HBOThe coronavirus disease (COVID-19) epidemic is a public health emergency of international concern. It was believed that SARS-CoV-2 virus was much less likely affect children. Statistics show that children account for 2–13% of all COVID-19 patients in individual countries. In the youngest population, acute respiratory failure is not as serious a problem as complications after COVID-19, mainly pediatric inflammatory multisystem syndrome (PIMS, MIS-C). Thirteen publications that quantitatively and qualitatively described the efficacy of HBOT application in the treatment of pediatric diseases were eligible among the studies; those relating to the use of hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) in the treatment of children with COVID-19 and its complications were not found. The bibliographic review showed that hyperbaric oxygen therapy can be used in the treatment of children after carbon to metoda leczenia polegająca na podaniu pacjentowi 100% tlenu o podwyższonym ciśnieniu w specjalnie skonstruowanej komorze hiperbarycznej. Ciśnienie wywierane podczas ekspozycji wyraża się jako suma ciśnienia atmosferycznego i ciśnienia panującego w komorze. Ciśnienie wywierane podczas ekspozycji wyraża się jako suma ciśnienia atmosferycznego i ciśnienia panującego w komorze. Uważa się, że powinno ono wynosić co najmniej 1,4 ciśnienia bezwzględnego (ATA). Interwencja HBOT przyczynia się do znacznego wzrostu ciśnienia tlenu we krwi poprzez dotlenienie hemoglobiny i rozpuszczenie jej w osoczu krwi. Procesy te znacznie zwiększają stopień dyfuzji tlenu z naczyń włosowatych do otaczających niedotlenionych komórek, poprawiając tym samym ich metabolizm [ monoxide15 ].]. pKoisoning, with soft tissue necrosis, bone necrosis, after burns, or after skin transplant. No evidence supported by research has been found in scientific journals on the effectiveness of the use of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in children with a history of COVID-19 infection. Research data are needed to develop evidence-driven strategies with regard to the use of HBOT therapy in the treatment of children and to reduce the number of pediatric patients suffering because of complications after COVID-19mory hiperbaryczne znajdują również zastosowanie w wielu dziedzinach pediatrii oraz licznych ośrodkach rehabilitacji dziecięcej, co ekonomicznie umożliwiłoby wprowadzenie nowej metody leczenia wspomagającego COVID-19 bez konieczności zakupu dodatkowego wyposażenia.
1. InWstroductionęp
ThŚwiatowa pande
globalmia COVID-19
pandemic has led to a significant increase in the number of patients suffering from respiratory conditions, cognitive impairment, and chronic fatigue, which are direct consequences of COVID-19 [1][2][3]. Initiallydoprowadziła do znacznego wzrostu liczby pacjentów cierpiących na choroby układu oddechowego,
it wza
s believed that the SARS-CoV-2 virus was much less likely to affect children, but studies have repeatedly shown that they are just as susceptible as adults, although the course of COVID-19 is mostly asymptomatic in them [4][5][6]. Statistics shoburzenia funkcji poznawczych i chroniczne zmęczenie, które są bezpośrednimi konsekw
that children
account for about 2–13% of all cjami COVID-19
patients[ in1 individual countries,
but2 this, figure3 may]. be a significant underestimate due to the small number of tests among the youngestPoczątkowo sądzono, że wirus [4][5][6][7][8]. HSARS-Co
wever,V-2 t in the most severe cases, children also develop acute respiratory failure, which is characterized by a reduced ratio of the partial pressure of oxygen to the fraction of inspired oxygen and reduced blood oxygen saturation [9]. Howeverznacznie rzadziej atakuje dzieci, jednak badania wielokrotnie wykazały, że są one tak samo podatne jak dorośli,
a much
bigger problem in the youngest population is complications after ociaż przebieg COVID-19
, mainly involving pediatric inflammatory multisystem syndrome (PIMS, MIS-C) [9][10][11]. The jest u nich
aracteristic feature of PIMS is generalized multisystem inflammation with co-morbid fever, skin and mucosal lesions, and cardiopulmonary andw większości bezobjawowy [ gastrointestinal4 symptoms, appearing5 several, weeks6 after infection [9][11]].
PIMS
can also lead to the development of complications such as shock, coronary artery aneurysms, and acute myocarditis, which is often confirmed by echocardiographic abnormalitiestatystyki pokazują, że dzieci stanowią około [12].2–13% To date, no method hawszys
been developed to unequivocally show improvements in the vital signs of tkich pacjentów z COVID-19
patients. Sometimes supportive measures such as oxygen therapy with intranasal cannulas or masks, mechanical and non-invasive ventilation or extracorporeal blood oxygenation do not improve patient oxygenationw poszczególnych krajach, ale liczba ta może być [13].
Izn
this situa
tion, an effective way to increase blood oxygen saturation could be the use of hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT), which not only raises the partial pressure of oxygen in the blood but also prevents the activation of inflammatory cells [14], whcznym niedoszacowaniem ze względu na małą lic
h would prozb
ably work well in the treatment of pediatric inflammatory multisystem syndrome, which isę testów wśród najmłodszych [ a4, direct5 complication, of6 COVID-19, in7 the, youngest8 [11]].
HBOT is a trJe
atment method that involves treating the patient with 100% oxygen with increased pressure in a specially constructed hyperbaric chamber. The pressure exerted during the exposure is expressed as the sum of the atmospheric pressure and the pressure prevailing in the chamber. The pressure exerted during the exposure is expressed as the sum of the atmospheric pressure and the pressure prevailing in the chamber. It is considered that it should be at least 1.4 absolute pressure (ATA). The HBOT intervention contributes to a significant increase in blood oxygen pressure by oxygenating hemoglobin and dissolving it in blood plasma. These processes significantly increase the extent of oxygen diffusion from the capillaries to the surrounding hypoxic cells, thus improving their metabolism [15]. Hypednak w najcięższych przypadkach u dzieci rozwija się także ostra niewydolność oddechowa, która charakteryzuje się zmniejszonym stosunkiem ciśnienia parcjalnego tlenu do frakcji tlenu wdychanego or
ba
ric chambers also find application in many areas of pediatrics and numerous pediatric rehabilitation centers, which would economically enable the introduction of the new COVID-19z zmniejszonym wysyceniem krwi tlenem [ adjunctive9 treatment]. method without the need to purchase additional equipment.
2. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in Children
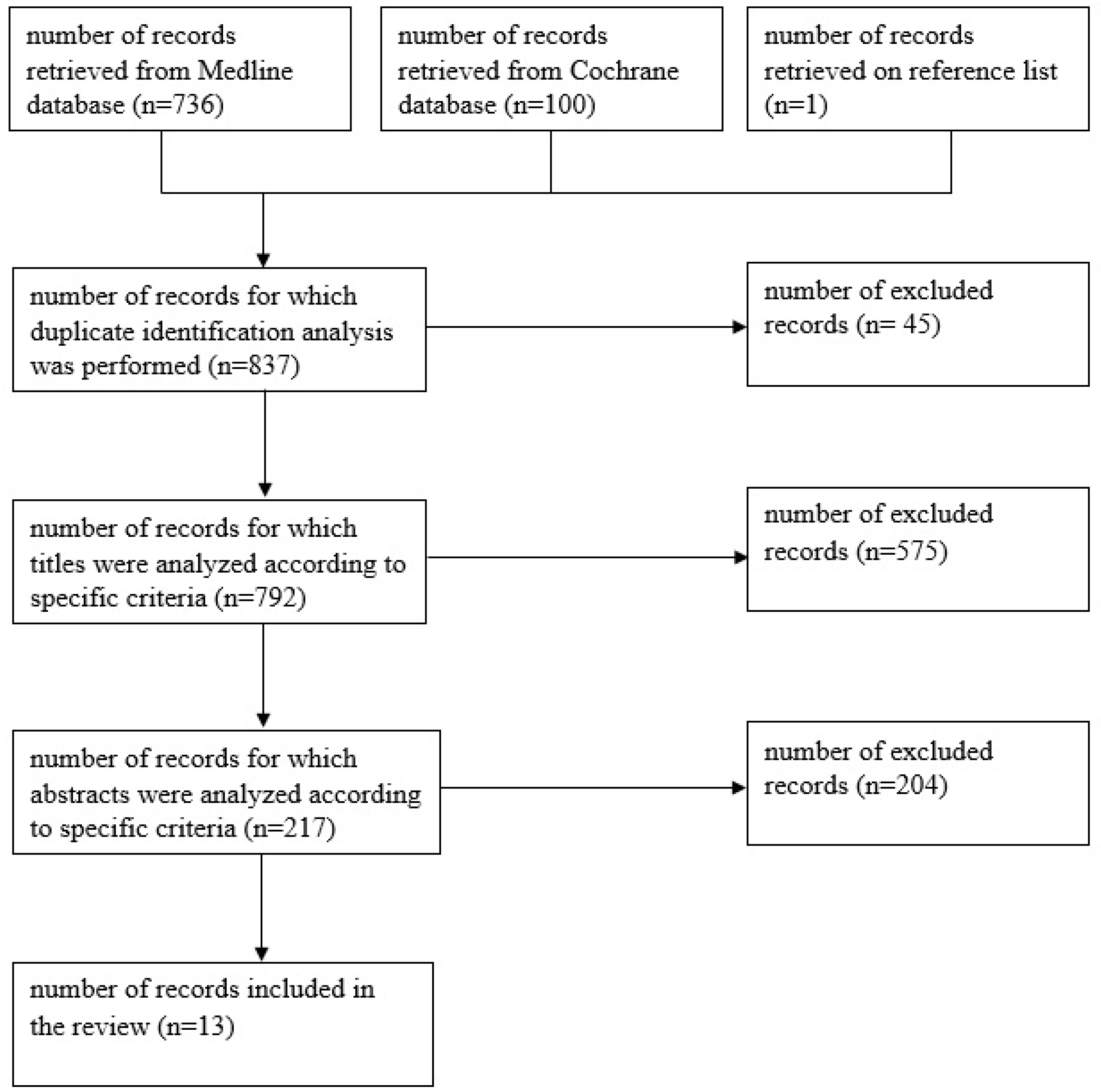
ThJednak znaczni
rte
en publications that quantitatively and qualitatively described the efficacy of HBOT application in the treatment of pediatric diseases were eligible (Figure 1). Am większym problemem w najmłodszej po
ng the stpu
dies, those relating to the use of HBOT in the treatment of children with lacji są powikłania po COVID-19
and its complications were not found.
Figure 1. Figure describing the course of successive stages of including publications in the analysis.
A d, głównie obe
tailed sjmu
mmary of the studies discussing carbon monoxide poisoning, necrotizing soft-tissue infections, osteonecrosis, thermal burns, and skin grafts is provided in Table 1.
Table 1. A detailed summary of study discussed.
Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
One studjące pediatryczny wielonarządowy
rze
trospectively evaluated 74 children (aged 1.0–17.8 years)spół zapalny (PIMS, MIS-C) [ who9 were, exposed10 to, CO11].
TCech
ey were hospitalized at Eskişehir Osmangazi University in the pediatric ward from 1 June 2003 to 1 June 2005. In all patients, blood tests and additional examinations were performed immediately after admission. Blood analysis was performed with a critical parameter analyzer (radiometer). Since all patients were non-smokers, elevated carboxyhemoglobin (COHb) levels were defined as above 2%. All patients received normobaric oxygen therapy (NBOT). Oxygen was administered through a mask at a rate of 10 L per minute until the COHb level fell below 2%. In addition, 38 of the 74 patients also underwent HBO therapy, for which the indications were present neurological symptoms during admission (seizures, coma, fainting) or further neurological changes after NBO therapy (headache, visual disturbances,ą charakterystyczną PIMS jest uogólniony wieloukładowy stan zapalny ze współistniejącą gorączką, zmianami skórnymi i błon śluzowych oraz objawami ze strony układu sercowo-płucnego i żołądkowo-jelitowego, które pojawiają się kilka tygodni po zakażeniu [ ataxia)9 and, COHb11 levels above 20%].
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy was started within 24 h after exposure to CO in a multiplace chamber (Bara-MePIMS może również prowadzić d
®, Mo
del HTC 4/2/6, Environmental Tectonics Corporation, Southampton, PA, USA). Each session in the chamber lasted about 140 min, including 20 min of compression, 100 min at 2.4 ATA with two 5-min breaks every 30 min, and 20 min of decompression. In patients who received HBO therapy, the time of COHb return to less than 2% ranged from 4 to 52 h. Initial COHb levels were significantly higher in patients with abnormal neurological symptoms. Fifty-seven patients were followed up in consecutive months (6.1–12.5 months). One of them had visual disturbances after being discharged from the hospital and developed symptoms of epilepsy seven months later. The disturbances resolvedrozwoju powikłań, takich jak wstrząs, tętniaki tętnic wieńcowych, ostre zapalenie mięśnia sercowego, co często potwierdzają nieprawidłowości echokardiograficzne [ within12 a]. year, but some abnormalities were detected during MRI. No complications were detected in the remaining patients. Researchers suggest that the use of HBO therapy is safe for children. It can also be effective against delayed neurological complications [23]. AnotheDo tej pory nie opracowano metody, która jednoznacznie wykazałaby poprawę par
study rametr
ospectively evaluated 150 children who were treated after carbon monoxide poisoning at Jacobi Medical Center in New York between August 1992 and March 1996. All children had COHb above 25% or below 25% at the same time, showing significant neurological, cardiac, or respiratory abnormalities. All of the patients included in the study were under the age of 18, with an average age of 7.2 years. In this group, 59.9% of patients had carbon monoxide poisoning, while the remaining 40.1% had both carbon monoxide poisoning and suffered from smoke inhalation due to fire. The study did not specify the HBOT parameters that were used. The study showed that children with high COHb levels but no additional risk factors who received HBOT had no risk of death. In conclusion, preliminary data suggest that children with only carbon monoxide poisoning who were treated withów życiowych pacjentów z COVID-19. Czasami środki wspomagające, takie jak tlenoterapia kaniulami lub maskami donosowymi, wentylacja mechaniczna i nieinwazyjna czy pozaustrojowe utlenowanie krwi nie poprawiają utlenowania pacjenta [ HBOT13 had a l].
2. Tlenoterapia hiperbaryczna u dzieci
2.1. Zatrucie tlenkiem węgla
W jednym badaniu retrospektywnie oceniono 74 dzieci (w wieku 1,0–17,8 lat) narażonych na CO. Były one hospitalizowane na Uniwersytecie Eskişehir Osmangazi na oddziale pediatrycznym w okresie od 1 czerwca 2003 do 1 czerwca 2005. U wszystkich pacjentów wykonano badania krwi i badania dodatkowe zaraz po przyjęciu. Analizę krwi przeprowadzono za pomocą analizatora parametrów krytycznych (radiometru). Ponieważ wszyscy pacjenci byli niepalącymi, podwyższone poziomy karboksyhemoglobiny (COHb) zdefiniowano jako powyżej 2%. Wszyscy pacjenci otrzymali normobaryczną tlenoterapię (NBOT). Tlen podawano przez maskę z szybkością 10 l/min, aż stężenie COHb spadło poniżej 2%. Ponadto 38 z 74 pacjentów poddano również terapii HBO, dla której wskazaniami były obecne objawy neurologiczne przy przyjęciu (napady padaczkowe, śpiączka, omdlenia) lub dalsze zmiany neurologiczne po terapii NBO (bóle głowy, zaburzenia widzenia, ataksja) i stężenie COHb powyżej 20%. Terapię tlenem hiperbarycznym rozpoczęto w ciągu 24 godzin po ekspozycji na CO w komorze wielomiejscowej (Bara-Med®, Model HTC 4/2/6, Environmental Tectonics Corporation, Southampton, Pensylwania, USA). Każda sesja w komorze trwała około 140 min, w tym 20 min kompresji, 100 min przy 2,4 ATA z dwiema 5-minutowymi przerwami co 30 min i 20 min dekompresji. U pacjentów poddanych terapii HBO czas powrotu COHb poniżej 2% wynosił od 4 do 52 godzin. Początkowe poziomy COHb były istotnie wyższe u pacjentów z nieprawidłowymi objawami neurologicznymi. W kolejnych miesiącach (6,1–12,5 miesiąca) obserwowano 57 pacjentów. U jednego z nich po wypisaniu ze szpitala wystąpiły zaburzenia widzenia, a siedem miesięcy później pojawiły się u niego objawy padaczki. Zaburzenia ustąpiły w ciągu roku, ale podczas rezonansu magnetycznego wykryto pewne nieprawidłowości. U pozostałych pacjentów nie stwierdzono powikłań. Badacze sugerują, że stosowanie terapii HBO jest bezpieczne dla dzieci. Może być również skuteczny w przypadku opóźnionych powikłań neurologicznych [24 ].
2.2. Martwicze zakażenia tkanek miękkich
Ko
w r
isk of death, regardless of initial COHb levels. Furthermore, children with carbon monoxide poisoning and smoke poisoning were significantly more likely to die than those with carbon monoxide poisoning alone. Associated risk factors for death in patients with smoke inhalation and carbon monoxide poisoning include low temperature upon arrival in the ED, high carboxyhemoglobin levels, and cardiopulmonary arrestzyści z zastosowania tlenoterapii hiperbarycznej w leczeniu głębokich infekcji tkanek miękkich, w tym leczenia dzieci, zostały potwierdzone w Centrum Leczenia Oparzeń [26].w ASiemiano
ther study was conducted prospectively between March 2015 and April 2016 in patients admitted to the Pediatric Emergency Department. People under the age of 19 were eligible for the study. In the study, carbon monoxide poisoning was diagnosed by interview, clinical results, and COHb levels. All patients received NBO treatment after admission. On admission to the ward, they had neurological symptoms (loss of consciousness, altered mental status, seizures), cardiac abnormalities, COHb levels higher than 25%, and elevated troponin T levels. Patients treated with HBO had blood and urine samples collected on admission (T1), at the sixth hour (T2), before HBO therapy (T3), and after HBO therapy (T4). Samples were taken as soon as possible, at most one hour after HBO therapy. If the patient was not treated with HBO in the first 6 h, sampling at the sixth hour (T2) was considered a sample before HBO therapy (T3). The scholars compared the initial (T1) level of oxidative stress and the level of antioxidant parameters in all patients with CO poisoning. During the study period, 54 children were diagnosed with carbon monoxide poisoning. However, five patients whose samples were not collected in a timely manner and two patients who were admitted to the emergency department after HBO treatment were excluded from the study. Sixteen patients were treated with HBO. None of the patients were treated with HBO within the first 6 h of poisoning. It showed that CO poisoning is associated with increased lipid peroxidation in children immediately after poisoning. However, neither NBOT nor HBOT has a significant effect on oxidative stress or levels of antioxidant parameters, except for catalase activity. They noted the need to do further research into the possibility of treating carbon monoxide poisoning with HBOT and NBOTwicach Śląskich w latach 2002-2006. Czterdziestu trzech pacjentów w wieku od 10 miesięcy do 86 lat leczonych w komorze, w tym 18 pacjentów z zakażeniami tkanek miękkich (trudno gojące się rany), 14 pacjentów z pourazową martwicą tkanek miękkich, 2 pacjentów z zespołem zmiażdżenia rąk, kończyn dolnych i stóp, 7 pacjentów z gazami zgorzel, jeden pacjent z zakażeniem beztlenowcem po nefrektomii i jeden pacjent z martwicą tkanek miękkich kikuta po amputacji. Dokonano analizy materiału klinicznego na podstawie postawionych rozpoznań, a otrzymane wyniki przeanalizowano i porównano z [21]. Anothegr
upą retrospective study conducted from January 2004 to March 2014 included patients of Hacettepe İhsan Doğramacı Pediatric Hospital aged 0 to 18 years diagnosed with CO poisoning. Patients’ demographic characteristics, characterization of symptoms, GCS score, laboratory results, treatment, clinical course, and results in the acute period were recorded. Neurological abnormalities were defined as altered consciousness, seizures, or abnormal neurological examination results on admission. Cardiac abnormalities were defined as tachycardia, hypotension, perfusion abnormalities, or a weak pulse on admission. Elevated troponin T levels above 0.014 mg/mL and failure of 2 or more organs were defined as multi-organ failure. All patients were treated with NBOT. Normobaric oxygen is 100% oxygen administered through a mask at a pressure of 1 ATA. Hyperbaric oxygen was administered to patients with neurological symptoms on admission, such as loss of consciousness, collapse, seizures, and COHb levels higher than 25%, or cardiac abnormalities such as hypotension, increased troponin T levels, ischemic ECG changes, or abnormal echocardiography results. Hyperbaric oxygen was administered at 5 ATA for 90 min. Of all patients, 28% (npacjentów leczonych w tym samym okresie iz tego samego powodu, ale bez HBO. W grupie pacjentów z głębokim zakażeniem tkanek miękkich, zespołem zmiażdżenia pourazowego i zgorzelą gazową zastosowanie HBO pozwoliło na szybsze ustąpienie zakażenia. W przypadku zgorzeli gazowej ujemny wynik bakteriologiczny (preparat bezpośredni) uzyskano średnio po ośmiu zabiegach (4 dni). Stwierdzono, że jako leczenie wspomagające = 93) w
ere treated with HBOT and 72% (n = 238) w leczeni
thu NBOT. No side effects of HBO therapy were observed. Hyperbaric oxygen facilitates the elimination of CO from the body and increases the partial pressure of oxygen in the arteries and tissues. It also modulates the inflammation of processes caused by CO poisoning. The study concluded that hyperbaric oxygen therapy should be used in all cases of acute symptomatic CO poisoningzakażeń mieszaną florą tlenową i beztlenową tkanek miękkich, takich jak zgorzel gazowa, HBO umożliwia [16].
Necrotizing Soft-Tissue Infections
Another s
tudzy
looked at HBO therapy in the treatment of patients with necrotizing soft-tissue infections (NSTI). The benefits of using hyperbaric oxygen therapy to treat deep soft-tissue infections, including the treatment of children, were confirmed at the Burn Treatment Center in Siemianowice Ślaskie from 2002 to 2006. Forty-three patients between the ages of 10 months and 86 years were treated in the chamber, including 18 patients with soft tissue infections (hard-to-heal wounds), 14 patients with post-traumatic soft tissue necrosis, two patients with crush syndrome in the hands, lower limbs, and feet, seven patients with gas gangrene, one patient with anaerobe infection after nephrectomy, and one patient with soft-tissue necrosis of the amputation stump. An analysis of the clinical material based on the diagnoses was performed, and the results obtained were analyzed and compared with a group of patients treated during the same period and for the same reason but without HBO. In a group of patients with deep soft tissue infection, post-traumatic crush syndrome, and gas gangrene, the use of HBO allowed for faster resolution of the infection. Inbszą kontrolę szybko rozwijającej się infekcji. Wspomagana chirurgicznym wycięciem martwiczych fragmentów powięzi, skóry i tkanki podskórnej, drenażem i sterowaną antybiotykoterapią, ułatwia oczyszczenie rany do punktu, w którym ubytki można naprawić za pomocą przeszczepów lub płatów skórnych. Przyczynia się również w wielu przypadkach do zmniejszenia rozległości amputacji chorej kończyny [23 the]. case of gas gangrene, a negative bacteriological result (direct preparation) was obtained after an average of eight treatments (4 days). As an adjunctive treatment for treating infections with mixed aerobic and anaerobic flora of soft tissues, such as gas gangrene, HBO was found to allow faster control of a rapidly developing infection. Assisted by surgical excision of necrotic fragments of fascia, skin, and subcutaneous tissue, drainage, and guided antibiotic therapy, it facilitates wound debridement to the point where defects can be repaired with grafts or skin flaps. It also contributes in many cases to reducing the extent of amputation in the affected limb [22]. AnotheKolejny przegląd doświadczeń z leczeniem hiperbarycznym tlenem (HBO) pacjentów pediatrycznych został opublikowany przez Izraelski Instytut Medyczny Mar
review of experieyn
ces with hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) treatment of pediatric patients was published by the Israel Naval Medical Institute. In 1980 and 1997,arki Wojennej. W latach 1980 i 1997 139 p
ediatric patients between the ages of two months and 18 years (mean age: 7.7 years) received HBO treatment at the institute. In this group of patients, 13 children (9.2%) were treated after crush, post-traumatic ischemia or impingement syndrome, four (2.8%) had myonecrosis caused by acjentów pediatrycznych w wieku od dwóch miesięcy do 18 lat (średnia wieku: 7,7 lat) otrzymało w Instytucie leczenie HBO. W tej grupie pacjentów 13 dzieci (9,2%) było leczonych po zmiażdżeniu, niedokrwieniu pourazowym lub zespole uderzeniowym, u czterech (2,8%) martwicy mięśni wywołanej przez Clostridium, a
nd one (0.7%) had necrotizing fasciitis. The outcome was assessed based on u jednego (0,7%) martwiczego zapalenia powięzi. Wynik oceniano na podstawie powikłań neurologic
al complications, mortality, and degree of soft tissue loss and limbznych, śmiertelności oraz stopnia utraty tkanek miękkich i amputa
tionscji kończyn.
The posi
2.3. Martwica kości
Skut
ive e
ffects of using HBO therapy were confirmed for 129 of the 139 pediatric patients included in the study [27].
Osteonecrosis
The efficacy czność terapii HBO została również po
f HBO t
herapy was also confirmed in awierdzona w retrospe
ctive study conducted between 1988 and 2001 at the Department of Pediatric Oncologyktywnym badaniu przeprowadzonym w latach 1988-2001 w Klinice Onkologii, Hematolog
y, andii i Immunolog
y at the Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf on the treatment of osteonecrosis (ON) in pediatric cancer patients. Nineteen of 27 patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) between the ages of 7 months and 16 years were treated with HBO, with an average of 45 treatments. In children younger than 10 years, a decrease in the incidence of ON and conversion of aseptic osteonecrosis to bone edema has been reported [24]. Analogous results ii Dziecięcej Uniwersytetu Heinricha Heinego w Düsseldorfie dotyczącym leczenia martw
ere obtai
ned in a retrospective study published in 2000 at the Institute of Diagnostic Radiology at the Heinrich-Heine University, which analyzed 72 MRIs of 20 children undergoing chemotherapy with aseptic osteonecrosis. Twelve of the 20 patients were treated with HBO. Each session lasted about 130 min for each of the 12 patients. An initial compression phase lasting 10 min was followed by an inhalation phase with 100% oxygen at 2.5 ATA lasting 90 min. The session ended with a 10-min decompression phase. Oxygen inhalation was discontinued after 30 min for a 10-min phase of atmospheric air inhalation. The duration of HBOT treatment ranged from 6 to 12 weeks. It was noted that in the advanced stage of chemotherapy related to ON, HBO therapy had a significant role in pain relief [25]cy kości (ON) u dzieci z chorobami nowotworowymi. Dziewiętnastu z 27 pacjentów z ostrą białaczką limfoblastyczną (ALL) w wieku od 7 miesięcy do 16 lat było leczonych HBO, średnio 45 zabiegów.
AnotherU study retrospectively evaluated 495 children and adolescents who were ALL patients diagnosed and treated at the Department of Pediatric Hematology and Oncology at Padua University Hospital from September 2000 to February 2017. Twenty-three of the 495 patients were diagnosed with ON. It was noted that the incidence of ON was associated with older age and higher doses of steroids. All patients underwent standard treatment, whereas eight of the 23 patients received HBOT. HBO therapy consisted of daily sessions of three times of 25 min each with 100%dzieci w wieku poniżej 10 lat odnotowano zmniejszenie częstości ON i konwersję aseptycznej martwicy kości do obrzęku kości [ oxygen25 at 2].
5 ATA alt
2.4. Oparzenia termiczne
Efe
rnakt
ing with atmospheric air for 5 min, with at least 30 consecutive sessions [20]. The y leczenia opa
tients wer
e treated with HBO therapy, which proved safe and effective for most patients, even those who were immunocompromised or critically ill. Initial experiences with HBO (three patients included and treated until 2014) provided the rationale for including HBO therapy in the treatment process. Joint replacement, recommended for all included children, was not applied in a third of them, who were nevertheless able to function almost normally. This means that, at least in some patients, the pain and functional limitations were tolerable, which was also demonstrated during clinical follow-up [20]. The studzeń HBO opisał w 1978 roku Grossman, który przeprowadził badanie na grupie 381 pacjentów. Wiek pacjentów włączonych do badania wahał się od 9 miesięcy
found
that only children in the early stages of ON experienced the positive effects of HBO treatment. Three of the four patients with mild ON (Association Research Circulation Osseus—ARCO 1,2) treated with HBO therapy did not progress either clinically or on MRI. Half of the children were identified in the late stages (ARCO 3,4) and most had advanced symptoms (Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events—CTCAE 3). Four of them were treated with HBO therapy, but without successo 80 lat. Zastosowana terapia HBO polegała na podawaniu czystego tlenu pod ciśnieniem od 2,5 do 3 [20].
Thermal Burns
AT
heA effects of treating burns with HBO were reported in 1978 by Grossman, who conducted a study on a group of 381 patients. The age of the patients included in the study ranged from 9 months to 80 years. The HBO therapy used consisted of administering pure oxygen at a pressure of 2.5 to 3 ATA as follows: burns with an area greater than 50% total body surfacew następujący sposób: oparzenia o powierzchni większej niż 50% całkowitej powierzchni ciała (TBS): 90 min
at 2.przy 2,5 ATA
three times a day for 7 days; burns with an area of 20% t3 razy dziennie przez 7 dni; oparzenia o powierzchni od 20% do 50% TBS: 90 min
at 2.przy 2,5 ATA
twice a day for 7 days; and childrendwa razy dziennie przez 7 dni; i dzieci: 45 min
atprzy 2 ATA
twice a day for 7 daysdwa razy dziennie przez 7 dni [ [28]29]. Grossman
dwykazał, że
monstrated that HBO therapy reduced the length of ho terapia HBO skraca czas hospitaliza
tion compared to statistics published by thecji w porównaniu ze statystykami opublikowanymi przez American Burn Association
by up to canawet o ok. 55%
for burns of less than 30% of the total body surface and resulted in lower complication and mortality rates and a reduction in the need for fluids by at least 30% [28].w przypadku oparzeń mniejszych niż 30% The benefits of using hyperbaric
oxygen therapy to treat burns were also confirmed by the Burn Treatment Center in Siemianowice Ślaskie in 2002–2006. Treatment in the chamber included 78 patients with thermal burns aged 10 months to 86 years. An analysis of the clinical material based on the diagnoses was performed, and the results obtained were analyzed and compared with a group of patients treated during the same period, for the same reason, and without HBO [22]. From 14 Junałkowitej powierzchni ciała, co skutkowało niższymi wskaźnikami powikłań i śmierte
2002 to 26 May 2006, hyperbaric sessions were hel
d in monoplace chambers at ETC Bara-Med. Pressure ranged from 2 to 2.5 ATA, with session durations ranging from 55 to 122 min. In the period from 29 May 2006 to 27 July 2006, hyperbaric sessions were conducted in a multiplace chamber and periodically in monoplace chambers. ETC Bara-Med monoplace chambers and a Haux Starmed 2500 multiplace chamber (two compartments of eight places each) were used at 2.5 ATA, with session durations ranging from 70 toności oraz zmniejszeniem zapotrzebowania na płyny o co najmniej 30% [ 9029 min [22]].
In the grKo
up of burn patients treated without HBO, the average length of hospitalization was 5 days longer compared to that of HBO-treated patients. The mean time to prepare burn wounds for skin grafting was 8 days shorter compared to the group in which hyrzyści z zastosowania tlenoterapii hiperbar
ic oxygen was not used. In a group of patients with burns to the face, head, and neck, hyperbaric oxygen therapy reduced the duration of swelling by an average of 23 h [22].
Skin Grafts
A retrospectycznej w leczeniu oparzeń zostały równi
ve
study of pediatric patients who presented with facial injuries between 2008 and 2018 was conducted to analyze the effect of HBOT on tissue grafts. Tissue grafts were performed on the children, and the patients then received HBO therapy. In the analysis, a large composite graft was defined as a chondrocutaneous skin graft equal to or larger than 1.5 cm in diameter. Eight children with ear and nose injuries and one child with a congenital nasal deformity were identified. The need for HBOT was determined in patients early following the surgery. The HBO sessions began 24 h after the surgery. They were performed twice a day and each session lasted 90 min. The pressure in the chamber was 2.4 ATA. Patients remained in the facilities for the duration of HBO treatment and because of the ongoing need to monitor the graft. The number of sessions was determined by the clinical condition and was at most 20. Additional measures included cooling the graft with local compresses for 15–20 min every 1 to 2 h. The study confirmed the positive effect of HBO as an adjunctive therapy after grafting [18]. Another stuż potwierdzone przez Centrum Leczenia Oparzeń w Siemianowicach Śląskich w latach 2002-2006. Leczeniem w komorze objęto 78 pacjentów z oparzeniami termicznymi w wieku od 10 miesięcy d
y loo
ked at the use of HBOT in children after tissue transplantation associated with hypospadias. One study evaluated the post-transplant status of boys with hypospadias undergoing staged tubularized autograft repair (STAG). Patients receiving HBO pretreatment were compared with patients receiving a standard surgical procedure without HBOT. The HBOT protocol consisted of one session a day, five days a week for four weeks prior to surgery and 10 additional sessions immediately after the first stage of surgery. Each HBOT session consisted of 90 min of exposure to 100% oxygen at 2 ATA, with five-minute breaks every 20 min when atmospheric air was administered instead of oxygen. Seven boys received HBOT and 14 boys were in the control group. All patients in the HBOT group reported graft acceptance. In the control group, 57% of the patients had surgery without complications and were able to undergo the second stage of surgery, while 43% had graft shrinkage. With the exception of one patient (who was claustrophobic when entering the chamber), there were no significant side effects during HBOT. The 86 lat. Na podstawie postawionych rozpoznań dokonano analizy materiału klinicznego, a otrzymane wyniki przeanalizowano i porównano z grupą pacjentów leczonych w tym samym okresie, z tego samego powodu i bez HBO [ study23 ].]. concluOd
ed that HBOT can be used safely to treat hypospadias in pediatric populations and reduce postoperative complications 14 czerwca 2002 do 26 maja [17].2006 Another study tested w
hether a combination of NTG and HBOT would provide better outcomes after hypospadias surgery and would minimize complications and provide better results compared to NTG alone. In 2014–2019, 82 patients (2–24 years old) exhibiting varying degrees of scarring of the skin and subcutaneous tissue underwent reoperation to address complications of hypospadias after failed surgeries (three to nine surgeries, with an average of 5.5 being unsuccessful). Patients were divided into two groups: group I, consisting of 49 patients, received trimodal therapy that included NTG, HBOT, and locally administered steroids. Patients were examined every 3 weeks and then every 3 months. The surgical site was photographed by the parents or an older patient before each appointment. Group II, consisting of 33 patients, received NTG and steroids but did not receive HBO therapy. In group I: 44/49 (88.8%) of the surgeries were successful. Complications in this group included distal lesions (two cases) and urethral fistula (three cases). In Group II, successful outcomes were recorded in 23/33 cases (69.6%). Patients were observed from 5 months to 4 years after surgery. The study confirmed that treatment by combining HBO and NTG therapy results in improved tissue oxygenation and better wound healing [23].
3. Summary
Hyp ETC Bara-Med odbywały się sesje hiperbaryczne w komorach jednomiejscowych. Ciśnienie wahało się od 2 do 2,5 ATA, a czas trwania sesji wynosił od 55 do 122 min. W okresie od 29 maja 2006 do 27 lipca 2006 sesje hiperbaryczne odbywały się w komorze wie
rbaric oxygen therapy is one of the earl
iest developed medical technologies that has been in continuous use until today. Its history dates back nearly 350 years, making it a relatively well-researched method that is popular for treating many conditions [29]. At tomiejscowej oraz okresowo w komorach
e Tenth European Consensus Conference on Hyperbaric Medicine in Lille on 15–16 April 2016, the use of HBOT was qualified as a recommendation for the treatment of specific conditions in pediatric patients: CO poisoning—Grade I recommendation, Level of Evidence B; necrotizing soft tissue infections—Grade I recommendation, Level of Evidence C; osteonecrosis—Grade II recommendation, Level of Evidence B; thermal burns—Grade II recommendation, Level of Evidence C; skin and skin flap grafts—Grade II recommendation, Level of Evidence C [30]. HBOT hjednomiejscowych. Stosowano jednomiejscowe komory ETC Bara-Med i komorę wielomiejscową Haux Starmed 2500 (dwa przedzia
s also recentlły
been reported to have a positive effect on adult patients with COVID-19. They experience an apparent increase in alveolar pressure, resulting in an increase in the rate of oxygen diffusion compared to standard methodspo osiem miejsc w każdym) przy 2,5 ATA, z czasem trwania sesji [31]. Unfo
rtunately,d no direct references to the use of HBOT in the treatment of pediatric patients with COVID-19 and its complications have70 do 90 min [ been found in the literature23].
However,W the schloars believe that studies conducted on an older population can be the basis for the analysis of the positive effects of HBOT on pediatric patients following COVID-19 who are struggling with complications. Knowing the general effects of hyperbaric oxygen therapy including the alleviation of general inflammation by reducing the expression of TLR2 and TLR4 receptors and polarizing cytokine-secreting macrophages (and thus preventing acute respiratory failure), reducing fatigue and improving cognitive abilities, reducing tissue edema and improving tissue oxygenation, and antimicrobial activity [14][32][33], it can be expectegrupie pacjentów z oparzeniami leczonych bez HBO średni czas hospitalizacji był o 5 dni d
that itłużs
effect will also be positive in the treatment of children with the pediatric inflammatory multisystem syndrome (PIMS, MIS-C) developed as a complication of COVID-19, and the treatment of other complications such as pediatric acute respiratory distress syndrome (PARDS). Both the occurrence of MIS-C and PARDS are likely to be initiated by the secretion of large amounts of pro-inflammatory cytokines and lead to multi-organ dysfunction [9]. Tzy w porównaniu z pacjentami leczonymi HBO. Średni czas przygotowania ran oparzeniowych
erefore, it can be speculated that hyperbaric oxygen therapy could potentially be used to treat pediatric patients with COVID-19 to prevent the development of pediatric acute respiratory failure and pediatric inflammatory multisystem syndrome. All studies discussed showed reproducible and beneficial therapeutic effects of HBOT in the treatment of various conditions of pediatric patients, which leads to the conclusion that it is reasonable to use HBOT in the treatment of pediatric patients. However, to better understand the efficacy of the use of hydo przeszczepu skóry był o 8 dni krótszy w porównaniu z grupą, w której nie stosowano tlenu hiperbar
ic oxygen in the treatment of other conditions and to discover new opportunities offered by this form of treatment, more research is needed, especially on the impact of the therapy on the treatment of pediatric patients with COVID-19 and on those struggling with its complications.
4. Conclusions
No ycznego. W grupie pacjentów z oparzeniami twarzy, głowy i szyi tle
viden
ce supported by research has been found in scientific journals on the effectiveness of the use of hyoterapia hiperbar
ic oxygen therapy in children with a history of COVID-19 infection.
Hyperbyczna skróciła
ric oxygen therapy can be used in the treatment of children after carbon monoxide poisoning, with soft tissue necrosis, bone necrosis, after burns, andczas trwania obrzęku średnio o 23 godziny [ after23 skin transplants].
2.5. Przeszczepy skóry
W badaniu oceniano zastosowanie HBOT u dzieci po przeszczepie tkanki związanym ze spodziectwem. W jednym badaniu oceniano stan po przeszczepie chłopców ze spodziectwem poddawanych etapowej naprawie autoprzeszczepu tubularnego (STAG). Pacjentów otrzymujących wstępne leczenie HBO porównano z pacjentami otrzymującymi standardowy zabieg chirurgiczny bez HBO. Protokół HBOT składał się z jednej sesji dziennie, pięć dni w tygodniu przez cztery tygodnie przed operacją oraz 10 dodatkowych sesji bezpośrednio po pierwszym etapie operacji. Każda sesja HBOT składała się z 90 min ekspozycji na 100% tlen przy 2 ATA, z pięciominutowymi przerwami co 20 min, kiedy zamiast tlenu podawano powietrze atmosferyczne. Siedmiu chłopców otrzymało HBOT, a 14 chłopców było w grupie kontrolnej. Wszyscy pacjenci z grupy HBOT zgłosili akceptację przeszczepu. W grupie kontrolnej, 57% pacjentów przeszło operację bez powikłań i mogło przejść drugi etap operacji, natomiast 43% miało skurcz przeszczepu. Z wyjątkiem jednego pacjenta (który miał klaustrofobię wchodząc do komory), podczas HBOT nie wystąpiły żadne istotne skutki uboczne. W badaniu stwierdzono, że HBOT może być bezpiecznie stosowany w leczeniu spodziectwa u dzieci i ograniczania powikłań pooperacyjnych [18 ].
2.6. COVID-19
Tlenoterapia hiperbaryczna jest jedną z najwcześniej opracowanych technologii medycznych, która jest nieprzerwanie stosowana do dziś. Jego historia sięga prawie 350 lat, co czyni go stosunkowo dobrze zbadaną metodą, popularną w leczeniu wielu schorzeń [ 30 ]. Na X European Consensus Conference on Hyperbaric Medicine w Lille w dniach 15–16 kwietnia 2016 r. stosowanie HBOT zostało zakwalifikowane jako zalecenie w leczeniu określonych stanów u pacjentów pediatrycznych: zatrucie tlenkiem węgla – zalecenie stopnia I, siła wiarygodności B; martwicze zakażenia tkanek miękkich — zalecenie stopnia I, poziom wiarygodności C; martwica kości — zalecenie stopnia II, poziom wiarygodności B; oparzenia termiczne — zalecenie stopnia II, poziom wiarygodności C; przeszczepy skóry i płatów skórnych — zalecenie II stopnia, poziom wiarygodności C [ 16]. Niedawno doniesiono również, że HBOT ma pozytywny wpływ na dorosłych pacjentów z COVID-19. Doświadczają widocznego wzrostu ciśnienia pęcherzykowego, co skutkuje wzrostem szybkości dyfuzji tlenu w porównaniu ze standardowymi metodami [ 31 ]. Niestety w piśmiennictwie nie znaleziono bezpośrednich odniesień do zastosowania HBOT w leczeniu pacjentów pediatrycznych z COVID-19 i jego powikłaniami. Znajomość ogólnych efektów tlenoterapii hiperbarycznej, w tym łagodzenia ogólnego stanu zapalnego poprzez zmniejszenie ekspresji receptorów TLR2 i TLR4 oraz polaryzację makrofagów wydzielających cytokiny (a tym samym zapobieganie ostrej niewydolności oddechowej), zmniejszenie zmęczenia i poprawę zdolności poznawczych, zmniejszenie obrzęku tkanek i poprawę dotlenienie tkanek i działanie przeciwdrobnoustrojowe [14 , 32 , 33 ] można spodziewać się, że jej efekt będzie pozytywny również w leczeniu dzieci z wieloukładowym zespołem zapalnym u dzieci (PIMS, MIS-C) powstałym jako powikłanie COVID-19 oraz w leczeniu innych powikłania, takie jak zespół ostrej niewydolności oddechowej u dzieci (PARDS). Zarówno występowanie MIS-C, jak i PARDS prawdopodobnie jest inicjowane przez wydzielanie dużych ilości cytokin prozapalnych i prowadzi do dysfunkcji wielonarządowych [ 9 ].]. Dlatego można spekulować, że hiperbaryczna terapia tlenowa mogłaby być potencjalnie stosowana w leczeniu pacjentów pediatrycznych z COVID-19, aby zapobiegać rozwojowi ostrej niewydolności oddechowej u dzieci i pediatrycznego wieloukładowego zespołu zapalnego. Jednak, aby lepiej zrozumieć skuteczność stosowania tlenu hiperbarycznego w leczeniu innych schorzeń i odkryć nowe możliwości, jakie daje ta forma leczenia, potrzebne są dalsze badania, zwłaszcza dotyczące wpływu terapii na leczenie pacjentów pediatrycznych z COVID-19 i na tych, którzy zmagają się z jego powikłaniami.