Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Mohammad Mansoob Khan and Version 2 by Catherine Yang.
Chalcogenides are essential in the conversion of solar energy into hydrogen fuel due to their narrow band gap energy. H2 is a clean fuel, and its usage can address many of the issues caused by using fossil fuels. It is widely used as a feedstock in the chemical industry to produce ammonia, methanol, and various fuels like diesel, gasoline, etc. It is also used as a transport fuel. It has several other applications in the production of metals and agricultural industries. A cost-effective and long-lasting chalcogenide-based photocatalysts can make the H2 generating process more economical and suitable. The use of binary chalcogenides and their modifications (compounds consisting of only one chalcogen and one electropositive atom) for photocatalytic water splitting will be discussed in the following subsections.
- chalcogenides
- photocatalysts
- photocatalysis
- semiconductors
- water splitting
1. Cd-Based Chalcogenides
CdS and CdSe have both been used extensively in the fields of photocatalysis and photovoltaics, particularly in photoelectrochemical cells. Despite having a favorable bandgap for water splitting (~2.42 eV) [1][2][37,38] CdS is unstable in an aqueous solution under light irradiation due to photocorrosion. Therefore, in order to improve its photostability and photocatalytic activity, many studies have focused on synthesizing different morphologies of CdS together with the addition of co-catalysts and sacrificial agents [2][38]. Some of the different morphologies of CdS nanostructures that have been studied include hollow spheres [3][27], quasi-nanospheres [4][39], nanowires [4][39], and nanotubes [4][39], all of which can be synthesized by hydrothermal methods. Among these, CdS nanospheres were found to exhibit the highest H2 evolution rate during photocatalytic testing in the presence of Na2SO3 and Na2S hole scavengers.
In a recent study, one-dimensional CdS nanotubes displayed a remarkably high valence band edge compared with bulk CdS due to quantum confinement effects, and it was found that the photocatalytic efficiency of CdS nanotubes is higher than that of bulk CdS. Furthermore, the stabilized valence band, tubular structure, and strong p-d orbital hybridization led to a significant enhancement in photostability, making applications in aqueous solutions feasible [5][40].
In addition to the aforementioned studies focused on enhancing CdS through the preparation of different morphologies and sizes, another strategy to impart anti-photocorrosion properties to CdS is surface-modification with non-noble co-catalysts such as Ni, Ni2P, and CuS-NixP [6][7][8][41,42,43] as well as noble metals such as Pt and Au [9][10][44,45].
Another strategy to improve the photostability of CdS in an aqueous solution is to coat it with a thin layer of ZnO. Tso and co-workers have synthesized composite nanowires comprising CdS cores covered with thin ZnO shells, yielding CdS/ZnO core–shell nanowires [11][46]. These heterostructures provided improved stability compared with bare CdS nanowires and also led to reduced electron-hole recombination, causing an increase in H2 evolution activity of over two orders of magnitude as shown in Figure 14. Investigations also revealed that nanowires with 10–30 nm-thick shells absorbed more incident light than nanowires with thinner ZnO shells and had a lower probability of electron-hole recombination, the combination of which led to higher H2 evolution activity.
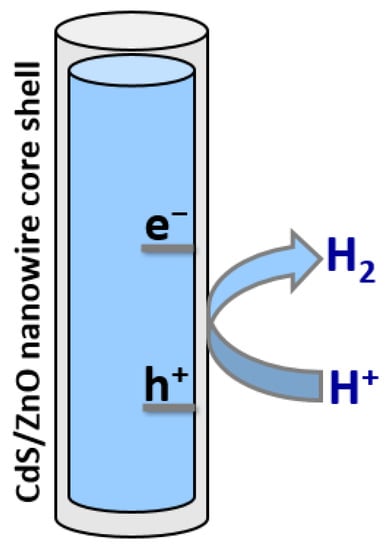
Figure 14.
Schematic diagram of photocatalytic H
2
production using CdS/ZnO core–shell nanowire.
Several recent studies have examined photogenerated electron-hole pair separation in CdS/CuS nanocomposites [11][46]. Pan and co-workers found a high H2 evolution rate of 561.7 μmol h−1 during photocatalytic water splitting using a CdS/CuS nanocomposite [12][47]. In another work, a CdS/CuS nanostructured heterojunction was synthesized [13][48]. The prepared material was applied as a water-splitting photocatalyst and showed that the nanocomposites exhibit an enhanced rate of photocatalytic H2 evolution under visible-light irradiation. It can be concluded that CuS as a non-noble catalyst can improve the stability of CdS for photocatalytic H2 production in an aqueous solution. The enhancement in stability found in the CdS/CuS system can be explained by the transfer of holes from CdS to CuS, which inhibits the photocorrosion of CdS (Figure 25) [14][49].
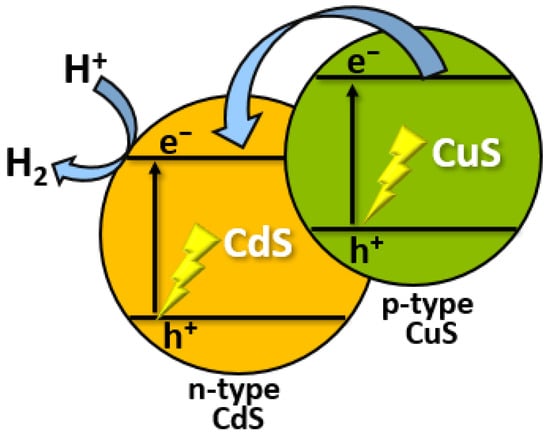
Figure 25.
Mechanism of photocatalytic H
2
evolution using CdS/CuS nanocomposite.
Several authors have studied the factors affecting the performance of nanocrystalline CdSe quantum dots (QD) in photocatalytic water-splitting applications. Osterloh and co-workers showed a clear relationship between the extent of quantum size confinement and the photocatalytic water-splitting activity of suspended CdSe QDs. They found that the rate of H2 evolution increased with QD size in nm as follows: 2.20 > 2.00 > 2.48 > 1.75 > 2.90 > 2.61 > 2.75 > 3.05 > 3.49 > 4.03 > 4.81. These results confirm that photocatalytic activity can be controlled by the extent of quantum confinement (Figure 36) [15][50].
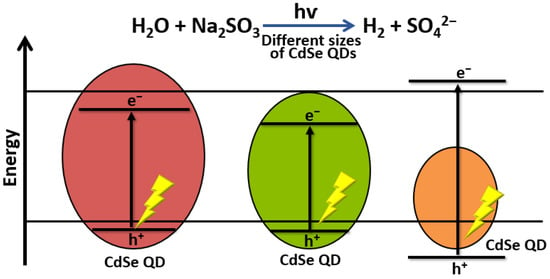
Figure 36.
Schematic illustration of the effect of CdSe QD size in photocatalytic H
2
production.
Covalent organic frameworks (COFs) have drawn research interest owing to their stability, porous structure, large surface area, and tunable band structure [16][51]. It is an organic polymer arranged periodically with high crystallinity and high porosity, that is built from the integration of selected organic blocks via covalent bond linkage [17][52]. For instance, You et al. have synthesized COFs-p-phenylenediamine@CdS (COFs-Ph@CdS) using the hydrothermal method [18][53]. The authors reported that of the H2 generation of bare CdS, COFs-Ph@CdS-x (x = 1, 2, 3, 4) photocatalysts were 16.4, 139.1,17.5, 37.0, and 15.2 μmol, respectively. The photocatalytic H2 production activity of solid COFs-Ph@CdS-1 exhibited 29 and eight times higher compared to those of pristine COFs and CdS, respectively. The enhanced activity may be attributed to a stable coordination bond between Cd2+ ions and N atoms in COFs-Ph@CdS was formed, which served as a migrated channel for photo-generated carriers and their unique hollow structure that enables the production of more photo-generated electrons and holes and absorb light more efficiently.
High rates of photocatalytic H2 production were demonstrated by Das and co-workers using a surface ligand that binds strongly to CdSe QDs via tridentate coordination [19][54]. These authors also reported the effects of surface stabilizing and solubilizing agent dynamics. In more recent work, the influence of ligand exchange on the photocatalytic activity of CdSe QDs in solar water-splitting cells was studied [20][55]. It was found that CdSe QDs bearing shorter ligands showed better photocatalytic activity when compared to pristine CdSe QDs in a photoelectrochemical cell. These results should assist with the design and optimization of photochemical energy conversion systems employing nanocrystalline CdSe QD photocatalysts.
2. Cu-Based Chalcogenides
Visible-light-active CuS/Au nanostructures were obtained by decorating CuS particles with Au nanoparticles, which were prepared by reducing HAuCl4 on the CuS surface [21][58]. The as-synthesized nanostructures displayed excellent catalytic performance in electrochemical H2 evolution tests, with good durability under acidic conditions. It was found that the CuS/Au nanostructured catalyst could produce a current density of 10 mA/cm2 upon the application of only 0.179 V versus the reversible hydrogen electrode (RHE). The CuS/Au catalyst also proved to be an efficient photocatalyst for the degradation of organic pollutants under visible-light irradiation.
The coupling of CuS with metal oxide has been shown to enhance its photocatalytic activities. For instance, Chandra and co-workers have synthesized CuS/TiO2 heterostructures with varying TiO2 contents using a simple hydrothermal method for the photocatalytic evolution of H2 [22][59]. The highest rate of visible-light photocatalytic H2 production was 1262 μmol h−1 g−1, which is around 9.7 and 9.3 times faster in comparison to pristine TiO2 nanospindles or CuS nanoflakes, respectively. The enhanced rate of H2 evolution is attributable to increased light harvesting and more efficient charge separation when an optimum amount of CuS is deposited on TiO2. Growing CuS nanoflakes on TiO2 nanoparticles to form a CuS/TiO2 heterostructure facilitates charge carrier separation at the heterostructure interface and thus enhances photocatalytic performance.
In another study, Dubale et al. fabricated nanocomposites comprising CuS and Cu2O/CuO heterostructures with and without decoration by Pt nanoparticles using an in-situ growth method [23][60]. Cu2O/CuO was prepared by straightforward anodization of Cu film, and a sputtering technique was used to deposit Pt nanoparticles onto the prepared Cu2O/CuO/CuS photocathodes. The prepared heterostructures were found to be very promising and highly stable photocathodes for H2 evolution under visible-light irradiation, with optimized Cu2O/CuO/CuS photocathodes reaching photocurrent densities of up to 5.4 mA cm2, some 2.5 times higher than that achieved by bare Cu2O/CuO. Upon decorating the Cu2O/CuO with both CuS and Pt, a further increase in photocurrent density to 5.7 mA/cm2 was achieved due to the suppression of the charge carrier recombination.
Metal loading on the surface of Cu-based chalcogenides has been reported to improve the photocatalytic evolution of H2. For instance, Ma and co-workers have reported that hydrothermally synthesized Au/CuSe/Pt nanoplates showed strong dual-plasmonic resonance and have been employed for photocatalytic H2 generation under irradiation of visible and near-infrared [24][61]. The as-prepared Au/CuSe/Pt nanoplates exhibited outstanding H2 generation activities of around 7.8 and 9.7 times those of Au/CuSe and Pt/CuSe composites, respectively. In the Au/CuSe/Pt system, light harvesting is enhanced by the plasmonic units (CuSe and Au), while Pt is mainly present as a co-catalyst promoting the H2 evolution reaction as shown in Figure 47.
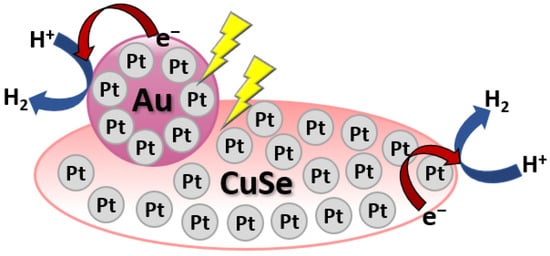
Figure 47.
Schematic diagram of Au/CuSe/Pt ultrathin nanoplate hybrid for H
2
evolution under visible and near-infrared irradiation.
3. Ga-Based Chalcogenides
Monolayers of GaS and GaSe have been studied as photocatalysts by several authors but their performance is limited by low optical absorption and inefficient electron-hole pair separation [25][26][64,65]. One strategy to overcome these limitations is the construction of van der Waals (vdW) heterostructures by pairing GaX (GaX, X = S, Se) with arsenene (two-dimensional arsenic), as demonstrated by Peng and co-workers using first-principle calculations [27][66]. Such GaX/As heterostructures possess band gaps and band alignment that satisfy the requirements for photocatalytic water splitting. In contrast to pristine GaX monolayers, the type of band gap in Se0.5GaS0.5/As and S0.5GaSe0.5/As changes favorably from indirect to direct as the interlayer distance is varied. Furthermore, these heterostructures exhibit transport anisotropy with high electron mobilities of up to ∼2000 cm2 V−1 s−1, which facilitates photogenerated electron-hole pair separation and migration. All of the GaX/As heterostructures studied also show enhanced visible-light absorption beyond that of pristine GaX monolayers. It seems likely that the exceptional properties of GaX/As heterostructures will render them competitive with existing photocatalysts for solar-driven water splitting [27][66].
4. Mo-Based Chalcogenides
Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) is a two-dimensional (2D) material, and it tends to exhibit more remarkable photocatalytic properties than its bulk counterparts [28][29][67,68]. Li and co-workers have investigated the photocatalytic properties of pristine MoS2 nanosheets and Ag-modified MoS2 nanosheets. They found that the rate of photocatalytic H2 production by Ag-modified MoS2 nanosheets could reach 2695 μmol h−1 g−1. They also found that Ag-doped MoS2 nanosheets exhibit superior stability and higher H2 evolution efficiency compared with pristine MoS2 nanosheets, which is mainly due to increased visible-light absorption with increasing Ag content (Figure 58) [30][69].
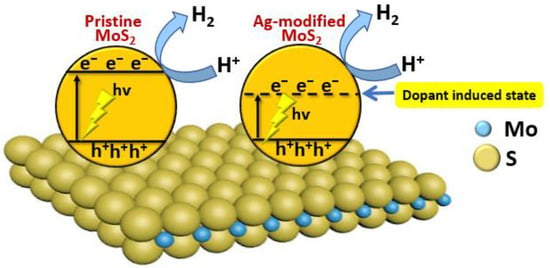
Figure 58.
The mechanism of photocatalytic H
2
production using Ag-modified MoS
2
nanosheets.
Photocorrosion-resistant material, MoS2/Zn0.5Cd0.5S/g-C3N4, has been successfully synthesized by Tang et al. to produce H2 under irradiation of visible light [31][35]. The authors reported that the as-prepared materials exhibited a maximum H2 production rate of 4914 μmol g−1h−1 in Na2S-Na2SO3 solutions which served as the sacrificial agent. The high evolution rate of H2 was owing to the improved charge separation between the interfaces.
In another study, Yuan et al. designed 2D-2D MoS2@Cu-ZnIn2S4 using the solvothermal method for photocatalytic production of H2 [32][70]. The highest H2 evolution rate of 5463 μmol g−1h−1 was observed for 6% MoS2@Cu-ZnIn2S4 under irradiation of visible light which is 72 times higher than that of pristine Cu-ZnIn2S4. The excellent activity may be ascribed to the high visible light absorption property and abundant active sites for the H2 evolution reaction to take place. Moreover, the production rate of H2 remain unchanged after three cycles which suggested the high durability of the synthesized MoS2@Cu-ZnIn2S4 for photocatalytic H2 production.
An enhanced photocatalytic H2 evolution was performed by Yin and co-workers with the maximum evolution rate of 872.3 mol h−1 using MoS2/C composites sensitized with Erythrosin B [33][32]. The enhanced performance was attributed to the efficient photo-generated charge transfer and separation between Erythrosin B and MoS2 or C as well as the presence of more active sites for H2 evolution. The photocatalytic evolution of H2 could also be achieved through photoelectrochemical catalytic activities. For instance, Hassan and co-workers have reported the optimized MoS2/GaN2 exhibited significantly higher photoelectrochemical performance in comparison to the bare materials under the same visible conditions [34][71]. The as-prepared photoanode achieved efficient light harvesting with a photocurrent density of 5.2 mA cm−2 which is 2.6 times higher than bare GaN. Moreover, MoS2/GaN2 exhibited enhanced applied-bias-photon-to-current conversion efficiency of 0.91%, while the reference GaN yielded an efficiency of 0.32%. The authors reported that the decrease in charge transfer resistance between the electrolyte and semiconductor interface and the improved separation charge carriers in the MoS2/GaN heterostructures were all attributed to significant improvements in photocurrent density and efficiency.
MoS2-based nanomaterials have been found to be an efficient visible light-responsive material for H2 production. Based on the reported work, revealed that the surface modification of the MoS2 could lead to an improved photocatalytic activity owing to the effective charge transfer and separation of photo-generated e−/h+ pairs.
New strategies have been developed to use MoSe2-based nanosheets as photocatalysts for the H2 evolution reaction. Zhao and co-workers achieved an enhancement in the photocatalytic activity of MoSe2 by surface modification and doping with Ni and Co [35][72]. Their study found that Ni0.15Mo0.85Se2 nanosheets exhibited the highest photocatalytic activity in both alkaline and acidic media. These results provide an attractive alternative to Pt-based catalysts.
5. Sn-Based Chalcogenides
Recently, it has been discovered that monolayers of the Sn-based mono- and dichalcogenides SnX and SnX2 (X = S or Se) are promising candidates for photocatalytic water splitting. These materials exhibit very good visible light absorption, low exciton binding energies, and high carrier mobility. However, in their pure and strain-free state, the valence band edges of Sn-monochalcogenide monolayers are predicted to be too high in energy for effective water oxidation. This issue can potentially be overcome by crystal engineering to induce a moderate tensile strain, which is predicted to lower the valence band edge to a level suitable for water oxidation [36][21]. Li and co-workers reported that monolayers of both SnX and SnX2 are expected to exhibit good optical absorption in the visible region of the solar spectrum, and the predicted sequence of visible light absorption strength is as follows: SnSe > SnSe2 > SnS > SnS2. Moreover, SnX and SnX2 monolayers also have excellent carrier mobility, which results in the fast migration of photogenerated carriers to the surface. Hence, the possibility of rapid redox reactions on the surface of the photocatalyst.
In another study, Lei et al. successfully prepared SnS/g-C3N4 nanosheets using a facile ultrasonic and microwave heating approach, which formed intimate interfacial contact and a suitable energy band structure [37][73]. The optimized sample displayed enhanced photocatalytic H2 evolution from H2O with the aid of Pt as a co-catalyst in comparison to pure g-C3N4. The stability of the photocatalysts was significantly improved after being loaded with MoO3 particles due to the formation of a Z-scheme heterojunction. Among all as-prepared samples, the 10% SnS/g-C3N4 exhibits the highest photocatalytic rate of 818.93 mmol h−1g−1 under AM1.5G irradiation, 2.90 times to pure g-C3N4, due to the matched energy band structure between g-C3N4 and SnS, which improves the separation efficiency of photo-generated carriers and hinders the recombination of hole-electron pairs. Additionally, SnS nanosheets have improved the light absorption efficiency of the prepared material and generated more catalytic active sites as well as shortening the carriers’ transport path as well.
Liu and co-workers have synthesized flower-like nanostructure SnS2 with generated sulfur vacancies using a new simple strategy of ion exchange [38][74]. The morphology of the flower-like structure provides shorter carrier diffusion lengths and more surface-active sites. While, the presence of S vacancies helps introduce defect levels in SnS2, which leads to a reduction in work function, eventually improving carrier density and separation efficiency. The well-engineered sample 5%Cu/SnS2-x shows the highest photocatalytic activity with an H2 yield of 1.37 mmol h−1, which is about six times higher than that of pure SnS2.
SnS2/ZnIn2S4 composites were successfully fabricated by decorating SnS2 nanosheets with ZnIn2S4 microspheres [39][75]. Geng and co-workers reported that the SnS2/ZnIn2S4 composites showed superior photocatalytic properties for H2 generation in comparison to pristine ZnIn2S4. Furthermore, a notable impact was observed on the photocatalytic activity of ZnIn2S4 when varying the mass ratio of SnS2. The 2.5% SnS2/ZnIn2S4 in particular exhibited the highest photocatalytic H2 generation rate of 769 μmol g−1h−1, which was about 10.5 times the photocatalytic activity of pristine ZnIn2S4. The enhanced photocatalytic activity may be due to the formation of SnS2/ZnIn2S4 heterojunction, which enabled highly active charge separation and transfers on the interface of SnS2 and ZnIn2S4.
6. Ti-Based Chalcogenides
The tri-chalcogenide TiS3 was found to be an effective photoanode for use in photoelectrochemical cells. Photocatalytic H2 evolution rates of up to 1.80 ± 0.05 μmol min−1 were obtained, corresponding to a photoconversion efficiency of ~7% [40][78]. Furthermore, the ternary compounds TixNb1-xS3 (Nb-rich) and NbxTi1−xS3 (Ti-rich) were tested as photoanodes and compared with the corresponding binary trisulfides. The binary compounds were polycrystalline with a nanoribbon morphology and adopted the monoclinic TiS3 (P21/m) and triclinic NbS3 (P2) crystal structures, respectively. H2 generation experiments revealed that the Ti-rich phase was a superior photocatalyst compared with the Nb-rich phase, exhibiting H2 production rates of up to 2.2 ± 0.1 mol/min cm2 [41][79]. Ti-based chalcogenides are not widely explored for their photocatalytic H2 production activity. Therefore, further studies and optimizations are required.
7. V-Based Chalcogenides
Certain transition metals located on the first row of the periodic table can participate in the formation of tetra-chalcogenides thanks to their ability to adopt +4 oxidation states (Figure 69). Among these metals is vanadium, which can form the binary tetra-chalcogenide VS4. Nanocomposites comprising VS4 and graphene were evaluated for solar-driven water splitting by Guo and co-workers. Excellent performance was obtained due to the formation of C–S bonds with a π-conjugated structure, which assists with transferring electrons from the S 2p orbital to graphene [42][80]. The ternary tetra-chalcogenides Cu3Nb1−xVxS4 and Cu3Ta1−xVxS4, which exist as solid solutions and adopt the sulvanite structure, were successfully synthesized in a solid-state reaction by Ikeda and co-workers [43][81]. The band gaps of the synthesized materials were estimated to fall in the range of 1.6–1.7 eV, and the band structure of the Cu3M1−xVxS4 system varies with composition. It was found that for most compositions of solid solution, superior photocatalytic activity was achieved compared with the ternary Cu3MS4 (M = V, Nb, Ta) compounds [43][81].
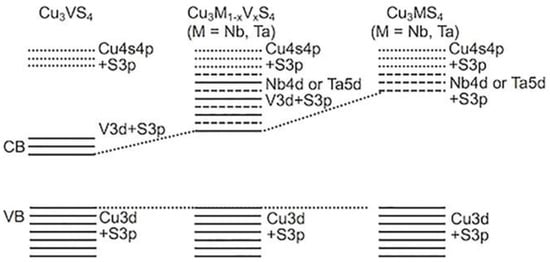
Figure 69.
Proposed band structures for Cu
3
M
1−x
V
x
S
4
(M = Nb and Ta) solid solutions.
Li et al. synthesized the VS2@C3N4 heterojunction with S vacancies via the in situ supramolecular self-assembly method [44][82]. The as-synthesized material shows a remarkable synergistic H2 production rate (9628 μmol g−1h−1) and wastewater degradation efficiency as well as stability, which is 16.0 times that of pristine C3N4. Based on the theoretical calculations and experiment findings, it shows that S vacancies have resulted in the formation of compact heterostructure and the reduction in the work function, which promotes interfacial carriers’ transfer and surface properties. The core–shell structure improves the stability of S vacancies.
In another study, Gopalakrishnan et al. synthesized a core–shell heterostructures photocathode consisting of VS2 deposited on a silicon nanowire surface via single-step chemical vapor deposition for H2 evolution under solar irradiation [45][34]. The core–shell nanowire heterostructure photocathode displayed an outstanding solar-assisted water reduction performance at pH∼7 over a pristine photocathode. The as-prepared material produces about 23 μmol cm−2 h−1 (at 0 V vs. RHE) of H2 gas. Recently, Zhong et al. have doped Ni3S2 with nitrogen and coupled it with VS2 using the hydrothermal method [46][83]. Based on their results, Ni3S2/VS2 without nitrogen doping exhibited improved oxygen evolution reaction (OER) performance with an extremely low overpotential of 227 mV at 10 mA/cm2 which may be attributed to the presence of high number of active sites and excellent interfaces. Moreover, Ni3S2/VS2 with nitrogen doping shows high electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) performance with a low HER overpotential (151 mV at 10 mA/cm2) and this is due to the presence of nitrogen doping that significantly improves the conductivity and increases the number of catalytic active sites.
8. Zn-Based Chalcogenides
Kurnia and co-workers have investigated the performance of ZnS thin films during photoelectrochemical H2 generation [47][84]. They found that ZnS is an inexpensive photocatalyst that exhibits activity under visible-light irradiation without the addition of a co-catalyst. The ZnS thin films were estimated to have band gaps of ~2.4 eV, and photocurrent densities exceeding 1.5 mA/cm2 were achieved under visible-light irradiation (λ ≥ 435 nm). These photocurrents are remarkably high for H2 generation by undoped ZnS under visible-light irradiation.
A modification of ZnO nanosheets, using a thin layer of ZnS, was developed to enhance visible light absorption, leading to improved photoelectrochemical activity in water-splitting experiments [48][49][85,86]. Sánchez-Tovar and co-workers have prepared ZnO/ZnS heterostructures using anodization of Zn in glycerol/water/NH4F electrolytes under controlled hydrodynamic conditions in the presence of various concentrations of Na2S [48][85]. In another work, Zhang et al. synthesized ZnS/ZnO/ZnS sandwich nanosheets with an effective band gap of ~2.72 eV using thermal evaporation, and these materials resulted in potent visible-light photocatalytic activity [49][86]. These works show that coating ZnO with an ultrathin surface layer of ZnS is an interesting approach for enhancing its water-splitting activity under solar irradiation.
Arai and co-workers have synthesized hollow Cu-doped ZnS particles as visible-light photocatalysts for the decomposition of hydrogen sulfide under solar irradiation to generate H2. The Cu-doped ZnS particles were synthesized starting from a ZnO precursor that was co-precipitated on Cu by exploiting the difference in reduction potential between Zn and Cu. The visible-light photoactivity of Cu-doped ZnS was six- and 130-times higher than the Cu-free “ZnS-shell” and pristine ZnS particles prepared using co-precipitation, respectively. A comparative study found that the “Cu-ZnS-shell” particles were highly active under visible-light irradiation (λ > 440 nm), and the rate of H2 evolution was optimized with a Cu (2 wt%)/ZnS photocatalyst [50][36]. In another recent study, Cu/ZnS microspheres were prepared using a template-free microwave irradiation method for H2 generation from an aqueous Na2S solution under visible-light irradiation. The optimized H2 evolution rate of 973.1 μmol h−1 g−1 was obtained for 2.0 mol% Cu-doped ZnS [51][87].
