, the increased number of followers might relate to the fact that men in Mozambique have to join the religion when marrying a Muslim woman and, consequently, their children are born as Muslims. On the other hand, when the man is Muslim, and the woman is from another religion, she frequently converts or does not prevent the children from being raised as Muslims. Both situations favor the expansion of Islam in Mozambique.
There are also followers and practitioners of local belief systems and spiritual practices. This group is possibly the most diverse because some can simultaneously follow the Judaic-Christian religions. Salite [71] studied farmers’ beliefs in the Gaza province; most seemed to practice or follow cults of nature and ancestors. It is well-known in Mozambique that some people have spiritual beliefs related to animals, such as snakes and some birds, associating them with ancestors or protector spirits for crops or sacred woods [72]. It is hard to know how many people belong to this group for several reasons, including a stigma and fear of traditional spiritual practices, leading some followers not to admit it publicly, and the lack of official congregations or equivalent to represent them. There is AMETRAMO (Association of Mozambican Traditional Healers) [73], but it is a syndicate rather than a religious group. The unfortunate discrimination of the traditional healers prevents the local authorities from harnessing their untapped potential, particularly regarding ethnobotanics [74].
References
- Guambe, J.J.J.; da Silva, J.J.; Victor, R.B.; Azevedo, H.A.M.d.A.; Chundo, D.M.I.; Gerente, B.J. COVID-19, Transporte Aéreo e Turismo em Moçambique. Geo. UERJ 2021, e61344.
- Nhamona, E.; Manjate, T. O provérbio e a retórica da prevenção contra a COVID-19 durante o estado de emergência nas cidades de Maputo e da Matola (Moçambique). In Ensaios Interdisciplinares em Humanidades; da Silva Filho, A.V., Subuhana, C., de Mello, I.M., de Carvalho, R.O., de Oliveira, M.R.D., Eds.; Editora Autografia Edição e Comunicação Ltda.: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2020; Volume 4, pp. 37–52.
- Culimua, A.S.; de Figueiredo, S.L.F. O ensino secundário e o recurso às TICs em tempos da COVID-19 em Moçambique. In Proceedings of the VII Congresso Nacional da Educação, Campina Grande, Brazil, 2–4 December 2021; pp. 1–11.
- Cambaza, E.M. The African miracle: Why COVID-19 seems to spread slowly in Sub-Saharan Africa. Rev. Cient. UEM Sér. Ciênc. Bioméd. Saúde Pública 2020.
- Cambaza, E.M.; Viegas, G.C.; Cambaza, C.M. Potential impact of temperature and atmospheric pressure on the number of cases of COVID-19 in Mozambique, Southern Africa. J. Public Health Epidemiol. 2020, 12, 246–260.
- Langa, E.S.; Massuanganhe, J.A.; Nhanala, G.A. O impacto do coronavírus (COVID-19) e as mudanças climáticas na taxa de câmbio: Abordagem multivariada para Moçambique. Prometeica-Rev. De Filos. Y Cienc. 2022, 210–226. Available online: https://dialnet.unirioja.es/descarga/articulo/8579728.pdf (accessed on 4 October 2022).
- Nyusi, F.J. Comunicação à Nação de Sua Excelência Filipe Jacinto Nyusi, Presidente da República de Moçambique, Sobre a Situação da Pandemia do Corona Vírus—COVID-19. 2020. Available online: https://www.presidencia.gov.mz/por/content/download/9052/64281/version/1/file/Comunica%C3%A7%C3%A3o+%C3%A0+Na%C3%A7%C3%A3o+-+16.07.2020.pdf (accessed on 4 October 2022).
- Denhard, L.; Kaviany, P.; Chicumbe, S.; Muianga, C.; Laisse, G.; Aune, K.; Sheffel, A. How prepared is Mozambique to treat COVID-19 patients? A new approach for estimating oxygen service availability, oxygen treatment capacity, and population access to oxygen-ready treatment facilities. Int. J. Equity Health 2021, 20, 1–13.
- Pereira, C.R.; da Silva, S.R. Práticas de consumo de smartphones no contexto de pandemia de COVID-19: Um olhar etnográfico para as apropriações das mulheres de Maputo–Moçambique Smartphone consumption practices in the context. Comun. Mídia E Consumo 2022, 19, 148–169.
- Martins, H.F.B.; Loquiha, O.; Hansine, R.; Macicame, I.; Maure, G.A.; Marrufo, T.J.; Sacarlal, J.; Abacassamo, F.; Mucavele, H.; Saúte, F.C.M. COVID-19 morbidity and case fatality rate: An analysis of possible confounding factors. J. Infect Dis. 2020, 1, 1–17.
- Cambaza, E. Influence of population density and access to sanitation on Covid-19 in Mozambique. Ang. J. Health Sci. 2021, 2, 3–8.
- Uamusse, M.M.; Aljaradin, M.; Nilsson, E.; Persson, K.M. Climate Change observations into Hydropower in Mozambique. Energy Procedia 2017, 138, 592–597.
- Classic Portfolio. Seasons: Mozambique—When to Go & What to Pack. Available online: http://www.classic-portfolio.com/PDF_Documents/Clients/Mozambique/SEASONS%20-%20MOZAMBIQUE.pdf (accessed on 15 August 2021).
- Ducrot, R.; Leite, M.; Gentil, C.; Bouarfa, S.; Rollin, D.; Famba, S. Strengthening the capacity of irrigation schemes to cope with flood through improved maintenance: A collaborative approach to analySe the case of Chókwè, Mozambique. Irrig. Drain. 2018, 69, 126–138.
- Vasco, S.A.J. Aplicabilidade do marketing digital como meio de promoção do marketing social em meio à pandemia da covid-19 no contexto moçambicano. Rev. Cient. UEM Sér. Ciênc. Bioméd. Saúde Pública 2021. Available online: http://www.revistacientifica.uem.mz/revista/index.php/cbsp/article/view/24 (accessed on 4 October 2022).
- Frederico, M.; Matsinhe, C. Resistência à Adopção das Medidas de Prevenção da COVID-19 em Moçambique; Centro de Estudos Africanos, Universidade Eduardo Mondlane: Maputo, Mozambique, 2020; p. 13.
- Teixeira, R.A.G.; Gonçalves, A.C.P.; Jorge, A.N. Educação remota no contexto da COVID-19 em Moçambique: Um olhar sobre as condições de acesso: Um olhar sobre as condições de acesso. SciELO Prepr. 2022. Available online: https://doi.org/10.1590/SciELOPreprints.4193 (accessed on 4 October 2022).
- Cambrão, P.; Julião, D. COVID-19 and its Implications in Mozambique: An Anthropo-sociological Analysis. Rev. Electrónica Investig. E Desenvolv. 2020, 2, 1–16.
- Ki-Zerbo, J. (Ed.) História Geral da Africa: Metodologia e Pré-História da África. UNESCO: Brasília, Brazil, 2010; Volume 1, p. 990.
- Times, P.I. The East African Coast: An Historical and Archaeological Review. In An Economic History of Tropical Africa, 1st ed.; Konczacki, Z.A., Konczacki, J.M., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK, 1977; p. 13.
- Vertriest, W.; Saeseaw, S. A Decade of Ruby from Mozambique: A Review. Gems Gemol. 2019, 55, 162–183.
- Banks, J. Adamastorying Mozambique: “Ualalapi” and “Os Lusíadas”. Luso-Braz. Rev. 2000, 37, 1–16.
- Evers, T. Iron Age Trade in the Eastern Transvaal, South Africa. S. Afr. Archaeol. Bull. 1974, 29, 33–37.
- Abraham, D.P. Ethno-History of the Empire of Mutapa. Problems and Methods. In The Historian in Tropical Africa; Routledge: London, UK, 2018; pp. 105–126.
- Liesegang, G. The 17th–19th Century Zimunye Tradition and 19th Century Nguni Empire Archaeology in Mozambique. Stud. Afr. Past 2019, 6. Available online: https://sap.udsm.ac.tz/index.php/sap/article/view/93 (accessed on 4 October 2022).
- Idejiora-Kalu, N. Understanding the effects of the resolutions of the 1884–85 Berlin Conference to Africa’s Development and Euro-Africa relations. Prague Pap. Hist. Int. Relat. 2019, 2, 99–108.
- Edgar, C. A glance at Mozambican dairy research. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2018, 13, 2945–2956.
- Wheeler, D.L. Joaquim Mouzinho de Albuquerque (1855–1902) ea política do colonialismo. Anal. Soc. 1980, 16, 295–318.
- Magalhães, J.P. Trajetórias e Resistências de Mulheres sob o Colonialismo Português (Sul de Moçambique, XX); Universidade de São Paulo: São Paulo, Brazil, 2016.
- Zeca, K.S.H.X. A Capacidade Estatal e as demandas da sociedade no contexto da COVID-19 no setor da educação em Moçambique. Conjunt. Austral 2021, 12, 07–18.
- Nyamunda, T. In Defence of White Rule in Southern Africa: Portuguese–Rhodesian Economic Relations to 1974. South Afr. Hist. J. 2019, 71, 394–422.
- Gerhart, G. Independence comes to Mozambique. Afr. Today 1975, 22, 11–14.
- Da Silva, C.A.; Monie, F.; Mulhaisse, R.A. Pandemia de coronavírus/COVID-19 em Moçambique: Desafios de reflexão sobre os contextos territoriais e socioeconômicos da política de saúde. Geosaberes 2020, 11, 674.
- Martins, H.F.B.; Hansine, R. Análise epidemiológica e demográfica da COVID-19 em África. An. Inst. Hig. E Med. Trop. 2020, 19, 7–42.
- Maúngue, H.B. Para uma sociologia do carisma na atualidade: Ensaio para leitura do carisma de Samora Machel. Em Tese 2014, 11, 91–108.
- Langa, P. O homem na sociedade ou a sociedade no homem: Desafios epistémico e metodológico para uma análise sociológica do carisma de Samora Machel. Rev. Ang. Sociol. 2014, 13, 67–79.
- Kajisa, K.; Payongayong, E. Potential of and constraints to the rice Green Revolution in Mozambique: A case study of the Chokwe irrigation scheme. Food Policy 2011, 36, 615–626.
- Shilomboleni, H. African Green Revolution, food sovereignty and constrained livelihood choice in Mozambique. Can. J. Afr. Stud./Rev. Can. Des Études Afr. 2018, 52, 115–137.
- Baloi, J.A. Políticas e Estratégias de Combate à Pobreza e de Promoção do Desenvolvimento em Moçambique: Elementos de Continuidade e Descontinuidade. Rev. Estud. Políticas Públicas 2018, 4, 203–214.
- Langa, E.N.B. Diplomacia e política externa em Moçambique: O primeiro governo pós-independência-Samora Machel. Rev. Bras. De Estud. Afr. 2021, 6, 11–32.
- Sambo, A.S.; Guambe, E. Abordagem ‘One Size Fits All’ Pode não ser a Mais Acertada: Declaração de Estado de Sítio em Cabo Delgado e Estado de Calamidade Pública Noutras Províncias do País? 2020. Available online: https://www.cartamz.com/index.php/politica/item/5785-declaracao-de-estado-de-sitio-em-cabo-delgado-e-estado-de-calamidade-publica-noutras-provincias-do-pais (accessed on 4 October 2022).
- Muchacona, J.J.; Romão, J.C. Da Reconstrução Económica à Emergência do Regime Democrático em Moçambique. Rev. Eletrônica Discente História. Com. 2018, 5, 86–99.
- Gallo, F.B.G. “A intestina batalha” socialista moçambicana através de ‘Crônica da Rua 513.2′, de João Paulo Borges Coelho. Abril: Rev. Estud. Lit. Port. E Afr.-NEPA UFF 2018, 10, 135–150.
- Pereira, C.; Forquilha, S. Navigating Civic Space in a Time of COVID-19: Mozambique Country Report; Institute for Social and Economic Studies: Maputo, Mozambique, 2021.
- Aliança Moçambicana da Sociedade Civil C-19. WordPress.com, 2020. Available online: https://aliancac19.wordpress.com/ (accessed on 4 October 2022).
- Assembleia da República de Moçambique. Lei da Revisão Pontual da Constituição da República de Moçambique. In Boletim da República: Publicação Oficial da República de Moçambique; de Moçambique, A.d.R., Ed.; Imprensa Nacional de Moçambique: Maputo, Mozambique, 2018; Volume 1, pp. 3–41.
- Niquice, A.R.; Filippi, E.E. Desafios socio-económicos de Moçambique no contexto da COVID-19. Rev. Cient. UEM Sér. Ciênc. Bioméd. Saúde Pública 2021. Available online: http://revistacientifica.uem.mz/revista/index.php/cbsp/article/view/103 (accessed on 4 October 2022).
- The World Bank Group. Mozambique. Available online: https://data.worldbank.org/country/mozambique?view=chart (accessed on 14 December 2022).
- World Population Prospects. Total Population, Both Sexes Combined (Thousands). Available online: http://data.un.org/Data.aspx?d=PopDiv&f=variableID%3a12 (accessed on 5 January 2020).
- INE. Censo 2017: IV Recenseamento Geral da População e Habitação; Instituto Nacional de Estatística: Maputo, Mozambique, 2017; p. 14.
- Instituto Nacional de Estatística. INE Destaques—Instituto Nacional de Estatistica. Available online: http://www.ine.gov.mz/ (accessed on 9 August 2021).
- Galle, A.; Vermandere, H.; Griffin, S.; de Melo, M.; Machaieie, L.; Van Braeckel, D.; Degomme, O. Quality of care in family planning services in rural Mozambique with a focus on long acting reversible contraceptives: A cross-sectional survey. BMC Women’s Health 2018, 18, 201.
- Marotta, C.; Nacareia, U.; Estevez, A.; Tognon, F.; Genna, G.; De Meneghi, G.; Occa, E.; Ramirez, L.; Lazzari, M.; Di Gennaro, F.; et al. Mozambican Adolescents and Youths during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Knowledge and Awareness Gaps in the Provinces of Sofala and Tete. Healthcare 2021, 9, 321.
- Worldometers.info. Mozambique Population (LIVE). Available online: https://www.worldometers.info/world-population/mozambique-population/ (accessed on 9 August 2021).
- Sumbana, J.; Sacarlal, J.; Rubino, S. Air pollution and other risk factors might buffer COVID-19 severity in Mozambique. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries 2020, 14, 994–1000.
- Moretti-Marques, R.; Salcedo, M.P.; Filho, D.C.; Lopes, A.; Vieira, M.; Cintra, G.F.; Ribeiro, M.; Changule, D.; Daud, S.; Rangeiro, R.; et al. Telementoring in gynecologic oncology training: Changing lives in Mozambique. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2019, 30, 150–151.
- Capurchande, R.D.; Coene, G.; Roelens, K.; Meulemans, H. Between compliance and resistance: Exploring discourses on family planning in Community Health Committees in Mozambique. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e006529.
- Lopes, S.C.; Constant, D.; Fraga, S.; Osman, N.B.; Harries, J. “There Are Things We Can Do and There Are Things We Cannot Do.” A Qualitative Study About Women’s Perceptions on Empowerment in Relation to Fertility Intentions and Family Planning Practices in Mozambique. Front. Glob. Women’s Health 2022, 3, 824650.
- da Câmara, C.L. COVID-19 e o multilinguismo em Moçambique. Rev. Cient. UEM Sér. Ciênc. Bioméd. Saúde Pública 2021, 1–13. Available online: http://www.revistacientifica.uem.mz/revista/index.php/cbsp/article/view/130 (accessed on 4 October 2022).
- Patel, S.; Majuisse, A.; Tem, F. Manual de Línguas Moçambicanas: Formação de Professores do Ensino Primário e Educação de Adultos; Ministério da Educação e Desenvolvimento Humano (DNFP & INDE) and Associação Progresso: Maputo, Mozambique, 2018.
- INAGE. População. Available online: https://www.portaldogoverno.gov.mz/por/Mocambique/Populacao (accessed on 20 September 2022).
- PopulationPyramid.net. Mozambique 2018. Available online: https://www.populationpyramid.net/mozambique/2018/ (accessed on 5 January 2020).
- Maunze, X.H.; Dade, A.; Zacarias, M.d.F.; Cubula, B.; Alfeu, M.; Mangue, J.; Mouzinho, R.; Cassimo, M.N.; Zunguze, C.; Zavale, O.; et al. IV Recenseamento Geral da População e Habitação, 2017: Resultados definitivos—Moçambique; Instituto Nacional de Estatística: Maputo Mozambique, 2019.
- Collinge, J. Criteria for commonwealth membership. Round Table 1996, 85, 279–286.
- do Nascimento Santos, Á.R.; de Macedo Mendes, A. A mulher na narrativa de Paulina Chiziane: Ressignificando papéis de gênero na sociedade moçambicana. Estrema-Rev. Interdiscip. De Humanid. 2015, 7, 19.
- Díaz-Szmidt, R. O legado tradicional africano e as influências ocidentais: A formação da identidade e da moçambicanidade na literatura pós-colonial de Moçambique. In Proceedings of the VII Congresso Ibérico de Estudos Africanos, Lisbon, Portugal, 9–11 September 2010; pp. 1–12.
- Mutiua, C. Religião no contexto da COVID-19 em Moçambique: Desafios e oportunidades adaptativas; Centro de Estudos Africanos, Universidade Eduardo Mondlane: Maputo, Mozambique, 2020; p. 10.
- Premawardhana, D. Faith in flux: Pentecostalism and mobility in rural Mozambique; University of Pennsylvania Press: Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, 2018; p. 228.
- van de Kamp, L. Violent Conversion: Brazilian Pentecostalism and Urban Women in Mozambique; Boydell & Brewer: Woodbridge, UK, 2016; Volume 1, p. 236.
- Van de Kamp, L. Burying life: Pentecostal religion and development in urban Mozambique. In Development and Politics from Below; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 152–171.
- Salite, D.L.J. The Role of Cultural Beliefs in Shaping Farmers’ Behavioural Decisions to Adapt to Drought Risks in Gaza Province-Southern Mozambique. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Reading, Reading, UK, May 2019.
- Simbine, M.G.Z. Fatores Antrópicos e Conservação da Floresta Sagrada de Chirindzene, Gaza-Moçambique. Master’s Thesis, Universidade do Porto, Porto, Portugal, July 2013. Available online: https://repositorio-aberto.up.pt/bitstream/10216/67495/2/24443.pdf (accessed on 4 October 2022).
- Jozane, T. Desafios para Regulamentação das Práticas da Medicina Tradicional e Alternativa no Sistema Nacional de Saúde em Moçambique: Documento Provisório; Universidade Eduardo Mondlane: Maputo, Mozambique, 2020.
- Guambe, A.J. Desafios da psicologia e da pesquisa no pós-COVID-19: Um olhar a partir do contexto de Moçambique. Rev. Psicol. Divers. E Saúde 2020, 9, 128–131.
More
