MSTN is a gene that makes instructions for producing the protein myostatin, a protein that is part of the transforming growth factor beta family (TGFβ). The TGFβ family of proteins control the growth of tissues in the body, myostatin is found nearly exclusively in the skeletal muscles where it is active before and after birth. The protein actually controls skeletal growth by restraining it, preventing muscles becoming excessively large. Current research that surrounds myostatin is based around its potential treatment in muscle wasting disorders, animals that have mutations in the encoding gene MSTN show greater muscle mass, strength and in some circumstances reduced bodyfat, which can be known as myostatin-related muscle hypertrophy.
This study aimed to see the prevalence of mutations in the male bodybuilder population (n = 92) and if having a mutation had any affect on their muscle size and/or muscle performance. The study which looked at mutation prevalence in rs1805086, arm circumference, pull-up max and push-up max.
The results show that 17% (16) of the subject group had one mutation (AG), 83% (76) had the common outcome (AA) and 0% (0) had two mutations (GG). Those with the AG outcome had an average arm circumference of 46.37cmcompared with AA which had an average of 42.02cm. Those with the AG outcome had an average pull-up max score of 21 compared with AA with an average of 12. Those with the AG outcome had an average push-up max of 61 compared with AA with an average of 40.
The study clearly shows that those with a mutation are rare, however the mutation does appear to give the subject a performance and size advantage over those with the common outcome.
- genetics
- bodybuilding
- myostatin
- MSTN
- genes
- weightlifting
- sports
- fitness
Introduction.
MSTN is a gene that makes instructions for producing the protein myostatin, a protein that is part of the transforming growth factor beta family (TGFβ). The TGFβ family of proteins control the growth of tissues in the body, myostatin is found nearly exclusively in the skeletal muscles where it is active before and after birth. The protein actually controls skeletal growth by restraining it, preventing muscles becoming excessively large. Current research that surrounds myostatin is based around its potential treatment in muscle wasting disorders, animals that have mutations in the encoding gene MSTN show greater muscle mass, strength and in some circumstances reduced bodyfat, which can be known as myostatin-related muscle hypertrophy. [1]
This is a study based on the extracted data from an anonymised data bank of genetic and individual data, it is aimed at building a basis for research on the gene MSTN and how it interacts with athletes.
Aim.
The study aims to discover if the gene MSTN, in particular mutations in the SNP rs1805086 have any impact on the male bodybuilding population (n = 92) from a muscle hypertrophy and muscle performance standpoint.
The secondary aim is to speculate if rare mutations are more prevalent in those who decide to choose a sport such as bodybuilding, as research indicates that mutations in MSTN can illicit larger muscle mass and a reduction in bodyfat.
Methods.
Data is taken from an anonymised genetic and individual data bank (Muhdo Health ltd.), which gains consent for research purposes. Individuals that fall within the study criteria (M, 22-29y/o, training for bodybuilding for 3 years +), complete the following tests and record scores:
Pull-up max – As many full pull-ups (palms pronated) as possible before having to cease (let go of the bar). No straps were permitted.
Push-up max – As many push-ups within one-minute, full push-ups.
Arm circumference – Measured arm circumference when arm is flexed.
This data is added to already collected data and the genetic outcome for rs1805086.
Results.
|
Individual |
rs1805086 (MSTN) variant: |
Pull-Up Results (60s) |
Push-Up Results (60s) |
Sex |
Age |
Weight KG |
Height CMs |
Arm Circumfrence CMs flexed |
Sport (3 years +) |
|
AOX1 |
AA |
11 |
48 |
M |
26 |
77 |
178 |
42.2 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX2 |
AA |
14 |
50 |
M |
25 |
73 |
179 |
41 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX3 |
AA |
12 |
38 |
M |
28 |
82 |
181 |
43 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX4 |
AA |
9 |
37 |
M |
27 |
85 |
180 |
41 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX5 |
AA |
14 |
34 |
M |
23 |
87 |
178 |
42 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX6 |
AA |
16 |
39 |
M |
28 |
82 |
182 |
43 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX7 |
AG |
18 |
62 |
M |
24 |
91 |
181 |
46 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX8 |
AA |
15 |
58 |
M |
26 |
85 |
182 |
43 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX9 |
AA |
10 |
50 |
M |
28 |
81 |
173 |
42 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX10 |
AG |
19 |
59 |
M |
23 |
90 |
183 |
45 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX11 |
AA |
10 |
34 |
M |
22 |
81 |
168 |
40 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX12 |
AA |
9 |
41 |
M |
25 |
78 |
175 |
41 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX13 |
AA |
12 |
43 |
M |
27 |
82 |
177 |
42 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX14 |
AA |
11 |
46 |
M |
23 |
84 |
173 |
43 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX15 |
AA |
15 |
32 |
M |
23 |
88 |
181 |
44 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX16 |
AA |
13 |
34 |
M |
28 |
87 |
181 |
43 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX17 |
AA |
16 |
38 |
M |
27 |
86 |
180 |
44 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX18 |
AA |
12 |
39 |
M |
26 |
82 |
184 |
42 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX19 |
AA |
11 |
41 |
M |
24 |
81 |
182 |
41 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX20 |
AA |
8 |
30 |
M |
25 |
79 |
173 |
42 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX21 |
AA |
9 |
26 |
M |
28 |
78 |
165 |
45 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX22 |
AA |
10 |
38 |
M |
23 |
72 |
181 |
40 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX23 |
AG |
21 |
63 |
M |
22 |
89 |
180 |
44 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX24 |
AA |
17 |
42 |
M |
29 |
76 |
172 |
43 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX25 |
AA |
13 |
47 |
M |
23 |
86 |
180 |
42 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX26 |
AA |
16 |
49 |
M |
24 |
73 |
171 |
40 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX27 |
AA |
18 |
51 |
M |
25 |
77 |
179 |
40 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX28 |
AA |
15 |
38 |
M |
28 |
79 |
176 |
42 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX29 |
AA |
17 |
42 |
M |
29 |
81 |
180 |
43 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX30 |
AA |
11 |
39 |
M |
25 |
82 |
181 |
44 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX31 |
AA |
9 |
33 |
M |
25 |
86 |
185 |
42 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX32 |
AG |
19 |
57 |
M |
26 |
93 |
183 |
48 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX33 |
AA |
10 |
38 |
M |
28 |
81 |
180 |
42 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX34 |
AA |
11 |
29 |
M |
23 |
72 |
176 |
41 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX35 |
AA |
15 |
49 |
M |
23 |
80 |
177 |
40 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX36 |
AA |
13 |
55 |
M |
26 |
71 |
175 |
44 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX37 |
AA |
11 |
51 |
M |
27 |
66 |
170 |
43 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX38 |
AA |
9 |
32 |
M |
28 |
91 |
184 |
42 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX39 |
AA |
10 |
42 |
M |
25 |
83 |
180 |
40 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX40 |
AA |
12 |
51 |
M |
24 |
88 |
182 |
41 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX41 |
AA |
11 |
43 |
M |
23 |
80 |
173 |
40 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX42 |
AA |
6 |
28 |
M |
28 |
72 |
178 |
40 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX43 |
AA |
8 |
33 |
M |
23 |
75 |
167 |
41 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX44 |
AG |
20 |
62 |
M |
26 |
94 |
190 |
47 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX45 |
AG |
25 |
65 |
M |
25 |
92 |
183 |
45 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX46 |
AG |
21 |
66 |
M |
26 |
98 |
180 |
45 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX47 |
AA |
11 |
57 |
M |
28 |
83 |
171 |
41 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX48 |
AA |
9 |
47 |
M |
27 |
81 |
180 |
43 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX49 |
AA |
13 |
39 |
M |
26 |
82 |
181 |
40 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX50 |
AA |
18 |
51 |
M |
25 |
80 |
179 |
41 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX51 |
AA |
14 |
52 |
M |
25 |
84 |
180 |
43 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX52 |
AA |
12 |
42 |
M |
23 |
85 |
181 |
43 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX53 |
AA |
16 |
45 |
M |
29 |
84 |
189 |
41 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX54 |
AG |
18 |
59 |
M |
24 |
92 |
183 |
45 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX55 |
AG |
21 |
58 |
M |
23 |
91 |
180 |
44 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX56 |
AG |
28 |
61 |
M |
23 |
88 |
181 |
45 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX57 |
AG |
17 |
60 |
M |
27 |
94 |
182 |
43 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX58 |
AG |
24 |
58 |
M |
28 |
101 |
192 |
49 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX59 |
AA |
9 |
43 |
M |
29 |
74 |
182 |
45 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX60 |
AA |
12 |
37 |
M |
25 |
73 |
183 |
44 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX61 |
AA |
17 |
44 |
M |
24 |
85 |
175 |
43 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX62 |
AA |
14 |
45 |
M |
25 |
87 |
182 |
42 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX63 |
AA |
16 |
48 |
M |
29 |
88 |
181 |
41 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX64 |
AA |
12 |
32 |
M |
22 |
81 |
180 |
43 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX65 |
AA |
11 |
31 |
M |
23 |
83 |
179 |
42 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX66 |
AA |
9 |
28 |
M |
24 |
85 |
174 |
41 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX67 |
AA |
13 |
34 |
M |
29 |
86 |
180 |
43 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX68 |
AA |
10 |
38 |
M |
25 |
90 |
181 |
45 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX69 |
AA |
9 |
27 |
M |
25 |
82 |
180 |
42 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX70 |
AA |
16 |
53 |
M |
27 |
85 |
178 |
41 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX71 |
AA |
14 |
42 |
M |
27 |
84 |
181 |
44 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX72 |
AA |
12 |
48 |
M |
26 |
81 |
183 |
45 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX73 |
AG |
20 |
61 |
M |
25 |
91 |
180 |
44 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX74 |
AG |
18 |
69 |
M |
23 |
89 |
184 |
46 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX75 |
AA |
13 |
38 |
M |
24 |
81 |
181 |
41 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX76 |
AA |
17 |
41 |
M |
29 |
73 |
180 |
40 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX77 |
AA |
13 |
38 |
M |
25 |
77 |
179 |
41 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX78 |
AA |
18 |
49 |
M |
22 |
84 |
183 |
42 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX79 |
AA |
16 |
41 |
M |
24 |
89 |
177 |
43 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX80 |
AA |
17 |
37 |
M |
28 |
90 |
172 |
41 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX81 |
AG |
28 |
61 |
M |
27 |
103 |
188 |
51 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX82 |
AA |
15 |
38 |
M |
24 |
77 |
183 |
42 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX83 |
AA |
17 |
36 |
M |
26 |
79 |
181 |
42 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX84 |
AA |
16 |
38 |
M |
25 |
81 |
182 |
41 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX85 |
AA |
15 |
41 |
M |
25 |
83 |
181 |
40 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX86 |
AA |
12 |
23 |
M |
25 |
71 |
179 |
42 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX87 |
AA |
11 |
33 |
M |
24 |
70 |
180 |
43 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX88 |
AA |
18 |
54 |
M |
23 |
69 |
168 |
44 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX89 |
AG |
30 |
58 |
M |
24 |
96 |
181 |
45 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX90 |
AA |
19 |
43 |
M |
23 |
86 |
179 |
41 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX91 |
AA |
9 |
44 |
M |
29 |
84 |
177 |
43 |
Bodybuilding |
|
AOX92 |
AA |
8 |
46 |
M |
25 |
88 |
181 |
41 |
Bodybuilding |
Table 1. Data set for study.
Population data
The population data for the group showed:
76 had the AA genotype
16 had the AG genotype
0 had the GG genotype
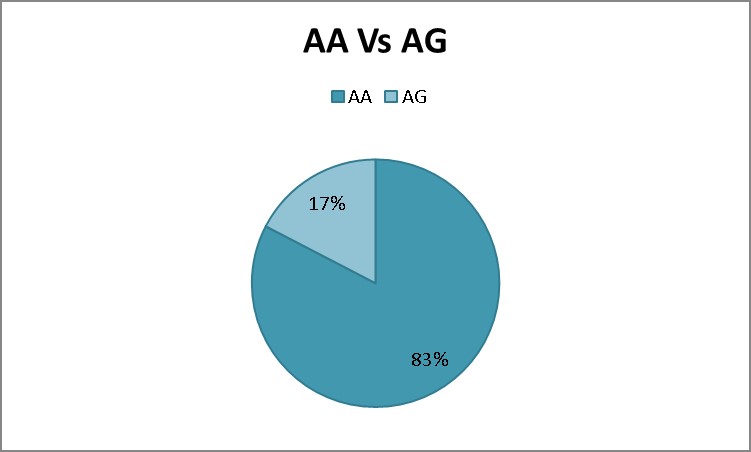
Figure 1: Averages for the bodybuilding population.
Pull-up max data
The Pull-up max average data showed:
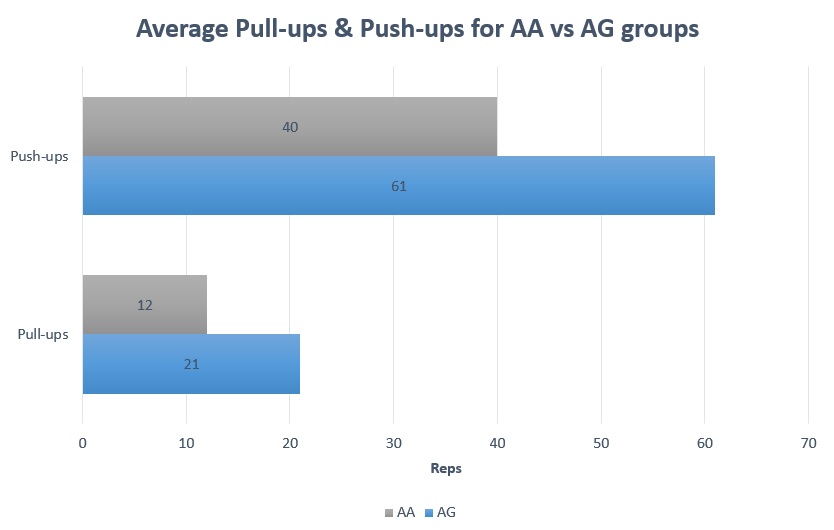
21 (rounded down) Pull-ups completed in the AG group
12 (rounded down) Pull-ups completed in the AA group
Push-up max data
The Push-up max average data showed:
61 (rounded down) Push-ups completed in one minute in the AG group
40 (rounded down) Push-ups completed in one minute in the AA group
Figure 1. Average results for push-ups and pull-ups in the AA and AG group.
Arm circumference data
The arm circumference average data showed:
46.375cm arm circumference in the AG group
42.028cm arm circumference in the AA group
ConDisclusion and follow-upussion.
The pris look into specific collated data has shown that the mutations in the genemary finding in this study is that carriers of one G variant are uncommon with no participants being homozygous for GG in rs1805086. Heterozygotes had significantly increased average arm size (46.375cm in AG vs 42.028cm in AA) and improved physical test outcomes. Although more research is required and that physical ability is likely polygenic, MSTN may illicit advantages for thoseis a good candidate gene to be analysed in any polygenic physical attribute analysis. We analysed physical strength stamina through two common tests the pull-up and push-up tests, both common exercises utilised in bodybuilding aprogrammes[2][3]. Bodybuildindg sports in general due to an increarequires hypertrophy of muscle tissue, this involves the increase of muscle size through either increasing myofibril size or/and sarcoplasmic storage (mainly glycogen and myoglobin) [4][5]. The most edffective approach to building muscle performance and apparremains a hotly debated topic, however it is considered that resistance training with adequate protein intake is the most applicable method [6]. As myostatin helps control muscle size. A deeper look into a greater number of subjects will offer a greater insight into how much impacgrowth and the level of MSTN is altered by the MSTN gene those born with certain mutations can be expected to have increased strength and muscle mass, in 2004 a German boy was diagnosed with a mutation in both copies of the MSTN gene which we failed to replicate in this study, however this mutation gave him significantly stronger muscles then his peers [7]. Due to this one gene may play in sports and the general populous.
Ae potential of myostatin inhibition causing greater athletic ability, muscle hyperplasia and hypertrophy there is worry that drugs that can alter the MSTN gene or affect myostatin full follow-up study with lab cevels will be abused by athletes, hence they are banned by the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA)[8].
Conclusion and follow-up.
This look introlled subjects during o specific collated data has shown that the mutations in the gene MSTN may illicit advantages for those in bodybuilding and sports in general due to an increased muscle performance testing and inand apparent muscle size. A deeper look into a greater number is recommend to draw firm conclusionof subjects will offer a greater insight into how much impact this one gene may play in sports and the general populous.
References
- Myostatin Related Hypertrophy . U.S. National Library of Medicine . Retrieved 2019-1-14
- How (And Why!) To Do Push-ups . www.bodybuilding.com. Retrieved 2020-11-2
- The benefits of pullups . www.powerbody.co.uk. Retrieved 2020-11-2
- Michael D. Roberts; Cody T. Haun; Christopher G. Vann; Shelby C. Osburn; Kaelin C. Young; Sarcoplasmic Hypertrophy in Skeletal Muscle: A Scientific “Unicorn” or Resistance Training Adaptation?. Frontiers in Physiology 2020, 11, 816, 10.3389/fphys.2020.00816.
- Cody T. Haun; Christopher G. Vann; Shelby C. Osburn; Petey W. Mumford; Paul A. Roberson; Matthew A. Romero; Carlton D. Fox; Christopher A. Johnson; Hailey A. Parry; Andreas N. Kavazis; et al.Jordan R. MoonVeera L. D. BadisaBenjamin M. MwashoteVictor IbeanusiKaelin C. YoungMichael D. Roberts Muscle fiber hypertrophy in response to 6 weeks of high-volume resistance training in trained young men is largely attributed to sarcoplasmic hypertrophy. PLOS ONE 2019, 14, e0215267, 10.1371/journal.pone.0215267.
- Michal Krzysztofik; Michal Wilk; Grzegorz Wojdala; Artur Golas; Maximizing Muscle Hypertrophy: A Systematic Review of Advanced Resistance Training Techniques and Methods. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2019, 16, 4897, 10.3390/ijerph16244897.
- Genetic mutation turns tot into superboy . www.nbcnews.com. Retrieved 2020-11-2
- PROHIBITED AT ALL TIMES . www.wada-ama.org. Retrieved 2020-11-2