Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 2 by Sirius Huang and Version 1 by Zala Štukovnik.
Viruses are responsible for many diseases that result in hundreds of thousands of deaths yearly. The ongoing outbreak of the COVID-19 disease has raised a global concern and intensified research on the detection of viruses and virus-related diseases. Novel methods for the sensitive, rapid, and on-site detection of pathogens, such as the recent SARS-CoV-2, are critical for diagnosing and treating infectious diseases before they spread and affect human health worldwide. In this sense, electrochemical impedimetric biosensors could be applied for virus detection on a large scale.
- electrochemical impedance spectroscopy
- impedimetric biosensor
- genosensor
- aptasensor
- immunosensor
- virus detection
1. Introduction
Electrochemical biosensors represent biosensing devices that contain an electrochemical transducer that converts biochemical information with high sensitivity into a measurable signal [18][1]. They also possess advantages such as time-saving, simple instrumentation, and cost-effectiveness [18,82][1][2]. Biosensors contain a bioreceptor that specifically responds to the analyte, linked to an interface and an element of signal transduction that translates the binding of the analyte into a measurable signal [2,17][3][4]. Different electrochemical biosensors can be developed to identify and quantify viruses depending on the integrated biological component (Figure 1). These sensors can be generically classified as immunoassays and DNA- or RNA-based assays such as genosensors and aptasensors. Comparing the application of immunoassays to DNA- or RNA-based assays depends on a variety of parameters. These variables include the infection stage, the antibody’s availability, and data on DNA or RNA sequences [5].
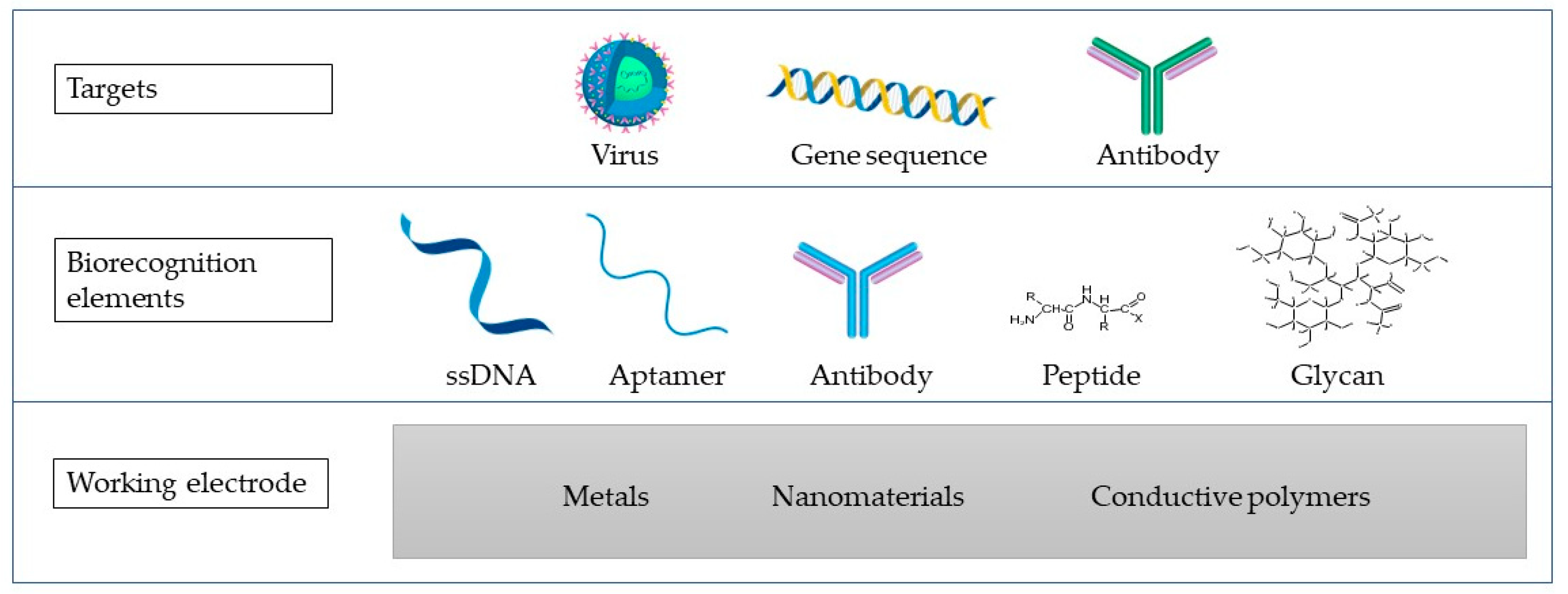
Figure 1. A biosensor scheme containing the working electrode (WE) made of different materials (metals, nanomaterials, or conductive polymers), biorecognition elements, and the targets that are commonly targeted in virus detection using the impedimetric biosensors.
Affinity sensors, which use selective binding of biomolecules, including antibodies, membrane receptors, or oligonucleotides with the analyte of interest to produce a quantifiable electrical signal, are the most often used biosensors for viral detection [83,84][6][7]. Generally, in affinity biosensors, the target analyte’s complementary binding site size and shape determine molecular recognition [84][7]. Thermodynamic considerations control the binding process, including DNA hybridization and antibody–antigen complexation [84][7]. Immobilized antibodies, antigens, and nucleic acids are the most common biorecognition elements used in the scientific literature to detect viruses [85][8]. Immobilization represents either a physical or a chemical process in which the entire biological recognition element is entrapped or there is an interaction of its portion with the surface of the transducer [86][9]. There exist four main types of immobilization, including adsorption and encapsulation, which belong to physical methods, as well as crosslinking and covalent bonding, which belong to chemical immobilization methods [87][10]. The selection of a suitable immobilization technique represents one of the crucial steps in the preparation of a biosensor, since the inactivation of the biological recognition element due to the choice of an inappropriate immobilization method is likely [88][11]. The most common immobilization strategies in the development of biosensors for virus detection consist of physical adsorption, covalent bonding, entrapment, and affinity-based interaction [89][12].
The detection principles employed in biosensors can be divided into label-based and label-free [90][13]. In label-free biosensors, the measurable signal is generated from a transducer, corresponding to the biorecognition event between the analyte of interest and the correlating receptor [91][14]. Sandwich assays are typical examples of label-based biosensors. In a sandwich assay, the analyte is captured by a receptor, such as an antibody, immobilized over the biosensor. The captured analyte attaches to the secondary receptor, such as a secondary antibody, which is then labeled with a fitting molecule to provide the measurable signal [91,92][14][15]. Due to their ability to be mass-produced at low-cost, electrochemical techniques have recently attracted much attention in the biosensor development [17,39][4][16]. In this aspect, EIS represents an essential technique for studying and comprehending the interfacial characteristics associated with particular biorecognition events, including the capture of antigen antibodies at the electrode surface or the molecular biorecognition of specific proteins, the identification of receptors, nucleic acids, or even whole cells [3,39][16][17].
However, there remain several limitations that need to be overcome. One of them is specificity, which is considered the most important property of a biosensor, as it describes the ability of a sensor to distinguish between target and non-target biological components of a sample [93][18]. Moreover, an unavoidable problem is the cross-talk between electrochemical and electrophysiological signals [94][19]. For example, some viral proteins share a certain sequence identity with other viral species (e.g., the envelope, nucleocapsid, membrane, and spike proteins of SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV, and MERS-CoV) [95][20]. To overcome these limitations, care must be taken in selecting biorecognition elements specific to each virus to reduce the cross-reactivity and to avoid false positive results [96][21]. Moreover, the use of biological receptors in biosensors has well-known limitations including low stability of the biological species, as well as low chemical and thermal stabilities [30][22]. The stability of the electrodes also plays an important role in the development of a biosensor. Electrodes made of Au are most commonly used, as they are both biocompatible and stable [19][23]. Compared to optical biosensors, where diagnostics are based on a sensitive detection of photon emission from dyes and other molecules excitable by light, impedimetric biosensors tend to have a lower sensitivity. However, unlike fluorescence and bioluminescence-based detection, electrochemical biosensors are easier to use with non-clear samples such as blood. In addition, electrochemical detection does not require a complex optical apparatus used in many fluorescence-based detections [97][24].
Several studies on impedimetric biosensors have been performed on designing the genosensors, the aptasensors, and the immunosensors.
Figure 2 depicts different approaches to biosensor development. In Figure 2a, a genosensor was developed using Au-SPE modified with cytosine. In Figure 2b, an aptasensor is presented, where a graphene electrode modified with PBASE was used to detect the S protein. In Figure 2c, a bare gold electrode was modified with thiol-modified aptamer, BSA and MCH, and NS1 was detected.
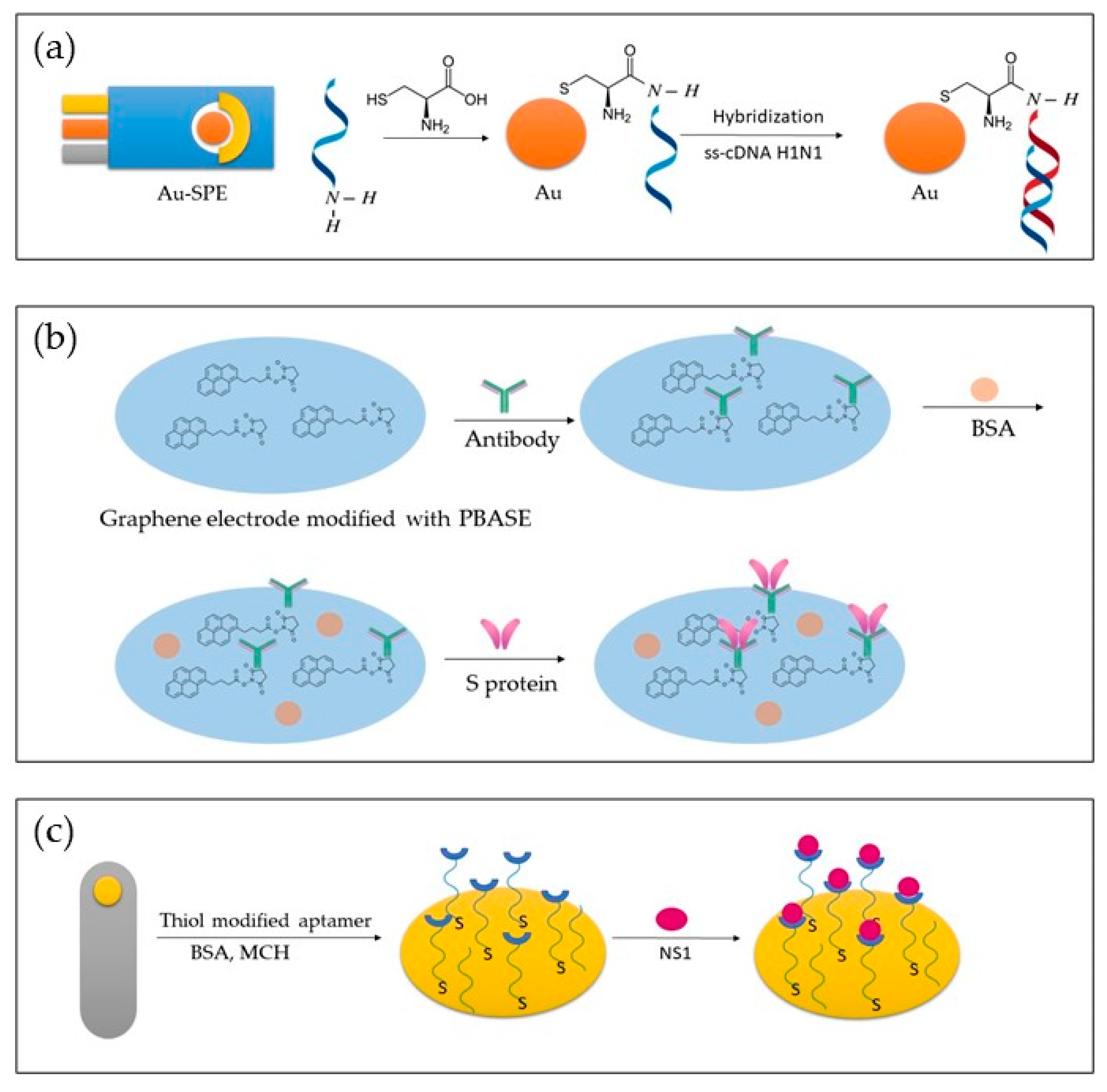
Figure 2.
Representation of different approaches in the development of genosensors (
a
), immunosensor (
b
), and aptasensor (
c
).
2. Genosensors for Virus Detection
One of the types of biosensors for virus detection receiving growing attention is the genosensor, which has been successfully applied for H1N1, HBV, EBOV, ZIKV, and HIV detection. A hybridization reaction between the DNA or RNA target and the ss-DNA sensing element in the genosensors allows for the detection of DNA or RNA targets [98,99][25][26]. The principle of detection with genosensors relies on the DNA or the RNA strand (probe) immobilization on the surface of a transducer to bind its complementary (target) sequence [60][27]. As the conventional biosensor assembly depends on single-strand hybridization, which is a reversible process, employing RNA or DNA has an advantage as it offers regeneration of the transducer surface [60,100][27][28]. Additionally, genosensors have a low limit of detection (LOD) [60,100][27][28].
The detection principle shown in Figure 3 is based on changes in the redox marker after the hybridization of the probe DNA with its complementary target DNA (ss-cDNA) [101][29].
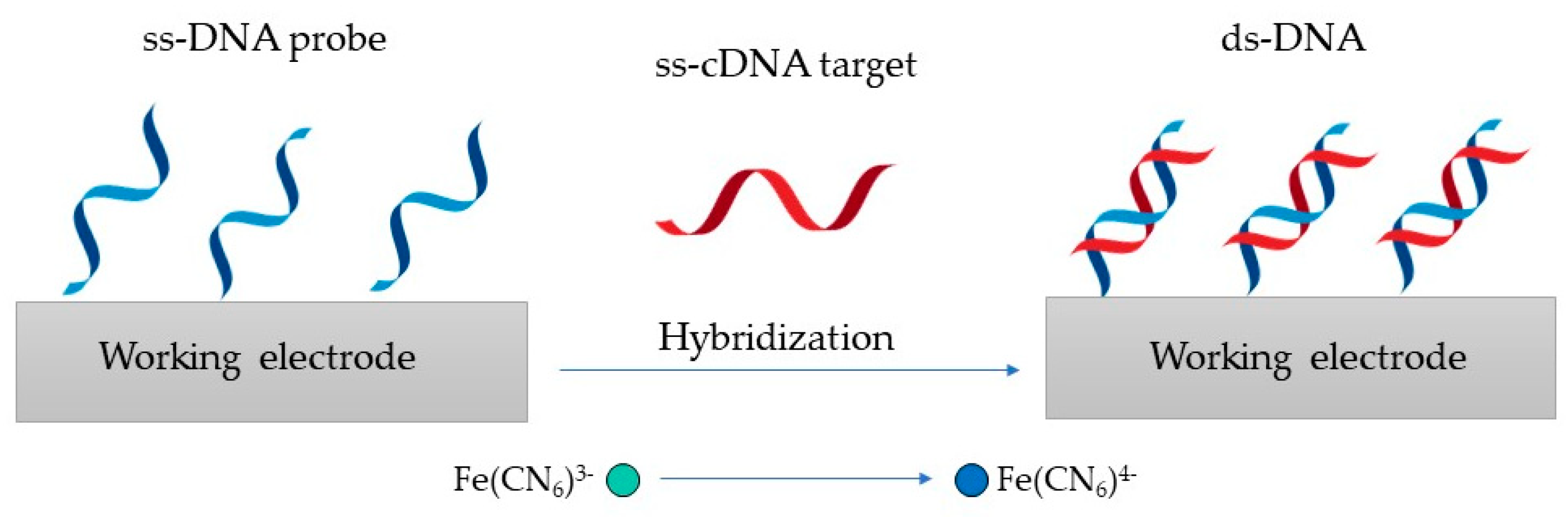
Figure 3.
Genosensor principle, where the ss-DNA probe is hybridized with its ss-cDNA to produce ds-DNA.
In recent years, many new genosensors have emerged to detect various virus-related diseases and pathogens through the efforts of researchers (Table 1).
Table 1.
Recently developed genosensors for virus detection.
| Virus | Recognition Element | Target | Electrode | Linear Range | LOD | Reference |
|---|
).
Table 2.
Recently developed aptasensors for virus detection.
| Virus | Recognition Element | Target | Electrode | Linear Range | LOD | Reference | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1N1 | ss-DNA H1N1 | ss-cDNA H1N1 (HA) | |||||||||||||
| MERS-CoV-2 | MF DNA aptamer | Cysteine modified Au-SPE | MERS-NV | / | GO-MoS | 2 | 0.667 ng/mL | 70–400 pg/mL | [102 | 0.4049 pg/mL | ] | [30] | |||
| [ | 112 | ] | [ | 41 | ] | HBV | ss-DNA HBV | ss-cDNA HBV | WO3/In2O3 nanowires | 0.1 pM–10 µM | 1 fM | [103] | [31] | ||
| HBV | |||||||||||||||
| H5N1 | H5N1 aptamer | H5N1 | Au-IDA microelectrode | 16–0.125 HAU | 0.25 HAU | [113] | [42] | ss-DNA HBV | ss-cDNA HBV | Te doped ZnO nanowires | |||||
| HCV | HCV aptamer | HCV core antigen | GCE/GQD | 1 pM–1 µM | 0.1 pM | [104] | [32] | ||||||||
| 10–70 pg/mL and 70–400 pg/mL | 3.3 pg/mL | [ | 114 | ] | [ | 43] | EBOV | ss-DNA EBOV | ss-cDNA EBOV | ||||||
| VACV | VACV aptamer | Au-SPE | / | 4.7 nM | VACV particles | [105] | Au microlectrode | 500–3000 PFU[ | 330 PFU33] | ||||||
| [ | 115 | ] | [ | 44 | ] | ZIKV | ss-DNA ZIKV | RNA (NS5 protein) | Au-PET | 54–340 nM | 25 nM | [106] | [34] | ||
| DENV | DENV aptamer | NS1 | MCH-Au electrodes | 10 pg/mL–1 μg/mL. | 22 pg/mL | [116] | [45] | HIV | ss-DNA HIV |
ss-cDNA HIV | Graphene-Nafion modified GCE | 0.1 pM–100 nM | 23 fM | [101] | [29] |
| HIV | ss-DNA HIV | ss-cDNA HIV | AuNPs/GF/CTP | 0.1 pM–10 nM | 13 fM | [107] | [35] |
An impedimetric genosensor based on a HA gene sequence was devised by Ravina et al. [102][30]. In this study, an amino-labeled ss-DNA probe was immobilized onto the cysteine-modified gold surface of the screen printed electrode (Au-SPE) for detection of the H1N1 influenza strain in humans. Researchers recorded the electrochemical impedance spectrums after the hybridization of the probe with the H1N1 ss-cDNA in the presence of a redox couple with a frequency ranging from 0.1 Hz to 0.01 mHz. This study reported that the fabricated impedimetric biosensor could detect 0.004 ng ss-cDNA of H1N1 in 6 μL within only 30 min.
Shariati and Sadeghi [103][31] devised a DNA biosensor for HBV detection, where EIS responses were biased under laser amplification. This biosensor was found on tin-doped WO3/In2O3 nanowires. The LOD of 1 fM was determined, where the corresponding Rct values decreased from 2487 to 806 Ω for DNA complementary target and probe. The developed biosensor reportedly had a linear detection range from 0.1 pM to 10 μM.
A label-free impedimetric biosensor for the detection of HBV DNA based on ZnO nanowires doped with tellurium (Te) was devised by Khosravi-Nejad et al. [104][32]. This HBV biosensor detection range was in concentrations ranging from 1 pM to 1 μM, where the LOD of the developed genosensor was 0.1 pM.
Ilkhani and Farhad [105][33] fabricated an EBOV DNA biosensing device. In this study, a biotinylated target strand DNA was hybridized with a thiolated DNA capture probe sequence that was immobilized on the SPE surface. The LOD of complementary oligonucleotides was determined at 4.7 nM.
Moreover, a three-electrode and label-free impedimetric electrochemical DNA biosensor for the detection of ZIKV was reported by Faria and Zucolotto [106][34]. EIS measurements were performed with an alternating current (AC) perturbation, decreasing in frequency from 30 kHz to 0.1 kHz with ten measurement points per decade in a logarithmic scattering. Impedance measurements identified a LOD of 25.0 ± 1.7 nM. The linearity in measurements was achieved in the range from 54 to 340 nM.
An impedimetric HIV-1 genosensor was devised by Gong et al. [101][29]. This genosensor was developed by adsorbing ss-DNA onto the graphene-Nafion-modified surface of a glassy carbon electrode (GCE). Researchers explained in their study that as the negative ss-DNA adsorbs and the steric hindrance occurs, the Rct of the electrodes toward the [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− gets limited. In the process, the ss-DNA probe was hybridized with the target DNA to form ds-DNA. The helix formation induces ds-DNA release from the surface of the biosensor. The decrease in Rct is logarithmically related to the concentration of the HIV-1 gene in a range from 0.1 pM to 100 nM. The LOD of this sensor is determined at 23 fM.
An alternative detection method for the HIV-1 gene using a label-free DNA impedimetric genosensor with gold nanoparticles (AuNPs)/carbonized glass fiber (GF) coal tar pitch electrodes (GTP) was designed by Yeter et al. [107][35]. The developed biosensor provided a LOD of 13 fM, with a linear range from 0.1 pM to 10 nM. Researchers used amine-crosslinking chemistry in preparation for the thiol-modified electrodes. In this study, the EIS with a frequency range from 100 to 0.1 kHz and a wave amplitude of 10 mV at a DC potential of 0.115 V was used for the determination.
3. Aptasensors for Virus Detection
Aptasensors are biosensors that use aptamers as biorecognition elements [108][36]. Aptamers represent short and synthetic single-stranded nucleic acids, either ss-DNA or ss-RNA [7][37]. Aptamers usually consist of lesser than 100 nucleotides, capable of selective binding onto a specific target [7][37]. Compared to genosensors, here, the DNA or the RNA aptamer plays the role of the receptor [98,109][25][38]. It is necessary to immobilize the aptamer strands and identify them to make detection easier when using aptamers in aptasensors. The preferred target for choosing virus-specific aptamers is either a protein produced from a virus or an inactivated virus particle [110][39]. The ss-DNA or ss-RNA oligonucleotide sequences used as the biorecognition element are screened in a SELEX (systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment) procedure [84][7]. In a SELEX, the ability of ss-DNA or ss-RNA to selectively bind to low molecular weight organic, inorganic, or protein targets is screened [84,111][7][40]. Several studies have been performed on EIS-based biosensors, in which the aptasensors were developed (Table 2
Kim et al. [112][41] devised a MERS-nanovesicle (NV) biosensor structured of multi-functional DNA aptamers and graphene oxide encapsulated molybdenum disulfide (GO-MoS2) hybrid nanocomposite. The electrical condition for an AC impedance measurement was a frequency ranging from 1 Hz to 100 kHz with an amplitude of 10 mV. The LOD of this biosensor was determined at 0.4049 pg/mL, and its linear range was from 70 pg/mL to 400 pg/mL.
Karash et al. [113][42] devised a label-based impedance aptasensor for H5N1 detection employing a specific aptamer for the H5N1 influenza strain and a gold interdigitated microelectrode (Au-IDE). In this study, a biotin-labeled H5N1 aptamer was bound to immobilize streptavidin on the surface of the microelectrode. According to the researchers, polyethylene glycol was utilized to block the microelectrode, and the attached aptamer captured the virus. Using a sinusoidal AC potential of 10 mV and a frequency range of 10 Hz to 1 MHz in the presence of [Fe(CN)6]3−/4−, the magnitude and phase of the impedance were measured at 54 points per decade. The LOD was determined at 0.25 HAU, and the linearity range was obtained from 0.125 to 16 HAU.
An electrochemical aptasensor for the detection of the HCV core antigen was developed by Ghanbari et al. [114][43]. In this study, the immobilization surface was prepared by the modification of a GCE with graphene quantum dots (GQD). With a 3.3 pg/mL LOD and a linear concentration range from 70 to 400 pg/mL, the EIS approach was used as a reliable detection technology for HCV core antigen.
A design of an aptamer-based viability impedimetric sensor for viruses was presented by Labib et al. [115][44]. In this study, cell-SELEX was employed to select highly specific DNA aptamers for intact vaccinia virus (VACV) that were later self-assembled onto Au microelectrode to form impedimetric biosensors. It was found that the developed aptasensor was highly selective and, therefore could detect viable VACV particles with a LOD of 60 virions/L or 330 PFU in a linear range from 500 to 3000 PFU, as well as differentiate them from non-viable viruses. In this research, EIS was applied to monitor the binding of the proposed aptamer to the target VACV, which decreased the interfacial resistance and, consequently, the Rct value. According to this study, this occurrence caused the aptamers to alter conformation after binding to VACV, allowing the [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− to adhere to the electrode surface more freely.
Bachour Junior et al. [116][45] devised an electrochemical biosensor for non-structural protein (NS1) detection using DNA aptamers. NS1 is a relevant biomarker that is seen in high concentrations in the blood during the early stages of dengue virus (DENV) infection. In this study, a self-assembled monolayer by immobilizing Au electrodes with particular aptamers and 6-mercapto-1-hexanol (MCH) was produced. Researchers obtained EIS results with a 10 mV amplitude in the frequency range of 100 kHz to 100 mHz. The device achieved a LOD of 22 pg/mL with a linear range from 10 pg/mL to 1 g/mL.
4. Immunosensors for Virus Detection
In the impedimetric immunosensors, the antibodies that interact with the viral antigens are immobilized on the electrodes. Due to their promising applications in various fields, they have recently gained great interest. [117,118][46][47]. In impedimetric immunosensors, an electrical signal difference results from the kinetic binding of antibodies and their antigens to the electrode surface. As a result, Rct is altered, corresponding to the amount of bound antigens [39][16].
In immonosensors, the most commonly used biological components are IgG antibodies, which are large Y-shaped glycoproteins produced by a host in reaction to the presence of a foreign molecule called an antigen [84,111][7][40].
In Figure 54, the process on the WE containing antibodies as biorecognition elements is depicted (an immunosensor). [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− is used as a redox probe in the process. The virus binds to the target bioreceptor (antibody) at the WE surface, and the redox reaction is hindered.
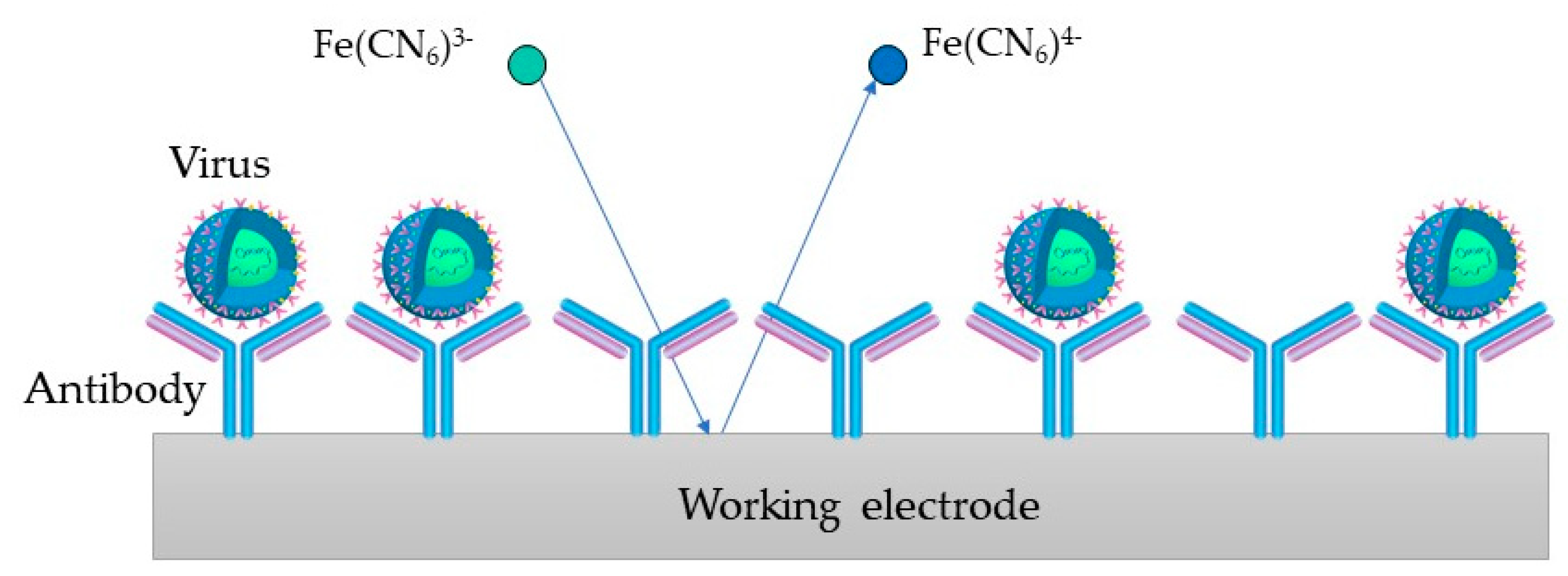
Figure 54.
Immunosesor principle, where the virus binds to the antibody at the WE surface and the redox reaction gets hindered.
Several studies on EIS-based biosensors have been performed by designing immunosensors for virus detection (Table 3).
Table 3.
Recently developed immunosensors for virus detection.
| Virus | Recognition Element | Target | Electrode | Linear Range | LOD | Reference | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H3N2 | Viral antibodies | Viral nucleoproteins | SPCE | 0.18 fM–0.18 nM | 0.79 fM | [119] | [48] | ||||||
| H1N1 | M1-antibody | M1 protein | BDD | 0–100 fg/mL | 1 fg/mL | [120] | [49] | ||||||
| HBV | Anti-HBs | HBsAg | BSA-SPCE | 5–3000 ng/mL | 2.1 ng/mL | [121] | [50] | ||||||
| HAV | Anti-HAs | HAsAg | CNPE | 2 × 10 | −4 | –5 × 10 | −3 | IU/mL | 6 × 10 | −5 | IU/mL | [122] | [51] |
| HEV | Anti-HEV antibody | HEV | PAc-GCE | / | 8 fg/mL | [123] | [52] | ||||||
| ZIKV | Zev-Abs | ZIKV-protein | IDE-Au | 10 pM–1 nM | 10 pM | [124] | [53] | ||||||
| ZIKV | Anti-NS1 | NS1 | SPCE | / | / | [125] | [54] |
Dunajová et al. [119][48] developed a highly selective and ultra-sensitive impedimetric immunobiosensor for detecting influenza A viruses. The reported immunosensor was based on the interaction with monoclonal antibodies using a screen-printed carbon electrode (SPCE). Measurements in this study were performed at frequencies ranging from 0.05 Hz to 30 kHz. Antibodies and viral nucleoproteins were reported to change the layer thickness, resulting in an altered charge transfer resistance (ΔRct). The biosensor was tested in an ideal buffered PBS solution where the LOD was 0.79 fM, and the linearity was obtained from 0.18 fM to 0.18 nM.
Nidzworski et al. [120][49] devised a diamond biosensor for the influenza virus that enables specific virus detection at ultralow concentrations, even before any clinical symptoms appear. In this study, the M1 protein, a universal biomarker for influenza viruses, was identified by surface functionalizing a diamond electrode with polyclonal anti-M1 antibodies. A LOD of 1 fg/mL for the M1 biomarker in a saliva buffer, which corresponds to about 5 to 10 viruses per sample in 5 min, was reported.
Akkapinyo et al. [121][50] reported an impedimetric immunosensor for hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) detection. This impedimetric immunosensor was developed by immobilizing hepatitis B surface antibody (Anti-HBs) through the N-ethyl-N0-(3-(dimethylamino)propyl)carbo-diimide/N-hydroxy succinimide (EDC/NHS) couple reaction, which involved the carboxyl group of the bovine serum albumin (BSA) cross-linked film on the SPCE. In this study, the scanning frequency was between 0.01 Hz and 100 kHz under an applied AC of 10 mV, where a linear relationship between ΔRct and HBsAg concentration was obtained in the range from 5 to 3000 ng/mL with a LOD of 2.1 ng/mL.
A label-based impedimetric biosensor was reported by Mandli et al. [122][51]. An indirect competitive electrochemical immunosensor for HAV detection was developed by immobilizing HAV antibodies on the carbon nanopowder paste electrode (CNPE) surface, using a secondary antibody labeled with peroxidase to target HAV antigen. The developed immunosensor provided exact data with a linear concentration range from 2 × 10−4 to 5 × 10−3 IU/mL, with the LOD at 26 × 10−5 IU/mL.
Chowdhury et al. [123][52] devised a biosensor where nanocomposites were deposited on an electropolymerized polyaniline-coated GCE to form an Ab-N,S-GQDs-AuNP-PAni/PAni||GCE sensor. HEV was then detected using an impedimetric response. The measurements were taken over a frequency range from 100 kHz to 100 mHz with an AC amplitude of 5 mV, where the LOD was determined at 8 fg/mL.
Kaushik et al. [124][53] presented an impedimetric immunosensor for ZIKV-protein detection. In this study, a functionalized interdigitated micro-electrode of gold (IDE-Au) was prepared by the immobilization of the ZIKV-specific envelope protein antibody (Zev-Abs). According to the findings of this EIS analysis, the biosensor selectively recognized ZIKV-protein in a linear detection range between 10 pM and 1 nM, with a LOD of 10 pM and a high sensitivity of 12 kΩ/M.
Cabral-Miranda et al. [125][54] designed an immunosensor based on the recombination of domain III of the envelope protein (EDIII) and ZIKV non-structural protein 1 (NS1). Using EIS and squarewave voltammetry (SWV), it was demonstrated that the biosensor is sensitive to ZIKV-specific antibodies in serum and saliva and can immediately distinguish between ZIKV- and DENV-specific antibodies. This study performed EIS assays at a potential of 0.14 V, with an amplitude of 0.01 V and 50 frequency values logarithmically distributed from 0.1 to 100,000 Hz.
References
- Khan, M.Z.H.; Hasan, M.R.; Hossain, S.I.; Ahommed, M.S.; Daizy, M. Ultrasensitive detection of pathogenic viruses with electrochemical biosensor: State of the art. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 166, 112431.
- Thévenot, D.; Toth, K.; Durst, R.; Wilson, G. Electrochemical Biosensors: Recommended Definitions and Classification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2001, 16, 121–131.
- Naresh, V.; Lee, N. A Review on Biosensors and Recent Development of Nanostructured Materials-Enabled Biosensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 1109.
- Kirchhain, A.; Bonini, A.; Vivaldi, F.; Poma, N.; Di Francesco, F. Latest developments in non-faradic impedimetric biosensors: Towards clinical applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 133, 116073.
- Cesewski, E.; Johnson, B.N. Electrochemical biosensors for pathogen detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 159, 112214.
- Ozer, T.; Geiss, B.J.; Henry, C.S. Review—Chemical and Biological Sensors for Viral Detection. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 167, 037523.
- Ronkainen, N.J.; Halsall, H.B.; Heineman, W.R. Electrochemical biosensors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 1747–1763.
- Sanati, A.; Jalali, M.; Raeissi, K.; Karimzadeh, F.; Kharaziha, M.; Mahshid, S.S.; Mahshid, S. A review on recent advancements in electrochemical biosensing using carbonaceous nanomaterials. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 773.
- Du, K.; Zhang, Z.L.; Li, T.H.; Rao, W. The Research Progress of Antibody Immobilization. China Biotechnol. 2018, 38, 78–89.
- Bhardwaj, T. A review on immobilization techniques of biosensors. Int. J. Eng. Res. 2014, 3, 294–298.
- Morales, M.A.; Halpern, J.M. Guide to Selecting a Biorecognition Element for Biosensors. Bioconjugate Chem. 2018, 29, 3231–3239.
- Rashid, J.I.A.; Yusof, N.A. The strategies of DNA immobilization and hybridization detection mechanism in the construction of electrochemical DNA sensor: A review. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2017, 16, 19–31.
- Sang, S.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Q.; Wei, Y.; Ji, J.; Zhang, W. Progress of new label-free techniques for biosensors: A review. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2016, 36, 465–481.
- Riu, J.; Giussani, B. Electrochemical biosensors for the detection of pathogenic bacteria in food. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 126, 115863.
- Lim, S.A.; Ahmed, M.U. CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Immunosensors. In Immunosensors; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2019; pp. 1–20.
- Magar, H.S.; Hassan, R.Y.A.; Mulchandani, A. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS): Principles, Construction, and Biosensing Applications. Sensors 2021, 21, 6578.
- Goode, J.A.; Rushworth, J.V.; Millner, P.A. Biosensor Regeneration: A Review of Common Techniques and Outcomes. Langmuir 2015, 31, 6267–6276.
- Varshney, M.; Mallikarjunan, K. Challenges in Biosensor Development--Detection limit, detection time, and specificity. Resour. Mag. 2009, 16, 18–21.
- Honda, H.; Kusaka, Y.; Wu, H.; Endo, H.; Tsuya, D.; Ohnuki, H. Toward a Practical Impedimetric Biosensor: A Micro-Gap Parallel Plate Electrode Structure That Suppresses Unexpected Device-to-Device Variations. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 11017–11022.
- Ahmed, S.F.; Quadeer, A.A.; McKay, M.R. Preliminary Identification of Potential Vaccine Targets for the COVID-19 Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) Based on SARS-CoV Immunological Studies. Viruses 2020, 12, 254.
- Chen, X.-F.; Zhao, X.; Yang, Z. Aptasensors for the detection of infectious pathogens: Design strategies and point-of-care testing. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 443.
- Guan, J.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, Q. Impedimetric Biosensors. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2004, 97, 219–226.
- Wang, Y.; Ye, Z.; Ying, Y. New trends in impedimetric biosensors for the detection of foodborne pathogenic bacteria. Sensors 2012, 12, 3449–3471.
- Pashchenko, O.; Shelby, T.; Banerjee, T.; Santra, S. A Comparison of Optical, Electrochemical, Magnetic, and Colorimetric Point-of-Care Biosensors for Infectious Disease Diagnosis. ACS Infect. Dis. 2018, 4, 1162–1178.
- Walper, S.A.; Lasarte Aragonés, G.; Sapsford, K.E.; Brown, C.W., 3rd; Rowland, C.E.; Breger, J.C.; Medintz, I.L. Detecting Biothreat Agents: From Current Diagnostics to Developing Sensor Technologies. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 1894–2024.
- Adley, C.C. Past, Present and Future of Sensors in Food Production. Foods 2014, 3, 491–510.
- Ribeiro, B.V.; Cordeiro, T.A.R.; Oliveira E Freitas, G.R.; Ferreira, L.F.; Franco, D.L. Biosensors for the detection of respiratory viruses: A review. Talanta Open 2020, 2, 100007.
- Manring, N.; Ahmed, M.M.N.; Tenhoff, N.; Smeltz, J.L.; Pathirathna, P. Recent Advances in Electrochemical Tools for Virus Detection. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 7149–7157.
- Gong, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H. A sensitive impedimetric DNA biosensor for the determination of the HIV gene based on graphene-Nafion composite film. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 89, 565–569.
- Mohan, H.; Gill, P.S.; Kumar, A. Hemagglutinin gene based biosensor for early detection of swine flu (H1N1) infection in human. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 130, 720–726.
- Shariati, M.; Sadeghi, M. Ultrasensitive DNA biosensor for hepatitis B virus detection based on tin-doped WO3/In2O3 heterojunction nanowire photoelectrode under laser amplification. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 5367–5377.
- Khosravi-Nejad, F.; Teimouri, M.; Jafari Marandi, S.; Shariati, M. The highly sensitive impedimetric biosensor in label free approach for hepatitis B virus DNA detection based on tellurium doped ZnO nanowires. Appl. Phys. A 2019, 125, 616.
- Ilkhani, H.; Farhad, S. A novel electrochemical DNA biosensor for Ebola virus detection. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 557, 151–155.
- Faria, H.A.M.; Zucolotto, V. Label-free electrochemical DNA biosensor for zika virus identification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 131, 149–155.
- Yeter, E.Ç.; Şahin, S.; Caglayan, M.O.; Üstündağ, Z. An electrochemical label-free DNA impedimetric sensor with AuNP-modified glass fiber/carbonaceous electrode for the detection of HIV-1 DNA. Chem. Pap. 2021, 75, 77–87.
- Di Pietrantonio, F.; Cannatà, D.; Benetti, M. Chapter 8-Biosensor technologies based on nanomaterials. In Functional Nanostructured Interfaces for Environmental and Biomedical Applications; Dinca, V., Suchea, M.P., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 181–242.
- Sánchez-Báscones, E.; Parra, F.; Lobo-Castañón, M.J. Aptamers against viruses: Selection strategies and bioanalytical applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 143, 116349.
- Paniel, N.; Baudart, J.; Hayat, A.; Barthelmebs, L. Aptasensor and genosensor methods for detection of microbes in real world samples. Methods 2013, 64, 229–240.
- van den Kieboom, C.H.; van der Beek, S.L.; Mészáros, T.; Gyurcsányi, R.E.; Ferwerda, G.; de Jonge, M.I. Aptasensors for viral diagnostics. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 74, 58–67.
- Srivastava, S.; Abraham, P.R.; Mukhopadhyay, S. Aptamers: An Emerging Tool for Diagnosis and Therapeutics in Tuberculosis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 656421.
- Kim, G.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.M.; Kato, T.; Yoon, J.; Noh, S.; Park, E.Y.; Park, C.; Lee, T.; Choi, J.-W. Fabrication of MERS-nanovesicle biosensor composed of multi-functional DNA aptamer/graphene-MoS2 nanocomposite based on electrochemical and surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 352, 131060.
- Karash, S.; Wang, R.; Kelso, L.; Lu, H.; Huang, T.J.; Li, Y. Rapid detection of avian influenza virus H5N1 in chicken tracheal samples using an impedance aptasensor with gold nanoparticles for signal amplification. J. Virol. Methods 2016, 236, 147–156.
- Ghanbari, K.; Roushani, M.; Azadbakht, A. Ultra-sensitive aptasensor based on a GQD nanocomposite for detection of hepatitis C virus core antigen. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 534, 64–69.
- Labib, M.; Zamay, A.S.; Muharemagic, D.; Chechik, A.V.; Bell, J.C.; Berezovski, M.V. Aptamer-Based Viability Impedimetric Sensor for Viruses. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 1813–1816.
- Bachour Junior, B.; Batistuti, M.R.; Pereira, A.S.; de Sousa Russo, E.M.; Mulato, M. Electrochemical aptasensor for NS1 detection: Towards a fast dengue biosensor. Talanta 2021, 233, 122527.
- Abbas, A.K.; Lichtman, A.H.; Pillai, S. Cellular and Molecular Immunology E-Book; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014.
- Bahadır, E.B.; Sezgintürk, M.K. A review on impedimetric biosensors. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2016, 44, 248–262.
- Dunajová, A.A.; Gál, M.; Tomčíková, K.; Sokolová, R.; Kolivoška, V.; Vaněčková, E.; Kielar, F.; Kostolanský, F.; Varečková, E.; Naumowicz, M. Ultrasensitive impedimetric imunosensor for influenza A detection. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 858, 113813.
- Nidzworski, D.; Siuzdak, K.; Niedziałkowski, P.; Bogdanowicz, R.; Sobaszek, M.; Ryl, J.; Weiher, P.; Sawczak, M.; Wnuk, E.; Goddard, W.A.; et al. A rapid-response ultrasensitive biosensor for influenza virus detection using antibody modified boron-doped diamond. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15707.
- Akkapinyo, C.; Khownarumit, P.; Waraho-Zhmayev, D.; Poo-arporn, R.P. Development of a multiplex immunochromatographic strip test and ultrasensitive electrochemical immunosensor for hepatitis B virus screening. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1095, 162–171.
- Mandli, J.; Attar, A.; Ennaji, M.M.; Amine, A. Indirect competitive electrochemical immunosensor for hepatitis A virus antigen detection. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2017, 799, 213–221.
- Chowdhury, A.D.; Takemura, K.; Li, T.-C.; Suzuki, T.; Park, E.Y. Electrical pulse-induced electrochemical biosensor for hepatitis E virus detection. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3737.
- Kaushik, A.; Yndart, A.; Kumar, S.; Jayant, R.D.; Vashist, A.; Brown, A.N.; Li, C.-Z.; Nair, M. A sensitive electrochemical immunosensor for label-free detection of Zika-virus protein. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9700.
- Cabral-Miranda, G.; Cardoso, A.R.; Ferreira, L.C.S.; Sales, M.G.F.; Bachmann, M.F. Biosensor-based selective detection of Zika virus specific antibodies in infected individuals. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 113, 101–107.
More
