A crossword is a word puzzle and word search game that usually takes the form of a square or a rectangular grid of white- and black-shaded squares. The game's goal is to fill the white squares with letters, forming words or phrases, by solving clues, which lead to the answers. In languages that are written left-to-right, the answer words and phrases are placed in the grid from left to right and from top to bottom. The shaded squares are used to separate the words or phrases.
- rectangular grid
- crossword
- square
1. Types
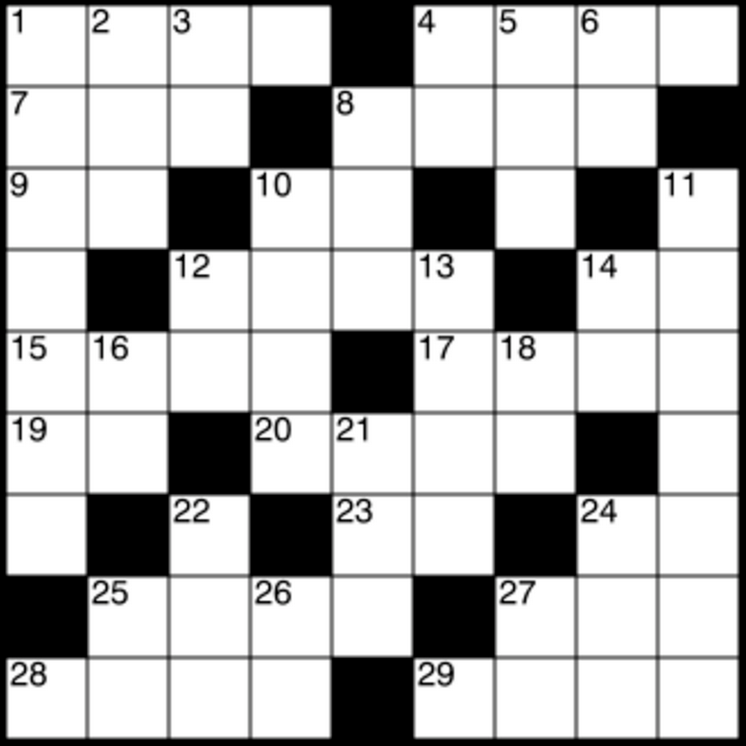

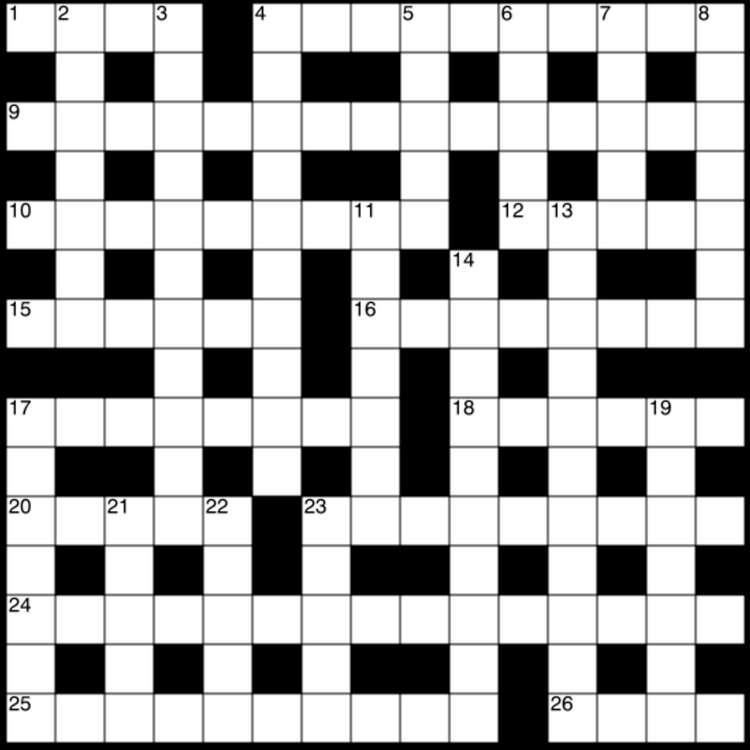

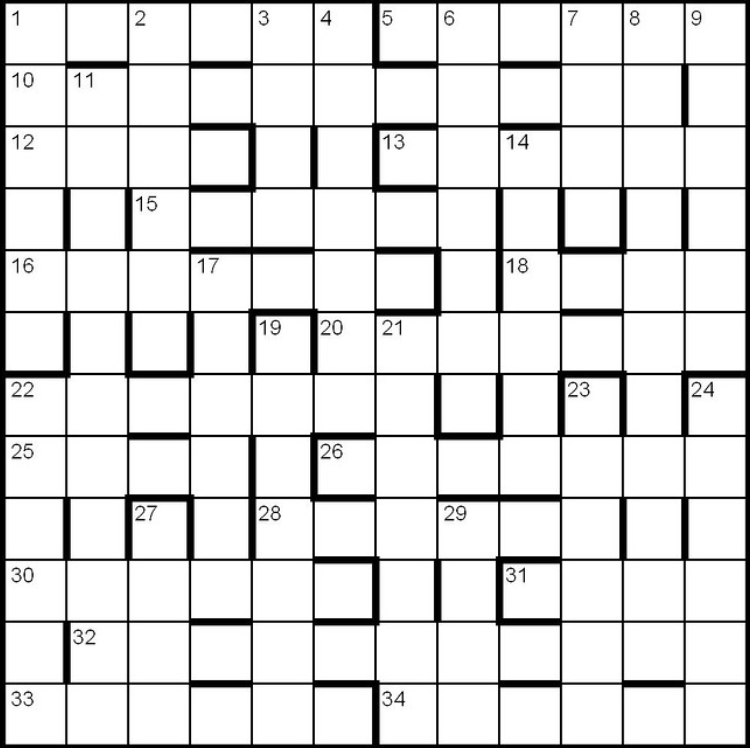
Crossword grids such as those appearing in most North American newspapers and magazines feature solid areas of white squares. Every letter is checked (i.e. is part of both an "across" word and a "down" word) and usually each answer must contain at least three letters. In such puzzles shaded squares are typically limited to about one-sixth of the total. Crossword grids elsewhere, such as in United Kingdom , South Africa , India and Australia , have a lattice-like structure, with a higher percentage of shaded squares (around 25%), leaving about half the letters in an answer unchecked. For example, if the top row has an answer running all the way across, there will often be no across answers in the second row.
Another tradition in puzzle design (in North America, India , and Britain particularly) is that the grid should have 180-degree rotational (also known as "radial") symmetry, so that its pattern appears the same if the paper is turned upside down. Most puzzle designs also require that all white cells be orthogonally contiguous (that is, connected in one mass through shared sides, to form a single polyomino).
The design of Japanese crossword grids often follows two additional rules: that shaded cells may not share a side (i.e. they may not be orthogonally contiguous) and that the corner squares must be white.
The "Swedish-style" grid (picture crosswords) uses no clue numbers, as the clues are contained in the cells which do not contain answers. Arrows indicate in which direction the clues have to be answered: vertical or horizontal. This style of grid is also used in several countries other than Sweden, often in magazines, but also in daily newspapers. The grid often has one or more photos replacing a block of squares as a clue to one or several answers, for example, the name of a pop star, or some kind of rhyme or phrase that can be associated with the photo. These puzzles usually have no symmetry in the grid but instead often have a common theme (literature, music, nature, geography, events of a special year, etc.)
Substantial variants from the usual forms exist. Two of the common ones are barred crosswords, which use bold lines between squares (instead of shaded squares) to separate answers, and circular designs, with answers entered either radially or in concentric circles. "Free form" crosswords ("criss-cross" puzzles), which have simple, asymmetric designs, are often seen on school worksheets, children's menus, and other entertainment for children. Grids forming shapes other than squares are also occasionally used.
Puzzles are often one of several standard sizes. For example, many weekday newspaper puzzles (such as the American New York Times crossword puzzle) are 15×15 squares, while weekend puzzles may be 21×21, 23×23, or 25×25. The New York Times puzzles also set a common pattern for American crosswords by increasing in difficulty throughout the week: their Monday puzzles are the easiest and the puzzles get harder each day until Saturday. Their larger Sunday puzzle is about the same level of difficulty as a weekday-size Thursday puzzle.[1] This has led U.S. solvers to use the day of the week as a shorthand when describing how hard a puzzle is: e.g. an easy puzzle may be referred to as a "Monday" or a "Tuesday", a medium-difficulty puzzle as a "Wednesday", and a truly difficult puzzle as a "Saturday". One of the smallest crosswords in general distribution is a 4×4 crossword compiled daily by John Wilmes, distributed online by USA Today as "QuickCross" and by Universal Uclick as "PlayFour".
Typically clues appear outside the grid, divided into an Across list and a Down list; the first cell of each entry contains a number referenced by the clue lists. For example, the answer to a clue labeled "17 Down" is entered with the first letter in the cell numbered "17", proceeding down from there. Numbers are almost never repeated; numbered cells are numbered consecutively, usually from left to right across each row, starting with the top row and proceeding downward. Some Japanese crosswords are numbered from top to bottom down each column, starting with the leftmost column and proceeding right.
2. Clues: Conventions and Types
2.1. Orthography
Capitalization of answer letters is conventionally ignored; crossword puzzles are typically filled in, and their answer sheets are almost universally published, in all caps, except in the rare cases of ambigrams. This ensures a proper name can have its initial capital letter checked with a non-capitalizable letter in the intersecting clue. Diacritical markings in foreign loanwords (or foreign-language words appearing in English-language puzzles) are ignored for similar reasons.
2.2. Straight or Quick
Some crossword clues, called straight or quick clues, are simple definitions of the answers. Some clues may feature anagrams, and these are usually explicitly described as such. Often, a straight clue is not in itself sufficient to distinguish between several possible answers, either because multiple synonymous answers may fit or because the clue itself is a homonym (e.g., "Lead" as in to be ahead in a contest or "Lead" as in the element), so the solver must make use of checks to establish the correct answer with certainty. For example, the answer to the clue "PC key" for a three-letter answer could be ESC, ALT, TAB, DEL, or INS, so until a check is filled in, giving at least one of the letters, the correct answer cannot be determined.
In most American-style crosswords,[2] the majority of the clues in the puzzle are straight clues,[3] with the remainder being one of the other types described below.
Crossword clues are generally consistent with the solutions. For instance, clues and their solutions should always agree in tense, number, and degree.[4] If a clue is in the past tense, so is the answer: thus "Traveled on horseback" would be a valid clue for the solution RODE, but not for RIDE. Similarly, "Family members" would be a valid clue for AUNTS but not UNCLE, while "More joyful" could clue HAPPIER but not HAPPIEST.
Some clue examples:
- Fill-in-the-blank clues are often the easiest in a puzzle and a good place to start solving, e.g., "_____ Boleyn" = ANNE.
- "Before and after" clues feature one word that is part of two phrases, often designated with parentheses and brackets, e.g., (Doing [____) keeper] = TIME.
- A question mark at the end of clue usually signals that the clue/answer combination involves some sort of pun or wordplay, e.g., "Grateful?" = ASHES, since a grate might be full of them.
- Most widely distributed American crosswords today (e.g., The New York Times , The Washington Post , The Boston Globe, USA Today, The American Values Club Crossword, etc.) also contain colloquial answers, i.e., entries in the puzzle grid that try to replicate everyday colloquial language. In such a puzzle one might see phrases such as WHAT'S UP, AS IF, or WHADDYA WANT.
2.3. Abbreviations
The constraints of the American-style grid (in which every letter is checked) often require a fair number of answers not to be dictionary words. As a result, the following ways to clue abbreviations and other non-words, although they can be found in "straight" British crosswords, are much more common in American ones:
- Abbreviations, the use of a foreign language, variant spellings, or other unusual word tricks are indicated in the clue. A crossword creator might choose to clue the answer SEN (as in the abbreviation for "senator") as "Washington bigwig: Abbr." or "Member of Cong.", with the abbreviation in the clue indicating that the answer is to be similarly abbreviated.[5] The use of "Var." indicates the answer is a variant spelling (e.g., EMEER instead of EMIR), while the use of foreign language or a foreign place name within the clue indicates that the answer is also in a foreign language. For example, ETE (été, French for "summer") might be clued as "Summer, in the Sorbonne". ROMA could be clued as "Italia's capital", whereas the clue "Italy's capital" would indicate the English spelling Rome.
- The eight possible abbreviations for a position on a compass, e.g., NNW (north-northwest) or ESE (east-southeast), occur with some frequency. They can be clued as simply "Compass point", where the desired answer is determined by a combination of logic—since the third letter can be only E or W, and the second letter can be only N or S—and a process of elimination using checks. Alternatively, compass point answers are more frequently clued as "XXX to YYY direction", where XXX and YYY are two place names. For example, SSW might be clued as "New York to Washington DC dir". Similarly, a clue such as "Right on the map" means EAST. A clue could also consist of objects that point a direction, e.g., "vane dir." or "windsock dir.".
- Roman numerals, and arithmetic involving them, frequently appear as well; the clue "IV times III" (4×3) would yield XII (12).
- In addition, partial answers are allowed in American-style crosswords, where the answer represents part of a longer phrase. For example, the clue "Mind your _____ Qs" gives the answer PSAND (Ps and).
- Non-dictionary phrases are also allowed in answers. Thus, the clue "Mocked" could result in the grid entry LAUGHED AT.
2.4. Themes
Many American crossword puzzles feature a "theme" consisting of a number of long entries (generally three to five in a standard 15×15-square "weekday-size" puzzle) that share some relationship, type of pun, or other element in common. As an example, the New York Times crossword of April 26, 2005 by Sarah Keller, edited by Will Shortz, featured five themed entries ending in the different parts of a tree: SQUAREROOT, TABLELEAF, WARDROBETRUNK, BRAINSTEM, and BANKBRANCH.
The above is an example of a category theme, where the theme elements are all members of the same set. Other types of themes include:
- Quote themes, featuring a famous quote broken up into parts to fit in the grid (and usually clued as "Quote, part 1", "Quote, part 2", etc.)
- Rebus themes, where multiple letters or even symbols occupy a single square in the puzzle (e.g., BERMUDAΔ)
- Addition themes, where theme entries are created by adding a letter, letters, or word(s) to an existing word or phrase. For example, "Crucial pool shot?" = CRITICAL MASSE (formed by taking the phrase "critical mass" and adding an "e" on the end. All the theme entries in a given puzzle must be formed by the same process (so another entry might be "Greco-Roman buddy?" = WRESTLING MATE—"wrestling mat" with an "e" added on). An example of a multiple-letter addition (and one that does not occur at the end of the entry) might be "Crazy about kitchen storage?" = CABINET FEVER (derived from "cabin fever").[6]
- Subtraction themes, the reverse of the above, where letters are removed to make a new word or phrase.[6]
- Compound themes, where the starts or ends of the theme entries can all precede or follow another word, which is given elsewhere in the puzzle. For example, a puzzle with theme entries that begin with PAPER, BALL, and WATER and elsewhere in the puzzle, the word BOY clued as "Word that can follow the start of [theme entries]".[6]
- Anniversary or tribute themes, commemorating a specific person, place, or event. For example, on October 7, 2011 The New York Times crossword commemorated the life of Apple CEO Steve Jobs who had died on October 5. Theme entries related to Jobs' life included MACINTOSH, PIXAR, THINK DIFFERENT, CREATIVE GENIUS, STEVE JOBS, and APPLE.[6][7]
- Synonym themes, where the theme entries all contain synonyms, e.g., a Los Angeles Times puzzle featuring a set of theme entries that contain the words RAVEN, JET, EBONY, and SABLE, all synonyms for "black"[6]
- Numerous other types have been identified, including spoonerisms, poems, shifted letters, rhyming phrases, puns, homophones, and combinations of two or more of other types of themes.[6]
The Simon & Schuster Crossword Puzzle Series has published many unusual themed crosswords. "Rosetta Stone", by Sam Bellotto Jr., incorporates a Caesar cipher cryptogram as the theme; the key to breaking the cipher is the answer to 1 Across. Another unusual theme requires the solver to use the answer to a clue as another clue. The answer to that clue is the real solution.
2.5. Indirect Clues
Many puzzles feature clues involving wordplay which are to be taken metaphorically or in some sense other than their literal meaning, requiring some form of lateral thinking. Depending on the puzzle creator or the editor, this might be represented either with a question mark at the end of the clue or with a modifier such as "maybe" or "perhaps". In more difficult puzzles, the indicator may be omitted, increasing ambiguity between a literal meaning and a wordplay meaning. Examples:
- "Half a dance" could clue CAN (half of CANCAN) or CHA (half of CHACHA).
- If taken literally, "Start of spring" could clue MAR (for March), but it could also clue ESS, the spelled-out form of the starting letter S.
- "Nice summer?" clues ETE, summer in Nice, France (été being French for "summer"), rather than a nice (pleasant) summer. This clue also takes advantage of the fact that in American-style crosswords, the initial letter of a clue is always capitalized, whether or not it is a proper noun. In this clue, the initial capitalization further obscures whether the clue is referring to "nice" as in "pleasant" or "Nice" as in the French city.
- "Pay addition", taken literally, clues BONUS. When taken as an indirect clue, however, it could also clue OLA (the addition of -ola to pay- results in PAYOLA).
2.6. Cryptic Crosswords
In cryptic crosswords, the clues are puzzles in themselves. A typical clue contains both a definition at the beginning or end of the clue and wordplay, which provides a way to manufacture the word indicated by the definition, and which may not parse logically. Cryptics usually give the length of their answers in parentheses after the clue, which is especially useful with multi-word answers. Certain signs indicate different forms of wordplay. Solving cryptics is harder to learn than standard crosswords, as learning to interpret the different types of cryptic clues can take some practice. In Great Britain and throughout much of the Commonwealth, cryptics of varying degrees of difficulty are featured in many newspapers.
There are several types of wordplay used in cryptics. One is straightforward definition substitution using parts of a word. For example, in one puzzle by Mel Taub, the answer IMPORTANT is given the clue "To bring worker into the country may prove significant". The explanation is that to import means "to bring into the country", the "worker" is a worker ant, and "significant" means important. Here, "significant" is the straight definition (appearing here at the end of the clue), "to bring worker into the country" is the wordplay definition, and "may prove" serves to link the two. Note that in a cryptic clue, there is almost always only one answer that fits both the definition and the wordplay, so that when one sees the answer, one knows that it is the right answer—although it can sometimes be a challenge to figure out why it is the right answer. A good cryptic clue should provide a fair and exact definition of the answer, while at the same time being deliberately misleading.
Another type of wordplay used in cryptics is the use of homophones. For example, the clue "A few, we hear, add up (3)" is the clue for SUM. The straight definition is "add up", meaning "totalize". The solver must guess that "we hear" indicates a homophone, and so a homophone of a synonym of "A few" ("some") is the answer. Other words relating to sound or hearing can be used to signal the presence of a homophone clue (e.g., "aloud", "audibly", "in conversation", etc.).
The double meaning is commonly used as another form of wordplay. For example, "Cat's tongue (7)" is solved by PERSIAN, since this is a type of cat, as well as a tongue, or language. This is the only type of cryptic clue without wordplay—both parts of the clue are a straight definition.
Cryptics often include anagrams, as well. The clue "Ned T.'s seal cooked is rather bland (5,4)" is solved by NEEDS SALT. The straight definition is "is rather bland", and the word "cooked" is a hint to the solver that this clue is an anagram (the letters have been "cooked", or jumbled up). Ignoring all punctuation, "Ned T.'s seal" is an anagram for NEEDS SALT. Besides "cooked", other common hints that the clue contains an anagram are words such as "scrambled", "mixed up", "confused", "baked", or "twisted".
Embedded words are another common trick in cryptics. The clue "Bigotry aside, I'd take him (9)" is solved by APARTHEID. The straight definition is "bigotry", and the wordplay explains itself, indicated by the word "take" (since one word "takes" another): "aside" means APART and I'd is simply ID, so APART and ID "take" HE (which is, in cryptic crossword usage, a perfectly good synonym for "him"). The answer could be elucidated as APART(HE)ID.
Another common clue type is the "hidden clue" or "container", where the answer is hidden in the text of the clue itself. For example, "Made a dug-out, buried, and passed away (4)" is solved by DEAD. The answer is written in the clue: "maDE A Dug-out". "Buried" indicates that the answer is embedded within the clue.
There are numerous other forms of wordplay found in cryptic clues. Backwards words can be indicated by words like "climbing", "retreating", or "ascending" (depending on whether it is an across clue or a down clue) or by directional indicators such as "going North" (meaning upwards) or "West" (right-to-left); letters can be replaced or removed with indicators such as "nothing rather than excellence" (meaning replace E in a word with O); the letter I can be indicated by "me" or "one;" the letter O can be indicated by "nought", "nothing", "zero", or "a ring" (since it visually resembles one); the letter X might be clued as "a cross", or "ten" (as in the Roman numeral), or "an illiterate's signature", or "sounds like your old flame" (homophone for "ex"). "Senselessness" is solved by "e", because "e" is what remains after removing (less) "ness" from "sense".
With the different types of wordplay and definition possibilities, the composer of a cryptic puzzle is presented with many different possible ways to clue a given answer. Most desirable are clues that are clean but deceptive, with a smooth surface reading (that is, the resulting clue looks as natural a phrase as possible). The Usenet newsgroup rec.puzzles.crosswords has a number of clueing competitions where contestants all submit clues for the same word and a judge picks the best one.
In principle, each cryptic clue is usually sufficient to define its answer uniquely, so it should be possible to answer each clue without use of the grid. In practice, the use of checks is an important aid to the solver.
2.7. Metapuzzles
Some crossword designers have started including a metapuzzle, or "meta" for short: a second puzzle within the completed puzzle.[8] After the player has correctly solved the crossword puzzle in the usual fashion, the solution forms the basis of a second puzzle. The designer usually includes a hint to the metapuzzle. For instance, the puzzle Eight Isn't Enough by Matt Gaffney gives the clue "This week's contest answer is a three-word phrase whose second word is 'or'."[9] The crossword solution includes the entries "BROUGHT TO NAUGHT", "MIGHT MAKES RIGHT", "CAUGHT A STRAIGHT", and "HEIGHT AND WEIGHT", which are all three-word phrases with two words ending in -ght. The solution to the meta is a similar phrase in which the middle word is "or": "FIGHT OR FLIGHT".
2.8. Schrödinger or Quantum Puzzles
Some puzzle grids contain more than one correct answer for the same set of clues. These are called Schrödinger or quantum puzzles, alluding to the Schrödinger's Cat thought experiment in quantum physics.[10] Schrödinger puzzles have frequently been published in venues including Fireball Crosswords and The American Values Club Crosswords, and at least ten have appeared in The New York Times since the late 1980s.[11] The daily New York Times puzzle for November 5, 1996, by Jeremiah Farrell, had a clue for 39 Across that read "Lead story in tomorrow's newspaper, with 43 Across (!)."[12] The answer for 43 Across was ELECTED; depending on the outcome of that day's Presidential Election, the answer for 39 Across would have been correct with either CLINTON or BOBDOLE, as would each of the corresponding Down answers.[13] On September 1, 2016, the daily New York Times puzzle by Ben Tausig had four squares which led to correct answers reading both across and down if solvers entered either "M" or "F."[14] The puzzle's theme, GENDERFLUID, was revealed at 37 Across in the center of the puzzle: "Having a variable identity, as suggested by four squares in this puzzle."[15]
2.9. The First Entries
In the 'Quick' crossword in The Daily Telegraph newspaper (Sunday and Daily, United Kingdom ), it has become a convention also to make the first few words (usually two or three, but can be more) into a phrase. For example, "Dimmer, Allies" would make "Demoralise" or "You, ill, never, walk, alone" would become "You'll never walk alone". This generally aids solvers in that if they have one of the words then they can attempt to guess the phrase. This has also become popular among other United Kingdom newspapers.
2.10. Double Clue Lists
Sometimes newspapers publish one grid that can be filled by solving either of two lists of clues—usually a straight and a cryptic. The solutions given by the two lists may be different, in which case the solver must decide at the outset which list they are going to follow, or the solutions may be identical, in which case the straight clues offer additional help for a solver having difficulty with the cryptic clues. For example, the solution APARTHEID might be clued as "Bigotry aside, I'd take him (9)" in the cryptic list, and "Racial separation (9)" in the straight list. Usually the straight clue matches the straight part of the cryptic clue, but this is not necessarily the case.
Every issue of GAMES Magazine contains a large crossword with a double clue list, under the title The World's Most Ornery Crossword; both lists are straight and arrive at the same solution, but one list is significantly more challenging than the other. The solver is prompted to fold a page in half, showing the grid and the hard clues; the easy clues are tucked inside the fold, to be referenced if the solver gets stuck.
A variant of the double-clue list is commonly called Siamese Twins: two matching grids are provided, and the two clue lists are merged such that the two clues for each entry are displayed together in random order. Determining which clue is to be applied to which grid is part of the puzzle.
2.11. Other Clue Variations
Any type of puzzle may contain cross-references, where the answer to one clue forms part of another clue, in which it is referred to by number and direction. E.g., a puzzle might have 1-Across clued as "Central character in The Lord of the Rings" = FRODO, with 17-Down clued as "Precious object for 1-Across" = RING.
When an answer is composed of multiple or hyphenated words, some crosswords (especially in Britain) indicate the structure of the answer. For example, "(3,5)" after a clue indicates that the answer is composed of a three-letter word followed by a five-letter word. Most American-style crosswords do not provide this information.
3. Major Variants
These are common crossword variants that vary more from a regular crossword than just an unusual grid shape or unusual clues; these crossword variants may be based on different solving principles and require a different solving skill set.
3.1. Cipher Crosswords
Cipher crosswords were invented in Germany in the 19th century. Published under various trade names (including Code Breakers, Code Crackers, and Kaidoku), and not to be confused with cryptic crosswords (ciphertext puzzles are commonly known as cryptograms), a cipher crossword replaces the clues for each entry with clues for each white cell of the grid—an integer from 1 to 26 inclusive is printed in the corner of each. The objective, as any other crossword, is to determine the proper letter for each cell; in a cipher crossword, the 26 numbers serve as a cipher for those letters: cells that share matching numbers are filled with matching letters, and no two numbers stand for the same letter. All resultant entries must be valid words. Usually, at least one number's letter is given at the outset. English-language cipher crosswords are nearly always pangrammatic (all letters of the alphabet appear in the solution). As these puzzles are closer to codes than quizzes, they require a different skillset; many basic cryptographic techniques, such as determining likely vowels, are key to solving these. Given their pangrammaticity, a frequent start point is locating where 'Q' and 'U' must appear.
3.2. Diagramless Crosswords
In a diagramless crossword, often called a diagramless for short or, in the United Kingdom , a skeleton crossword or carte blanche, the grid offers overall dimensions, but the locations of most of the clue numbers and shaded squares are unspecified. A solver must deduce not only the answers to individual clues, but how to fit together partially built-up clumps of answers into larger clumps with properly set shaded squares. Some of these puzzles follow the traditional symmetry rule, others have left-right mirror symmetry, and others have greater levels of symmetry or outlines suggesting other shapes. If the symmetry of the grid is given, the solver can use it to his/her advantage.
A variation is the Blankout puzzle in the Daily Mail Weekend magazine. The clues are not individually numbered, but given in terms of the rows and columns of the grid, which has rectangular symmetry. The list of clues gives hints of the locations of some of the shaded squares even before one starts solving them, e.g. there must be a shaded square where a row having no clues intersects a column having no clues.
3.3. Fill-iIn Crosswords
A fill-in crossword (also known as crusadex or cruzadex) features a grid and the full list of words to be entered in that grid, but does not give explicit clues for where each word goes. The challenge is figuring out how to integrate the list of words together within the grid so that all intersections of words are valid. Fill-in crosswords may often have longer word length than regular crosswords to make the crossword easier to solve, and symmetry is often disregarded. Fitting together several long words is easier than fitting together several short words because there are fewer possibilities for how the long words intersect together. These types of crosswords are also used to demonstrate artificial intelligence abilities, such as finding solutions to the puzzle based on a set of determined constraints.[16]
3.4. Crossnumbers
A crossnumber (also known as a cross-figure) is the numerical analogy of a crossword, in which the solutions to the clues are numbers instead of words. Clues are usually arithmetical expressions, but can also be general knowledge clues to which the answer is a number or year. There are also numerical fill-in crosswords.
The Daily Mail Weekend magazine used to feature crossnumbers under the misnomer Number Word. This kind of puzzle should not be confused with a different puzzle that the Daily Mail refers to as Cross Number.
3.5. Acrostic Puzzles
An acrostic is a type of word puzzle, in eponymous acrostic form, that typically consists of two parts. The first is a set of lettered clues, each of which has numbered blanks representing the letters of the answer. The second part is a long series of numbered blanks and spaces, representing a quotation or other text, into which the answers for the clues fit. In most forms of the puzzle, the first letters of each correct clue answer, read in order from clue A on down the list, will spell out the author of the quote and the title of the work it is taken from; this can be used as an additional solving aid.
3.6. Arroword
The arroword is a variant of a crossword that does not have as many black squares as a true crossword, but has arrows inside the grid, with clues preceding the arrows. It has been called the most popular word puzzle in many European countries, and is often called the Scandinavian crossword, as it is believed to have originated in Sweden.[17]
4. History


The title for the world's first crossword puzzle is disputed. Some such puzzles were included in The Stockton Bee (1793–1795), an ephemeral publication.[18] The phrase "cross word puzzle" was first written in 1862 by Our Young Folks in the United States. Crossword-like puzzles, for example Double Diamond Puzzles, appeared in the magazine St. Nicholas, published since 1873.[19] Another crossword puzzle appeared on September 14, 1890, in the Italian magazine Il Secolo Illustrato della Domenica. It was designed by Giuseppe Airoldi and titled "Per passare il tempo" ("To pass the time"). Airoldi's puzzle was a four-by-four grid with no shaded squares; it included horizontal and vertical clues.[20]
Crosswords in England during the 19th century were of an elementary kind, apparently derived from the word square, a group of words arranged so the letters read alike vertically and horizontally, and printed in children's puzzle books and various periodicals.
On December 21, 1913, Arthur Wynne, a journalist from Liverpool, England, published a "word-cross" puzzle in the New York World that embodied most of the features of the modern genre. This puzzle is frequently cited as the first crossword puzzle, and Wynne as the inventor. An illustrator later reversed the "word-cross" name to "cross-word.[21][22][23]
Crossword puzzles became a regular weekly feature in the New York World, and spread to other newspapers; the Pittsburgh Press, for example, was publishing them at least as early as 1916[24] and The Boston Globe by 1917.[25]

By the 1920s, the crossword phenomenon was starting to attract notice. In October 1922, newspapers published a comic strip by Clare Briggs entitled "Movie of a Man Doing the Cross-Word Puzzle," with an enthusiast muttering "87 across 'Northern Sea Bird'!!??!?!!? Hm-m-m starts with an 'M', second letter is 'U'... I'll look up all the words starting with an 'M-U...' mus-musi-mur-murd—Hot Dog! Here 'tis! Murre!"[26] In 1923 a humorous squib in The Boston Globe has a wife ordering her husband to run out and "rescue the papers... the part I want is blowing down the street." "What is it you're so keen about?" "The Cross-Word Puzzle. Hurry, please, that's a good boy."[27] In The New Yorker's first issue, released in 1925, the "Jottings About Town" section wrote, "Judging from the number of solvers in the subway and "L" trains, the crossword puzzle bids fair to become a fad with New Yorkers." [28] In 1925, the New York Public Library reported that "The latest craze to strike libraries is the crossword puzzle," and complained that when "the puzzle 'fans' swarm to the dictionaries and encyclopedias so as to drive away readers and students who need these books in their daily work, can there be any doubt of the Library's duty to protect its legitimate readers?"[29]
The first book of crossword puzzles was published by Simon & Schuster in 1924, after a suggestion from co-founder Richard Simon's aunt. The publisher was initially skeptical that the book would succeed, and only printed a small run at first. The book was promoted with an included pencil, and "This odd-looking book with a pencil attached to it"[30] was an instant hit, leading crossword puzzles to become a craze of 1924. To help promote its books, Simon & Schuster also founded the Amateur Cross Word Puzzle League of America, which began the process of developing standards for puzzle design.[23]
The crossword puzzle fad received extensive attention, not all of it positive: In 1924, The New York Times complained of the "sinful waste in the utterly futile finding of words the letters of which will fit into a prearranged pattern, more or less complex. This is not a game at all, and it hardly can be called a sport... [solvers] get nothing out of it except a primitive form of mental exercise, and success or failure in any given attempt is equally irrelevant to mental development."[31] A clergyman called the working of crossword puzzles "the mark of a childish mentality" and said, "There is no use for persons to pretend that working one of the puzzles carries any intellectual value with it.".[32] However, another wrote a complete "Bible Cross-Word Puzzle Book". Also in 1925, Time Magazine noted that nine Manhattan dailies and fourteen other big newspapers were carrying crosswords, and quoted opposing views as to whether "This crossword craze will positively end by June!" or "The crossword puzzle is here to stay!"[33] In 1925, The New York Times noted, with approval, a scathing critique of crosswords by The New Republic; but concluded that "Fortunately, the question of whether the puzzles are beneficial or harmful is in no urgent need of an answer. The craze evidently is dying out fast and in a few months it will be forgotten."[34] and in 1929 declared, "The cross-word puzzle, it seems, has gone the way of all fads...."[35] In 1930, a correspondent noted that "Together with The Times of London, yours is the only journal of prominence that has never succumbed to the lure of the cross-word puzzle" and said that "The craze—the fad—stage has passed, but there are still people numbering it to the millions who look for their daily cross-word puzzle as regularly as for the weather predictions."[36]
The term "crossword" first appeared in the Oxford English Dictionary in 1933.[37]
The New York Times began to publish a crossword puzzle on 15 February 1942, spurred on by the idea that the puzzle could be a welcome distraction from the harsh news of World War II. The New York Times's first puzzle editor was Margeret Petherbridge Farrar, who was editor from 1942 to 1969.[23] She was succeeded by Will Weng, who was succeeded by Eugene T. Maleska. Since 1993, they have been edited by Will Shortz, the fourth crossword editor in Times. In 1978 Shortz founded and still directs the annual American Crossword Puzzle Tournament. However, a number of other high-profile puzzles have since emerged in the United States in particular, many of which rival the Times in quality and prestige. These include The New Yorker, The Washington Post , The Wall Street Journal, Brendan Emmett Quigley, The American Values Club, Inkubator Crosswords, and Fireball Crosswords (the latter four of which are distributed digitally).
Simon & Schuster continues to publish the Crossword Puzzle Book Series books that it began in 1924, currently under the editorship of John M. Samson. The original series ended in 2007 after 258 volumes. Since 2008, these books are now in the Mega series, appearing three times per year and each featuring 300 puzzles.
The British cryptic crossword was imported to the US in 1968 by composer and lyricist Stephen Sondheim in New York magazine. Until 2006, The Atlantic Monthly regularly featured a cryptic crossword "puzzler" by Emily Cox and Henry Rathvon, which combines cryptic clues with diabolically ingenious variations on the construction of the puzzle itself. In both cases, no two puzzles are alike in construction, and the intent of the puzzle authors is to entertain with novelty, not to establish new variations of the crossword genre.
In the United Kingdom , the Sunday Express was the first newspaper to publish a crossword on November 2, 1924, a Wynne puzzle adapted for the UK. The first crossword in Britain, according to Tony Augarde in his Oxford Guide to Word Games (1984), was in Pearson's Magazine for February 1922.
The 2006 documentary Wordplay, about enthusiasts of The New York Times's puzzle, increased public interest in crosswords. It highlighted attendees of Will Shortz's American Crossword Puzzle Tournament, including former American president Bill Clinton and American comedian Jon Stewart.[23]
4.1. World War II
In 1944, Allied security officers were disturbed by the appearance, in a series of crosswords in The Daily Telegraph, of words that were secret code names for military operations planned as part of Operation Overlord.
Some cryptologists for Bletchley Park were selected after doing well in a crossword-solving competition.[38]
4.2. Records
According to Guinness World Records, May 15, 2007, the most prolific crossword compiler is Roger Squires of Ironbridge, Shropshire, UK. On May 14, 2007, he published his 66,666th crossword,[39] equivalent to 2 million clues. He is one of only four setters to have provided cryptic puzzles to The Times, The Daily Telegraph, The Guardian , the Financial Times and The Independent. He also holds the record for the longest word ever used in a published crossword—the 58-letter Welsh town Llanfairpwllgwyngyllgogerychwyrndrobwllllantysiliogogogoch clued as an anagram.
Enthusiasts have compiled a number of record-setting achievements in New York Times and other venues. [40]
- The lowest word count in a published weekday-size 15x15 puzzle is the June 29, 2013 The New York Times crossword by Joe Krozel, with just 50 words.
- The fewest shaded squares in a 15x15 American crossword is 17 (leaving 208 white spaces), set by the July 27, 2012 Times crossword by Joe Krozel.[41]
- The record for most crosswords published in The New York Times is held by Manny Nosowsky, who has had 241 puzzles in that outlet.
- A. N. Prahlada Rao, based in Bangalore, has composed/ constructed some 35,000 crossword puzzles in the language Kannada, including 7,500 crosswords based on films made in Kannada, with a total of 1,000,000 (Ten lakhs) clues. His name has recorded in LIMCA BOOK OF RECORDS – 2015 for creating highest crosswords in the Indian Regional Languages. His name has continued in the LIMCA BOOK OF RECORDS – 2015, 2016 and 2017 also.[35]
4.3. Women Crossword Constructors
Women editors such as Margaret Farrar were influential in the first few decades of puzzle-making, and women constructors such as Bernice Gordon and Elizabeth Gorski have each contributed hundreds of puzzles to The New York Times.[42] However, in recent years the number of women constructors has declined, and crossword editors at most major papers are all male. During the years that Will Weng and Eugene Maleska edited the New York Times crossword (1969–1993), women constructors accounted for 35% of puzzles,[43][44] while during the editorship of Will Shortz (1993–present), this percentage has gone down, with women constructors (including collaborations) accounting for only 15% of puzzles in both 2014 and 2015, 17% of puzzles published in 2016, 13%—the lowest in the "Shortz Era"—in 2017, and 16% in 2018.[45][46] Several reasons have been given for the decline in women constructors. One explanation is that the gender imbalance in crossword construction is similar to that in related fields, such as journalism, and that more freelance male constructors than females submit puzzles on spec to The New York Times and other outlets.[47] Another explanation is that computer-assisted construction and the increased influence of computational approaches in generating word lists may be making crossword construction more like STEM fields in which women are underrepresented for a number of factors.[43] However, it has also been argued that this explanation risks propagating myths about gender and technology.[48] Some have argued that the relative absence of women constructors and editors has had an influence on the content of the puzzles themselves, and that clues and entries can be insensitive regarding language related to gender and race.[49][50] Several approaches have been suggested to develop more women in the field, including mentoring novice women constructors and encouraging women constructors to publish their puzzles independently.[48][51]
Crossword venues other than New York Times have recently published higher percentages of women than that puzzle. In the spring of 2018, Patti Varol and Amy Reynaldo organized and edited a pack of 18 puzzles constructed by women called "Women of Letters".[52] Inspired by this, Laura Braunstein and Tracy Bennett launched The Inkubator, a "twice-monthly subscription service that will publish crosswords constructed by cis women, trans women, and woman-aligned constructors."[53] The Inkubator raised over $30,000 in its initial Kickstarter campaign,[54] and began publishing puzzles on January 17, 2019.
5. Non-English Languages
Due to the large amount of words ending on a vowel, Italian crossword-makers have perhaps the most difficult task. The right margin and the bottom can be particularly difficult to put together. From such a perspective, Swedish crossword-makers have a far easier task. Especially in the large picture crosswords, both conjugation of verbs and declension of adjectives and nouns are allowed. A Swedish clue like "kan sättas i munnen" = "sked" ("can be put in the mouth" = "spoon") can be grammatically changed; "den kan sättas i munnen" = "skeden" ("it can be put in the mouth" = "the spoon"), as the definite form of a noun includes declension.
5.1. Orthography
From their origin in New York, crosswords have spread to many countries and languages. In languages other than English, the status of diacritics varies according to the orthography of the particular language, thus:
- in Afrikaans all diacritical markings are ignored. Words such as TEË (meaning opposed) and TEE (meaning tea) are both simply written TEE. The same goes for SÊ (say) and SE (belonging to) and many others.
- in Czech and Slovak, diacritics are respected and ch, being considered one letter, occupies one square.
- in Dutch crosswords, the ij digraph is considered one letter, filling one square, and the IJ and the Y (see Dutch alphabet) are considered distinct. Rules may vary in other word games.
- in Esperanto crosswords, diacritics are respected, as they form separate letters (graphemes).[55].
- in French, in Spanish and in Italian, accent marks and most other diacritical markings are ignored, except the tilde in Spanish: for instance, in French, the final E of answer ÊTRE can double as the final É of CONGÉ when written ETRE and CONGE; but in Spanish, N and Ñ are distinct letters.
- in German language crosswords, the umlauts ä, ö, and ü are dissolved into ae, oe, and ue, and ß is dissolved into ss.
- in Hungarian, diacritics are either fully respected, or not respected where it denotes length, that is I/Í, O/Ó, Ö/Ő, U/Ú, Ü/Ű are considered the same, but not A/Á and E/É which mark different sounds; although the difference between the short/long pairs of letters is a distinctive feature in Hungarian. Digraphs fill two squares.
- in Irish crosswords, the accents on Á É Í Ó Ú are all respected, so (for example) the Í in SÍB cannot double as the I in SLIABH.
- in Latin, diacritics are ignored. Therefore, A is considered the same as Ă or Ā. Ecclesiastical Latin is normally used. See the monthly magazine of Latin crosswords Hebdomada aenigmatum as a reference.[56]
- in Portuguese, diacritics are ignored with the exception of Ç. Therefore, A could be checked with à or Á.
- in Romanian, diacritics are ignored.
- in Russian, Ё doubles as Е but Й is considered different from И; the soft sign Ь and the hard sign Ъ occupy a separate square, different from that of the previous letter.
- in Spanish crosswords, the digraphs ch and ll fill two squares, although in some old crosswords (from prior to the 1996 spelling reform) they filled one square.

Person solving a Finnish crossword puzzle. https://handwiki.org/wiki/index.php?curid=1617747
5.2. Grid Design, Clues, and Conventions

French-language crosswords are smaller than English-language ones, and not necessarily square: there are usually 8–13 rows and columns, totaling 81–130 squares. They need not be symmetric and two-letter words are allowed, unlike in most English-language puzzles. Compilers strive to minimize use of shaded squares. A black-square usage of 10% is typical; Georges Perec compiled many 9×9 grids for Le Point with four or even three black squares.[57] Rather than numbering the individual clues, the rows and columns are numbered as on a chessboard. All clues for a given row or column are listed, against its number, as separate sentences. This is similar to the notation used in the aforementioned Daily Mail Blankout puzzles.
In Italy, crosswords are usually oblong and larger than French ones, 13×21 being a common size. As in France, they usually are not symmetrical; two-letter words are allowed; and the number of shaded squares is minimized. Nouns (including surnames) and the infinitive or past participle of verbs are allowed, as are abbreviations; in larger crosswords, it is customary to put at the center of the grid phrases made of two to four words, or forenames and surnames. A variant of Italian crosswords does not use shaded squares: words are delimited by thickening the grid. Another variant starts with a blank grid: the solver must insert both the answers and the shaded squares, and Across and Down clues are either ordered by row and column or not ordered at all.
Modern Hebrew is normally written with only the consonants; vowels are either understood, or entered as diacritical marks. This can lead to ambiguities in the entry of some words, and compilers generally specify that answers are to be entered in ktiv male (with some vowels) or ktiv haser (without vowels). Further, since Hebrew is written from right to left, but Roman numerals are used and written from left to right, there can be an ambiguity in the description of lengths of entries, particularly for multi-word phrases. Different compilers and publications use differing conventions for both of these issues.
In the Japanese language crossword; because of the writing system, one syllable (typically katakana) is entered into each white cell of the grid rather than one letter, resulting in the typical solving grid seeming small in comparison to those of other languages. Any second Yōon character is treated as a full syllable and is rarely written with a smaller character. Even cipher crosswords have a Japanese equivalent, although pangrammaticity does not apply. Crosswords with kanji to fill in are also produced, but in far smaller number as it takes far more effort to construct one. Despite Japanese having three writing forms, hiragana, katakana and kanji, they are rarely mixed in a single crossword puzzle.
A. N. Prahlada Rao, based in Bangalore, has composed/ constructed some 35,000 crossword puzzles in the language Kannada, including 7,500 crosswords based on films made in Kannada, with a total of 10,00,000 (ten lakhs, or one million) clues.[58][59] His name has recorded in LIMCA BOOK OF RECORDS – 2015 for creating highest crosswords in the Indian Regional Languages. His name has continued in the LIMCA BOOK OF RECORDS – 2016 and 2017 also.[60] A five volume set of his puzzles was released in February 2008 In 2013 two more crossword books released. In 2017 his 5 Crossword Books published.[61] Bengali is also well known for its crossword puzzles. Crosswords are published regularly in almost all the Bengali dailies and periodicals. The grid system is quite similar to the British style and two-letter words are usually not allowed.
In Poland , crosswords typically use British-style grids, but some do not have shaded cells. Shaded cells are often replaced by boxes with clues—such crosswords are called Swedish puzzles or Swedish-style crosswords. In a vast majority of Polish crosswords, nouns are the only allowed words.
Swedish crosswords are mainly in the illustrated (photos or drawings), in-line clue style typical of the "Swedish-style grid" mentioned above. This tradition prospered already in the mid-1900s, in family magazines and sections of newspapers. Then the specialised magazines took off. Around the turn of the millennium, approximately half a dozen Swedish magazine publishers produced specialised crossword magazines, totaling more than twenty titles, often published on a monthly basis. The oldest extant crossword magazine published in Swedish is Krysset[62] (from Bonnier), founded in 1957. Additionally, nearly all newspapers publish crosswords of some kind, and at weekends often devote specialised sections in the paper to crosswords and similar type of pastime material. Both major evening dailies (Aftonbladet and Expressen) publish a weekly crossword supplement, named Kryss & Quiz and Korsord[63] respectively. Both are available as paid supplements on Mondays and Tuesdays, as part of the ongoing competition between the two newspapers.
6. Construction
American-Style Crosswords
In typical themed American-style crosswords, the theme is created first, as a set of symmetric long Across answers will be needed around which the grid can be created.[64][65] Since the grid will typically have 180-degree rotational symmetry, the answers will need to be also: thus a typical 15×15 square American puzzle might have two 15-letter entries and two 13-letter entries that could be arranged appropriately in the grid (e.g., one 15-letter entry in the third row, and the other symmetrically in the 13th row; one 13-letter entry starting in the first square of the 6th row and the other ending in the last square of the 10th row).[65][66] The theme must not only be funny or interesting, but also internally consistent. In the April 26, 2005 by Sarah Keller mentioned above, the five themed entries contained in the different parts of a tree: SQUAREROOT, TABLELEAF, WARDROBETRUNK, BRAINSTEM, and BANKBRANCH. In this puzzle, CHARTER OAK would not be an appropriate entry, as all the other entries contain different parts of a tree, not the name of a kind of tree. Similarly, FAMILY TREE would not be appropriate unless it were used as a revealer for the theme (frequently clued with a phrase along the lines "...and a hint to..."). Given the existing entries, SEED MONEY would also be unacceptable, as all the other theme entries end in the part of a tree as opposed to beginning with it, though the puzzle could certainly be changed to have a mix of words in different positions.[64]
Once a consistent, appropriate theme has been chosen, a grid is designed around that theme, following a set of basic principles:
- Generally, most American puzzles are 15×15 squares; if another size, they typically have an odd number of rows and columns: e.g., 21×21 for "Sunday-size" puzzles; GAMES Magazine will accept 17×17 puzzles, Simon & Schuster accepts both 17×17 and 19×19 puzzles, and The New York Times requires diagramless puzzles to be 17×17.[67] The odd number of squares on a side ensures that achieving symmetry is easier; with even-numbered puzzles the central block of four squares makes constructing a symmetrical puzzle considerably more difficult.[68]
- The black squares must be arranged so as to (1) ensure there are no two-letter words; (2) form 180-degree rotational symmetry (so that if the grid is turned upside-down, the pattern of black squares remains the same); (3) ensure that every letter is checked (appears in both an Across and a Down word); (4) not occupy too much of the puzzle (generally speaking, 16% of the puzzle is considered a rough limit for the percentage of black squares); (5) ensure that the entire puzzle has "all-over interlock"—that is, that the black squares do not "cut" the puzzle into separate sections; and (6) ensure that (generally) no non-theme entry is longer than any of the theme entries. In addition, it is considered advisable to minimize the number of so-called "cheater" black squares, i.e., black squares whose removal would not change the word count of the puzzle but which make it easier to fill by shortening the length of the words therein.[65][66][69]
- The grid is then filled with suitable words, keeping in mind that (1) no word can be repeated in the grid (with the exception of prepositions or articles); (2) profanity or graphic or "unpleasant" words are generally not allowed; (3) obscurity is strongly discouraged in easy puzzles and should be kept to a minimum in more difficult puzzles, where two obscure words should never be allowed to cross (and, ideally, where the obscure word would be of interest to most solvers—a genus of little-known water bugs would not be a good choice); (4) uncommon abbreviations and variant foreign spellings should be avoided, as well as the use of crosswordese (those words that no longer appear in common speech but that occur frequently in crosswords due to their favorable letter combinations, such as the Asian buffalo ANOA); (5) in modern puzzles, pop figures and corporate and brand names are generally considered acceptable; (6) no made-up words are permitted—there should be a dictionary or other reference that can cite each entry if asked.[65][69]
- Modern constructors frequently (although not always) use software to speed the task. Several programs are available, of which the most widely accepted is Crossword Compiler.[64] These programs, although they cannot create themes and cannot distinguish between "good" fill (fun, interesting words vs. dull obscurity), do speed up the process and will allow the constructor to realize if he or she has hit a dead end.[70]
Crossword puzzle payments for standard 15×15 puzzles from the major outlets range from $50 (GAMES Magazine) to $500 (The New York Times) while payments for 21×21 puzzles range from $150 (Newsday) to $1,500 (The New York Times).[71]
The compensation structure of crosswords generally entails authors selling all rights to their puzzles upon publication, and as a result receiving no royalties from republication of their work in books or other forms. This system has been criticized by American Values Club crossword editor Ben Tausig, among others.[72]
7. Software
Software that aids in creating crossword puzzles has been written since at least 1976;[73] one popular example was Crossword Magic for the Apple II in the 1980s.[74] The earliest software relied on people to input a list of fill words and clues, and automatically maps the answers onto a suitable grid. This is a search problem in computer science because there are many possible arrangements to be checked against the rules of construction. Any given set of answers might have zero, one, or multiple legal arrangements. Modern open source libraries exist that attempt to efficiently generate legal arrangements from a given set of answers.[75]
In the late 1990s, the transition began from mostly hand-created arrangements to computer-assisted, which creators generally say has allowed authors to produce more interesting and creative puzzles, reducing crosswordese.[76]
Modern software includes large databases of clues and answers, allowing the computer to randomly select words for the puzzle, potentially with guidance from the user as to the theme or a specific set of words to pick with greater probability. Many serious users add words to the database as an expression of personal creativity or for use in a desired theme. Software can also be used to assist the user in finding words for a specific spot in an arrangement by quickly searching through the dictionary for all words that fit.[76]
8. Notation
Originally Petherbridge called the two dimensions of the crossword puzzle "Horizontal" and "Vertical". Among various numbering schemes, the standard became that in which only the start squares of each word were numbered, from left to right and top to bottom. "1 Horizontal" and "1 Vertical" and the like were names for the clues, the cross words, or the grid locations, interchangeably.
Later in the Times these terms commonly became "Across" and "Down" and notations for clues could either use the words or the letters "A" and "D", with or without hyphens.
References
- (Shortz) "How to Solve the New York Times Crossword Puzzle" https://www.nytimes.com/2001/04/08/magazine/08PUZZLE.html?ex=1236830400&en=5e6b94bdf1884b70&ei=5070
- "American-style crosswords". Theguardian. https://www.theguardian.com/crosswords/series/american-style/.
- Berry, Patrick (2015). Crossword Constructor's Handbook. pp. 62–80. http://aframegames.com/store/?download=21.
- D. S. MacNutt with A. Robins, Ximenes on the art of the crossword, Methuen & Co Ltd, London (1966) p. 49.
- "How to Make a Crossword Puzzle". http://crosswordhobbyist.com/how-to-make-a-crossword-puzzle.
- "Identified theme. types". Cruciverb.com. http://www.cruciverb.com/index.php?action=ezportal;sa=page;p=70. Retrieved 5 March 2013.
- Der, Kevin G. "New York Times crossword of October 7, 2011". XWordInfo.com. http://www.xwordinfo.com/Crossword?date=10/7/2011. Retrieved 5 March 2013.
- Gaffney, Matt. "Matt Gaffney's Weekly Crossword Contest Frequently Asked Questions". http://xwordcontest.com/faq. Retrieved 30 September 2015.
- Gaffney, Matt. "Eight Isn't Enough". http://xwordcontest.com/2015/08/mgwcc-376-friday-august-14th-2015-eight-isnt-enough.html. Retrieved 30 September 2015.
- Pahk, Joon (2012-05-09). "Comment, Thursday, May 9, 2012". https://crosswordfiend.com/2012/05/09/thursday-51012/#comment-147469.
- "Quantum". http://www.xwordinfo.com/Quantum.
- Farrell, Jeremiah. "New York Times puzzle of Tuesday, November 5, 1996". http://www.xwordinfo.com/Crossword?date=11/5/1996. Retrieved 16 January 2017.
- Amende, Coral (2001). The Crossword Obsession. New York: Berkley Books. ISBN 978-0756790868. https://archive.org/details/crosswordobsessi00amen.
- Tausig, Ben. "New York Times puzzle of Thursday, September 1, 2016". http://www.xwordinfo.com/Crossword?date=9/1/2016. Retrieved 16 January 2017.
- Roeder, Oliver. "One of the Most Important Crosswords in New York Times History". http://www.slate.com/articles/life/gaming/2016/09/ben_tausig_s_new_york_times_puzzle_is_one_of_history_s_most_important_crosswords.html. Retrieved 16 January 2017.
- Poole, David L.; Mackworth, Alan K. (2010). Artificial Intelligence: Foundations of Computational Agents. New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-51900-7.
- "Arroword". puzzler.com. http://www.puzzler.com/Puzzles-encyclopedia/Arroword.htm. Retrieved May 17, 2011.
- "Archived copy". http://www.roteiroromanceado.com/cruzadas/historia/ancestrais/crossword/enigmas/enigmas2.html.
- "St. Nicholas. September 1875". Childrenslibrary.org. http://www.childrenslibrary.org/icdl/BookPage?bookid=dodstni_00362329&pnum1=66&twoPage=false&route=alsoby&size=17&fullscreen=false&lang=English&ilang=English. Retrieved 2013-11-26.
- "Storia delle parole crociate e del cruciverba" (in Italian). Crucienigmi. http://www.crucienigmi.it/Storia_delle_parole_crociate.htm. Retrieved August 28, 2009.
- "The Crossword Puzzle". Massachusetts Institute of Technology. August 1997. http://web.mit.edu/invent/iow/crosswordhome.html. Retrieved 2010-12-18.
- Bellis, Mary. "The History of Crossword Puzzles". About.com. http://inventors.about.com/od/cstartinventions/a/crossword.htm. Retrieved 2010-12-18.
- Amlen, Deb. "How the Crossword Became an American Pastime" (in en). https://www.smithsonianmag.com/arts-culture/crossword-became-american-pastime-180973558/.
- "Cross-Word Puzzle". The Pittsburgh Press. June 11, 1916. https://news.google.com/newspapers?nid=djft3U1LymYC&dat=19160611&printsec=frontpage&hl=en. Comic section's fifth page.
- The Boston Globe, April 8, 1917, p. 43 contains a puzzle and a solution to a previous week's puzzle.
- "Movie of a Man Doing the Cross-Word Puzzle," by "Briggs," Morning Oregonian, October 3, 1922, p. 14; also published in several other newspapers
- "There Goes My Crossword Puzzle, Get Up Please." The Boston Daily Globe, October 1, 1923, p. 7.
- "Jottings About Town." The New Yorker, February 25, 1925, p. 30.
- Report of the New York Public Library for 1924; published by The Library, 1925 https://books.google.com/books?id=P_4aAAAAMAAJ&ots=2F4d8YpQcK&pg=RA3-PA24
- Frederick Lewis Allen (1931). Only Yesterday. Harper and Row. https://archive.org/details/onlyyesterdayinf00alle. , p. 159 of 1964 Perennial Library paperback reprint
- "Topics of the Times." The New York Times, November 17, 1924, p. 18
- "Condemns Cross-Word Fad." The New York Times, December 23, 1924, p. 17
- "Barometer". Time Magazine. January 5, 1925. http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,719730,00.html. Retrieved 2008-08-05.
- Topics of the Times: Sees Harm, Not Education" The New York Times, March 10, 1925, p. 20,
- "All About the Insidious Game of Anagrams," The New York Times, December 29, 1929, p. BR3
- Richard H. (1930), "The Lure of the Puzzle." The New York Times, February 4, 1930, p. 20
- "crossword." OED Online. March 2017. Oxford University Press. http://www.oed.com/view/Entry/44952?redirectedFrom=crossword& (accessed April 28, 2017).
- The Daily Telegraph – 80 Years of Cryptic Crosswords, p. 44.
- (Pat-Ella) "Crossword setter hits puzzling landmark", Richard Savill, The Daily Telegraph, May 15, 2007 https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/main.jhtml?xml=/news/2007/05/14/nclue14.xml
- "XWord Info". https://www.xwordinfo.com/. Retrieved 2020-04-14.
- "Friday, July 27, 2012 crossword by Joe Krozel". Xwordinfo.com. 2012-07-27. http://www.xwordinfo.com/Crossword?date=7/27/2012. Retrieved 2013-11-26.
- "Elizabeth C. Gorski". http://www.xwordinfo.com/Thumbs?author=Elizabeth+C.+Gorski.
- Shechtman, Anna (2014). "Puzzle Trouble: Women and Crosswords in the Age of Autofill". http://theamericanreader.com/puzzle-trouble-women-and-crosswords-in-the-age-of-autofill/.
- Steinberg, David. "The Pre-Shortzian Puzzle Project". http://www.preshortzianpuzzleproject.com/.
- "Women constructors in the Shortz Era". http://www.xwordinfo.com/Women.
- Kosman, Joshua; Picciotto, Henry (2014). "Puzzling Women: Where are the female constructors?". https://www.thenation.com/article/puzzling-women/.
- Tausig, Ben (2013). "The Crossword Puzzle: Where'd the Women Go?". https://thehairpin.com/the-crossword-puzzle-whered-the-women-go-c25dee229b3f#.ufszwy6ib.
- "Elizabeth Gorski: New York Times Crossword Creator". 2014. http://www.ravishly.com/ladies-we-love/elizabeth-gorski-new-york-times-crossword-creator.
- Graham, Ruth (2016). "Why Is the New York Times Crossword So Clueless About Race and Gender?". http://www.slate.com/blogs/xx_factor/2016/06/28/the_new_york_times_crossword_can_be_clueless_about_race_and_gender.html.
- Jeffries, Adrianne (2017). "The NYT Crossword Is Old and Kind Of Racist". https://theoutline.com/post/1651/the-nyt-crossword-is-old-and-kind-of-racist.
- Reynaldo, Amy (2014). "Women and Crossword Construction, Part 1: Why the underrepresentation?". http://crosswordfiend.com/2014/03/06/women-and-crossword-construction-part-1-why-the-underrepresentation/.
- https://www.pattivarol.com/women-of-letters
- Gavin, Hailey. "The Inkubator Is on a Mission to Publish More Female Crossword Puzzle Constructors". Slate. https://slate.com/culture/2018/10/inkubator-aims-to-publish-more-female-crossword-constructors.html. Retrieved 16 January 2019.
- "The Inkubator – Kickstarter". https://www.kickstarter.com/projects/laurabrarian/the-inkubator/description. Retrieved 16 January 2019.
- "Home". http://www.semajnodeenigmoj.com. Retrieved 25 March 2018.
- "Latin crosswords – Cruciverba in latino – Aenigmata latina". https://www.latincrosswords.com/.
- "Histoire des mots croisés. Chapitre VI". Homepage.urbanet.ch. http://homepage.urbanet.ch/cruci.com/textes/histoire6.htm. Retrieved 2013-11-26.
- "Making clues". Thehindubusinessline.in. 2001-05-14. http://www.thehindubusinessline.in/2001/05/14/stories/101444g3.htm. Retrieved 2013-11-26.
- "Details". http://www.vijaykarnatakaepaper.com/Details.aspx?id=6041&boxid=1222762.
- "Limca Book of Records". https://www.coca-colaindia.com/stories/most-crosswords-created--regional-language-.
- "Karnataka / Bangalore News : Kannada crossword puzzles launched". The Hindu. 2008-02-17. http://www.hindu.com/2008/02/17/stories/2008021753500400.htm. Retrieved 2013-11-26.
- "Krysset – klassikern med kvalitet och kunskap." Krysset.se. Retrieved 2012-01-04. (in Swedish) http://krysset.se/Corpbiz/1164/
- "Dagens bilaga med Expressen – Korsord." Expressen.se. Retrieved 2012-01-04. (in Swedish) http://www.expressen.se/omexpressen/1.2460276/dagens-bilaga-med-expressen-korsord
- Salomon, Nancy. "Notes from a Mentor". cruciverb.com. http://www.cruciverb.com/index.php?action=ezportal;sa=page;p=22. Retrieved 25 February 2013.
- Rosen, Mel (1995). Random House Puzzlemaker's Handbook. New York: Random House. ISBN 9780812925449.
- Kurzban, Stanley A. (1981). The Compleat Cruciverbalist: Or How to Solve and Compose Crossword Puzzles for Fun and Profit. Van Nostrand Reinhold. ISBN 978-0442257385. https://archive.org/details/compleatcruciver00kurz.
- "Publisher Specifications". cruciverb.com. http://www.cruciverb.com/index.php?action=ezportal;sa=page;p=9. Retrieved 25 February 2013.
- Gore, Molly (15 November 2007). "Math professor and crossword constructor gives puzzle advice". The Santa Clara (Santa Clara, California). http://www.thesantaclara.com/2.14532/math-professor-and-crossword-constructor-gives-puzzle-advice-1.1870291?pagereq=1#.USwF4xnDN_0. Retrieved 25 February 2013.
- "Basic Rules". cruciverb.com. http://www.cruciverb.com/index.php?action=ezportal;sa=page;p=21. Retrieved 25 February 2013.
- Holmes, Kristin E. (29 April 2007). "A passion to fit words together". The Philadelphia Inquirer (archived at crosswordtournament.com). Archived from the original on 20 April 2013. https://web.archive.org/web/20130420160823/http://www.crosswordtournament.com/articles/inq042907.htm. Retrieved 25 February 2013.
- "Publisher chart". cruciverb.com. http://www.cruciverb.com/index.php?action=ezportal;sa=page;p=19. Retrieved 25 February 2013.
- Tausig, Ben (7 December 2012). "Fixing the Broken Crossword Puzzle Economy". TheAwl.com. http://www.theawl.com/2012/12/solving-the-broken-crossword-puzzle-economy. Retrieved 10 March 2013.
- ""Dr.Fill" Vies for Crossword Solving Supremacy". 19 Sep 2014. https://www.sciencefriday.com/segments/dr-fill-vies-for-crossword-solving-supremacy/.
- "1980–84 Misc". 9 July 2010. http://apple2history.org/appendix/aha/aha80/.
- "Crossword Layout Generator – Open Source". 17 November 2019. https://projectboard.engineering.com/project/crossword-layout-generator---open-source.
- Julie Leibach (19 September 2014). "Inside the Box: Crossword Puzzle Constructing in the Computer Age". https://www.sciencefriday.com/articles/inside-the-box-crossword-puzzle-constructing-in-the-computer-age/.
