Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 2 by Conner Chen and Version 1 by Antonio Maria Fea.
Glaucoma is a multifactorial neurodegenerative illness requiring early diagnosis and strict monitoring of the disease progression. Artificial intelligence algorithms can extract various optic disc features and automatically detect glaucoma from fundus photographs.
- biomarkers
- artificial intelligence
- genetics
1. Artificial Intelligence in Glaucoma
The use of artificial intelligence is expanding rapidly. Machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) allowed a more sophisticated and self-programming way to use machines in automatic data analysis. More in detail, in machine learning, a system can automatically improve its performance and learn by itself with experience without being specifically programmed to do so. Specifically, using a convolutional neural network (CNN) architecture, the deep learning algorithm can take in an input image, assign importance (learnable weights and biases) to various aspects/objects in the image, and be able to differentiate one from the other [5][1]. Similar to neurons derived from the mammalian visual cortex, the neural network’s architecture consists of many hidden layers, each with its specific receptive field and connection to a further layer (Figure 1).
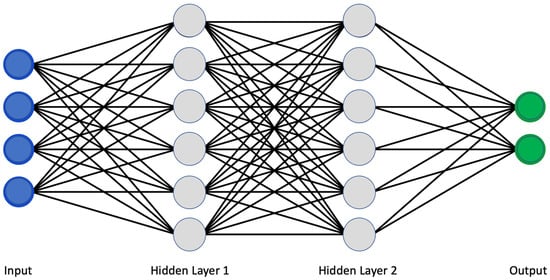
Figure 1.
Classical scheme of a convolutional neural network.
The deep learning network works as a two-step process. The first is the feature learning step, in which convolution, pooling, and activation functions make the ‘jump ahead’ between hidden layers. Secondly, the classification function converts the probability value to a label, providing a clinical output such as healthy or pathologic [6,7][2][3].
Although this architecture traditionally provided a high degree of computational power, in recent years, more advanced network architectures have been developed, allowing the system to analyze more complex data sources. AlexNet (2012) was introduced to improve the results of the ImageNet challenge. VGGNet (2014) was introduced to reduce the number of parameters in the CNN layers and improve the training time. ResNet (2015) architecture makes use of shortcut connections to solve the vanishing gradient problem (which is encountered when during the iteration of training, each of the neural network’s weights receives an update proportional to the partial derivative of the error function with respect to the current weight) [8][4]. The basic building block of ResNet is a residual block that is repeated throughout the network. There are multiple versions of ResNet architectures, each with a different number of layers. Inception (2014) increases the network space from which the best network is to be chosen via training. Each inception module can capture salient features at different levels [9][5].
Traditional metrics assessing the DL algorithm’s quality are sensitivity, specificity, precision, accuracy, positive predictive value, negative predictive value, and area under the receiver operating curve (AUC).
It is known that the early detection of glaucoma could eventually preserve vision in affected people. However, due to its clinical history of being symptomatic only in advanced stages and when most of the retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) are already compromised, it is crucial to introduce a tool to detect glaucoma in clinical practice in pre-symptomatic form automatically. Furthermore, it could be of clinical relevance also to find new ways to provide targeted treatment and forecast the clinical progression.
2. Fundus Photography
In clinical practice, ophthalmologists suspect glaucoma by analyzing optic nerve head (ONH) anatomy, cup-to-disc ratio (CDR), optic nerve head notching or vertical elongation, retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) thinning, presence of disc hemorrhages, nasal shifting of vessels, or the presence of parapapillary atrophy. However, the diagnostic process could be challenging considering the extreme variance of these parameters [10][6]. It has been shown that agreement among experts on detecting glaucoma from optic nerve anatomy is barely moderate [11][7]. Furthermore, with standard fundus photography, not only the variability of anatomy could be misleading, but also the parameters of acquisition such as exposition, focus, depth of focus, contrast, quality, magnification, and state of mydriasis. In this scenario, artificial intelligence algorithms can extract various optic disc features and automatically detect glaucoma from fundus photographs. For example, Ting et al. [7][3] collected 197,085 images and trained an artificial intelligence algorithm to automatically determine the cup-disc ratio (CDR) with an AUC of the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve of 0.942 and sensibility and specificity, respectively, of 0.964 and 0.872. Similarly, Li et al. [12][8] developed an algorithm based on 48,116 fundus images reporting high sensitivity (95.6%), specificity (92.0%), and AUC (0.986). Although the importance of automatically detecting the excavation of the optic nerve head, it is known that high inter-subject variability characterizes CDR; some large optic nerve heads have bigger cupping even without any sign of glaucoma. To reduce the rate of false positives, other researchers trained a deep learning algorithm to determine the presence of glaucoma based on fundus photographs and implemented it with the visual field severity [13][9]. Li and coworkers used a pre-trained CNN called ResNet101 and implemented it with raw clinical data in the last connected layer of the network; interestingly, there were no statistically significant changes in AUC, but they found an improvement in the overall sensitivity and specificity of the model, confirming the importance of multi-source data to improve the discriminative capacity of the glaucomatous optic disc [14][10]. More recently, Hemelings et al. utilized a pre-trained CNN structure relying on active and transfer learning to develop an algorithm with an AUC of 0.995. They also introduced the possibility for clinicians to use heatmaps and occlusion tests to understand better the predominant areas from which the algorithm based its predictions; it is an exciting way of trying to overcome some problems related to the well-known ‘black-box’ effect [15][11]. The majority of the publications that were analyzed suggested that an automated system for diagnosing glaucoma could be developed (Table 1). The severity of the disease and its high incidence rates support the studies that have been conducted. Deep learning and other recent computational methods have proven to be promising fundus imaging technologies. Some recent technologies, such as data augmentation and transfer learning, have been used as an alternative way to optimize and reduce network training, even though such techniques necessitate a large database and high computational costs.Table 1.
Summary of studies on glaucoma detection using fundus photography.
| Author | Year | N. of Images | Structure | SEN | SPEC | ACC | AUC | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kolar et al. [16][12] | 2008 | 30 | FD | |||||||||
| OCT Fundus | Thompson et al. | 93.80% | ||||||||||
| [ | 47][43] | 2019 | 1. Global BMO-MRW prediction | ResNet34 | Nayak et al. [17][13] | 2009 | 61 | Morphological | 100% | 80% | 90% | |
| Bock et al. [18][14] | 2010 | 575 | Glaucoma Risk Index | 73% | 85% | 80% | ||||||
| Acharya et al. [19][15] | 2011 | 60 | SVM | 91% | ||||||||
| Dua et al. [20][16] | 2012 | 60 | DWT | |||||||||
| 0.914 | ||||||||||||
ARCH = Architecture; SEN = Sensibility; SPEC = Specificity; ACC = Accuracy; AUC = Area under the curve. SEN = Sensibility, SPEC = Specificity, ACC = Accuracy, AUC = Area under the curve.
SEN = Sensibility, SPEC = Specificity, ACC = Accuracy, AUC = Area under the curve.
4. Standard Automatic Perimetry
Visual field testing represents a fundamental exam for diagnosing and monitoring glaucoma. In distinction from the fundus photographs and OCT, it allows the interpretation of the functionality of the whole visual pathway. Given the importance of visual function testing for the detection and clinical forecast of glaucoma, many researchers recently developed DL algorithms using the complex quantitative data it contains. Asaoka et al. [69][65] trained a DL algorithm to automatically detect glaucomatous visual field loss with an AUC of 0.926; the performance of their model was higher if compared to other machine learning classifiers methods, such as random forests (AUC 0.790) and support vector machines (AUC 0.712). Elze et al. [70][66] employed archetypal analysis technology to obtain a quantitative measurement of the impact of the archetypes or prototypical patterns constituting visual field alterations. Similarly, Wang et al. developed an artificial intelligence approach to detect visual field progression based on spatial pattern analysis [71][67]. Given the importance of predicting visual loss patterns in glaucoma patients, specifically for prescribing a personalized treatment, researchers have developed interesting tools to predict the probability of disease progression based on visual field data. DeRoos et al. [72][68] were able to compare forecasted changes in mean deviation (MD) on perimetry at different target pressures using a machine-learning technique called Kalman Filtering (KF). KF is a machine-learning technique derived from the aero-spatial industry that compares the course of the disease of a single patient to a population of patients with the same chronic disease; in this scenario, it could potentially predict the rate of conversion to glaucoma in patients with ocular hypertension as well as disease progression in the future for patients with manifest glaucoma (Table 3). [73,74][69][70].Table 3.
Summary of studies on artificial intelligence applied to visual field testing.
| Author | Year | Outcomes Mesures | Architecture | SEN | SPEC | ACC | AUC | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asaoka et al. [69][65] | 0.945 | ||||||||||||||
| 2016 | Pre-perimetric VFs vs. VFs in healthy eyes | FNN | 0.926 | 2. Yes glaucoma vs. No glaucoma | |||||||||||
| Kucur et al. [75] | |||||||||||||||
| [71] | 2018 | Early glaucomatous VF loss vs. no glaucoma | CNN with Voronoi representation | Medeiros et al. [53][49] | 2019 | 1. RNFL thickness prediction | ResNet34 | 80% | 83.7% | ||||||
| Li et al. [12][ | 0.944 | ||||||||||||||
| 8] | 2018 | Glaucomatous VF loss vs. no glaucoma | VGG I 5 | 93% | 83% | 88% | 0.966 | 2. Glaucoma vs. Suspect/healthy | |||||||
| Li et al. [76][72] | 2018 | Glaucoma vs. Healthy | VGG | 93% | 3% | 0.966 | 93.3% | ||||||||
| Jammal et al. [52][48] | 2020 | RNFL prediction | ResNet34 | 0.801 | Mookiah et al. [21][17] | 2012 | 60 | DWT, HOS | 86.7% | ||||||
| Berchuck et al. Lee et al. | 93.3% | 93.3% | |||||||||||||
| [62][58] | 2021 | RFNL prediction | M2M | ||||||||||||
| Medeiros et al. [54][50] | 2021 | Detection of RFNL thinning from fundus photos | CNN | ||||||||||||
| [77][73] | 2019 | Rates of VF progression compared to SAP MD; Prediction of future VF compared to point-wise regression predictions | Deep variational autoencoder | ||||||||||||
| Wen et al. [78][74] | 2019 | HFA points and Mean Deviation | CascadeNet-5 | Noronha et al. [22][18] | 2014 | OCT 2D | Asaoka et al. [55][51] | 2019 | Early POAG vs. no POAG | ||||||
| Kazemian et al. [74][70 | 272 | Higher order cumulant features | 100% | 92% | 92.6% | ||||||||||
| ] | 2018 | Forecasting visual field progression | Kalman Filtering Forecasting | Acharya et al. [23][19] | 2015 | 510 | Gabor transform | Novel CNN | 80% | 83.3% | |||||
| Garcia et al. [73 | 0.937 | ||||||||||||||
| ][69] | 2019 | Forecasting visual field progression | Kalman Filtering Forecasting | 89.7% | 96.2% | 93.1% | |||||||||
| Isaac et al. [24][20] | 2015 | 67 | Cropped input image after segmentation | 100% | 90% | 94.1% | |||||||||
| Muhammad et al. [63][59] | 2017 | ||||||||||||||
| DeRoos et al. [72] | Early glaucoma vs. health/suspected eyes | CNN + transfer learning | [ | 93.1% | 0.97 | ||||||||||
| 68] | 2021 | Forecasting visual field progression | Kalman Filtering Forecasting | Raja et al. [25][21] | 2015 | 158 | Hybrid PSO | 97.5% | 98.3% | 98.2% | |||||
| Lee et al. [64][60] | 2020 | GON vs. No GON | CNN (NASNet) | 94.7% | 100% | 0.990 | Singh et al. [26][22] | 2016 | 63 | ||||||
| Devalla et al. [65][61 | Wavelet feature extraction | ] | 100% | 90.9% | 94.7% | ||||||||||
| 2018 | Glaucoma vs. normal | Digital stain of RNFL | 92% | 99% | 94% | Acharya et al. [27][23] | 2017 | 702 | kNN (K = 2) Glaucoma Risk index | 96.2% | 93.7% | 95.7% | |||
| Maheshwari et al. | |||||||||||||||
| Wang et al. [56][52] | 2020 | Glaucoma vs. no glaucoma | CNN + transfer learning | 0.979 | [28][24] | 2017 | 488 | Variational mode decomposition | |||||||
| Thompson et al. [51] | 93.6% | [47 | 95.9% | ] | 94.7% | ||||||||||
| 2020 | POAG vs. no glaucoma | ResNet34 | 95% | 81% | 0.96 | Raghavendra et al. [29][25] | 2017 | 1000 | RT, MCT, GIST | ||||||
| 97.80% | 95.8% | 97% | |||||||||||||
| Pre-perimetric vs. no glaucoma | 95% | 70% | 0.92 | Ting et al. [7][3] | 2017 | 494,661 | VGGNet | 96.4% | |||||||
| 87.2% | 0.942 | ||||||||||||||
| Glaucoma with any VF loss (perimetric) vs. no glaucoma | 95% | 80% | 0.97 | Kausu et al. [30][26] | 2018 | 86 | Wavelet feature extraction, Morphological | 98% | 97.1% | 97.7% | |||||
| Mild VF loss vs. no glaucoma | 95% | 85% | 0.92 | Koh et al. [31][27] | 2018 | 2220 | Pyramid histogram of visual words and Fisher vector | 96.73% | 96.9% | 96.7% | |||||
| Moderate VF loss vs. no glaucoma | 95% | 93% | 0.99 | Soltani et al. [32][28] | 2018 | 104 | Randomized Hough transform | 97.8% | 94.8% | 96.1% | |||||
| Li et al. [12][8] | 2018 | 48,116 | Inception-v3 | 95.6% | 92% | 92% | 0.986 | ||||||||
| Fu et al. [33][29] | 2018 | 8109 | Disc-aware ensemble network (DENet) | 85% | 84% | 84% | 0.918 | ||||||||
| Raghavendra et al. [29][25] | 2018 | 1426 | Eighteen-layer CNN | 98% | 98.30% | 98% | |||||||||
| Christopher et al. [34][30] | 2018 | 14,822 | VGG6, Inception-v3, ResNet50 | 84–92% | 83–93% | 0.91–0.97 | |||||||||
| Chai et al. [35][31] | 2018 | 2000 | MB-NN | 92.33% | 90.9% | 91.5% | |||||||||
| Severe VF loss vs. no glaucoma | 95% | 98% | 0.99 | ||||||||||||
| Mariottoni et al. [66][62] | 2020 | Global RNFL thickness value | ResNet34 | ||||||||||||
| OCT 3D | Ran et al. [58][54] | 2019 | Yes GON vs. No GON | CNN (NASNet) | 89% | 96% | 91% | 0.969 | |||||||
| 78–90% | 86% | 86% | 0.893 | ||||||||||||
| Maetschke et al. [57][53] | 2019 | POAG vs. no POAG | Feature-agnostic CNN | 0.94 | |||||||||||
| 0.92 | Ahn et al. [36][32] | 2018 | 1542 | Inception-v3 Custom 3-layer CNN |
84.5% 87.9% |
||||||||||
| Russakoff et al. [59][55] | 0.93 | 2020 | Referable glaucoma vs. non-referable glaucoma | gNet3D-CNN | 0.94 | ||||||||||
| 0.88 | Shibata et al. [37][33] | 2018 | 3132 | ResNet-18 | |||||||||||
| AS-OCT | Fu et al. [60] | [56] | 2019 | Open angle vs. Angle closure | 0.965 | ||||||||||
| VGG-16 + transfer learning | 90% | 92% | 0.96 | Mohamed et al. [38][34] | 2019 | 166 | Simple Linear Iterative Clustering (SLIC) | 97.6% | 92.3% | 98.6% | |||||
| Fu et al. [67][63] | 2019 | Open angle vs. Angle closure | CNN | 0.9619 | Bajwa et al. [39][35] | 2019 | 780 | R-CNN | 71.2% | 0.874 | |||||
| Xu et al. [61][57] | 2019 | 1. Open angle vs. angle closure | CNN (ResNet18) + transfer learning | 0.928 | Liu et al. [40][36] | 2019 | 241,032 | ResNet (local validation) | 96.2% | 97.7% | 0.996 | ||||
| 2. Yes/PACD vs. no PACD | Al-Aswad et al. [41][37] | 2019 | 110 | ResNet-50 | 83.7% | 88.2% | 0.926 | ||||||||
| 0.964 | |||||||||||||||
| Hao et al. [68][64] | 2019 | Open angle vs. Narrowed Angle vs. Angle closure | MSRCNN | Asaoka et al. [42][38] | 2019 | 3132 | ResNet-34 | 0.965 | |||||||
| ResNet-34 without augmentation | 0.905 | ||||||||||||||
| VGGI I | 0.955 | ||||||||||||||
| VGGI 6 | 0.964 | ||||||||||||||
| Inception-v3 | 0.957 | ||||||||||||||
| Kim et al. [43][39] | 2019 | 1903 | Inception-V4 | 92% | 98% | 93% | 0.99 | ||||||||
| Orlando et al. [44][40] | 2019 | 1200 | Refuge Data Set | 85% | 97.6% | 0.982 | |||||||||
| Phene et al. [45][41] | 2019 | 86,618 | Inception-v3 | 80% | 90.2% | 0.945 | |||||||||
| Rogers et al. [46][42] | 2019 | 94 | ResNet-50 | 80.9% | 86.2% | 83.7% | 0.871 | ||||||||
| Thompson et al. [47][43] | 2019 | 9282 | ResNet-34 | 0.945 | |||||||||||
| Hemelings et al. [15][11] | 2020 | 8433 | ResNet-50 | 99% | 93% | 0.996 | |||||||||
| Zhao et al. [48][44] | 2020 | 421 | MFPPNet | 0.90 | |||||||||||
| Li et al. [49][45] | 2020 | 26,585 | ResNet101 | 96% | 93% | 94.1% | 0.992 |
ARCH = Architecture; SEN = Sensibility; SPEC = Specificity; ACC = Accuracy; AUC = Area under the curve.
The possibility of low-cost screening tests for the disease has been made possible by the consistent demonstration of deep learning models’ ability to detect and quantify glaucomatous damage using standard automated perimetry automatic assessment. Additionally, it has been demonstrated that DL enhances the evaluation of the damage on unprocessed visual field data, which could enhance the utility of these tests in clinical practice. As already stated, the validation of new diagnostic tests, despite how exciting AI technologies may be, should be based on a rigorous methodology, with special attention to the way the reference standards are classified and the clinical settings in which the tests will be adopted.
3. Optical Coherence Tomography
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is an essential tool to capture not only the glaucomatous optic disc in two dimensions (2D) but to provide a three-dimensional (3D) visualization, including the deeper structures. It is a technique based on the optical backscattering of biological structures; it has been widely adopted to assess glaucoma damage both on the anterior segment (e.g., with anterior segment OCT to detect angle closure) and posterior segment (e.g., with traditional OCT to detect ONH morphology and RFNL thickness) [50][46]. For this reason, depending on the input data, it is possible to differentiate five subgroups of deep learning models: (1) models for prediction of OCT measurements from fundus photography, (2) models based on traditionally segmented OCT acquisitions, (3) models for glaucoma classification based on segmentation-free B-scans, (4) models for glaucoma classification based on segmentation-free 3D volumetric data and (5) models based on anterior segment OCT acquisitions. Thompson et al. showed that it is possible to predict the Bruch membrane opening-based minimum rim width (BMO-MRW) using optic disc photographs with high accuracy (AUC was 0.945) [51][47]. Similarly, other researchers reported a high AUC for their model to predict RNFL thickness from fundus images [52,53,54][48][49][50]. Asaoka et al. developed a CNN algorithm to diagnose glaucoma based on thickness segmentations of RNFL and ganglion cells with inner plexiform layer (GCIPL) [42,55][38][51]. Wang et al. used 746,400 segmentation-free B-scans from 2669 glaucomatous eyes to automatically develop a model to detect glaucoma with an AUC of 0.979 [56][52]. Maetschke et al. [57][53] developed a DL model with an AUC of 0.94 using raw unsegmented 3D volumetric optic disc scans. Similarly, Ran et al. [58][54] validated a 3D DL model based on 6921 OCT optic disc volumetric scans; the AUC was 0.969, with a comparable performance between the model and glaucoma experts. Russakoff et al. used OCT macular cube scans to train a model to classify referable from non-referable glaucoma; despite the quality of the model, it did not perform as expected on external datasets [59][55]. At last, DL models based on AS-OCT have been developed to detect the presence of primary angle closure glaucoma (PACG), such as the one proposed by Fu et al. [60][56]. Xu et al. further developed this type of algorithm to predict the PACG as well as the spectrum of primary angle-closure diseases (PACD) (e.g., primary angle-closure suspect, primary angle-closure) [61][57]. The papers cited clearly demonstrated that using DL on OCT for glaucoma assessment is effective, precise, and encouraging (Table 2). Despite that, prior to implementing DL on OCT monitoring, more research is required to address some current challenges, including annotation standardization, the AI “black box” explanation problem, and the cost-effective analysis after integrating DL in a real clinical scenario.Table 2.
Summary of studies on glaucoma detection using OCT technology.
| Author | Year | Outcome Measures | Arch | SEN | SPEC | ACC | AUC |
|---|
References
- Sumit, S. A Comprehensive Guide to Convolutional Neural Networks—The ELI5 Way. Available online: https://towardsdatascience.com/a-comprehensive-guide-to-convolutional-neural-networks-the-eli5-way-3bd2b1164a53 (accessed on 11 November 2022).
- Nuzzi, R.; Boscia, G.; Marolo, P.; Ricardi, F. The Impact of Artificial Intelligence and Deep Learning in Eye Diseases: A Review. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 710329.
- Ting, D.S.W.; Cheung, C.Y.-L.; Lim, G.; Tan, G.S.W.; Quang, N.D.; Gan, A.; Hamzah, H.; Garcia-Franco, R.; Yeo, I.Y.S.; Lee, S.Y.; et al. Development and Validation of a Deep Learning System for Diabetic Retinopathy and Related Eye Diseases Using Retinal Images from Multiethnic Populations with Diabetes. JAMA 2017, 318, 2211–2223.
- Basodi, S.; Ji, C.; Zhang, H.; Pan, Y. Gradient amplification: An efficient way to train deep neural networks. Big Data Min. Anal. 2020, 3, 196–207.
- Aqeel, A. Difference between AlexNet, VGGNet, ResNet, and Inception. Available online: https://towardsdatascience.com/the-w3h-of-alexnet-vggnet-resnet-and-inception-7baaaecccc96 (accessed on 11 November 2022).
- Quigley, H.A. The Size and Shape of the Optic Disc in Normal Human Eyes. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1990, 108, 51–57.
- Varma, R.; Steinmann, W.C.; Scott, I.U. Expert Agreement in Evaluating the Optic Disc for Glaucoma. Ophthalmology 1992, 99, 215–221.
- Li, Z.; He, Y.; Keel, S.; Meng, W.; Chang, R.T.; He, M. Efficacy of a Deep Learning System for Detecting Glaucomatous Optic Neuropathy Based on Color Fundus Photographs. Ophthalmology 2018, 125, 1199–1206.
- Masumoto, H.; Tabuchi, H.; Nakakura, S.; Ishitobi, N.; Miki, M.; Enno, H. Deep-learning Classifier with an Ultrawide-field Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscope Detects Glaucoma Visual Field Severity. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 27, 647–652.
- Li, F.; Yan, L.; Wang, Y.; Shi, J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, M.; Wu, Z.; Zhou, K. Deep learning-based automated detection of glaucomatous optic neuropathy on color fundus photographs. Graefe Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2020, 258, 851–867.
- Hemelings, R.; Elen, B.; Barbosa-Breda, J.; Lemmens, S.; Meire, M.; Pourjavan, S.; Vandewalle, E.; Van De Veire, S.; Blaschko, M.B.; De Boever, P.; et al. Accurate prediction of glaucoma from colour fundus images with a convolutional neural network that relies on active and transfer learning. Acta Ophthalmol. 2020, 98, e94–e100.
- Kolář, R.; Jan, J. Detection of Glaucomatous Eye via Color Fundus Images Using Fractal Dimensions. Radioengineering 2008, 17, 109–114.
- Nayak, J.; Acharya, U.R.; Bhat, P.S.; Shetty, N.; Lim, T.-C. Automated Diagnosis of Glaucoma Using Digital Fundus Images. J. Med. Syst. 2009, 33, 337–346.
- Bock, R.; Meier, J.; Nyúl, L.G.; Hornegger, J.; Michelson, G. Glaucoma risk index: Automated glaucoma detection from color fundus images. Med. Image Anal. 2010, 14, 471–481.
- Acharya, U.R.; Dua, S.; Du, X.; S, V.S.; Chua, C.K. Automated Diagnosis of Glaucoma Using Texture and Higher Order Spectra Features. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2011, 15, 449–455.
- Dua, S.; Acharya, U.R.; Chowriappa, P.; Sree, S.V. Wavelet-Based Energy Features for Glaucomatous Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2012, 16, 80–87.
- Mookiah, M.R.K.; Acharya, U.R.; Lim, C.M.; Petznick, A.; Suri, J.S. Data mining technique for automated diagnosis of glaucoma using higher order spectra and wavelet energy features. Knowl. Based Syst. 2012, 33, 73–82.
- Noronha, K.P.; Acharya, U.R.; Nayak, K.P.; Martis, R.J.; Bhandary, S.V. Automated classification of glaucoma stages using higher order cumulant features. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2014, 10, 174–183.
- Acharya, U.R.; Ng, E.; Eugene, L.W.J.; Noronha, K.P.; Min, L.C.; Nayak, K.P.; Bhandary, S.V. Decision support system for the glaucoma using Gabor transformation. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2015, 15, 18–26.
- Issac, A.; Sarathi, M.P.; Dutta, M.K. An adaptive threshold based image processing technique for improved glaucoma detection and classification. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2015, 122, 229–244.
- Raja, C.; Gangatharan, N. A Hybrid Swarm Algorithm for optimizing glaucoma diagnosis. Comput. Biol. Med. 2015, 63, 196–207.
- Singh, A.; Dutta, M.K.; ParthaSarathi, M.; Uher, V.; Burget, R. Image processing based automatic diagnosis of glaucoma using wavelet features of segmented optic disc from fundus image. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2016, 124, 108–120.
- Acharya, U.R.; Bhat, S.; Koh, J.E.; Bhandary, S.V.; Adeli, H. A novel algorithm to detect glaucoma risk using texton and local configuration pattern features extracted from fundus images. Comput. Biol. Med. 2017, 88, 72–83.
- Maheshwari, S.; Pachori, R.B.; Kanhangad, V.; Bhandary, S.V.; Acharya, U.R. Iterative variational mode decomposition based automated detection of glaucoma using fundus images. Comput. Biol. Med. 2017, 88, 142–149.
- Raghavendra, U.; Bhandary, S.V.; Gudigar, A.; Acharya, U.R. Novel expert system for glaucoma identification using non-parametric spatial envelope energy spectrum with fundus images. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 38, 170–180.
- Kausu, T.; Gopi, V.P.; Wahid, K.A.; Doma, W.; Niwas, S.I. Combination of clinical and multiresolution features for glaucoma detection and its classification using fundus images. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 38, 329–341.
- Koh, J.E.; Ng, E.Y.; Bhandary, S.V.; Hagiwara, Y.; Laude, A.; Acharya, U.R. Automated retinal health diagnosis using pyramid histogram of visual words and Fisher vector techniques. Comput. Biol. Med. 2018, 92, 204–209.
- Soltani, A.; Battikh, T.; Jabri, I.; Lakhoua, N. A new expert system based on fuzzy logic and image processing algorithms for early glaucoma diagnosis. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2018, 40, 366–377.
- Fu, H.; Cheng, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wong, D.W.K.; Liu, J.; Cao, X. Disc-Aware Ensemble Network for Glaucoma Screening from Fundus Image. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 2493–2501.
- Christopher, M.; Belghith, A.; Bowd, C.; Proudfoot, J.A.; Goldbaum, M.H.; Weinreb, R.N.; Girkin, C.A.; Liebmann, J.M.; Zangwill, L.M. Performance of Deep Learning Architectures and Transfer Learning for Detecting Glaucomatous Optic Neuropathy in Fundus Photographs. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16685.
- Chai, Y.; Liu, H.; Xu, J. Glaucoma diagnosis based on both hidden features and domain knowledge through deep learning models. Knowl. Based Syst. 2018, 161, 147–156.
- Ahn, J.M.; Kim, S.; Ahn, K.-S.; Cho, S.-H.; Lee, K.B.; Kim, U.S. A deep learning model for the detection of both advanced and early glaucoma using fundus photography. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207982.
- Shibata, N.; Tanito, M.; Mitsuhashi, K.; Fujino, Y.; Matsuura, M.; Murata, H.; Asaoka, R. Development of a deep residual learning algorithm to screen for glaucoma from fundus photography. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14665.
- Mohamed, N.A.; Zulkifley, M.A.; Zaki, W.M.D.W.; Hussain, A. An automated glaucoma screening system using cup-to-disc ratio via Simple Linear Iterative Clustering superpixel approach. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2019, 53, 101454.
- Bajwa, M.N.; Malik, M.I.; Siddiqui, S.A.; Dengel, A.; Shafait, F.; Neumeier, W.; Ahmed, S. Two-stage framework for optic disc localization and glaucoma classification in retinal fundus images using deep learning. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2019, 19, 153.
- Liu, H.; Li, L.; Wormstone, I.M.; Qiao, C.; Zhang, C.; Liu, P.; Li, S.; Wang, H.; Mou, D.; Pang, R.; et al. Development and Validation of a Deep Learning System to Detect Glaucomatous Optic Neuropathy Using Fundus Photographs. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2019, 137, 1353–1360.
- Al-Aswad, L.A.; Kapoor, R.; Chu, C.K.; Walters, S.; Gong, D.; Garg, A.; Gopal, K.; Patel, V.; Sameer, T.; Rogers, T.W.; et al. Evaluation of a Deep Learning System for Identifying Glaucomatous Optic Neuropathy Based on Color Fundus Photographs. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 28, 1029–1034.
- Asaoka, R.; Tanito, M.; Shibata, N.; Mitsuhashi, K.; Nakahara, K.; Fujino, Y.; Matsuura, M.; Murata, H.; Tokumo, K.; Kiuchi, Y. Validation of a Deep Learning Model to Screen for Glaucoma Using Images from Different Fundus Cameras and Data Augmentation. Ophthalmol. Glaucoma 2019, 2, 224–231.
- Kim, M.; Han, J.C.; Hyun, S.H.; Janssens, O.; Van Hoecke, S.; Kee, C.; De Neve, W. Medinoid: Computer-Aided Diagnosis and Localization of Glaucoma Using Deep Learning †. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3064.
- Orlando, J.I.; Fu, H.; Breda, J.B.; van Keer, K.; Bathula, D.R.; Diaz-Pinto, A.; Fang, R.; Heng, P.-A.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.; et al. REFUGE Challenge: A unified framework for evaluating automated methods for glaucoma assessment from fundus photographs. Med. Image Anal. 2020, 59, 101570.
- Phene, S.; Dunn, R.C.; Hammel, N.; Liu, Y.; Krause, J.; Kitade, N.; Schaekermann, M.; Sayres, R.; Wu, D.J.; Bora, A.; et al. Deep Learning and Glaucoma Specialists. Ophthalmology 2019, 126, 1627–1639.
- Rogers, T.W.; Jaccard, N.; Carbonaro, F.; Lemij, H.G.; Vermeer, K.A.; Reus, N.; Trikha, S. Evaluation of an AI system for the automated detection of glaucoma from stereoscopic optic disc photographs: The European Optic Disc Assessment Study. Eye 2019, 33, 1791–1797.
- Thompson, A.C.; Jammal, A.A.; Medeiros, F.A. A Deep Learning Algorithm to Quantify Neuroretinal Rim Loss from Optic Disc Photographs. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 201, 9–18.
- Zhao, R.; Chen, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, Z.; Guo, F.; Li, S. Direct Cup-to-Disc Ratio Estimation for Glaucoma Screening via Semi-Supervised Learning. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2019, 24, 1104–1113.
- Zhao, R.; Li, S. Multi-indices quantification of optic nerve head in fundus image via multitask collaborative learning. Med. Image Anal. 2020, 60, 101593.
- Schuman, J.; Hee, M.R.; Arya, A.V.; Pedut-Kloizman, T.; Puliafito, C.A.; Fujimoto, J.G.; Swanson, E.A. Optical coherence tomography: A new tool for glaucoma diagnosis. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 1995, 6, 89–95.
- Thompson, A.C.; Jammal, A.A.; Berchuck, S.I.; Mariottoni, E.; Medeiros, F.A. Assessment of a Segmentation-Free Deep Learning Algorithm for Diagnosing Glaucoma from Optical Coherence Tomography Scans. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2020, 138, 333–339.
- Jammal, A.A.; Thompson, A.C.; Mariottoni, E.B.; Berchuck, S.I.; Urata, C.N.; Estrela, T.; Wakil, S.M.; Costa, V.P.; Medeiros, F.A. Human Versus Machine: Comparing a Deep Learning Algorithm to Human Gradings for Detecting Glaucoma on Fundus Photographs. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 211, 123–131.
- Medeiros, F.A.; Jammal, A.A.; Thompson, A.C. From Machine to Machine. Ophthalmology 2019, 126, 513–521.
- Medeiros, F.A.; Jammal, A.A.; Mariottoni, E.B. Detection of Progressive Glaucomatous Optic Nerve Damage on Fundus Photographs with Deep Learning. Ophthalmology 2021, 128, 383–392.
- Asaoka, R.; Murata, H.; Hirasawa, K.; Fujino, Y.; Matsuura, M.; Miki, A.; Kanamoto, T.; Ikeda, Y.; Mori, K.; Iwase, A.; et al. Using Deep Learning and Transfer Learning to Accurately Diagnose Early Onset Glaucoma from Macular Optical Coherence Tomography Images. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 198, 136–145.
- Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Ran, A.-R.; Luo, L.; Chan, P.P.; Tham, C.C.; Chang, R.T.; Mannil, S.S.; Cheung, C.Y.; Heng, P.-A. Towards multi-center glaucoma OCT image screening with semi-supervised joint structure and function multi-task learning. Med. Image Anal. 2020, 63, 101695.
- Maetschke, S.; Antony, B.; Ishikawa, H.; Wollstein, G.; Schuman, J.; Garnavi, R. A feature agnostic approach for glaucoma detection in OCT volumes. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219126.
- Ran, A.R.; Cheung, C.Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Luo, L.-Y.; Chan, P.P.; Wong, M.O.M.; Chang, R.T.; Mannil, S.S.; Young, A.L.; et al. Detection of glaucomatous optic neuropathy with spectral-domain optical coherence tomography: A retrospective training and validation deep-learning analysis. Lancet Digit. Health 2019, 1, e172–e182.
- Russakoff, D.B.; Mannil, S.S.; Oakley, J.D.; Ran, A.R.; Cheung, C.Y.; Dasari, S.; Riyazzuddin, M.; Nagaraj, S.; Rao, H.L.; Chang, D.; et al. A 3D Deep Learning System for Detecting Referable Glaucoma Using Full OCT Macular Cube Scans. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 12.
- Fu, H.; Baskaran, M.; Xu, Y.; Lin, S.; Wong, D.W.K.; Liu, J.; Tun, T.A.; Mahesh, M.; Perera, S.A.; Aung, T. A Deep Learning System for Automated Angle-Closure Detection in Anterior Segment Optical Coherence Tomography Images. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 203, 37–45.
- Xu, B.Y.; Chiang, M.; Chaudhary, S.; Kulkarni, S.; Pardeshi, A.A.; Varma, R. Deep Learning Classifiers for Automated Detection of Gonioscopic Angle Closure Based on Anterior Segment OCT Images. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 208, 273–280.
- Lee, T.; Jammal, A.A.; Mariottoni, E.B.; Medeiros, F.A. Predicting Glaucoma Development with Longitudinal Deep Learning Predictions from Fundus Photographs. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 225, 86–94.
- Muhammad, H.; Fuchs, T.J.; De Cuir, N.; De Moraes, C.G.; Blumberg, D.M.; Liebmann, J.M.; Ritch, R.; Hood, D.C. Hybrid Deep Learning on Single Wide-field Optical Coherence tomography Scans Accurately Classifies Glaucoma Suspects. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 26, 1086–1094.
- Lee, J.; Kim, Y.K.; Park, K.H.; Jeoung, J.W. Diagnosing Glaucoma with Spectral-Domain Optical Coherence Tomography Using Deep Learning Classifier. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 29, 287–294.
- Devalla, S.K.; Chin, K.S.; Mari, J.-M.; Tun, T.A.; Strouthidis, N.G.; Aung, T.; Thiéry, A.H.; Girard, M.J.A. A Deep Learning Approach to Digitally Stain Optical Coherence Tomography Images of the Optic Nerve Head. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2018, 59, 63–74.
- Mariottoni, E.B.; Jammal, A.A.; Urata, C.N.; Berchuck, S.I.; Thompson, A.C.; Estrela, T.; Medeiros, F.A. Quantification of Retinal Nerve Fibre Layer Thickness on Optical Coherence Tomography with a Deep Learning Segmentation-Free Approach. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 402.
- Fu, H.; Xu, Y.; Lin, S.; Wong, D.W.K.; Baskaran, M.; Mahesh, M.; Aung, T.; Liu, J. Angle-Closure Detection in Anterior Segment OCT Based on Multilevel Deep Network. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2020, 50, 3358–3366.
- Hao, H.; Zhao, Y.; Fu, H.; Shang, Q.; Li, F.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J. Anterior Chamber Angles Classification in Anterior Segment OCT Images via Multi-Scale Regions Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Berlin, Germany, 23–27 July 2019; Volume 2019, pp. 849–852.
- Asaoka, R.; Murata, H.; Iwase, A.; Araie, M. Detecting Preperimetric Glaucoma with Standard Automated Perimetry Using a Deep Learning Classifier. Ophthalmology 2016, 123, 1974–1980.
- Elze, T.; Pasquale, L.R.; Shen, L.; Chen, T.C.; Wiggs, J.L.; Bex, P.J. Patterns of functional vision loss in glaucoma determined with archetypal analysis. J. R. Soc. Interface 2015, 12, 20141118.
- Wang, M.; Shen, L.Q.; Pasquale, L.R.; Petrakos, P.; Formica, S.; Boland, M.V.; Wellik, S.R.; De Moraes, C.G.; Myers, J.S.; Saeedi, O.; et al. An Artificial Intelligence Approach to Detect Visual Field Progression in Glaucoma Based on Spatial Pattern Analysis. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2019, 60, 365–375.
- DeRoos, L.; Nitta, K.; Lavieri, M.S.; Van Oyen, M.P.; Kazemian, P.; Andrews, C.A.; Sugiyama, K.; Stein, J.D. Comparing Perimetric Loss at Different Target Intraocular Pressures for Patients with High-Tension and Normal-Tension Glaucoma. Ophthalmol. Glaucoma 2021, 4, 251–259.
- Garcia, G.-G.P.; Lavieri, M.S.; Andrews, C.; Liu, X.; Van Oyen, M.P.; Kass, M.A.; Gordon, M.O.; Stein, J.D. Accuracy of Kalman Filtering in Forecasting Visual Field and Intraocular Pressure Trajectory in Patients with Ocular Hypertension. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2019, 137, 1416–1423.
- Kazemian, P.; Lavieri, M.S.; Van Oyen, M.P.; Andrews, C.; Stein, J.D. Personalized Prediction of Glaucoma Progression Under Different Target Intraocular Pressure Levels Using Filtered Forecasting Methods. Ophthalmology 2018, 125, 569–577.
- Kucur, S.; Holló, G.; Sznitman, R. A deep learning approach to automatic detection of early glaucoma from visual fields. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206081.
- Li, F.; Wang, Z.; Qu, G.; Song, D.; Yuan, Y.; Xu, Y.; Gao, K.; Luo, G.; Xiao, Z.; Lam, D.S.C.; et al. Automatic differentiation of Glaucoma visual field from non-glaucoma visual filed using deep convolutional neural network. BMC Med. Imaging 2018, 18, 1–7.
- Berchuck, S.I.; Mukherjee, S.; Medeiros, F.A. Estimating Rates of Progression and Predicting Future Visual Fields in Glaucoma Using a Deep Variational Autoencoder. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 35.
- Wen, J.C.; Lee, C.S.; Keane, P.A.; Xiao, S.; Rokem, A.S.; Chen, P.P.; Wu, Y.; Lee, A.Y. Forecasting future Humphrey Visual Fields using deep learning. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214875.
More
