The main glucocorticoids involved in the stress response are cortisol and cortisone in most mammals and corticosterone in birds and rodents. Therefore, these analytes are currently the biomarkers more frequently used to evaluate the physiological response to a stressful situation. In addition, “total glucocorticoids”, which refers to the quantification of various glucocorticoids by immunoassays showing cross-reactivity with different types of glucocorticoids or related metabolites, can be measured.
- glucocorticoids
- cortisol
- cortisone
1. Introduction
Glucocorticoid, also known as glucocorticoid (English: glucocorticoid), is an adrenocortical hormone, a steroid hormone secreted by the fascicular zone of the middle layer of the adrenal cortex, which can also be synthesized by chemical methods. Cortisone and cortisol in human body belong to glucocorticoids. Because it can be used for diseases that are not matched by ordinary antibiotics or anti-inflammatory drugs, such as SARS, septicemia, etc., it has the function of regulating the biosynthesis and metabolism of sugar, fat, and protein, and also has the anti-inflammatory effect. It is called "glucocorticoid" because its activity of regulating carbohydrate metabolism is first known by people.
2. General Characteristics of the Main Glucocorticoids
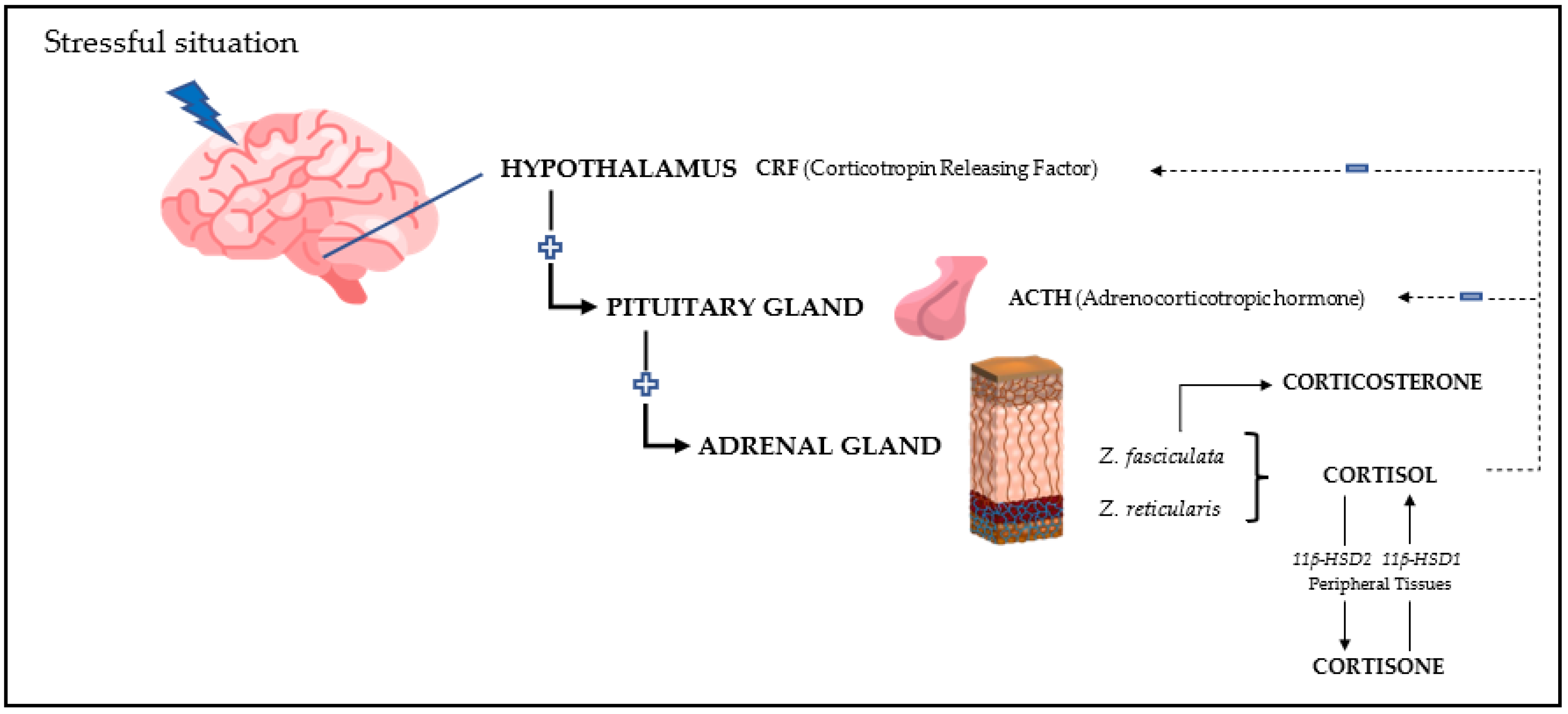
Glucocorticoids are a group of endogenous adrenal hormones with a 21-carbon skeleton that are derived from cholesterol and that are released in a stressful situation. When released, they bind mainly to the corticosteroid-binding globulin (CBG), making them available for use at systemic or tissue level [13][12]. Their function is performed by intracellular binding to glucocorticoid receptors (GRs), which belong to the family of nuclear receptors [14][13]. Although the name “glucocorticoids” originates from their effects on plasma glucose, they are also involved in catabolic metabolism, inflammatory and immune response, and other physiological functions [15,16][14][15]. The main glucocorticoids involved in the stress response are cortisol, cortisone, and corticosterone (Table 1). Their concentrations allow the species to be classified as cortisol-dominant (most mammals) or corticosterone-dominant (such as rats, mice, birds or reptiles). Cortisone is produced mainly in the cortisol-dominant species, and its concentration depends on the activity of the 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (11β-HSD) type 2 enzyme, which is expressed mainly in kidney, colon, and salivary glands [14][13].| Cortisol | Cortisone | Corticosterone | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Formula | 11β,17α,21-trihydroxypregn-4-ene-3,20-dione [17][16] 1 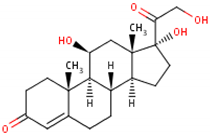 |
17-hydroxy-11-dehydrocorticosterone [18][17] 2 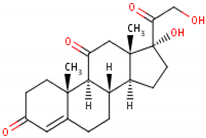 |
11β,21-dihydroxypregn-4-ene-3,20-dione [19][18] 3 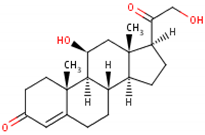 |
| Structural differences | An extra hydroxyl group attached to the 17th carbon [20][19]. | A ketone group attached to the 17th carbon [21][20]. | No extra hydroxyl group on the 17th carbon [20][19]. |
| Metabolism | Synthesised from pregnenolone in adrenal gland. Inactivated mainly in the kidney by 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (11β-HSD) type 2 into cortisone [22,23][21][22]. |
Transformation in the liver, lungs, ovaries, and central nervous system by 11β-HSD type 1 into cortisol [24][23]. | Derived from pregnenolone in adrenal gland [19][18]. |
| Activity | Active molecule [25][24] | Inactive molecule | Active molecule |
| Half-life | In plasma: 66 min In tissues: 12 h [26,27][25][26] |
In plasma: 90 min [21][20] | In plasma: 60–90 min [28][27] |
| Predominant species | It is the main glucocorticoid in most mammals [29][28] | Same species as cortisol | It is the main glucocorticoid in rats, mice, birds, and reptiles, due to a lack of the enzyme 17-α hydroxylase [9] |
3. Measurement
In general, there are two types of assays for the quantification of glucocorticoids:- (1)
-
Those using techniques based on the reaction of an antibody with the analyte to be measured, such as radioimmunoassay (RIA), enzyme immunoassay (EIA), chemiluminescence, and, more recently, bead-based luminescent amplification assays (AlphaLISA). RIA assays are currently used with less frequency due to the need of special facilities and the radioactive nature of some components.
- (2)
-
Techniques based on the direct quantification of the analyte, including high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) [35,36][34][35] and liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) [37,38][36][37], with the latter being the most sensitive [8].Glucocorticoids can be measured in different sample types. Although blood has been traditionally frequently used, the stress that individuals suffer from blood collection [29][28] can interfere with the results. In this line, non-invasive alternatives, such as saliva, hair, faeces, or feathers, are becoming increasingly important [40,59,60,61][39][58][59][60]. There are three main glucocorticoids used to evaluate stress: cortisol, cortisone, and corticosterone, which vary in their amounts in different sample types and animal species. In addition, there is the concept of total steroids, which is used when immunoassays with antibodies showing cross-reactivity with different glucocorticoids or related metabolites are employed, being mostly used in faeces.Table 2.Main methods used for glucocorticoid measurement.
Analyte Analytical Method Reference Cortisol EIA [34,39,40][33][38][39] RIA [41,42][40][41] Chemiluminescence [43][42] AlphaLISA [44][43] HPLC [35,36][34][35] LC-MS/MS [37,38][36][37] Cortisone AlphaLISA [44][43] UHPLC-MS/MS [45,46][44][45] LC-MS/MS [47][46] LC-MS3 [48,49][47][48] Corticosterone EIA [50,51][49][50] RIA [52,53][51][52] Total steroids EIA [54,]55,[56][5354][55] RIA [57,58][56][57]
References
- Lu, S.; Wei, F.; Li, G. The Evolution of the Concept of Stress and the Framework of the Stress System. Cell Stress 2021, 5, 76.
- Ralph, C.R.; Tilbrook, A.J. INVITED REVIEW: The Usefulness of Measuring Glucocorticoids for Assessing Animal Welfare. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 94, 457–470.
- Fink, G. Stress: Definition and History Introduction and Historical Outline of Several Stress Concepts; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017.
- Martínez-Miró, S.; Tecles, F.; Ramón, M.; Escribano, D.; Hernández, F.; Madrid, J.; Orengo, J.; Martínez-Subiela, S.; Manteca, X.; Cerón, J.J. Causes, Consequences and Biomarkers of Stress in Swine: An Update. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 171.
- Selye, H. Stress in Health and Disease; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 1976.
- Zulkifli, I. Review of Human-Animal Interactions and Their Impact on Animal Productivity and Welfare. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2013, 4, 25.
- Sadoul, B.; Geffroy, B. Measuring Cortisol, the Major Stress Hormone in Fishes. J. Fish. Biol. 2019, 94, 540–555.
- Blair, J.; Adaway, J.; Keevil, B.; Ross, R. Salivary Cortisol and Cortisone in the Clinical Setting. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2017, 24, 161–168.
- Raff, H. CORT, Cort, B, Corticosterone, and Now Cortistatin: Enough Already! Endocrinology 2016, 157, 3307–3308.
- Sopinka, N.M.; Patterson, L.D.; Redfern, J.C.; Pleizier, N.K.; Belanger, C.B.; Midwood, J.D.; Crossin, G.T.; Cooke, S.J. Manipulating Glucocorticoids in Wild Animals: Basic and Applied Perspectives. Conserv. Physiol. 2015, 3, cov031.
- Di Francesco, J.; Mastromonaco, G.F.; Rowell, J.E.; Blake, J.; Checkley, S.L.; Kutz, S. Fecal Glucocorticoid Metabolites Reflect Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Adrenal Axis Activity in Muskoxen (Ovibos moschatus). PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0249281.
- Perogamvros, I.; Aarons, L.; Miller, A.G.; Trainer, P.J.; Ray, D.W. Corticosteroid-Binding Globulin Regulates Cortisol Pharmacokinetics. Clin. Endocrinol. 2011, 74, 30–36.
- De Guia, R.M. Stress, Glucocorticoid Signaling Pathway, and Metabolic Disorders. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2020, 14, 1273–1280.
- Steroid Definition and Examples—Biology Online Dictionary. Available online: https://www.biologyonline.com/dictionary/steroid (accessed on 21 November 2022).
- Nicolaides, N.C.; Kyratzi, E.; Lamprokostopoulou, A.; Chrousos, G.P.; Charmandari, E. Stress, the Stress System and the Role of Glucocorticoids. Neuroimmunomodulation 2015, 22, 6–19.
- Cortisol (CHEBI:17650). Available online: https://www.ebi.ac.uk/chebi/searchId.do?chebiId=CHEBI:17650 (accessed on 28 November 2022).
- Cortisone (CHEBI:16962). Available online: https://www.ebi.ac.uk/chebi/searchId.do?chebiId=CHEBI:16962 (accessed on 28 November 2022).
- Corticosterone (CHEBI:16827). Available online: https://www.ebi.ac.uk/chebi/chebiOntology.do?chebiId=CHEBI:16827 (accessed on 21 November 2022).
- What Are the Differences and Similarities between Cortisol vs Corticosterone?—Brain Stuff. Available online: https://brainstuff.org/blog/differences-similarities-between-cortisol-corticosterone (accessed on 21 November 2022).
- Cortisone |C21H28O5—PubChem. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Cortisone (accessed on 21 November 2022).
- Tomlinson, J.W.; Stewart, P.M. Cortisol Metabolism and the Role of 11β-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 15, 61–78.
- Hydrocortisone|C21H30O5—PubChem. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Hydrocortisone (accessed on 21 November 2022).
- Terao, M.; Katayama, I. Local Cortisol/Corticosterone Activation in Skin Physiology and Pathology. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2016, 84, 11–16.
- Ruis, M.A.; Te Brake, J.H.; Engel, B.; Ekkel, E.D.; Buist, W.G.; Blokhuis, H.J.; Koolhaas, J.M. The Circadian Rhythm of Salivary Cortisol in Growing Pigs: Effects of Age, Gender, and Stress. Physiol. Behav. 1997, 62, 623–630.
- Weitzman, E.D.; Fukushima, D.; Nogeire, C.; Roffwarg, H.; Gallagher, T.F.; Hellman, L. Twenty-Four Hour Pattern of the Episodic Secretion of Cortisol in Normal Subjects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1971, 33, 14–22.
- Wood, P.J.; Barth, J.H.; Freedman, D.B.; Perry, L.; Sheridan, B. Evidence for the Low Dose Dexamethasone Suppression Test to Screen for Cushing’s Syndrome-Recommendations for a Protocol for Biochemistry Laboratories. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 1997, 34, 222–229.
- Barrett, K.E.; Barman, S.M.; Boitano, S.; Brooks, H.L. The Adrenal Medulla & Adrenal Cortex. In Ganong’s Review of Medical Physiology, 25e; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2018.
- Palme, R. Non-Invasive Measurement of Glucocorticoids: Advances and Problems. Physiol. Behav. 2019, 199, 229–243.
- Majelantle, T.L.; Mcintyre, T.; Ganswindt, A. Monitoring the Effects of Land Transformation on African Clawless Otters (Aonyx capensis) Using Fecal Glucocorticoid Metabolite Concentrations as a Measure of Stress. Integr. Zool. 2020, 15, 293–306.
- Möstl, E.; Rettenbacher, S.; Palme, R. Measurement of Corticosterone Metabolites in Birds’ Droppings: An Analytical Approach. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1046, 17–34.
- Cavigelli, S.A.; Monfort, S.L.; Whitney, T.K.; Mechref, Y.S.; Novotny, M.; McClintock, M.K. Frequent Serial Fecal Corticoid Measures from Rats Reflect Circadian and Ovarian Corticosterone Rhythms. J. Endocrinol. 2005, 184, 153–163.
- Khan, M.Z.; Altmann, J.; Isani, S.S.; Yu, J. A Matter of Time: Evaluating the Storage of Fecal Samples for Steroid Analysis. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2002, 128, 57–64.
- Wolf, T.E.; Mangwiro, N.; Fasina, F.O.; Ganswindt, A. Non-Invasive Monitoring of Adrenocortical Function in Female Domestic Pigs Using Saliva and Faeces as Sample Matrices. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0234971.
- De Palo, E.F.; Antonelli, G.; Benetazzo, A.; Prearo, M.; Gatti, R. Human Saliva Cortisone and Cortisol Simultaneous Analysis Using Reverse Phase HPLC Techn.nique. Clin. Chim. Acta 2009, 405, 60–65.
- Okumura, T.; Nakajima, Y.; Takamatsu, T.; Matsuoka, M. Column-Switching High.-Performance Liquid Chromatographic System with a Laser-Induced Fluorimetric Detector for Direct, Automated Assay of Salivary Cortisol. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1995, 670, 11–20.
- Carrozza, C.; Lapolla, R.; Gervasoni, J.; Rota, C.A.; Locantore, P.; Pontecorvi, A.; Zuppi, C.; Persichilli, S. Assessment of Salivary Free Cortisol Levels by Liquid Chromatography with Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) in Patients Treated with Mitotane. Hormones 2012, 11, 344–349.
- Jonsson, B.A.G.; Malmberg, B.; Amilon, A.; Garde, A.H.; Ørbaek, P.D. Etermination of Cortisol in Human Saliva Using Liquid Chromatography-Electrospray Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2003, 784, 63–68.
- Agusti, C.; Carbajal, A.; Olvera-Maneu, S.; Domingo, M.; Lopez-Bejar, M. Blubber and Serum Cortisol Concentrations as Indicators of the Stress Response and Overall Health Status in Striped Dolphins. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2022, 272, 111268.
- Prims, S.; vanden Hole, C.; van Cruchten, S.; van Ginneken, C.; van Ostade, X.; Casteleyn, C. Hair or Salivary Cortisol Analysis to Identify Chronic Stress in Piglets? Vet. J. 2019, 252, 105357.
- Naskar, S.; Borah, S.; Vashi, Y.; Thomas, R.; Sarma, D.K.; Goswami, J.; Dhara, S.K. Steroid and Metabolic Hormonal Profile of Porcine Serum Vis-à-Vis Ovarian Follicular Fluid. Vet. World 2016, 9, 1320–1323.
- Zhao, F.; Wei, Q.-W.; Li, B.-J.; Weng, Q.-N.; Jiang, Y.; Ning, C.-B.; Liu, K.-Q.; Wu, W.-J.; Liu, H.-L. Impact of Adrenocorticotropin Hormone Administration on the Endocrinology, Estrus Onset, and Ovarian Function of Weaned Sows. Endocr. J. 2022, 69, 23–33.
- Escribano, D.; Fuentes-Rubio, M.; Cerón, J.J. Validation of an Automated Chemiluminescent Immunoassay for Salivary Cortisol Measurements in Pigs. J. Vet. Diagn Investig. 2012, 24, 918–923.
- López-Arjona, M.; Tecles, F.; Mateo, S.V.; Contreras-Aguilar, M.D.; Martínez-Miró, S.; Cerón, J.J.; Martínez-Subiela, S. Measurement of Cortisol, Cortisone and 11β-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Type 2 Activity in Hair of Sows during Different Phases of the Reproductive Cycle. Vet. J. 2020, 259–260.
- Aydin, E.; Drotleff, B.; Noack, H.; Derntl, B.; Lämmerhofer, M. Fast Accurate Quantification of Salivary Cortisol and Cortisone in a Large-Scale Clinical Stress Study by Micro-UHPLC-ESI-MS/MS Using a Surrogate Calibrant Approach. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2021, 1182, 122939.
- Puglisi, S.; Leporati, M.; Amante, E.; Parisi, A.; Pia, A.R.; Berchialla, P.; Terzolo, M.; Vincenti, M.; Reimondo, G. Limited Role of Hair Cortisol and Cortisone Measurement for Detecting Cortisol Autonomy in Patients with Adrenal Incidentalomas. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 833514.
- Chiesa, L.; Pavone, S.; Pasquale, E.; Pavlovic, R.; Panseri, S.; Valiani, A.; Arioli, F.; Manuali, E. Study on Cortisol, Cortisone and Prednisolone Presence in Urine of Chianina Cattle Breed. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2017, 101, 893–903.
- Lang, J.; Stickel, S.; Gaum, P.M.; Habel, U.; Bertram, J.; Eickhoff, S.B.; Chechko, N. Predicting Hair Cortisol and Cortisone Concentration in Postpartum Women through Repeated Measurements of Perceived Stress. Metabolites 2021, 11, 815.
- Scharlau, F.; Pietzner, D.; Vogel, M.; Gaudl, A.; Ceglarek, U.; Thiery, J.; Kratzsch, J.; Hiemisch, A.; Kiess, W. Evaluation of Hair Cortisol and Cortisone Change during Pregnancy and the Association with Self-Reported Depression, Somatization, and Stress Symptoms. Stress 2018, 21, 43–50.
- Hamilton, J.; Allard, S.; Racine, H.; Skalican Guthrie, K.; Hill, T.; Loughman, Z. Impact of Indigestible Materials on the Efficiency of Fecal Corticosterone Immunoassay Testing in Pituophis Species. Animals 2022, 12, 1410.
- Rowell, M.K.; Santymire, R.M.; Rymer, T.L. Corticosterone Metabolite Concentration Is Not Related to Problem Solving in the Fawn-Footed Mosaic-Tailed Rat Melomys Cervinipes. Animals 2021, 12, 82.
- Rodrigues, L.G.F.; de Araujo, L.D.; Roa, S.L.R.; Bueno, A.C.; Uchoa, E.T.; Antunes-Rodrigues, J.; Moreira, A.C.; Elias, L.L.K.; de Castro, M.; Martins, C.S. Restricted Feeding Modulates Peripheral Clocks and Nutrient Sensing Pathways in Rats. Arch. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 65, 549–561.
- Zietek, M.; Sochaczewska, D.; Swiatkowska-Freund, M.; Celewicz, Z.; Szczuko, M. The Possible Role of Corticosterone in Regulating Sodium and Potassium Concentrations in Human Milk. Ginekol. Pol. 2021, 92, 1–6.
- Jepsen, E.M.; Scheun, J.; Dehnhard, M.; Kumar, V.; Umapathy, G.; Ganswindt, A. Non-Invasive Monitoring of Glucocorticoid Metabolite Concentrations in Native Indian, as Well as Captive and Re-Wilded Tigers in South Africa. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2021, 308, 113783.
- Xie, S.; McWhorter, T.J. Fecal Glucocorticoid Metabolite Concentration as a Tool for Assessing Impacts of Interventions in Humboldt Penguins (Spheniscus humboldti). Birds 2021, 2, 106–113.
- Yarnell, K.; Purcell, R.S.; Walker, S.L. Fecal Glucocorticoid Analysis: Non-Invasive Adrenal Monitoring in Equids. J. Vis. Exp. 2016, 110, 53479.
- Washburn, B.E.; Millspaugh, J.J.; Schulz, J.H.; Jones, S.B.; Mong, T. Using Fecal Glucocorticoids for Stress Assessment in Mourning Doves. Available online: https://digitalcommons.unl.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1516&context=icwdm_usdanwrc (accessed on 16 November 2022).
- Young, A.M.; Hallford, D.M. Validation of a Fecal Glucocorticoid Metabolite Assay to Assess Stress in the Budgerigar (Melopsittacus undulatus). Zoo Biol. 2013, 32, 112.
- Accorsi, P.A.; Carloni, E.; Valsecchi, P.; Viggiani, R.; Gamberoni, M.; Tamanini, C.; Seren, E. Cortisol Determination in Hair and Faeces from Domestic Cats and Dogs. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2008, 155, 398–402.
- Bechshøft, T.; Sonne, C.; Dietz, R.; Born, E.W.; Novak, M.A.; Henchey, E.; Meyer, J.S. Cortisol Levels in Hair of East Greenland Polar Bears. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 831–834.
- Romero, L.M.; Fairhurst, G.D. Measuring Corticosterone in Feathers: Strengths, Limitations, and Suggestions for the Future. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2016, 202, 112–122.
