Transition metal complexes have been deeply studied for different applications, such as catalysis, antimicrobial, and also antitumoral drugs. Platinum complexes are probably the most well-known and studied in the field of anticancer compounds, also thanks to the omnipresence of cisplatin and its derivatives as a starting point.
Two promising new strategies to increase the efficacy of transition metal-based complexes have been described. First, we considered the possibility of assembling two biologically active fragments containing different metal centres into the same molecule were considered, thus obtaining a heterobimetallic complex. Secondly, the conjugation of metal-based complexes to a targeting moiety was discussed.
- platinum compounds
- gold compounds
- metal-based drugs
- heterobimetallic complexes
- targeting strategies
1. Introduction
2. Heteronuclear Metal Complexes with Anticancer Activity
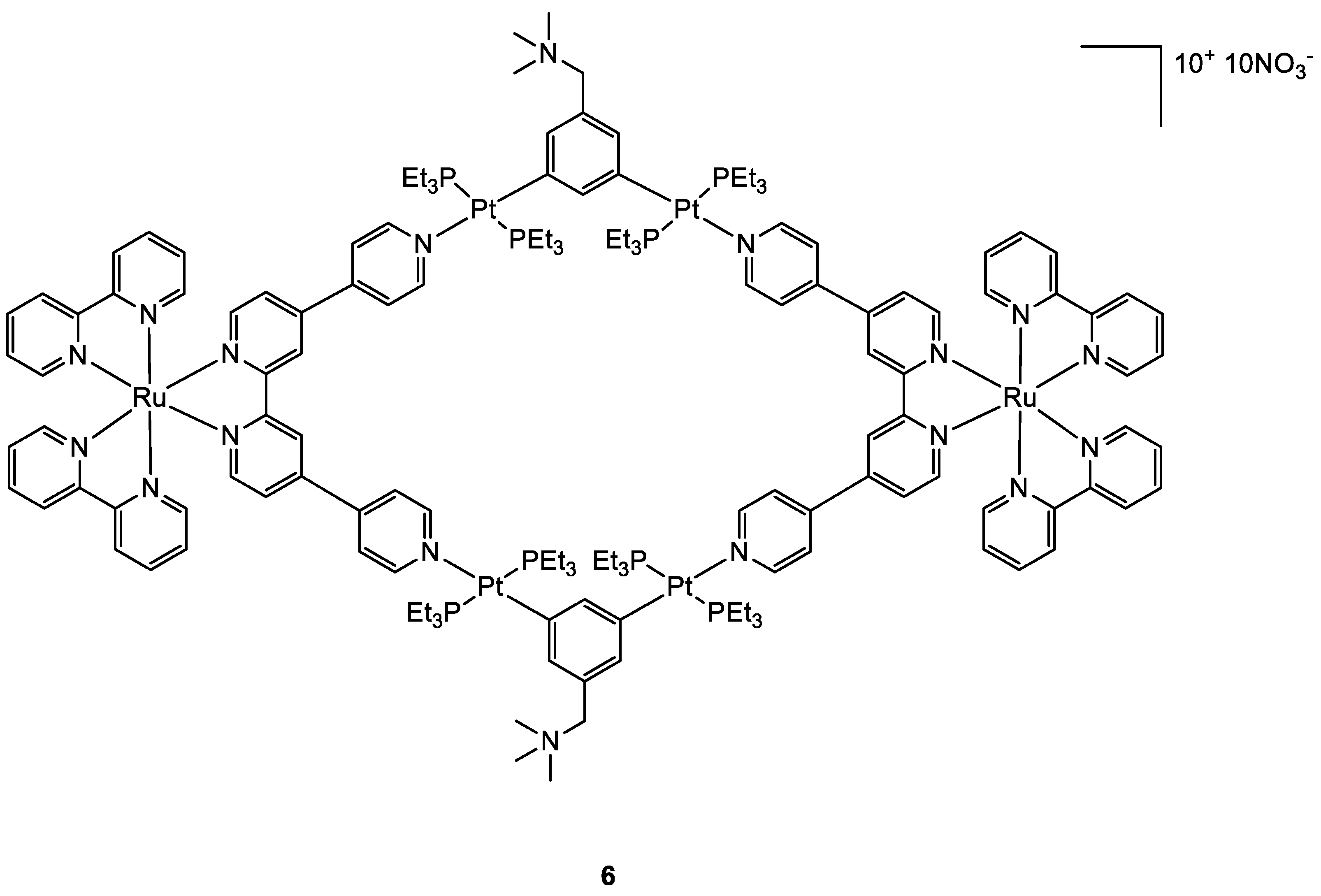
One of the new strategies here presented concerns the combination of two different metal centres in one single drug to build a heteronuclear metal complex. The combination of more than one metal was already used for other types of applications, such as catalysis, where electronically different metals could synergistically cooperate and have better properties compared to the monometallic precursors in a catalytic process [15][14]. The same approach was used more recently for potential anticancer applications. The opportunity to use different metal-based compounds, which act as anticancer but have different mechanisms of action from each other, could promote cooperative activity and synergistic effects. In this revisew, wearch, researchers divided different examples into two main groups, one of platinum and one of gold. These two metal centres, as monometallic compounds, have been extensively studied and they are known to exploit their anticancer activity in different types of final targets. Platinum compounds generally act in the genomic moiety [16][15], while gold complexes are considered good inhibitors of thioredoxin reductase [17][16]. One of the most recent and interesting results of the literature concerns the combination of platinum or gold with different metal centres or a combination of them. A discussion on the possible synergistic effects of the new heteronuclear metal drugs has been done. To be sure that the enhanced anticancer activity is truly done by the cooperative action of the two metal centres, a comparison with the monometallic fragments is always needed.2.1. The Case of Platinum
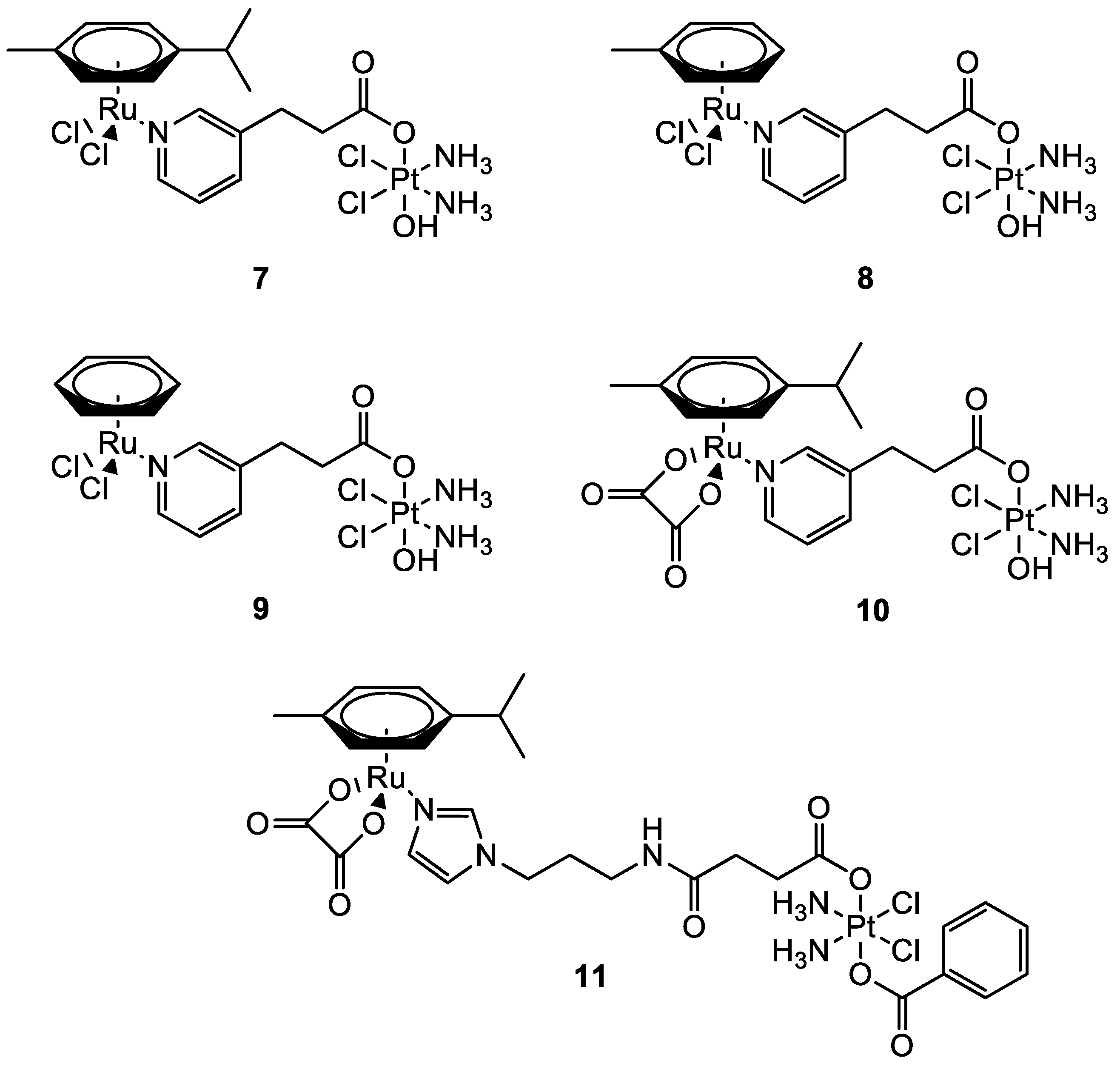
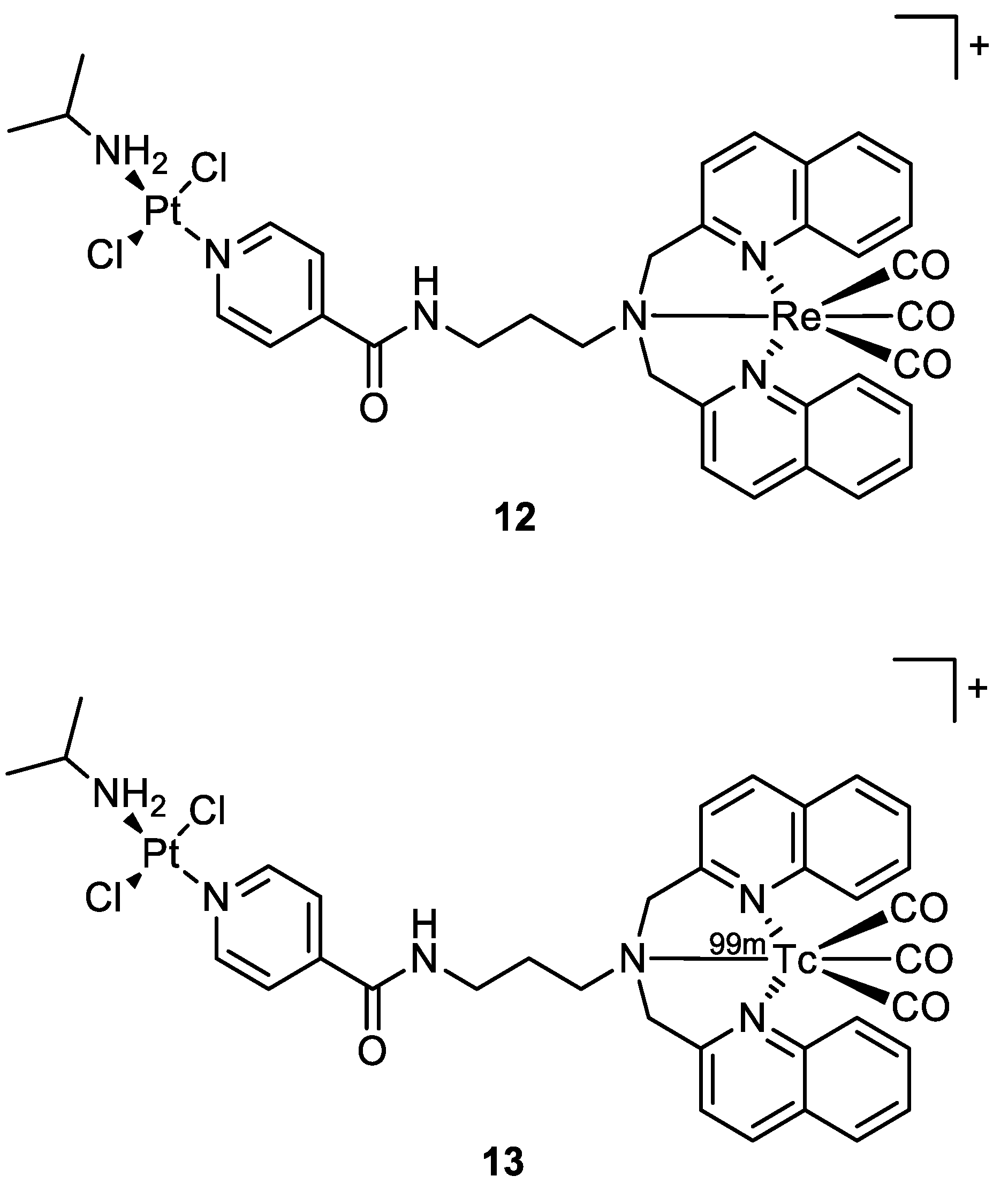
Transition metal complexes have been deeply studied for different applications, such as catalysis, antimicrobial, and also antitumoral drugs [18][17]. Platinum complexes are probably the most well-known and studied in the field of anticancer compounds, also thanks to the omnipresence of cisplatin and its derivatives as a starting point [19,20][18][19]. To overcome all the side effects of cisplatin such as neurotoxicity, nephro-, oto-, and gastrointestinal toxicity, alternative transition metal centres gained a place in this field [21,22,23][20][21][22]. In the last years, there are many examples of Pt(II) complexes combined with different metal centres such as Ru(II), Rh(III), Au(I), Re(I), Tc(I) [17,24,25,26,27][16][23][24][25][26]. Platinum-based complexes are mainly binders of genomic targets via a covalent bond between the Pt metal centre and N-7 atom of guanine base [16][15], even if there is also evidence of protein binding, as serum albumin [28][27]. Here wresearchers present the most recent and promising results of bimetallic complexes that involve different types of compounds such as photoactivable, macrocycle, or prodrugs compounds. The possible synergistic effects of two metal centres with different targets were evaluated. Starting from the ruthenium and rhodium ones, these metal centres can form organometallic complexes usually by the coordination to nitrogen atoms or with arene ligands, making the coordination easily achievable [29][28]. Ruthenium-based compounds, usually considered to have antimetastatic activity, received interest as anticancer agents after the discovery of the antitumoral properties of NAMI-A, KP1019, and KP1339 mentioned above. These organometallic Ru(II)-arene derivatives have a different mechanism of action compared to cisplatin to exploit the anticancer activity, which involves the binding to the biomolecule transferrin, an iron-binding protein [30][29]. In 2019 Askari and co-workers published their work, where the synthesis of three heterobimetallic Pt(II)-Ru(II) and Pt(II)-Rh(III) complexes (1–3) (Figure 1) is described. The three bimetallic complexes 1–3 turned out to be active in the human 20S proteasome, one of the main targets for cancer therapy. Compounds 1–3 also inhibited cathepsin B and L, which take part in tumour progression and invasion. The cytotoxic activity has been evaluated also in comparison to the Pt(II)-based precursors and cisplatin. The bimetallic complexes showed a good reduction of cell viability in different tumour cell lines such as neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y, melanoma SKMel-28, hepatocellular adenocarcinoma HepG2, and colorectal adenocarcinoma Caco-2 tumour cell lines, comparable or in some cases even greater than cisplatin, while for the healthy cell line of human fibroblasts WI 38 there is no sign of cytotoxicity. The flow cytometry analyses with Annexin-V/PI staining revealed that the cell death mechanism in the SH-SY5Y line is apoptotic after 72 h of treatment. Pt(II) precursors showed no significant inhibition or antiproliferative activity, which makes them a structural feature of the proposed heterobimetallic complexes [25][24].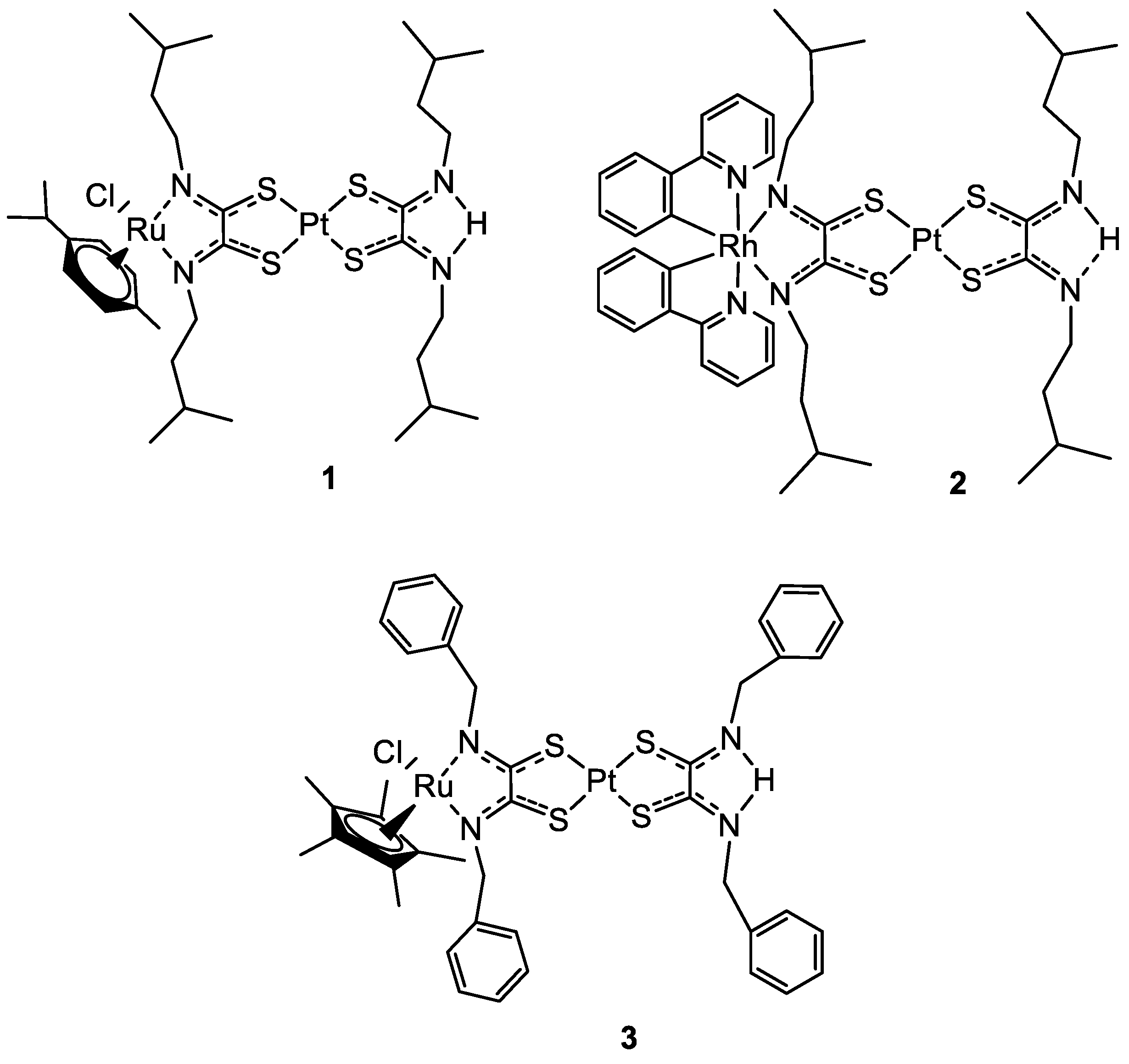
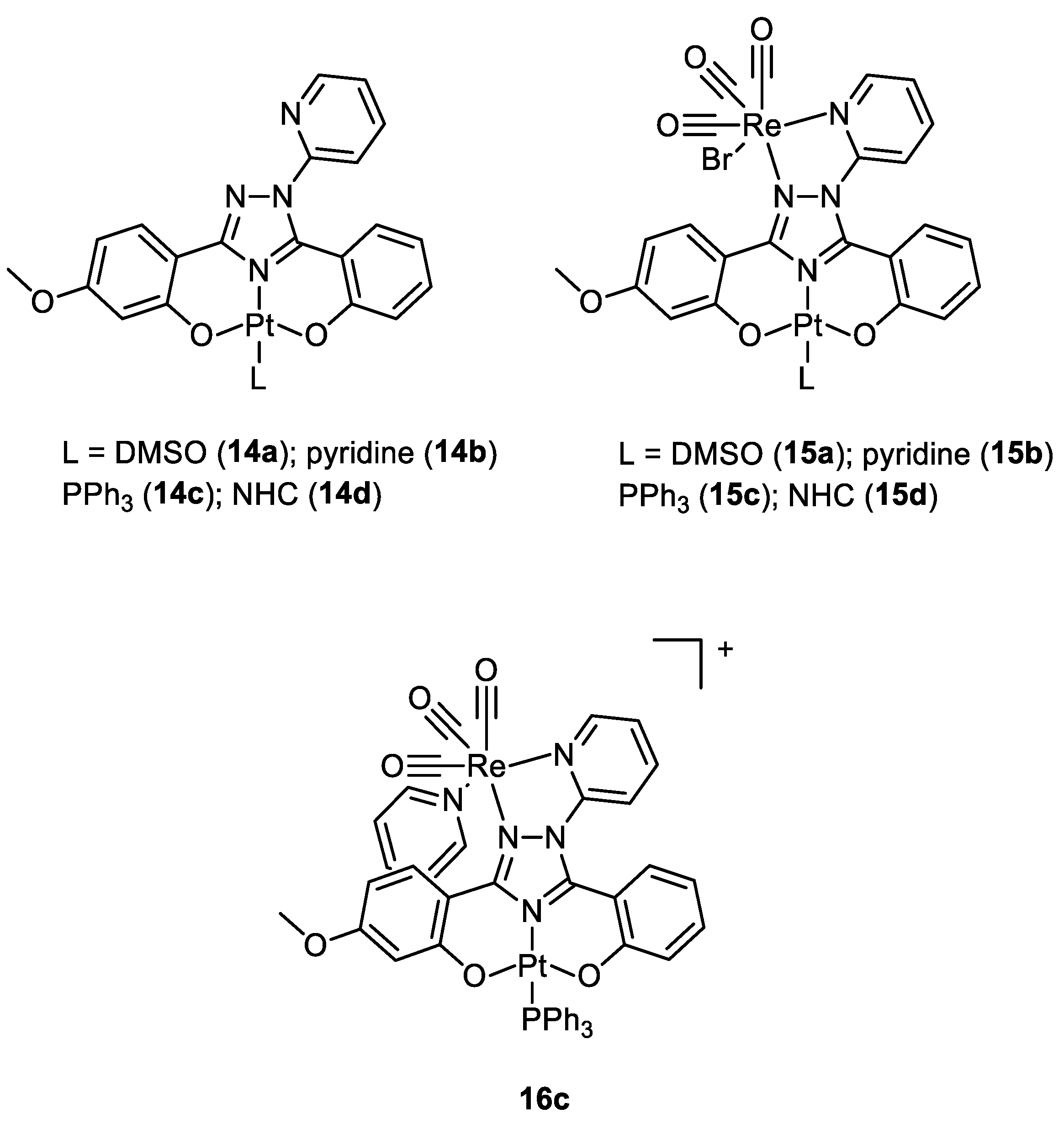
| Complex | IC50 ± SD (µM) | Log Po/w | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDA-MB-231 | MCF-7 | A2780 | MCF-10F | ||
| 14a | 3.1 ± 0.5 | 1.6 ± 0.9 | 1.5 ± 0.6 | 1.1 ± 0.2 | 3.7 |
| 14b | n. d. | n. d. | n. d. | n. d. | 3.3 |
| 14c | n. d. | n. d. | n. d. | n. d. | 6.9 |
| 14d | n. d. | n. d. | n. d. | n. d. | 4.5 |
| 15a | 2.1 ± 0.6 | 2.2 ± 0.4 | 1.5 ± 0.3 | 1.82 ± 0.06 | 3.6 |
| 15b | n. d. | n. d. | n. d. | n. d. | 4.9 |
| 15c | n. d. | n. d. | n. d. | n. d. | 8.1 |
| 15d | 9.2 ± 3.5 | 20.3 ± 1.9 | 34.5 ± 7.2 | 17.4 ± 2.6 | 5.8 |
| 16c | 1.7 ± 0.3. | 1.1 ± 0.4 | 1.3 ± 0.2 | 3.3 ± 0.3 | 2.4 |
| cisplatin | 20.4 ± 3.4 | 14 ± 3.5 | 1.0 ± 0.2 | 2.9 ± 0.8 | −2.4 a |
2.2. The Case of Gold
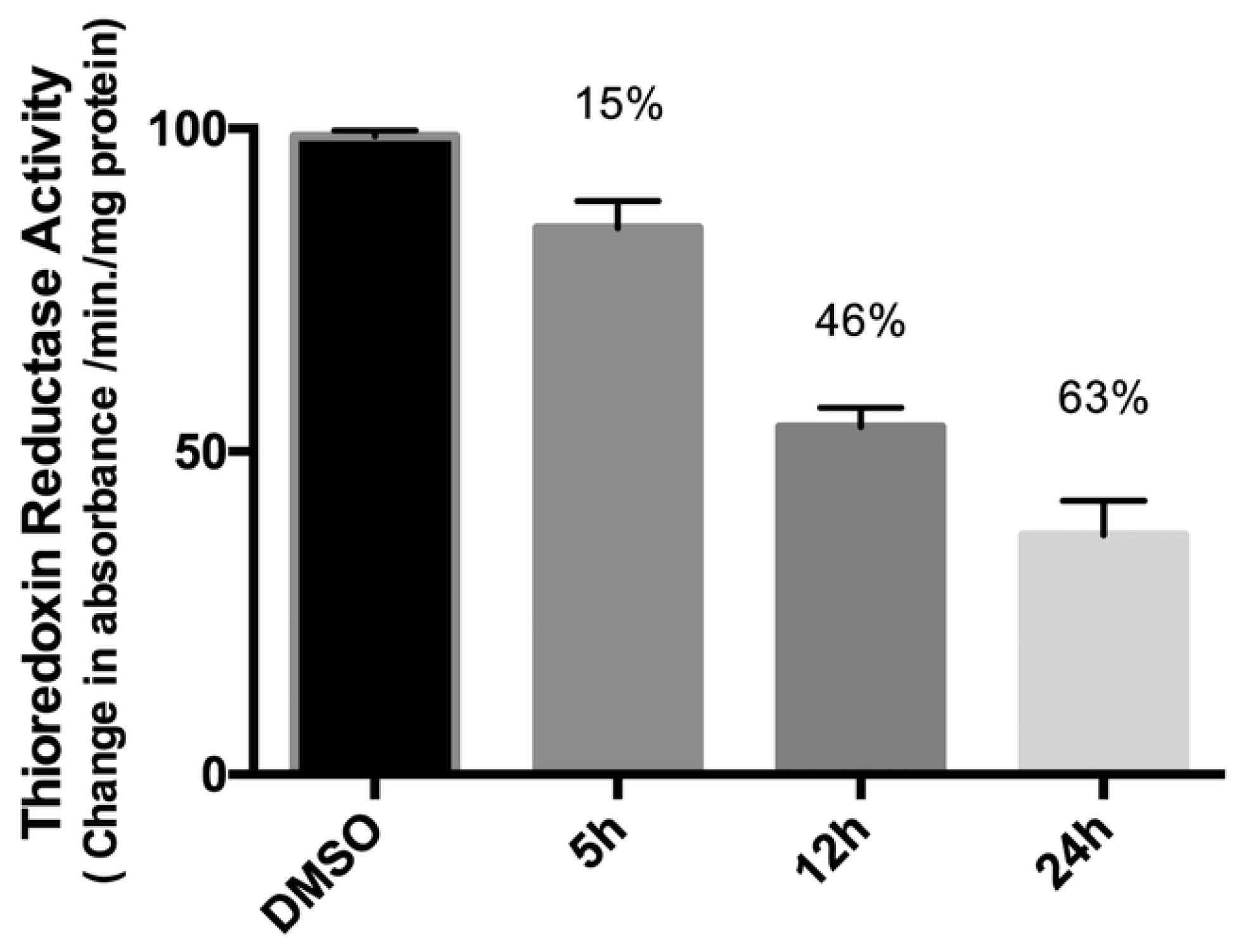
Other types of combinations involve gold compounds. Gold complexes are usually composed by the coordination of the soft metal centre with phosphine or sulphur ligands, but carbenes ligands have also gained much interest [42,43][41][42]. Gold complexes express anticancer activity by disrupting the reduction/oxidation (redox) system within the cell via the inhibition of thioredoxin reductases (TrxRs). This enzyme is present in the mitochondria and an alteration of its activity could lead to apoptosis [17,44,45,46,47][16][43][44][45][46]. Here wresearchers present some relevant examples of recently synthesised complexes that combine the cytotoxic potential of gold-based compounds with other metal centres which exploit their anticancer activity differently, such as Pt(II), Ru(II), Ti(IV), Ir(III), and Re(I). To date, there are only a few examples in the literature on the combination of Au(I) and Pt(II) metal centres [13,48,49][13][47][48]. Some of the most promising examples are the heterometallic Pt–Au complexes depicted in Figure 9 (18a–c), which have shown synergistic effects by an improvement of the antiproliferative activity against A549 (lung), SKOV3 (ovarian), and MCF-7 (breast) cancer cell lines in comparison to their Pt-based precursor complexes 17a–c and [ClAu(μ-dppm)AuCl], which are not toxic to any of the cell lines investigated. Inhibition of cell proliferation was also compared to cisplatin and Auranofin, revealing 18b as the most promising complex, and apoptosis is the cell death mechanism in MCF-7 cancer cells in a dose-dependent manner. Furthermore, 18a effectively internalises in MCF-7 cells, and the nucleus showed the highest accumulation of the complex, which was revealed by fluorescence microscopy, with less dispersion in the cytoplasm. Selectivity for cancer cells was investigated by comparing the IC50 values of the healthy cell line MCF-10A (epithelial breast), with the one obtained with MCF-7. All the complexes showed good selectivity for the tumorigenic cell line, and complexes 18b and 18c demonstrated higher specificity for human breast cancer cells with minor damage to normal epithelial breast cells [13].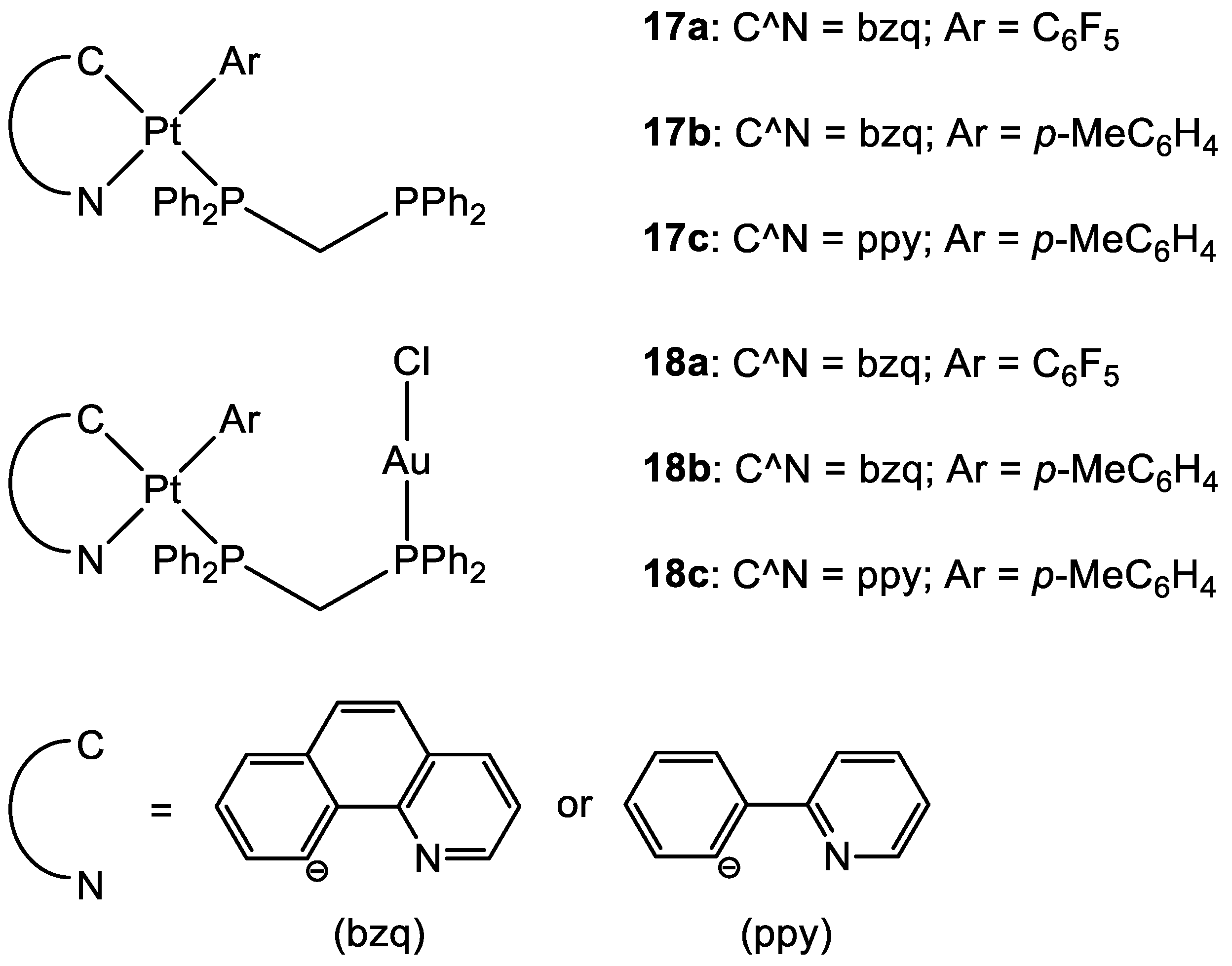
References
- Bailar, J.C.; Gornik, H.L. Cancer Undefeated. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 336, 1569–1574.
- Cirri, D.; Bartoli, F.; Pratesi, A.; Baglini, E.; Barresi, E.; Marzo, T. Strategies for the Improvement of Metal-Based Chemotherapeutic Treatments. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 504.
- Jia, P.; Ouyang, R.; Cao, P.; Tong, X.; Zhou, X.; Lei, T.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, N.; Chang, H.; Miao, Y.; et al. Review: Recent Advances and Future Development of Metal Complexes as Anticancer Agents. J. Coord. Chem. 2017, 70, 2175–2201.
- Chern, Y.J.; Tai, I.T. Adaptive Response of Resistant Cancer Cells to Chemotherapy. Cancer Biol. Med. 2020, 17, 842–863.
- Galluzzi, L.; Vitale, I.; Michels, J.; Brenner, C.; Szabadkai, G.; Harel-Bellan, A.; Castedo, M.; Kroemer, G. Systems Biology of Cisplatin Resistance: Past, Present and Future. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1257.
- Mei, Y. Review of the Toxicological Mechanism of Anticancer Drug Cisplatin. AIP Conf. Proc. 2021, 2350, 020010.
- Roder, C.; Thomson, M.J. Auranofin: Repurposing an Old Drug for a Golden New Age. Drugs RD 2015, 15, 13–20.
- Abdalbari, F.H.; Telleria, C.M. The Gold Complex Auranofin: New Perspectives for Cancer Therapy. Discov. Oncol. 2021, 12, 42.
- Meier-Menches, S.M.; Gerner, C.; Berger, W.; Hartinger, C.G.; Keppler, B.K. Structure-Activity Relationships for Ruthenium and Osmium Anticancer Agents-towards Clinical Development. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 909–928.
- Strebhardt, K.; Ullrich, A. Paul Ehrlich’s Magic Bullet Concept: 100 Years of Progress. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 473–480.
- van Niekerk, A.; Chellan, P.; Mapolie, S.F. Heterometallic Multinuclear Complexes as Anti-Cancer Agents-An Overview of Recent Developments. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 2019, 3432–3455.
- Redrado, M.; Fernández-Moreira, V.; Gimeno, M.C. Theranostics Through the Synergistic Cooperation of Heterometallic Complexes. ChemMedChem 2021, 16, 932–941.
- Shahsavari, H.R.; Giménez, N.; Lalinde, E.; Moreno, M.T.; Fereidoonnezhad, M.; Babadi Aghakhanpour, R.; Khatami, M.; Kalantari, F.; Jamshidi, Z.; Mohammadpour, M. Heterobimetallic PtII-AuI Complexes Comprising Unsymmetrical 1,1-Bis(Diphenylphosphanyl)Methane Bridges: Synthesis, Photophysical, and Cytotoxic Studies. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 2019, 1360–1373.
- Cooper, B.G.; Napoline, J.W.; Thomas, C.M. Catalytic Applications of Early/Late Heterobimetallic Complexes. Catal. Rev. Sci. Eng. 2012, 54, 1–40.
- Longato, B.; Bandoli, G.; Trovo, G.; Marasciulo, E.; Valle, G. Mono- and Polynuclear Guanine Complexes of Platinum(II). Syntheses and Crystal and Molecular Structures of Bis(9-Methylguanine-N(7))Bis(Trimethylphosphine)Platinum(II) Dinitrate and Cyclo-Hexakis(9-Methylguanine(-H)-N(1),N(7))Hexakis(Cis-Bis(Trimethylphosphine)Platinum(II)) Hexanitrate. Inorg. Chem. 1995, 34, 1745–1750.
- Berners-Price, S.J.; Filipovska, A. Gold Compounds as Therapeutic Agents for Human Diseases. Metallomics 2011, 3, 863–873.
- Bertrand, B.; Casini, A. A Golden Future in Medicinal Inorganic Chemistry: The Promise of Anticancer Gold Organometallic Compounds. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 4209–4219.
- O’Dwyer, P.J.; Stevenson, J.P.; Johnson, S.W. Clinical Status of Cisplatin, Carboplatin, and Other Platinum-Based Antitumor Drugs. Cisplatin Chem. Biochem. Lead. Anticancer Drug 2006, 29–69.
- Rozencweig, M.; von Hoff, D.D.; Slavik, M.; Muggia, F.M. Cis-Diamminedichloroplatinum (II). A New Anticancer Drug. Ann. Intern. Med. 1977, 86, 803–812.
- dos Santos, N.A.G.; Ferreira, R.S.; Santos, A.C. dos Overview of Cisplatin-Induced Neurotoxicity and Ototoxicity, and the Protective Agents. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 136, 111079.
- Crona, D.J.; Faso, A.; Nishijima, T.F.; McGraw, K.A.; Galsky, M.D.; Milowsky, M.I. A Systematic Review of Strategies to Prevent Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity. The Oncologist 2017, 22, 609–619.
- Manohar, S.; Leung, N. Cisplatin Nephrotoxicity: A Review of the Literature. J. Nephrol. 2018, 31, 15–25.
- Bertrand, B.; Botuha, C.; Forté, J.; Dossmann, H.; Salmain, M. A Bis-Chelating ONO^ /NN^ Ligand for the Synthesis of Heterobimetallic Platinum(II)/Rhenium(I) Complexes: Tools for the Optimization of a New Class of Platinum(II) Anticancer Agents. Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 26, 12846–12861.
- Askari, B.; Rudbari, H.A.; Micale, N.; Schirmeister, T.; Maugeri, A.; Navarra, M. Anticancer Study of Heterobimetallic Platinum(II)-Ruthenium(II) and Platinum(II)-Rhodium(III) Complexes with Bridging Dithiooxamide Ligand. J. Organomet. Chem. 2019, 900, 120918.
- Tsolis, T.; Nikolaou, N.; Ypsilantis, K.; Kougioumtzi, A.; Kordias, D.; Magklara, A.; Garoufis, A. Synthesis, Characterization, Interactions with 9-MeG and Cytotoxic Activity of Heterobimetallic RuII-PtII Complexes Bridged with 2, 2′-Bipyrimidine. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2021, 219, 111435.
- Quental, L.; Raposinho, P.; Mendes, F.; Santos, I.; Navarro-Ranninger, C.; Alvarez-Valdes, A.; Huang, H.; Chao, H.; Rubbiani, R.; Gasser, G.; et al. Combining Imaging and Anticancer Properties with New Heterobimetallic Pt(II)/M(i) (M = Re, 99mTc) Complexes. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 14523–14536.
- Massai, L.; Pratesi, A.; Gailer, J.; Marzo, T.; Messori, L. The Cisplatin/Serum Albumin System: A Reappraisal. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2019, 495, 118983.
- Dougan, S.J.; Sadler, P.J. The Design of Organometallic Ruthenium Arene Anticancer Agents. Chimia 2007, 61, 704–715.
- Smith, C.A.; Sutherland-Smith, A.J.; Keppler, B.K.; Kratz, F.; Baker, E.N. Binding of Ruthenium(III) Anti-Tumor Drugs to Human Lactoferrin Probed by High Resolution X-Ray Crystallographic Structure Analyses. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 1996, 1, 424–431.
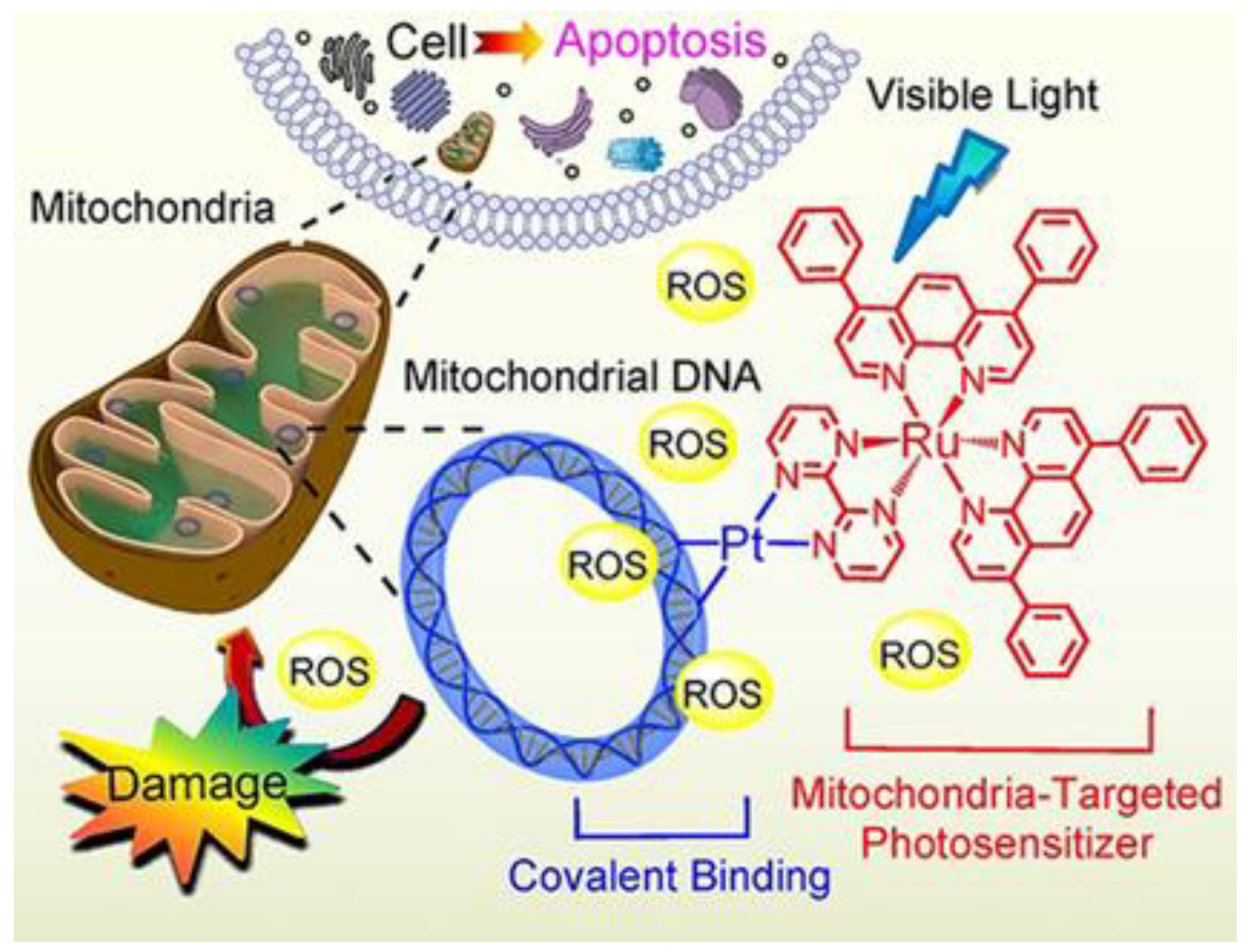
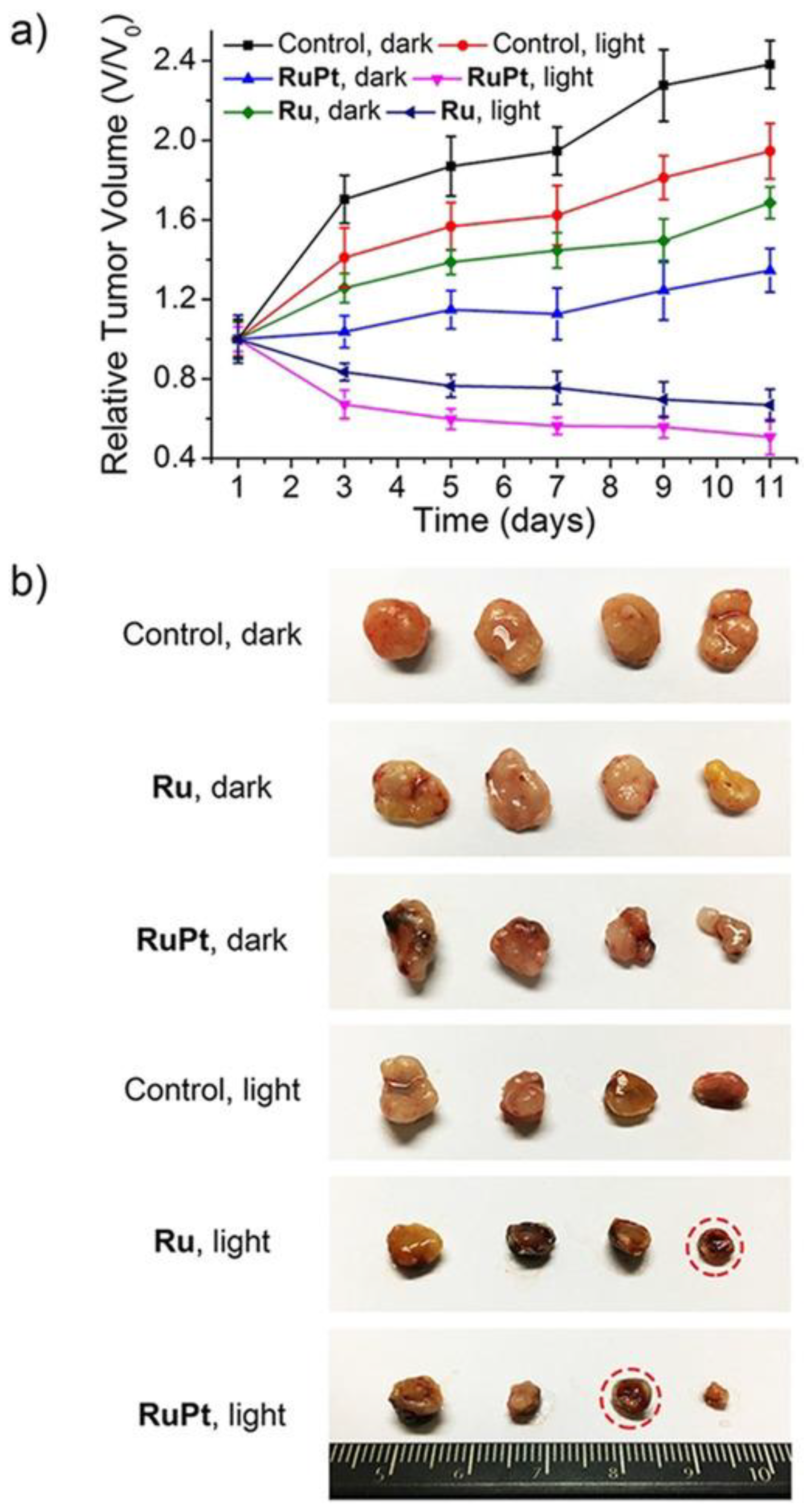
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, D.-Y.; Zhang, H.; Cao, J.-J.; Tan, C.-P.; Ji, L.-N.; Mao, Z.-W. Photodamaging of Mitochondrial DNA to Overcome Cisplatin Resistance by a RuII–PtII Bimetallic Complex. Chem.–Eur. J. 2018, 24, 18971–18980.
- Zhou, Z.; Liu, J.; Rees, T.W.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Chao, H.; Stang, P.J. Heterometallic Ru–Pt Metallacycle for Two-Photon Photodynamic Therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 5664–5669.
- Hall, M.D.; Mellor, H.R.; Callaghan, R.; Hambley, T.W. Basis for Design and Development of Platinum(IV) Anticancer Complexes. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 3403–3411.
- Yempala, T.; Babu, T.; Karmakar, S.; Nemirovski, A.; Ishan, M.; Gandin, V.; Gibson, D. Expanding the Arsenal of PtIV Anticancer Agents: Multi-Action PtIV Anticancer Agents with Bioactive Ligands Possessing a Hydroxy Functional Group. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 18218–18223.
- Babu, T.; Sarkar, A.; Karmakar, S.; Schmidt, C.; Gibson, D. Multiaction Pt(IV) Carbamate Complexes Can Codeliver Pt(II) Drugs and Amine Containing Bioactive Molecules. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 5182–5193.
- Harringer, S.; Hejl, M.; Enyedy, É.A.; Jakupec, M.A.; Galanski, M.S.; Keppler, B.K.; Dyson, P.J.; Varbanov, H.P. Multifunctional Pt(Iv) Prodrug Candidates Featuring the Carboplatin Core and Deferoxamine. Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 8167–8178.
- Da Veiga Moreira, J.; Hamraz, M.; Abolhassani, M.; Bigan, E.; Pérès, S.; Paulevé, L.; Nogueira, M.L.; Steyaert, J.M.; Schwartz, L. The Redox Status of Cancer Cells Supports Me—Chanisms behind the Warburg Effect. Metabolites 2016, 6, 33.
- Johnstone, T.C.; Suntharalingam, K.; Lippard, S.J. The Next Generation of Platinum Drugs: Targeted Pt(II) Agents, Nanoparticle Delivery, and Pt(IV) Prodrugs. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 3436–3486.
- Ma, L.; Lin, X.; Li, C.; Xu, Z.; Chan, C.-Y.; Tse, M.-K.; Shi, P.; Zhu, G. A Cancer Cell-Selective and Low-Toxic Bifunctional Heterodinuclear Pt(IV)–Ru(II) Anticancer Prodrug. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 2917–2924.
- Ma, L.; Ma, R.; Wang, Z.; Yiu, S.M.; Zhu, G. Heterodinuclear Pt(IV)-Ru(II) Anticancer Prodrugs to Combat Both Drug Resistance and Tumor Metastasis. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 10735–10738.
- Cirri, D.; Fabbrini, M.G.; Pratesi, A.; Ciofi, L.; Massai, L.; Marzo, T.; Messori, L. The Leading Established Metal-Based Drugs: A Revisitation of Their Relevant Physico-Chemical Data. BioMetals 2019, 32, 813–817.
- Marzo, T.; Cirri, D.; Gabbiani, C.; Gamberi, T.; Magherini, F.; Pratesi, A.; Guerri, A.; Biver, T.; Binacchi, F.; Stefanini, M.; et al. Auranofin, Et3PAuCl, and Et3PAuI Are Highly Cytotoxic on Colorectal Cancer Cells: A Chemical and Biological Study. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 997–1001.
- Binacchi, F.; Guarra, F.; Cirri, D.; Marzo, T.; Pratesi, A.; Messori, L.; Gabbiani, C.; Biver, T. On the Different Mode of Action of Au(I)/Ag(I)-NHC Bis-Anthracenyl Complexes Towards Selected Target Biomolecules. Molecules 2020, 25, 5446.
- Cirri, D.; Massai, L.; Giacomelli, C.; Trincavelli, M.L.; Guerri, A.; Gabbiani, C.; Messori, L.; Pratesi, A. Synthesis, Chemical Characterization, and Biological Evaluation of a Novel Auranofin Derivative as an Anticancer Agent. Dalton Trans. 2022, 51, 13527–13539.
- Menconi, A.; Marzo, T.; Massai, L.; Pratesi, A.; Severi, M.; Petroni, G.; Antonuzzo, L.; Messori, L.; Pillozzi, S.; Cirri, D. Anticancer Effects against Colorectal Cancer Models of Chloro(Triethylphosphine)Gold(I) Encapsulated in PLGA-PEG Nanoparticles. Biometals Int. J. Role Met. Ions Biol. Biochem. Med. 2021, 34, 867–879.
- Gamberi, T.; Pratesi, A.; Messori, L.; Massai, L. Proteomics as a Tool to Disclose the Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Selected Anticancer Gold Compounds. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 438, 213905.
- Magherini, F.; Fiaschi, T.; Valocchia, E.; Becatti, M.; Pratesi, A.; Marzo, T.; Massai, L.; Gabbiani, C.; Landini, I.; Nobili, S.; et al. Antiproliferative Effects of Two Gold(I)-N-Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes in A2780 Human Ovarian Cancer Cells: A Comparative Proteomic Study. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 28042–28068.
- Serratrice, M.; Maiore, L.; Zucca, A.; Stoccoro, S.; Landini, I.; Mini, E.; Massai, L.; Ferraro, G.; Merlino, A.; Messori, L.; et al. Cytotoxic Properties of a New Organometallic Platinum(II) Complex and Its Gold(i) Heterobimetallic Derivatives. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 579–590.
- Wenzel, M.; Bigaeva, E.; Richard, P.; Le Gendre, P.; Picquet, M.; Casini, A.; Bodio, E. New Heteronuclear Gold(I)–Platinum(II) Complexes with Cytotoxic Properties: Are Two Metals Better than One? J. Inorg. Biochem. 2014, 141, 10–16.
- Boncler, M.; Rózalski, M.; Krajewska, U.; Podswdek, A.; Watala, C. Comparison of PrestoBlue and MTT Assays of Cellular Viability in the Assessment of Anti-Proliferative Effects of Plant Extracts on Human Endothelial Cells. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2014, 69, 9–16.
- Fernández-Gallardo, J.; Elie, B.T.; Sanaú, M.; Contel, M. Versatile Synthesis of Cationic N-Heterocyclic Carbene-Gold(I) Complexes Containing a Second Ancillary Ligand. Design of Heterobimetallic Ruthenium-Gold Anticancer Agents. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 3155–3158.
- Elie, B.T.; Pechenyy, Y.; Uddin, F.; Contel, M. A Heterometallic Ruthenium–Gold Complex Displays Antiproliferative, Antimigratory, and Antiangiogenic Properties and Inhibits Metastasis and Angiogenesis-Associated Proteases in Renal Cancer. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 23, 399–411.
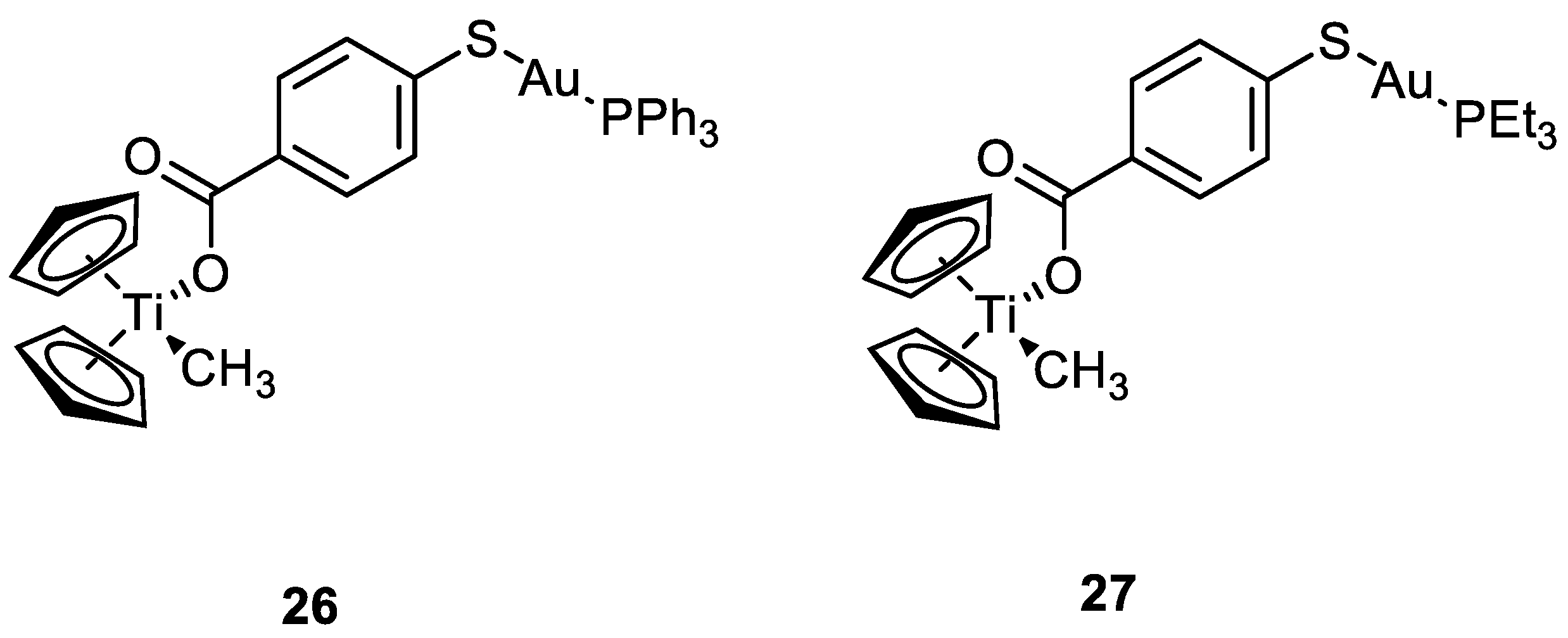
- Mui, Y.F.; Fernández-Gallardo, J.; Elie, B.T.; Gubran, A.; Maluenda, I.; Sanaú, M.; Navarro, O.; Contel, M. Titanocene-Gold Complexes Containing N-Heterocyclic Carbene Ligands Inhibit Growth of Prostate, Renal, and Colon Cancers in Vitro. Organometallics 2016, 35, 1218–1227.
- Fernández-Gallardo, J.; Elie, B.T.; Sadhukha, T.; Prabha, S.; Sanaú, M.; Rotenberg, S.A.; Ramos, J.W.; Contel, M. Heterometallic Titanium-Gold Complexes Inhibit Renal Cancer Cells in Vitro and in Vivo. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 5269–5283.
- Elie, B.T.; Fernández-Gallardo, J.; Curado, N.; Cornejo, M.A.; Ramos, J.W.; Contel, M. Bimetallic Titanocene-Gold Phosphane Complexes Inhibit Invasion, Metastasis, and Angiogenesis-Associated Signaling Molecules in Renal Cancer. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 161, 310–322.
- Li, T.Y.; Wu, J.; Wu, Z.G.; Zheng, Y.X.; Zuo, J.L.; Pan, Y. Rational Design of Phosphorescent Iridium(III) Complexes for Emission Color Tunability and Their Applications in OLEDs. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 374, 55–92.
- Wilde, A.P.; King, K.A.; Watts, R.J. Resolution and Analysis of the Components in Dual Emission of Mixed-Chelate/Ortho-Metalate Complexes of Iridium(III). J. Phys. Chem. 1991, 95, 629–634.
- Hao, L.; Li, Z.W.; Zhang, D.Y.; He, L.; Liu, W.; Yang, J.; Tan, C.P.; Ji, L.N.; Mao, Z.W. Monitoring Mitochondrial Viscosity with Anticancer Phosphorescent Ir(Iii) Complexes: Via Two-Photon Lifetime Imaging. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 1285–1293.
- Liu, Z.; Li, J.J.; Ge, X.X.; Zhang, S.; Xu, Z.; Gao, W. Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of Phosphorescent Ir(III)Complexes with Anticancer Activity. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2019, 197, 110703.
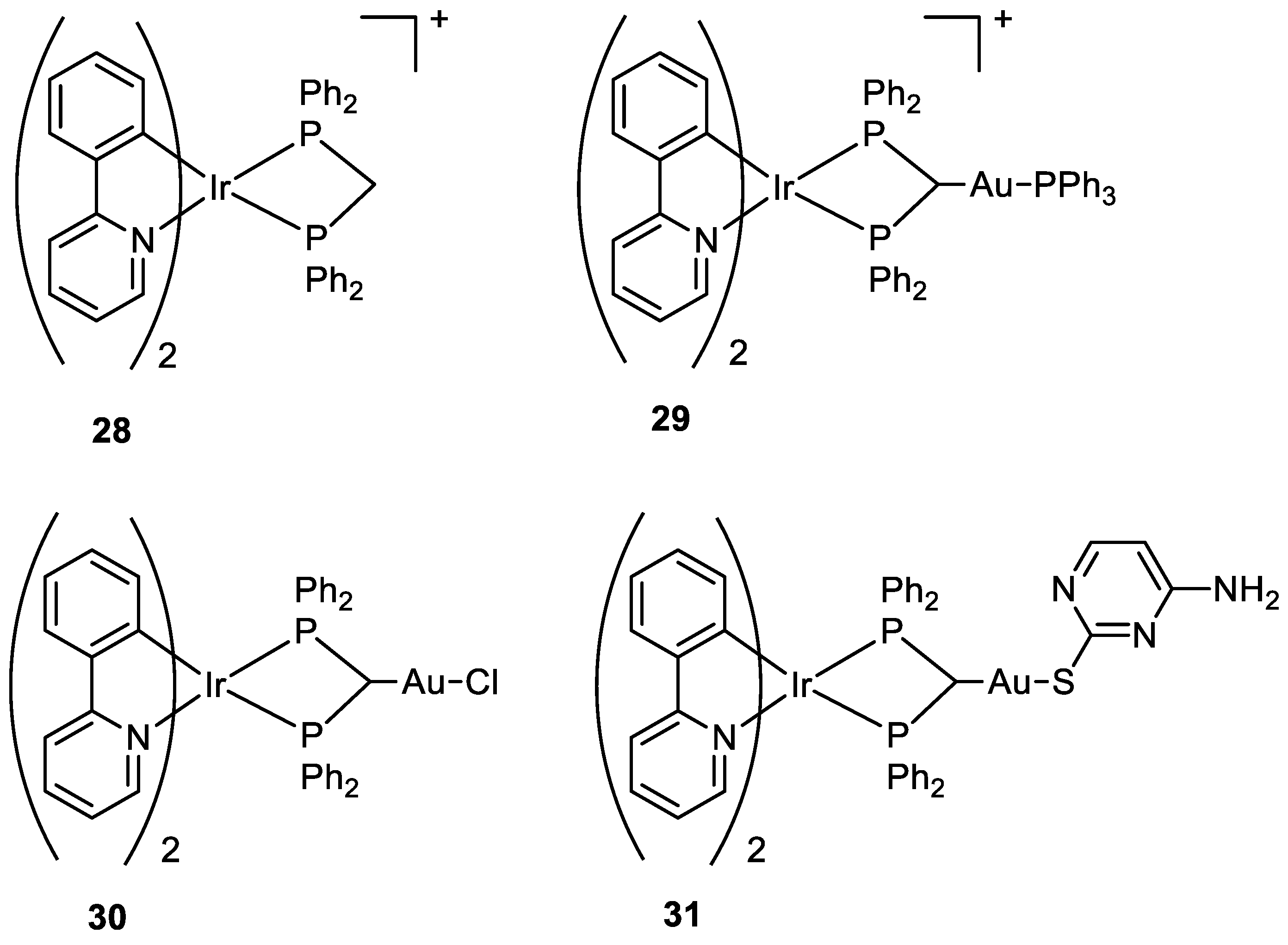
- Redrado, M.; Benedi, A.; Marzo, I.; García-Otín, A.L.; Fernández-Moreira, V.; Concepción Gimeno, M. Multifunctional Heterometallic IrIII−AuI Probes as Promising Anticancer and Antiangiogenic Agents. Chem. Eur. J. 2021, 27, 9885–9897.
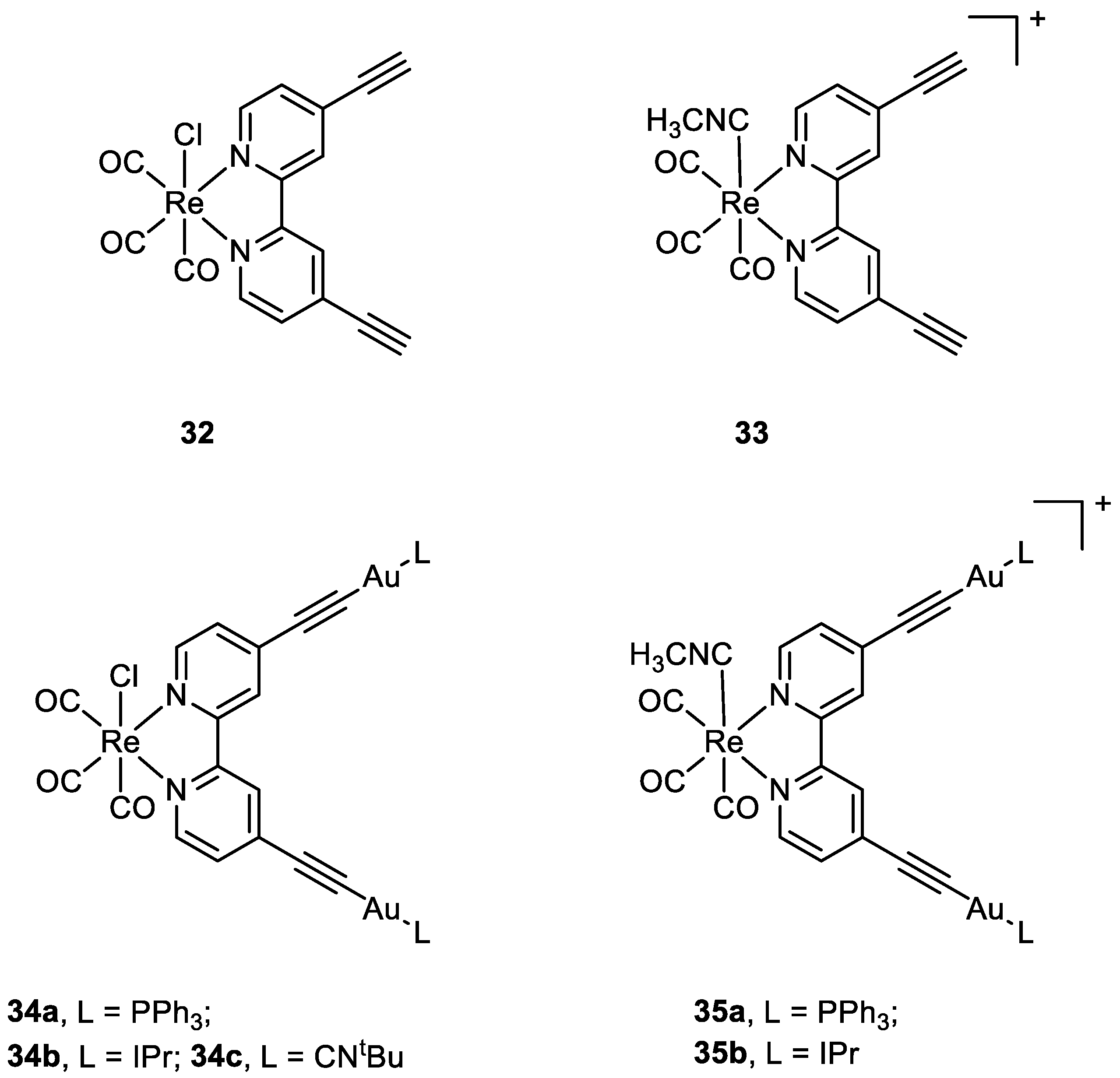
- Luengo, A.; Redrado, M.; Marzo, I.; Fernández-Moreira, V.; Gimeno, M.C. Luminescent Re(I)/Au(I) Species As Selective Anticancer Agents for HeLa Cells. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 8960–8970.
