Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) is the catalytic subunit of the polycomb repressor complex 2 (PRC2), which trimethylates histone 3 at Lys-27 and regulates the expression of downstream target genes through epigenetic mechanisms.
- enhancer of zeste homolog 2
- H3K27
- epigenetics
1. Introduction
1.Introduction
Gastric cancer (GC) is the fifth most diagnosed malignancy worldwide, with more than 1 million new cases annually [1]. There is a lack of methods to diagnose GC early, so many patients are diagnosed at a later stage, which leads to a high mortality rate for GC patients [1]. It was reported that more than 784,000 GC patients died worldwide in 2018, making it the third most common cause of death among oncologic diseases [2]. The complicated pathogenesis, late diagnosis and lack of effective treatment for GC lead to the poor prognosis of patients. To fundamentally prevent and treat GC, it is highly significant to understand the pathogenesis of GC [3]. In addition to genetic changes and environmental factors, it has been proven that epigenetic inheritance guides the occurrence and development of cancer and is a hallmark of gastric malignancies [4]. It was known that the polycomb group (PcG) was one of the most important epigenetic regulators, which influences the expression of many genes involved in the development of the body [5]. As a core member of the PcG family, EZH2 plays a vital role in cell proliferation, differentiation and tumor formation through H3K27me3-mediated downstream gene silencing. The expression of H3K27me3 in GC tissues is significantly increased, and it is the most common type of histone methylation modification in GC studies, which is closely related to the pathogenesis of GC and the prognosis of patients [4][6][4,6]. In conclusion, EZH2 plays a role in the pathogenesis of GC through H3K27me3. For these reasons, EZH2 can be considered an exciting target for developing targeted therapies for GC.
2. Overview of EZH2
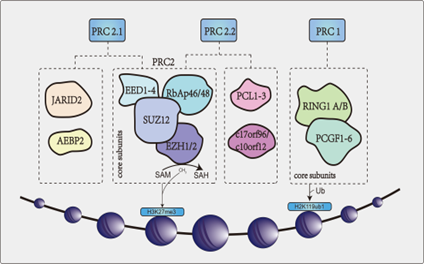
PcG proteins are a group of transcriptional repressors that regulate target genes through chromatin modification and can induce tumor development. These proteins chemically and functionally represent the core proteins of the polycomb repressive complexes (PRCs) [5]. PRCs are enzyme complexes that modify lysine residues on histones [7][8][7,8]. There are two major PRCs in mammals: Polycomb repressive complex 1 (PCR1) and polycomb repressive complex 2 (PCR2). PRC1 consists of ring finger protein 1 (RING 1) (RING1A or RING1B) and PcG ring finger protein (PCGF1-6) that monoubiquitinates lysine 119 on histone H2A (H2AK119ub1) [9]. PRC2 complexes are histone methyltransferases (HMTases) that are dependent on S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM) and contain four major core subunits: EZH2/1, suppressor of zeste 12 (SUZ12), embryonic ectoderm development 1-4 (EED1-4) and RBAP46/48 [9][10][9,10]. It catalyzes the mono-methylation, di-methylation and tri-methylation of lysine 27 on histone H3 (H3K27me1, H3K27me2 and H3K27me3 [11]. PRC2 is further divided into two different subclasses: PRC2.1 and PRC2.2. In addition to the four major core structures, the former includes Jumonji AT-rich interactive domain 2 (JARID2) and adipocyte enhancer binding protein 2 (AEBP2), the latter of which includes PCL1-3 and c17orf96/c10orf12 [11] (Figure 1). At present, the accessory proteins have been shown to regulate PRC2 activity and play a role in cells by localizing PRC2 to chromatin. However, the exact function of these proteins is unknown.
3. Histone Modificaton of EZH2
| Genes |
|---|
|
Genes |
| Mechanism of Action of EZH2 |
|---|
Mechanism of Action of EZH2 |
| The Role of Genes |
|---|
The Role of Genes |
| Reference |
|---|
Reference |
| Induce cell cycle progression and inhibit cell senescence | |
| [ | |
| 27 | ] |
|
METTL3 |
EZH2 overexpression leads to increases in H3K27me3, up-regulating the expression of METTL3 |
Drug resistance |
[25] |
|
P16 |
EZH2 overexpression leads to increases in H3K27me3, inhibiting the expression of P16 |
Inhibition of tumor growth; |
[26] |
|
E-cadherin |
EZH2 overexpression leads to increases in H3K27me3, inhibiting E-cadherin |
Inhibition of tumor growth |
[26] |
|
HIF-1α |
EZH2 stabilizes the expression of HIF-1α |
Promotion of tumor growth and metabolism favoring glycolysis |
[5] |
|
INK4B-ARF-INK4A |
EZH2 suppresses the expression of INK4B–ARF–INK4A |
Induce cell cycle progression and inhibit cell senescence |
[27] |
| METTL3 | EZH2 overexpression leads to increases in H3K27me3, up-regulating the expression of METTL3 | Drug resistance | [25] |
| P16 | EZH2 overexpression leads to increases in H3K27me3, inhibiting the expression of P16 | Inhibition of tumor growth; Drive cellular differentiation |
[26] |
| E-cadherin | EZH2 overexpression leads to increases in H3K27me3, inhibiting E-cadherin | Inhibition of tumor growth | [26] |
| HIF-1α | EZH2 stabilizes the expression of HIF-1α | Promotion of tumor growth and metabolism favoring glycolysis | [5] |
| INK4B-ARF-INK4A | EZH2 suppresses the expression of INK4B–ARF–INK4A |
Note: METTL3: methyltransferase-like 3; HIF-1α: hypoxia inducible factor-1
References
- Smyth, E.C.; Nilsson, M.; Grabsch, H.I.; van Grieken, N.C.; Lordick, F. Gastric cancer. Lancet 2020, 396, 635–648. Han Li, C.; Chen, Y. Targeting EZH2 for cancer therapy: Progress and perspective. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2015, 16, 559–570. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389203716666150409100233.
- Cai, Z.; Liu, Q. Understanding the Global Cancer Statistics 2018: Implications for cancer control. Sci. China Life Sci. 2021, 64, 1017–1020. Zhu, K.; Du, D.; Yang, R.; Tao, H.; Zhang, H. Identification and Assessments of Novel and Potent Small-Molecule Inhibitors of EED-EZH2 Interaction of Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 by Computational Methods and Biological Evaluations. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 68, 58–63. https://doi.org/10.1248/cpb.c19-00550.
- Canale, M.; Casadei-Gardini, A.; Ulivi, P.; Arechederra, M.; Berasain, C.; Lollini, P.L.; Fernández-Barrena, M.G.; Avila, M.A. Epigenetic Mechanisms in Gastric Cancer: Potential New Therapeutic Opportunities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5500. Varambally, S.; Dhanasekaran, S.M.; Zhou, M.; Barrette, T.R.; Kumar-Sinha, C.; Sanda, M.G.; Ghosh, D.; Pienta, K.J.; Sewalt, R.G.; Otte, A.P.; et al. The polycomb group protein EZH2 is involved in progression of prostate cancer. Nature 2002, 419, 624–629. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01075.
- Ramezankhani, R.; Solhi, R.; Es, H.A.; Vosough, M.; Hassan, M. Novel molecular targets in gastric adenocarcinoma. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 220, 107714. Kim, K.H.; Roberts, C.W. Targeting EZH2 in cancer. Nature Med. 2016, 22, 128–134. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4036.
- Papale, M.; Ferretti, E.; Battaglia, G.; Bellavia, D.; Mai, A.; Tafani, M. EZH2, HIF-1, and Their Inhibitors: An Overview on Pediatric Cancers. Front. Pediatr. 2018, 6, 328. Hanaki, S.; Shimada, M. Targeting EZH2 as cancer therapy. J. Biochem. 2021, 170, 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1093/jb/mvab007.
- He, L.J.; Cai, M.Y.; Xu, G.L.; Li, J.J.; Weng, Z.J.; Xu, D.Z.; Luo, G.Y.; Zhu, S.L.; Xie, D. Prognostic significance of overexpression of EZH2 and H3k27me3 proteins in gastric cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2012, 13, 3173–3178. Bracken, A.P.; Kleine-Kohlbrecher, D.; Dietrich, N.; Pasini, D.; Gargiulo, G.; Beekman, C.; Theilgaard-Mönch, K.; Minucci, S.; Porse, B.T.; Marine, J.C.; et al. The Polycomb group proteins bind throughout the INK4A-ARF locus and are disassociated in senescent cells. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 525–530. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.415507.
- Wang, J.; Wang, G.G. No Easy Way Out for EZH2: Its Pleiotropic, Noncanonical Effects on Gene Regulation and Cellular Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9501. Li, F.; Chen, S.; Yu, J.; Gao, Z.; Sun, Z.; Yi, Y.; Long, T.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Pan, Y.; et al. Interplay of m(6) A and histone modifications contributes to temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma. Clin. Transl. Med. 2021, 11, e553. https://doi.org/10.1002/ctm2.553.
- Stairiker, C.J.; Thomas, G.D.; Salek-Ardakani, S. EZH2 as a Regulator of CD8+ T Cell Fate and Function. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 593203. Eich, M.L.; Athar, M.; Ferguson, J.E., 3rd; Varambally, S. EZH2-Targeted Therapies in Cancer: Hype or a Reality. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 5449–5458. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-20-2147.
- Chittock, E.C.; Latwiel, S.; Miller, T.C.; Müller, C.W. Molecular architecture of polycomb repressive complexes. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2017, 45, 193–205. Chittock, E.C.; Latwiel, S.; Miller, T.C.; Müller, C.W. Molecular architecture of polycomb repressive complexes. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2017, 45, 193–205. https://doi.org/10.1042/bst20160173.
- Kuzmichev, A.; Nishioka, K.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Tempst, P.; Reinberg, D. Histone methyltransferase activity associated with a human multiprotein complex containing the Enhancer of Zeste protein. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 2893–2905. Kuzmichev, A.; Nishioka, K.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Tempst, P.; Reinberg, D. Histone methyltransferase activity associated with a human multiprotein complex containing the Enhancer of Zeste protein. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 2893–2905. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1035902.
- Margueron, R.; Li, G.; Sarma, K.; Blais, A.; Zavadil, J.; Woodcock, C.L.; Dynlacht, B.D.; Reinberg, D. Ezh1 and Ezh2 maintain repressive chromatin through different mechanisms. Mol. Cell 2008, 32, 503–518. Margueron, R.; Li, G.; Sarma, K.; Blais, A.; Zavadil, J.; Woodcock, C.L.; Dynlacht, B.D.; Reinberg, D. Ezh1 and Ezh2 maintain repressive chromatin through different mechanisms. Mol. Cell 2008, 32, 503–518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2008.11.004.
- Simon, J.A.; Lange, C.A. Roles of the EZH2 histone methyltransferase in cancer epigenetics. Mutat. Res. 2008, 647, 21–29. Simon, J.A.; Lange, C.A. Roles of the EZH2 histone methyltransferase in cancer epigenetics. Mutat. Res. 2008, 647, 21–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2008.07.010.
- Duan, R.; Du, W.; Guo, W. EZH2: A novel target for cancer treatment. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 104. Duan, R.; Du, W.; Guo, W. EZH2: A novel target for cancer treatment. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 104. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-020-00937-8.
- Millán-Zambrano, G.; Burton, A.; Bannister, A.J.; Schneider, R. Histone post-translational modifications—Cause and consequence of genome function. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2022, 23, 563–580. Millán-Zambrano, G.; Burton, A.; Bannister, A.J.; Schneider, R. Histone post-translational modifications—Cause and consequence of genome function. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2022, 23, 563–580. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41576-022-00468-7.
- Chen, Y.; Ren, B.; Yang, J.; Wang, H.; Yang, G.; Xu, R.; You, L.; Zhao, Y. The role of histone methylation in the development of digestive cancers: A potential direction for cancer management. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 143. Chen, Y.; Ren, B.; Yang, J.; Wang, H.; Yang, G.; Xu, R.; You, L.; Zhao, Y. The role of histone methylation in the development of digestive cancers: A potential direction for cancer management. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 143. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-020-00252-1.
- Zhang, T.; Cooper, S.; Brockdorff, N. The interplay of histone modifications—Writers that read. EMBO Rep. 2015, 16, 1467–1481. Zhang, T.; Cooper, S.; Brockdorff, N. The interplay of histone modifications—Writers that read. EMBO Rep. 2015, 16, 1467–1481. https://doi.org/10.15252/embr.201540945.
- Viré, E.; Brenner, C.; Deplus, R.; Blanchon, L.; Fraga, M.; Didelot, C.; Morey, L.; Van Eynde, A.; Bernard, D.; Vanderwinden, J.M.; et al. The Polycomb group protein EZH2 directly controls DNA methylation. Nature 2006, 439, 871–874. Viré, E.; Brenner, C.; Deplus, R.; Blanchon, L.; Fraga, M.; Didelot, C.; Morey, L.; Van Eynde, A.; Bernard, D.; Vanderwinden, J.M.; et al. The Polycomb group protein EZH2 directly controls DNA methylation. Nature 2006, 439, 871–874. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04431.
- Cyrus, S.; Burkardt, D.; Weaver, D.D.; Gibson, W.T. PRC2-complex related dysfunction in overgrowth syndromes: A review of EZH2, EED, and SUZ12 and their syndromic phenotypes. Am. J. Med. Genetics. Part C Semin. Med. Genet. 2019, 181, 519–531. Cyrus, S.; Burkardt, D.; Weaver, D.D.; Gibson, W.T. PRC2-complex related dysfunction in overgrowth syndromes: A review of EZH2, EED, and SUZ12 and their syndromic phenotypes. Am. J. Med. Genetics. Part C Semin. Med. Genet. 2019, 181, 519–531. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.c.31754.
- Hsu, J.H.; Rasmusson, T.; Robinson, J.; Pachl, F.; Read, J.; Kawatkar, S.; O’Donovan, D.H.; Bagal, S.; Code, E.; Rawlins, P.; et al. EED-Targeted PROTACs Degrade EED, EZH2, and SUZ12 in the PRC2 Complex. Cell Chem. Biol. 2020, 27, 41–46.e17. Hsu, J.H.; Rasmusson, T.; Robinson, J.; Pachl, F.; Read, J.; Kawatkar, S.; DH, O.D.; Bagal, S.; Code, E.; Rawlins, P.; et al. EED-Targeted PROTACs Degrade EED, EZH2, and SUZ12 in the PRC2 Complex. Cell Chem. Biol. 2020, 27, 41–46.e17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2019.11.004.
- Zhu, K.; Du, D.; Yang, R.; Tao, H.; Zhang, H. Identification and Assessments of Novel and Potent Small-Molecule Inhibitors of EED-EZH2 Interaction of Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 by Computational Methods and Biological Evaluations. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 68, 58–63. Zhu, K.; Du, D.; Yang, R.; Tao, H.; Zhang, H. Identification and Assessments of Novel and Potent Small-Molecule Inhibitors of EED-EZH2 Interaction of Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 by Computational Methods and Biological Evaluations. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 68, 58–63. https://doi.org/10.1248/cpb.c19-00550.
- Varambally, S.; Dhanasekaran, S.M.; Zhou, M.; Barrette, T.R.; Kumar-Sinha, C.; Sanda, M.G.; Ghosh, D.; Pienta, K.J.; Sewalt, R.G.; Otte, A.P.; et al. The polycomb group protein EZH2 is involved in progression of prostate cancer. Nature 2002, 419, 624–629. Varambally, S.; Dhanasekaran, S.M.; Zhou, M.; Barrette, T.R.; Kumar-Sinha, C.; Sanda, M.G.; Ghosh, D.; Pienta, K.J.; Sewalt, R.G.; Otte, A.P.; et al. The polycomb group protein EZH2 is involved in progression of prostate cancer. Nature 2002, 419, 624–629. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01075.
- Kim, K.H.; Roberts, C.W. Targeting EZH2 in cancer. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 128–134. Kim, K.H.; Roberts, C.W. Targeting EZH2 in cancer. Nature Med. 2016, 22, 128–134. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4036.
- Hanaki, S.; Shimada, M. Targeting EZH2 as cancer therapy. J. Biochem. 2021, 170, 1–4. Hanaki, S.; Shimada, M. Targeting EZH2 as cancer therapy. J. Biochem. 2021, 170, 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1093/jb/mvab007.
- Bracken, A.P.; Kleine-Kohlbrecher, D.; Dietrich, N.; Pasini, D.; Gargiulo, G.; Beekman, C.; Theilgaard-Mönch, K.; Minucci, S.; Porse, B.T.; Marine, J.C.; et al. The Polycomb group proteins bind throughout the INK4A-ARF locus and are disassociated in senescent cells. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 525–530. Bracken, A.P.; Kleine-Kohlbrecher, D.; Dietrich, N.; Pasini, D.; Gargiulo, G.; Beekman, C.; Theilgaard-Mönch, K.; Minucci, S.; Porse, B.T.; Marine, J.C.; et al. The Polycomb group proteins bind throughout the INK4A-ARF locus and are disassociated in senescent cells. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 525–530. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.415507.
- Li, F.; Chen, S.; Yu, J.; Gao, Z.; Sun, Z.; Yi, Y.; Long, T.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Pan, Y.; et al. Interplay of m(6) A and histone modifications contributes to temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma. Clin. Transl. Med. 2021, 11, e553. Li, F.; Chen, S.; Yu, J.; Gao, Z.; Sun, Z.; Yi, Y.; Long, T.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Pan, Y.; et al. Interplay of m(6) A and histone modifications contributes to temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma. Clin. Transl. Med. 2021, 11, e553. https://doi.org/10.1002/ctm2.553.
- Eich, M.L.; Athar, M.; Ferguson, J.E., 3rd; Varambally, S. EZH2-Targeted Therapies in Cancer: Hype or a Reality. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 5449–5458. Eich, M.L.; Athar, M.; Ferguson, J.E., 3rd; Varambally, S. EZH2-Targeted Therapies in Cancer: Hype or a Reality. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 5449–5458. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-20-2147.
- Han Li, C.; Chen, Y. Targeting EZH2 for cancer therapy: Progress and perspective. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2015, 16, 559–570. Han Li, C.; Chen, Y. Targeting EZH2 for cancer therapy: Progress and perspective. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2015, 16, 559–570. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389203716666150409100233.
