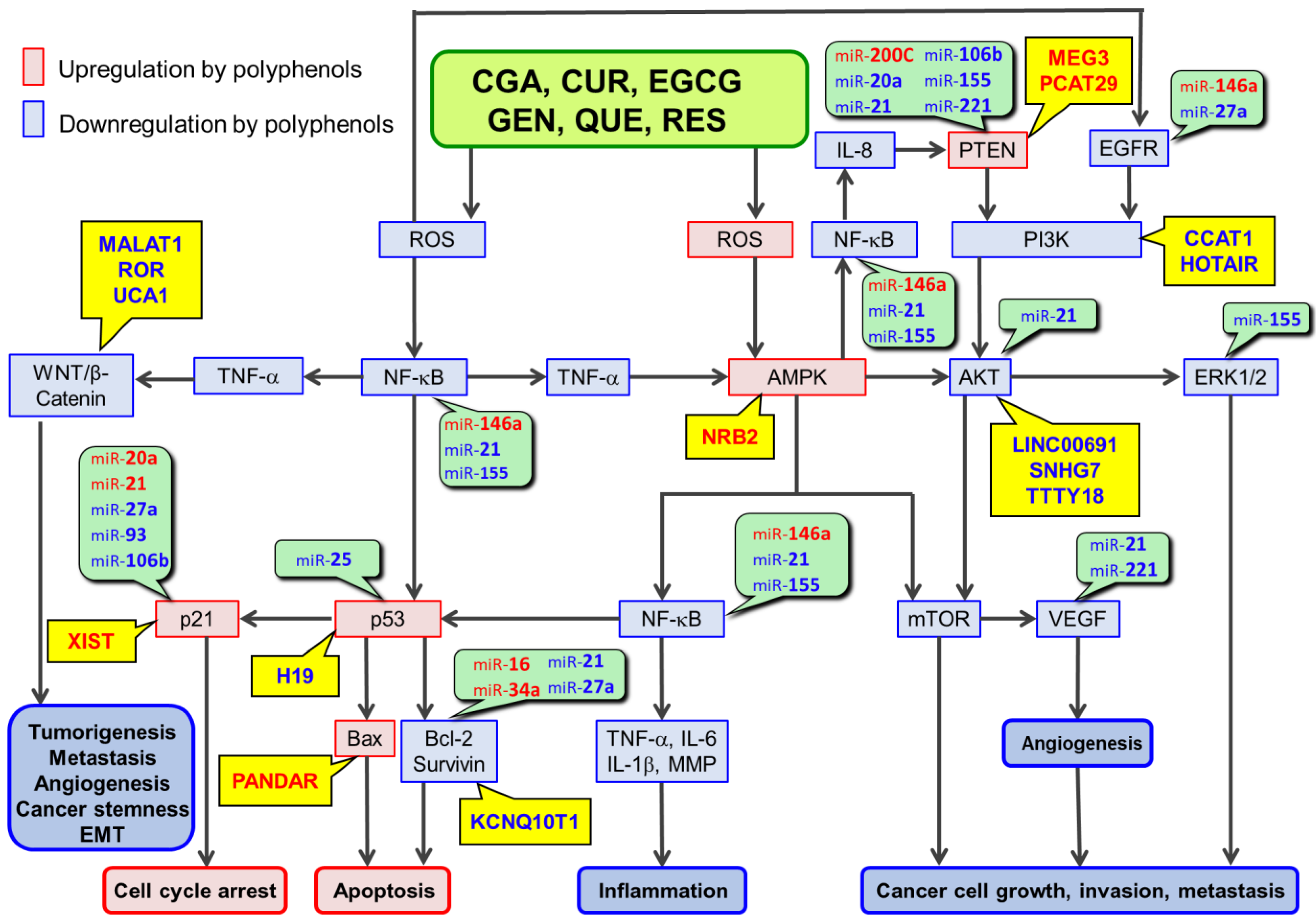
The anticancer effects of daily consumption of polyphenols. These dietary polyphenols include chlorogenic acid, curcumin, epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate, genistein, quercetin, and resveratrol. These polyphenols have similar chemical and biological properties in that they can act as antioxidants and exert the anticancer effects via cell signaling pathways involving their reactive oxygen species (ROS)-scavenging activity. These polyphenols may also act as pro-oxidants under certain conditions, especially at high concentrations. Epigenetic modifications, including dysregulation of noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) such as microRNAs, long noncoding RNAs, and circular RNAs are now known to be involved in the anticancer effects of polyphenols. These polyphenols can modulate the expression/activity of the component molecules in ROS-scavenger-triggered anticancer pathways (RSTAPs) by increasing the expression of tumor-suppressive ncRNAs and decreasing the expression of oncogenic ncRNAs in general. Multiple ncRNAs are similarly modulated by multiple polyphenols. Many of the targets of ncRNAs affected by these polyphenols are components of RSTAPs. Therefore, ncRNA modulation may enhance the anticancer effects of polyphenols via RSTAPs in an additive or synergistic manner, although other mechanisms may be operating as well.
- anticancer
- ROS
- polyphenols
1. Introduction
| miRs | miR-16 | miR-22 | miR-34a | miR-141 | miR-145 | miR-146a | miR-200c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CUR | EGCG | GEN | QUE | RES | |||
| Polyphenols |
| CGA | CUR | EGCG | GEN | QUE | RES | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-7 SET8↓, Bcl-2↓, p53↑ [80]; Skp2↓, p57↑, p21↑ [81] miR-9 AKT↓, FOXO1↓ [82]; GSK-3β↑, β-catenin↑, Cyclin D1↓ [83] miR-15a Bcl-2↓ [9]; WT1↓ [84] miR-16-1 WT1↓ [84] miR-28-5p BECN1↓ [85] miR-29a DNMT1↓, 3A↓, 3B↓ [86] miR-30c-5p MTA1↓ [87] miR-33b HMGA2↓ [88]; XIAP↓ [89] miR-98 LIN28A↓, MMP2↓, MMP9↓ [90] miR-99a JAK1↓, STAT1↓, STAT3↓ [91 | CUR Yang et al. [9] EGCG Tsang et al.[10] QUE Sonoki et al. [11]; Zhao et al. [12] RES Hagiwara et al. [13]; Azimi et al. [14] |
CUR Sun et al. [15]; Sreenivasan et al. [16]; | 25 | ] | Cancer stemness↓ | RES: Hagiwara et al. [13] EMT↓ via vimentin, ZEB1↑, E-cadherin↓ RES: Dermani et al. [45] |
| miRs | miR-20a | miR-21 | miR-25 | miR-27a | miR-93 | miR-106b | miR-155 | miR-221 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyphenols | ] miR-101 EZH2↓, EpCAM↓ [92]; Notch1↓ [93]; EZH2↓ [94] miR-124 Midkine↓ [95]CGA Huang et al. [46] CUR Gandhy et al. [47] EGCG Mirzaaghaei et al. [48] RES Dhar et al. [49]; Dhar et al. [50] |
miR-125a ERRα↓ [96] miR-138 Smad4↓, NF-kB↓, Cyclin D3↓ [97] miR-143 NF-kB↓ [98]; PGK1↓ [99]; Autophagy via ATG2B↓ [100] miR-181b CXCL1↓ [101] miR-185 DNMT1↓, 3A↓, 3B↓ [86] miR-192-5p XIAP↓ [102]; PI3K↓, AKT↓ [103]; Wnt/β-catenin↓ [104] miR-196b ** BCR-ABL↓ [55] miR-206 mTOR↓, AKT↓ [105] miR-215 XIAP↓ [102] miR-340 XIAP↓ [106] miR-384 circ-PRKCA↓ [107] miR-491 PEG10↓ [108]
* Upregulation (↑) and downregulation (↓) of miR targets by polyphenols are indicated. ** Downregulation by RES is reported [130]. SET8; SET domain-containing lysine methyltransferase 8, Bcl-2; B-cell lymphoma 2, Skp2; S-phase kinase-associated protein 2, AKT; AKT serine/threonine kinase 1, FOXO1; forkhead Box O1, GSK-3β; glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta, WT1; Wilms’ tumor-1, BECN1; beclin 1, DNMT; DNA methyltransferase, MTA1; metastasis-associated 1, HMGA2; high mobility group A2, XIAP; X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis, LIN28A; Lin-28 homolog A, MMP; matrix metalloproteinase, JAK1; Janus kinase 1; STAT; signal transducer and activator of transcription, EZH2; enhancer of zeste homolog 2, EpCAM; epithelial cell adhesion molecule, Notch1; neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 1, ERRα; estrogen-related receptor alpha, PGK1; phosphoglycerate kinase 1, ATG2B; autophagy-related 2B, CXCL1; chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1, PI3K; phosphoinositide-3 kinase, Wnt; wingless and int-1, BCR-ABL; BCR-ABL fusion gene, mTOR; mammalian target of rapamycin, circ-PRKCA; circ_0007580, PEG10; paternally expressed gene 10, MDR1; multidrug resistance mutation1, STIM2; Stromal interaction molecule 2, Orai1; ORAI calcium release-activated calcium modulator 1, KDM2A; lysine demethylase 2A, RXRα; retinoid X receptor alpha, RAC1; ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1, EGFR; epidermal growth factor receptor, EP300; E1A-associated protein P300, THBS1; thrombospondin 1, TAGLN2; transgelin 2, WEE1; WEE1 G2 checkpoint kinase, SNHG7; small nucleolar RNA host gene 7, HSP; heat shock protein, IGFBP; insulin-like growth factor binding protein, KRAS; KRAS proto-oncogene, GTPase, Numbl; NUMB like endocytic adaptor protein, Mcl1; myeloid cell leukemia 1, IGF2BP; insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein.
|
References
- Hayakawa, S.; Ohishi, T.; Miyoshi, N.; Oishi, Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Isemura, M. Anti-Cancer Effects of Green Tea Epigallocatchin-3-Gallate and Coffee Chlorogenic Acid. Molecules 2020, 25, 4553.
- Fukutomi, R.; Ohishi, T.; Koyama, Y.; Pervin, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Isemura, M. Beneficial Effects of Epigallocatechin-3-O-Gallate, Chlorogenic Acid, Resveratrol, and Curcumin on Neurodegenerative Diseases. Molecules 2021, 26, 415.
- Ohishi, T.; Fukutomi, R.; Shoji, Y.; Goto, S.; Isemura, M. The Beneficial Effects of Principal Polyphenols from Green Tea, Coffee, Wine, and Curry on Obesity. Molecules 2021, 26, 453.
- Veeraraghavan, V.P.; Mony, U.; Renu, K.; Surapaneni, K.M.; Ammar, R.B.; AlZahrani, A.M.; Ahmed, E.A.; Rajendran, P. Effects of Polyphhenols on NcRNAs in Cancer-An Update. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2022, 49, 613–623.
- Tanabe, H.; Pervin, M.; Goto, S.; Isemura, M.; Nakamura, Y. Beneficial Effects of Plant Polyphenols on Obesity Symbiosis Symbiosis Group. Obes. Control 2017, 4, 1–16.
- Sharma, E.; Attri, D.C.; Sati, P.; Dhyani, P.; Szopa, A.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Hano, C.; Calina, D.; Cho, W.C. Recent Updates on Anticancer Mechanisms of Polyphenols. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 1005910.
- Ohishi, T.; Hayakawa, S.; Miyoshi, N. Involvement of MicroRNA Modifications in Anticancer Effects of Major Polyphenols from Green Tea, Coffee, Wine, and Curry. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 15, 1–32.
- Yoshioka, Y.; Ohishi, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Fukutomi, R.; Miyoshi, N. Anti-Cancer Effects of Dietary Polyphenols via ROS-Mediated Pathway with Their Modulation of MicroRNAs. Molecules 2022, 27, 3816.
- Yang, J.; Cao, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y. Curcumin Reduces the Expression of Bcl-2 by Upregulating MiR-15a and MiR-16 in MCF-7 Cells. Med. Oncol. 2010, 27, 1114–1118.
- Tsang, W.P.; Kwok, T.T. Epigallocatechin Gallate Up-Regulation of MiR-16 and Induction of Apoptosis in Human Cancer Cells. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2010, 21, 140–146.
- Sonoki, H.; Sato, T.; Endo, S.; Matsunaga, T.; Yamaguchi, M.; Yamazaki, Y.; Sugatani, J.; Ikari, A. Quercetin Decreases Claudin-2 Expression Mediated by Up-Regulation of MicroRNA MiR-16 in Lung Adenocarcinoma A549 Cells. Nutrients 2015, 7, 4578–4592.
- Zhao, J.; Fang, Z.; Zha, Z.; Sun, Q.; Wang, H.; Sun, M.; Qiao, B. Quercetin Inhibits Cell Viability, Migration and Invasion by Regulating MiR-16/HOXA10 Axis in Oral Cancer. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 847, 11–18.
- Hagiwara, K.; Kosaka, N.; Yoshioka, Y.; Takahashi, R.-U.; Takeshita, F.; Ochiya, T. Stilbene Derivatives Promote Ago2-Dependent Tumour-Suppressive MicroRNA Activity. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 314.
- Azimi, A.; Hagh, M.F.; Talebi, M.; Yousefi, B.; Feizi, A.A.H.p.; Baradaran, B.; Movassaghpour, A.A.; Shamsasenjan, K.; Khanzedeh, T.; Ghaderi, A.H.; et al. Time--and Concentration--Dependent Effects of Resveratrol on MiR 15a and MiR16-1 Expression and Apoptosis in the CCRF-CEM Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Cell Line. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 16, 6463–6468.
- Sun, M.; Estrov, Z.; Ji, Y.; Coombes, K.R.; Harris, D.H.; Kurzrock, R. Curcumin (Diferuloylmethane) Alters the Expression Profiles of MicroRNAs in Human Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 464–473.
- Sreenivasan, S.; Thirumalai, K.; Danda, R.; Krishnakumar, S. Effect of Curcumin on MiRNA Expression in Human Y79 Retinoblastoma Cells. Curr. Eye Res. 2012, 37, 421–428.
- Sibbesen, N.A.; Kopp, K.L.; Litvinov, I.V.; Jønson, L.; Willerslev-Olsen, A.; Fredholm, S.; Petersen, D.L.; Nastasi, C.; Krejsgaard, T.; Lindahl, L.M.; et al. Jak3, STAT3, and STAT5 Inhibit Expression of MiR-22, a Novel Tumor Suppressor MicroRNA, in Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 20555–20569.
- Li, B.-B.; Huang, G.-L.; Li, H.-H.; Kong, X.; He, Z.-W. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Modulates MicroRNA Expression Profiles in Human Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma CNE2 Cells. Chin. Med. J. 2017, 130, 93–99.
- Zhang, C.; Hao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, P. Quercetin Suppresses the Tumorigenesis of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Regulating MicroRNA-22/WNT1/β-Catenin Axis. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 140, 128–136.
- Guo, J.; Li, W.; Shi, H.; Xie, X.; Li, L.; Tang, H.; Wu, M.; Kong, Y.; Yang, L.; Gao, J.; et al. Synergistic Effects of Curcumin with Emodin against the Proliferation and Invasion of Breast Cancer Cells through Upregulation of MiR-34a. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2013, 382, 103–111.
- Sun, C.; Zhang, S.; Liu, C.; Liu, X. Curcumin Promoted MiR-34a Expression and Suppressed Proliferation of Gastric Cancer Cells. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2019, 34, 634–641.
- Toden, S.; Okugawa, Y.; Buhrmann, C.; Nattamai, D.; Anguiano, E.; Baldwin, N.; Shakibaei, M.; Boland, C.R.; Goel, A. Novel Evidence for Curcumin and Boswellic Acid-Induced Chemoprevention through Regulation of MiR-34a and MiR-27a in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Prev. Res. 2015, 8, 431–443.
- Chakrabarti, M.; Khandkar, M.; Banik, N.L.; Ray, S.K. Alterations in Expression of Specific MicroRNAs by Combination of 4-HPR and EGCG Inhibited Growth of Human Malignant Neuroblastoma Cells. Brain Res. 2012, 1454, 1–13.
- Chakrabarti, M.; Ai, W.; Banik, N.L.; Ray, S.K. Overexpression of MiR-7-1 Increases Efficacy of Green Tea Polyphenols for Induction of Apoptosis in Human Malignant Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y and SK-N-DZ Cells. Neurochem. Res. 2013, 38, 420–432.
- Toden, S.; Tran, H.-M.; Tovar-Camargo, O.A.; Okugawa, Y.; Goel, A. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Targets Cancer Stem-like Cells and Enhances 5-Fluorouracil Chemosensitivity in Colorectal Cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 16158–16171.
- Mostafa, S.M.; Gamal-Eldeen, A.M.; Maksoud, N.A.E.; Fahmi, A.A. Epigallocatechin Gallate-Capped Gold Nanoparticles Enhanced the Tumor Suppressors Let-7a and MiR-34a in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2020, 92, e20200574.
- Hsieh, P.-L.; Liao, Y.-W.; Hsieh, C.-W.; Chen, P.-N.; Yu, C.-C. Soy Isoflavone Genistein Impedes Cancer Stemness and Mesenchymal Transition in Head and Neck Cancer through Activating MiR-34a/RTCB Axis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1924.
- Xia, J.; Duan, Q.; Ahmad, A.; Bao, B.; Banerjee, S.; Shi, Y.; Ma, J.; Geng, J.; Chen, Z.; Rahman, K.M.W.; et al. Genistein Inhibits Cell Growth and Induces Apoptosis through Up-Regulation of MiR-34a in Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Curr. Drug Targets 2012, 13, 1750–1756.
- Chiyomaru, T.; Yamamura, S.; Fukuhara, S.; Yoshino, H.; Kinoshita, T.; Majid, S.; Saini, S.; Chang, I.; Tanaka, Y.; Enokida, H.; et al. Genistein Inhibits Prostate Cancer Cell Growth by Targeting MiR-34a and Oncogenic HOTAIR. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70372.
- Otsuka, K.; Yamamoto, Y.; Ochiya, T. Regulatory Role of Resveratrol, a MicroRNA-Controlling Compound, in HNRNPA1 Expression, Which Is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Breast Cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 24718–24730.
- Kumazaki, M.; Noguchi, S.; Yasui, Y.; Iwasaki, J.; Shinohara, H.; Yamada, N.; Akao, Y. Anti-Cancer Effects of Naturally Occurring Compounds through Modulation of Signal Transduction and MiRNA Expression in Human Colon Cancer Cells. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2013, 24, 1849–1858.
- Yao, S.; Gao, M.; Wang, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhan, L.; Wei, B. Upregulation of MicroRNA-34a Sensitizes Ovarian Cancer Cells to Resveratrol by Targeting Bcl-2. Yonsei Med. J. 2021, 62, 691–701.
- Toden, S.; Okugawa, Y.; Jascur, T.; Wodarz, D.; Komarova, N.L.; Buhrmann, C.; Shakibaei, M.; Boland, C.R.; Goel, A. Curcumin Mediates Chemosensitization to 5-Fluorouracil through MiRNA-Induced Suppression of Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Chemoresistant Colorectal Cancer. Carcinogenesis 2015, 36, 355–367.
- Gordon, M.W.; Yan, F.; Zhong, X.; Mazumder, P.B.; Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; Zou, D.; Young, K.H.; Ramos, K.S.; Li, Y. Regulation of P53-Targeting MicroRNAs by Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Implications in the Etiology of Multiple Myeloma. Mol. Carcinog. 2015, 54, 1060–1069.
- Chiyomaru, T.; Fukuhara, S.; Saini, S.; Majid, S.; Deng, G.; Shahryari, V.; Chang, I.; Tanaka, Y.; Enokida, H.; Nakagawa, M.; et al. Long Non-Coding RNA HOTAIR Is Targeted and Regulated by MiR-141 in Human Cancer Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 12550–12565.
- Tahmasebi Mirgani, M.; Isacchi, B.; Sadeghizadeh, M.; Marra, F.; Bilia, A.R.; Mowla, S.J.; Najafi, F.; Babaei, E. Dendrosomal Curcumin Nanoformulation Downregulates Pluripotency Genes via MiR-145 Activation in U87MG Glioblastoma Cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 403–417.
- Liu, T.; Chi, H.; Chen, J.; Chen, C.; Huang, Y.; Xi, H.; Xue, J.; Si, Y. Curcumin Suppresses Proliferation and in Vitro Invasion of Human Prostate Cancer Stem Cells by CeRNA Effect of MiR-145 and LncRNA-ROR. Gene 2017, 631, 29–38.
- Wei, D.; Yang, L.; Lv, B.; Chen, L. Genistein Suppresses Retinoblastoma Cell Viability and Growth and Induces Apoptosis by Upregulating MiR-145 and Inhibiting Its Target ABCE1. Mol. Vis. 2017, 23, 385–394.
- Zhou, J.; Gong, J.; Ding, C.; Chen, G. Quercetin Induces the Apoptosis of Human Ovarian Carcinoma Cells by Upregulating the Expression of MicroRNA-145. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 3127–3131.
- Sachdeva, M.; Liu, Q.; Cao, J.; Lu, Z.; Mo, Y.-Y. Negative Regulation of MiR-145 by C/EBP-β through the Akt Pathway in Cancer Cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 6683–6692.
- Wu, H.; Liu, Q.; Cai, T.; Chen, Y.-D.; Wang, Z.-F. Induction of MicroRNA-146a Is Involved in Curcumin-Mediated Enhancement of Temozolomide Cytotoxicity against Human Glioblastoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 5461–5466.
- Li, Y.; Vandenboom, T.G.; Wang, Z.; Kong, D.; Ali, S.; Philip, P.A.; Sarkar, F.H. MiR-146a Suppresses Invasion of Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 1486–1495.
- Tao, S.-F.; He, H.-F.; Chen, Q. Quercetin Inhibits Proliferation and Invasion Acts by Up-Regulating MiR-146a in Human Breast Cancer Cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 402, 93–100.
- Soubani, O.; Ali, A.S.; Logna, F.; Ali, S.; Philip, P.A.; Sarkar, F.H. Re-Expression of MiR-200 by Novel Approaches Regulates the Expression of PTEN and MT1-MMP in Pancreatic Cancer. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 1563–1571.
- Karimi Dermani, F.; Saidijam, M.; Amini, R.; Mahdavinezhad, A.; Heydari, K.; Najafi, R. Resveratrol Inhibits Proliferation, Invasion, and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition by Increasing MiR-200c Expression in HCT-116 Colorectal Cancer Cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 118, 1547–1555.
- Huang, S.; Wang, L.-L.; Xue, N.-N.; Li, C.; Guo, H.-H.; Ren, T.-K.; Zhan, Y.; Li, W.-B.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.-G.; et al. Chlorogenic Acid Effectively Treats Cancers through Induction of Cancer Cell Differentiation. Theranostics 2019, 9, 6745–6763.
- Gandhy, S.U.; Kim, K.; Larsen, L.; Rosengren, R.J.; Safe, S. Curcumin and Synthetic Analogs Induce Reactive Oxygen Species and Decreases Specificity Protein (Sp) Transcription Factors by Targeting MicroRNAs. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 564.
- Mirzaaghaei, S.; Foroughmand, A.M.; Saki, G.; Shafiei, M. Combination of Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate and Silibinin: A Novel Approach for Targeting Both Tumor and Endothelial Cells. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 8421–8430.
- Dhar, S.; Kumar, A.; Rimando, A.M.; Zhang, X.; Levenson, A.S. Resveratrol and Pterostilbene Epigenetically Restore PTEN Expression by Targeting OncomiRs of the MiR-17 Family in Prostate Cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 27214–27226.
- Dhar, S.; Hicks, C.; Levenson, A.S. Resveratrol and Prostate Cancer: Promising Role for MicroRNAs. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, 1219–1229.
- Wang, Y.; Yang, F.; Xue, J.; Zhou, X.; Luo, L.; Ma, Q.; Chen, Y.-F.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.-L.; Zhao, L. Antischistosomiasis Liver Fibrosis Effects of Chlorogenic Acid through IL-13/MiR-21/Smad7 Signaling Interactions In Vivo and In Vitro. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e01347-16.
- Mudduluru, G.; George-William, J.N.; Muppala, S.; Asangani, I.A.; Kumarswamy, R.; Nelson, L.D.; Allgayer, H. Curcumin Regulates MiR-21 Expression and Inhibits Invasion and Metastasis in Colorectal Cancer. Biosci. Rep. 2011, 31, 185–197.
- Subramaniam, D.; Ponnurangam, S.; Ramamoorthy, P.; Standing, D.; Battafarano, R.J.; Anant, S.; Sharma, P. Curcumin Induces Cell Death in Esophageal Cancer Cells through Modulating Notch Signaling. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30590.
- Zhang, W.; Bai, W.; Zhang, W. MiR-21 Suppresses the Anticancer Activities of Curcumin by Targeting PTEN Gene in Human Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer A549 Cells. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2014, 16, 708–713.
- Taverna, S.; Giallombardo, M.; Pucci, M.; Flugy, A.; Manno, M.; Raccosta, S.; Rolfo, C.; De Leo, G.; Alessandro, R. Curcumin Inhibits in Vitro and in Vivo Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Cells Growth: A Possible Role for Exosomal Disposal of MiR-21. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 21918–21933.
- Yallapu, M.M.; Khan, S.; Maher, D.M.; Ebeling, M.C.; Sundram, V.; Chauhan, N.; Ganju, A.; Balakrishna, S.; Gupta, B.K.; Zafar, N.; et al. Anti-Cancer Activity of Curcumin Loaded Nanoparticles in Prostate Cancer. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 8635–8648.
- Fix, L.N.; Shah, M.; Efferth, T.; Farwell, M.A.; Zhang, B. MicroRNA Expression Profile of MCF-7 Human Breast Cancer Cells and the Effect of Green Tea Polyphenon-60. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2010, 7, 261–277.
- Siddiqui, I.A.; Asim, M.; Hafeez, B.B.; Adhami, V.M.; Tarapore, R.S.; Mukhtar, H. Green Tea Polyphenol EGCG Blunts Androgen Receptor Function in Prostate Cancer. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 1198–1207.
- Zaman, M.S.; Shahryari, V.; Deng, G.; Thamminana, S.; Saini, S.; Majid, S.; Chang, I.; Hirata, H.; Ueno, K.; Yamamura, S.; et al. Up-Regulation of MicroRNA-21 Correlates with Lower Kidney Cancer Survival. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31060.
- Tili, E.; Michaille, J.-J.; Alder, H.; Volinia, S.; Delmas, D.; Latruffe, N.; Croce, C.M. Resveratrol Modulates the Levels of MicroRNAs Targeting Genes Encoding Tumor-Suppressors and Effectors of TGFβ Signaling Pathway in SW480 Cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 80, 2057–2065.
- Sheth, S.; Jajoo, S.; Kaur, T.; Mukherjea, D.; Sheehan, K.; Rybak, L.P.; Ramkumar, V. Resveratrol Reduces Prostate Cancer Growth and Metastasis by Inhibiting the Akt/MicroRNA-21 Pathway. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51655.
- Liu, P.; Liang, H.; Xia, Q.; Li, P.; Kong, H.; Lei, P.; Wang, S.; Tu, Z. Resveratrol Induces Apoptosis of Pancreatic Cancers Cells by Inhibiting MiR-21 Regulation of BCL-2 Expression. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2013, 15, 741–746.
- Li, H.; Jia, Z.; Li, A.; Jenkins, G.; Yang, X.; Hu, J.; Guo, W. Resveratrol Repressed Viability of U251 Cells by MiR-21 Inhibiting of NF-ΚB Pathway. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2013, 382, 137–143.
- Zhou, C.; Ding, J.; Wu, Y. Resveratrol Induces Apoptosis of Bladder Cancer Cells via MiR-21 Regulation of the Akt/Bcl-2 Signaling Pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 9, 1467–1473.
- Zan, L.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, L.; Li, X. Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG) Suppresses Growth and Tumorigenicity in Breast Cancer Cells by Downregulation of MiR-25. Bioengineered 2019, 10, 374–382.
- Noratto, G.D.; Jutooru, I.; Safe, S.; Angel-Morales, G.; Mertens-Talcott, S.U. The Drug Resistance Suppression Induced by Curcuminoids in Colon Cancer SW-480 Cells Is Mediated by Reactive Oxygen Species-Induced Disruption of the MicroRNA-27a-ZBTB10-Sp Axis. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 1638–1648.
- Xia, J.; Cheng, L.; Mei, C.; Ma, J.; Shi, Y.; Zeng, F.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z. Genistein Inhibits Cell Growth and Invasion through Regulation of MiR-27a in Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 5348–5353.
- Xu, L.; Xiang, J.; Shen, J.; Zou, X.; Zhai, S.; Yin, Y.; Li, P.; Wang, X.; Sun, Q. Oncogenic MicroRNA-27a Is a Target for Genistein in Ovarian Cancer Cells. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 1126–1132.
- Sun, Q.; Cong, R.; Yan, H.; Gu, H.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, N.; Chen, J.; Wang, B. Genistein Inhibits Growth of Human Uveal Melanoma Cells and Affects MicroRNA-27a and Target Gene Expression. Oncol. Rep. 2009, 22, 563–567.
- Singh, B.; Shoulson, R.; Chatterjee, A.; Ronghe, A.; Bhat, N.K.; Dim, D.C.; Bhat, H.K. Resveratrol Inhibits Estrogen-Induced Breast Carcinogenesis through Induction of NRF2-Mediated Protective Pathways. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 1872–1880.
- Zeng, J.; Zhang, D.; Wan, X.; Bai, Y.; Yuan, C.; Wang, T.; Yuan, D.; Zhang, C.; Liu, C. Chlorogenic Acid Suppresses MiR-155 and Ameliorates Ulcerative Colitis through the NF-ΚB/NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2020, 64, 1901329–2000452.
- Ma, F.; Liu, F.; Ding, L.; You, M.; Yue, H.; Zhou, Y.; Hou, Y. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Curcumin Are Associated with down Regulating MicroRNA-155 in LPS-Treated Macrophages and Mice. Pharm. Biol. 2017, 55, 1263–1273.
- de la Parra, C.; Castillo-Pichardo, L.; Cruz-Collazo, A.; Cubano, L.; Redis, R.; Calin, G.A.; Dharmawardhane, S. Soy Isoflavone Genistein-Mediated Downregulation of MiR-155 Contributes to the Anticancer Effects of Genistein. Nutr. Cancer 2016, 68, 154–164.
- Boesch-Saadatmandi, C.; Loboda, A.; Wagner, A.E.; Stachurska, A.; Jozkowicz, A.; Dulak, J.; Döring, F.; Wolffram, S.; Rimbach, G. Effect of Quercetin and Its Metabolites Isorhamnetin and Quercetin-3-Glucuronide on Inflammatory Gene Expression: Role of MiR-155. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2011, 22, 293–299.
- Tili, E.; Michaille, J.-J.; Adair, B.; Alder, H.; Limagne, E.; Taccioli, C.; Ferracin, M.; Delmas, D.; Latruffe, N.; Croce, C.M. Resveratrol Decreases the Levels of MiR-155 by Upregulating MiR-663, a MicroRNA Targeting JunB and JunD. Carcinogenesis 2010, 31, 1561–1566.
- Zhang, S.; Tang, D.; Zang, W.; Yin, G.; Dai, J.; Sun, Y.U.; Yang, Z.; Hoffman, R.M.; Guo, X. Synergistic Inhibitory Effect of Traditional Chinese Medicine Astragaloside IV and Curcumin on Tumor Growth and Angiogenesis in an Orthotopic Nude-Mouse Model of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 465–473.
- Allegri, L.; Rosignolo, F.; Mio, C.; Filetti, S.; Baldan, F.; Damante, G. Effects of Nutraceuticals on Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer Cells. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 144, 285–294.
- Chen, Y.; Zaman, M.S.; Deng, G.; Majid, S.; Saini, S.; Liu, J.; Tanaka, Y.; Dahiya, R. MicroRNAs 221/222 and Genistein-Mediated Regulation of ARHI Tumor Suppressor Gene in Prostate Cancer. Cancer Prev. Res. 2011, 4, 76–86.
- Sarkar, S.; Dubaybo, H.; Ali, S.; Goncalves, P.; Kollepara, S.L.; Sethi, S.; Philip, P.A.; Li, Y. Down-Regulation of MiR-221 Inhibits Proliferation of Pancreatic Cancer Cells through up-Regulation of PTEN, P27(Kip1), P57(Kip2), and PUMA. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2013, 3, 465–477.
- Ma, J.; Fang, B.; Zeng, F.; Pang, H.; Zhang, J.; Shi, Y.; Wu, X.; Cheng, L.; Ma, C.; Xia, J.; et al. Curcumin Inhibits Cell Growth and Invasion through Up-Regulation of MiR-7 in Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 231, 82–91.
- Feng, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Yang, G.; Liang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, G. Curcumin Exerts Its Antitumor Activity through Regulation of MiR-7/Skp2/P21 in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells. OncoTargets Ther. 2017, 10, 2377–2388.
- Zhao, S.-F.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.-J.; Shi, X.-Q.; Yu, Z.-J.; Kan, Q.-C. Induction of MicroRNA-9 Mediates Cytotoxicity of Curcumin against SKOV3 Ovarian Cancer Cells. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 3363–3368.
- Xiao, C.; Wang, L.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, J. Curcumin Inhibits Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma SCC-9 Cells Proliferation by Regulating MiR-9 Expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 454, 576–580.
- Gao, S.; Yang, J.; Chen, C.; Chen, J.; Ye, L.; Wang, L.; Wu, J.; Xing, C.; Yu, K. Pure Curcumin Decreases the Expression of WT1 by Upregulation of MiR-15a and MiR-16-1 in Leukemic Cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 31, 27.
- Kang, T.; Sun, W.-L.; Lu, X.-F.; Wang, X.-L.; Jiang, L. MiR-28-5p Mediates the Anti-Proliferative and pro-Apoptotic Effects of Curcumin on Human Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Cells. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 300060520943792.
- Zamani, M.; Sadeghizadeh, M.; Behmanesh, M.; Najafi, F. Dendrosomal Curcumin Increases Expression of the Long Non-Coding RNA Gene MEG3 via up-Regulation of Epi-MiRs in Hepatocellular Cancer. Phytomedicine 2015, 22, 961–967.
- Lu, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, L.; Yu, L.; Zhao, N.; Zhou, X.; Lu, X. Curcumin Increases the Sensitivity of Paclitaxel-Resistant NSCLC Cells to Paclitaxel through MicroRNA-30c-Mediated MTA1 Reduction. Tumour Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317698353.
- Zhang, P.; Bai, H.; Liu, G.; Wang, H.; Chen, F.; Zhang, B.; Zeng, P.; Wu, C.; Peng, C.; Huang, C.; et al. MicroRNA-33b, Upregulated by EF24, a Curcumin Analog, Suppresses the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) and Migratory Potential of Melanoma Cells by Targeting HMGA2. Toxicol. Lett. 2015, 234, 151–161.
- Sun, Q.; Zhang, W.; Guo, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Du, Y.; Zang, W.; Zhao, G. Curcumin Inhibits Cell Growth and Induces Cell Apoptosis through Upregulation of MiR-33b in Gastric Cancer. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 13177–13184.
- Liu, W.-L.; Chang, J.-M.; Chong, I.-W.; Hung, Y.-L.; Chen, Y.-H.; Huang, W.-T.; Kuo, H.-F.; Hsieh, C.-C.; Liu, P.-L. Curcumin Inhibits LIN-28A through the Activation of MiRNA-98 in the Lung Cancer Cell Line A549. Molecules 2017, 22, 929.
- Li, Y.; Sun, W.; Han, N.; Zou, Y.; Yin, D. Curcumin Inhibits Proliferation, Migration, Invasion and Promotes Apoptosis of Retinoblastoma Cell Lines through Modulation of MiR-99a and JAK/STAT Pathway. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1230.
- Bao, B.; Ali, S.; Banerjee, S.; Wang, Z.; Logna, F.; Azmi, A.S.; Kong, D.; Ahmad, A.; Li, Y.; Padhye, S.; et al. Curcumin Analogue CDF Inhibits Pancreatic Tumor Growth by Switching on Suppressor MicroRNAs and Attenuating EZH2 Expression. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 335–345.
- Wu, G.-Q.; Chai, K.-Q.; Zhu, X.-M.; Jiang, H.; Wang, X.; Xue, Q.; Zheng, A.-H.; Zhou, H.-Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X.-C.; et al. Anti-Cancer Effects of Curcumin on Lung Cancer through the Inhibition of EZH2 and NOTCH1. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 26535–26550.
- Wu, C.; Ruan, T.; Liu, W.; Zhu, X.; Pan, J.; Lu, W.; Yan, C.; Tao, K.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, C. Effect and Mechanism of Curcumin on EZH2-MiR-101 Regulatory Feedback Loop in Multiple Myeloma. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 564–575.
- Zhao, J.; Pan, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Xue, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhao, S.; Hou, Y. Dihydroartemisinin and Curcumin Synergistically Induce Apoptosis in SKOV3 Cells Via Upregulation of MiR-124 Targeting Midkine. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 589–601.
- Chen, P.; Wang, H.; Yang, F.; Chen, H.; He, W.; Wang, J. Curcumin Promotes Osteosarcoma Cell Death by Activating MiR-125a/ERRα Signal Pathway. J. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 118, 74–81.
- Yu, D.; An, F.; He, X.; Cao, X. Curcumin Inhibits the Proliferation and Invasion of Human Osteosarcoma Cell Line MG-63 by Regulating MiR-138. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 14946–14952.
- Qiu, B.; Xu, X.; Yi, P.; Hao, Y. Curcumin Reinforces MSC-Derived Exosomes in Attenuating Osteoarthritis via Modulating the MiR-124/NF-KB and MiR-143/ROCK1/TLR9 Signalling Pathways. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 10855–10865.
- Cao, H.; Yu, H.; Feng, Y.; Chen, L.; Liang, F. Curcumin Inhibits Prostate Cancer by Targeting PGK1 in the FOXD3/MiR-143 Axis. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2017, 79, 985–994.
- Liu, J.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Luo, J. Curcumin Sensitizes Prostate Cancer Cells to Radiation Partly via Epigenetic Activation of MiR-143 and MiR-143 Mediated Autophagy Inhibition. J. Drug Target. 2017, 25, 645–652.
- Kronski, E.; Fiori, M.E.; Barbieri, O.; Astigiano, S.; Mirisola, V.; Killian, P.H.; Bruno, A.; Pagani, A.; Rovera, F.; Pfeffer, U.; et al. MiR181b Is Induced by the Chemopreventive Polyphenol Curcumin and Inhibits Breast Cancer Metastasis via Down-Regulation of the Inflammatory Cytokines CXCL1 and -2. Mol. Oncol. 2014, 8, 581–595.
- Ye, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Miao, Q.; Yao, L.; Zhang, J. Curcumin Promotes Apoptosis by Activating the P53-MiR-192-5p/215-XIAP Pathway in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Lett. 2015, 357, 196–205.
- Jin, H.; Qiao, F.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Shang, Y. Curcumin Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis of Human Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells through the Upregulation of MiR-192-5p and Suppression of PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 34, 2782–2789.
- Pan, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, C. MiR-192-5p Upregulation Mediates the Suppression of Curcumin in Human NSCLC Cell Proliferation, Migration and Invasion by Targeting C-Myc and Inactivating the Wnt/Β-catenin Signaling Pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 1594–1604.
- Wang, N.; Feng, T.; Liu, X.; Liu, Q. Curcumin Inhibits Migration and Invasion of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells through up-Regulation of MiR-206 and Suppression of PI3K/AKT/MTOR Signaling Pathway. Acta Pharm. 2020, 70, 399–409.
- Yang, D.; Li, Y.; Zhao, D. Curcumin Induces Apoptotic Cell Death in Human Pancreatic Cancer Cells via the MiR-340/XIAP Signaling Pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 1811–1816.
- Xu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z. Curcumin Suppresses the Malignancy of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer by Modulating the Circ-PRKCA/MiR-384/ITGB1 Pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 138, 111439.
- Li, B.; Shi, C.; Li, B.; Zhao, J.-M.; Wang, L. The Effects of Curcumin on HCT-116 Cells Proliferation and Apoptosis via the MiR-491/PEG10 Pathway. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 3091–3098.
- Fan, H.; Shao, M.; Huang, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Diao, J.; Liu, Y.; Tong, L.I.; Fan, Q. MiR-593 Mediates Curcumin-Induced Radiosensitization of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells via MDR1. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 3729–3734.
- Zhang, S.; Al-Maghout, T.; Bissinger, R.; Zeng, N.; Pelzl, L.; Salker, M.S.; Cheng, A.; Singh, Y.; Lang, F. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG) up-Regulates MiR-15b Expression Thus Attenuating Store Operated Calcium Entry (SOCE) into Murine CD4+ T Cells and Human Leukaemic T Cell Lymphoblasts. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 89500–89514.
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, X.; Jiang, J.; Wan, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, P. Epigallocatechin Gallate Reverses Gastric Cancer by Regulating the Long Noncoding RNA LINC00511/MiR-29b/KDM2A Axis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165856.
- Jiang, P.; Xu, C.; Chen, L.; Chen, A.; Wu, X.; Zhou, M.; Haq, I.U.; Mariyam, Z.; Feng, Q. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Inhibited Cancer Stem Cell-like Properties by Targeting Hsa-Mir-485-5p/RXRα in Lung Cancer. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 8623–8635.
- Yamada, S.; Tsukamoto, S.; Huang, Y.; Makio, A.; Kumazoe, M.; Yamashita, S.; Tachibana, H. Epigallocatechin-3-O-Gallate up-Regulates MicroRNA-Let-7b Expression by Activating 67-KDa Laminin Receptor Signaling in Melanoma Cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19225.
- Chiyomaru, T.; Yamamura, S.; Fukuhara, S.; Hidaka, H.; Majid, S.; Saini, S.; Arora, S.; Deng, G.; Shahryari, V.; Chang, I.; et al. Genistein Up-Regulates Tumor Suppressor MicroRNA-574-3p in Prostate Cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58929.
- Ma, C.-H.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Tang, L.-H.; Yang, X.-J.; Cui, W.-M.; Han, C.-C.; Ji, W.-Y. MicroRNA-1469, a P53-Responsive MicroRNA Promotes Genistein Induced Apoptosis by Targeting Mcl1 in Human Laryngeal Cancer Cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 665–671.
- Asama, H.; Suzuki, R.; Hikichi, T.; Takagi, T.; Masamune, A.; Ohira, H. MicroRNA Let-7d Targets Thrombospondin-1 and Inhibits the Activation of Human Pancreatic Stellate Cells. Pancreatology 2019, 19, 196–203.
- Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Xia, C. Quercetin Antagonizes Esophagus Cancer by Modulating MiR-1-3p/TAGLN2 Pathway-Dependent Growth and Metastasis. Nutr. Cancer 2022, 74, 1872–1881.
- Wang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Lu, H.; Wang, H.; Feng, H.; Xu, J.; Zhang, B. Quercetin Radiosensitizes Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells through the Regulation of MiR-16-5p/WEE1 Axis. IUBMB Life 2020, 72, 1012–1022.
- Chai, R.; Xu, C.; Lu, L.; Liu, X.; Ma, Z. Quercetin Inhibits Proliferation of and Induces Apoptosis in Non-Small-Cell Lung Carcinoma via the LncRNA SNHG7/MiR-34a-5p Pathway. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2021, 43, 693–703.
- MacKenzie, T.N.; Mujumdar, N.; Banerjee, S.; Sangwan, V.; Sarver, A.; Vickers, S.; Subramanian, S.; Saluja, A.K. Triptolide Induces the Expression of MiR-142-3p: A Negative Regulator of Heat Shock Protein 70 and Pancreatic Cancer Cell Proliferation. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 1266–1275.
- Hu, S.-A.; Cheng, J.; Zhao, W.-H.; Zhao, H.-Y. Quercetin Induces Apoptosis in Meningioma Cells through the MiR-197/IGFBP5 Cascade. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 80, 103439.
- Nwaeburu, C.C.; Abukiwan, A.; Zhao, Z.; Herr, I. Quercetin-Induced MiR-200b-3p Regulates the Mode of Self-Renewing Divisions in Pancreatic Cancer. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 23.
- Zhang, X.; Guo, Q.; Chen, J.; Chen, Z. Quercetin Enhances Cisplatin Sensitivity of Human Osteosarcoma Cells by Modulating MicroRNA-217-KRAS Axis. Mol. Cells 2015, 38, 638–642.
- Park, S.; Lim, W.; Bazer, F.W.; Whang, K.-Y.; Song, G. Quercetin Inhibits Proliferation of Endometriosis Regulating Cyclin D1 and Its Target MicroRNAs in Vitro and in Vivo. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2019, 63, 87–100.
- Chen, L.; Xia, J.-S.; Wu, J.-H.; Chen, Y.-G.; Qiu, C.-J. Quercetin Suppresses Cell Survival and Invasion in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma via the MiR-1254/CD36 Cascade in Vitro. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2021, 40, 1413–1421.
- Shaalan, Y.M.; Handoussa, H.; Youness, R.A.; Assal, R.A.; El-Khatib, A.H.; Linscheid, M.W.; El Tayebi, H.M.; Abdelaziz, A.I. Destabilizing the Interplay between MiR-1275 and IGF2BPs by Tamarix Articulata and Quercetin in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 2217–2220.
- Appari, M.; Babu, K.R.; Kaczorowski, A.; Gross, W.; Herr, I. Sulforaphane, Quercetin and Catechins Complement Each Other in Elimination of Advanced Pancreatic Cancer by MiR-Let-7 Induction and K-Ras Inhibition. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 45, 1391–1400.
- Nwaeburu, C.C.; Bauer, N.; Zhao, Z.; Abukiwan, A.; Gladkich, J.; Benner, A.; Herr, I. Up-Regulation of MicroRNA Let-7c by Quercetin Inhibits Pancreatic Cancer Progression by Activation of Numbl. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 58367–58380.
- El-Kott, A.F.; Shati, A.A.; Ali Al-Kahtani, M.; Alharbi, S.A. The Apoptotic Effect of Resveratrol in Ovarian Cancer Cells Is Associated with Downregulation of Galectin-3 and Stimulating MiR-424-3p Transcription. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e13072.
- Zhou, W.; Wang, S.; Ying, Y.; Zhou, R.; Mao, P. MiR-196b/MiR-1290 Participate in the Antitumor Effect of Resveratrol via Regulation of IGFBP3 Expression in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 1075–1083.
- Li, X.; Xie, W.; Xie, C.; Huang, C.; Zhu, J.; Liang, Z.; Deng, F.; Zhu, M.; Zhu, W.; Wu, R.; et al. Curcumin Modulates MiR-19/PTEN/AKT/P53 Axis to Suppress Bisphenol A-Induced MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cell Proliferation. Phytother. Res. 2014, 28, 1553–1560.
- Gao, W.; Chan, J.Y.-W.; Wong, T.-S. Curcumin Exerts Inhibitory Effects on Undifferentiated Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma by Inhibiting the Expression of MiR-125a-5p. Clin. Sci. 2014, 127, 571–579.
- Dou, H.; Shen, R.; Tao, J.; Huang, L.; Shi, H.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, T. Curcumin Suppresses the Colon Cancer Proliferation by Inhibiting Wnt/β-Catenin Pathways via MiR-130a. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 877.
- Wang, K.; Tan, S.-L.; Lu, Q.; Xu, R.; Cao, J.; Wu, S.-Q.; Wang, Y.-H.; Zhao, X.-K.; Zhong, Z.-H. Curcumin Suppresses MicroRNA-7641-Mediated Regulation of P16 Expression in Bladder Cancer. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2018, 46, 1357–1368.
- Jiang, P.; Wu, X.; Wang, X.; Huang, W.; Feng, Q. NEAT1 Upregulates EGCG-Induced CTR1 to Enhance Cisplatin Sensitivity in Lung Cancer Cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 43337–43351.
- Zaman, M.S.; Thamminana, S.; Shahryari, V.; Chiyomaru, T.; Deng, G.; Saini, S.; Majid, S.; Fukuhara, S.; Chang, I.; Arora, S.; et al. Inhibition of PTEN Gene Expression by Oncogenic MiR-23b-3p in Renal Cancer. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50203.
- Chiyomaru, T.; Yamamura, S.; Zaman, M.S.; Majid, S.; Deng, G.; Shahryari, V.; Saini, S.; Hirata, H.; Ueno, K.; Chang, I.; et al. Genistein Suppresses Prostate Cancer Growth through Inhibition of Oncogenic MicroRNA-151. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43812.
- Ma, J.; Cheng, L.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Shi, Y.; Zeng, F.; Miele, L.; Sarkar, F.H.; Xia, J.; Wang, Z. Genistein Down-Regulates MiR-223 Expression in Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Curr. Drug Targets 2013, 14, 1150–1156.
- Ma, J.; Zeng, F.; Ma, C.; Pang, H.; Fang, B.; Lian, C.; Yin, B.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Xia, J. Synergistic Reversal Effect of Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition by MiR-223 Inhibitor and Genistein in Gemcitabine-Resistant Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2016, 6, 1384–1395.
- Yu, Y.; Xing, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, S.; Li, X.; Gao, C. Soy Isoflavone Genistein Inhibits Hsa_circ_0031250/MiR-873-5p/FOXM1 Axis to Suppress Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Progression. IUBMB Life 2021, 73, 92–107.
- Hirata, H.; Hinoda, Y.; Shahryari, V.; Deng, G.; Tanaka, Y.; Tabatabai, Z.L.; Dahiya, R. Genistein Downregulates Onco-MiR-1260b and Upregulates SFRP1 and Smad4 via Demethylation and Histone Modification in Prostate Cancer Cells. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 1645–1654.
- Hirata, H.; Ueno, K.; Nakajima, K.; Tabatabai, Z.L.; Hinoda, Y.; Ishii, N.; Dahiya, R. Genistein Downregulates Onco-MiR-1260b and Inhibits Wnt-Signalling in Renal Cancer Cells. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 2070–2078.
- C Yilmaz, U.; Bagca, B.G.; Karaca, E.; Durmaz, A.; Durmaz, B.; Aykut, A.; Kayalar, H.; Avci, C.B.; Susluer, S.Y.; Pariltay, E.; et al. Propolis Extract Regulates MicroRNA Expression in Glioblastoma and Brain Cancer Stem Cells. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2022, 22, 378–389.
- Ma, B.; Hottiger, M.O. Crosstalk between Wnt/β-Catenin and NF-ΚB Signaling Pathway during Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 378.
- Vallée, A.; Lecarpentier, Y. Crosstalk Between Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma and the Canonical WNT/β-Catenin Pathway in Chronic Inflammation and Oxidative Stress During Carcinogenesis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 745.
- Lee, S.H.; Hong, H.S.; Liu, Z.X.; Kim, R.H.; Kang, M.K.; Park, N.-H.; Shin, K.-H. TNFα Enhances Cancer Stem Cell-like Phenotype via Notch-Hes1 Activation in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 424, 58–64.
- Zhang, L.; Jiao, M.; Wu, K.; Li, L.; Zhu, G.; Wang, X.; He, D.; Wu, D. TNF-α Induced Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition Increases Stemness Properties in Renal Cell Carcinoma Cells. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2014, 7, 4951–4958.
- Chen, Y.; Wen, H.; Zhou, C.; Su, Q.; Lin, Y.; Xie, Y.; Huang, Y.; Qiu, Q.; Lin, J.; Huang, X.; et al. TNF-α Derived from M2 Tumor-Associated Macrophages Promotes Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Cancer Stemness through the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway in SMMC-7721 Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2019, 378, 41–50.
