In geometry, an intersection is a point, line, or curve common to two or more objects (such as lines, curves, planes, and surfaces). The simplest case in Euclidean geometry is the intersection of two distinct lines, which either is one point or does not exist if the lines are parallel. Determination of the intersection of flats – linear geometric objects embedded in a higher-dimensional space – is a simple task of linear algebra, namely the solution of a system of linear equations. In general the determination of an intersection leads to non-linear equations, which can be solved numerically, for example using Newton iteration. Intersection problems between a line and a conic section (circle, ellipse, parabola, etc.) or a quadric (sphere, cylinder, hyperboloid, etc.) lead to quadratic equations that can be easily solved. Intersections between quadrics lead to quartic equations that can be solved algebraically.
- ellipse
- hyperboloid
- quartic equations
1. On a Plane
1.1. Two Lines
For the determination of the intersection point of two non-parallel lines
- [math]\displaystyle{ a_1x+b_1y=c_1, \ a_2x+b_2y=c_2 }[/math]
one gets, from Cramer's rule or by substituting out a variable, the coordinates of the intersection point [math]\displaystyle{ (x_s,y_s) }[/math] :
- [math]\displaystyle{ x_s=\frac{c_1b_2-c_2b_1}{a_1b_2-a_2b_1} , \quad y_s=\frac{a_1c_2-a_2c_1}{a_1b_2-a_2b_1}. \ }[/math]
(If [math]\displaystyle{ a_1b_2-a_2b_1=0 }[/math] the lines are parallel and these formulas cannot be used because they involve dividing by 0.)
1.2. Two Line Segments
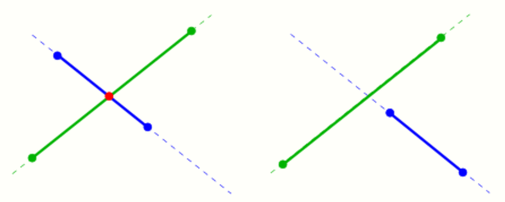
For two non-parallel line segments [math]\displaystyle{ (x_1,y_1),(x_2,y_2) }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ (x_3,y_3),(x_4,y_4) }[/math] there is not necessarily an intersection point (see diagram), because the intersection point [math]\displaystyle{ (x_0,y_0) }[/math] of the corresponding lines need not to be contained in the line segments. In order to check the situation one uses parametric representations of the lines:
- [math]\displaystyle{ (x(s),y(s))=(x_1+s(x_2-x_1),y_1+s(y_2-y_1)), }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ (x(t),y(t))=(x_3+t(x_4-x_3),y_3+t(y_4-y_3)). }[/math]
The line segments intersect only in a common point [math]\displaystyle{ (x_0,y_0) }[/math] of the corresponding lines if the corresponding parameters [math]\displaystyle{ s_0,t_0 }[/math] fulfill the condition [math]\displaystyle{ 0\le s_0,t_0 \le 1 }[/math]. The parametrs [math]\displaystyle{ s_0,t_0 }[/math] are the solution of the linear system
- [math]\displaystyle{ s(x_2-x_1)-t(x_4-x_3)=x_3-x_1, }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ s(y_2-y_1)-t(y_4-y_3)=y_3-y_1 \ . }[/math]
It can be solved for s and t using Cramer's rule (see above). If the condition [math]\displaystyle{ 0\le s_0,t_0 \le 1 }[/math] is fulfilled one inserts [math]\displaystyle{ s_0 }[/math] or [math]\displaystyle{ t_0 }[/math] into the corresponding parametric representation and gets the intersection point [math]\displaystyle{ (x_0,y_0) }[/math].
Example: For the line segments [math]\displaystyle{ (1,1),(3,2) }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ (1,4),(2,-1) }[/math] one gets the linear system
- [math]\displaystyle{ 2s-t=0 }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ s+5t=3 }[/math]
and [math]\displaystyle{ s_0=\tfrac{3}{11}, t_0=\tfrac{6}{11} }[/math]. That means: the lines intersect at point [math]\displaystyle{ (\tfrac{17}{11},\tfrac{14}{11}) }[/math].
Remark: Considering lines, instead of segments, determined by pairs of points, each condition [math]\displaystyle{ 0\le s_0,t_0 \le 1 }[/math] can be dropped and the method yields the intersection point of the lines (see above).
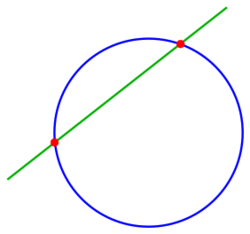
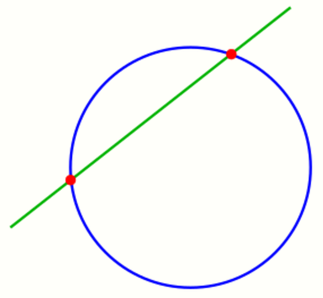
1.3. A Line and a Circle
For the intersection of
- line [math]\displaystyle{ ax+by=c }[/math] and circle [math]\displaystyle{ x^2+y^2=r^2 }[/math]
one solves the line equation for x or y and substitutes it into the equation of the circle and gets for the solution (using the formula of a quadratic equation) [math]\displaystyle{ (x_1,y_1),(x_2,y_2) }[/math] with
- [math]\displaystyle{ x_{1/2}= \frac{ac\pm b\sqrt{r^2(a^2+b^2)-c^2}}{a^2+b^2} \ , }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ y_{1/2}= \frac{bc\mp a\sqrt{r^2(a^2+b^2)-c^2}}{a^2+b^2} \ , }[/math]
if [math]\displaystyle{ r^2(a^2+b^2)-c^2\ge0 \ . }[/math] If this condition holds with strict inequality, there are two intersection points; in this case the line is called a secant line of the circle, and the line segment connecting the intersection points is called a chord of the circle.
If [math]\displaystyle{ r^2(a^2+b^2)-c^2=0 }[/math] holds, there exists only one intersection point and the line is tangent to the circle. If the weak inequality does not hold, the line does not intersect the circle.
If the circle's midpoint is not the origin, see.[1] The intersection of a line and a parabola or hyperbola may be treated analogously.
1.4. Two Circles
The determination of the intersection points of two circles
- [math]\displaystyle{ (x-x_1)^2+(y-y_1)^2=r_1^2 ,\ \quad (x-x_2)^2+(y-y_2)^2=r_2^2 }[/math]
can be reduced to the previous case of intersecting a line and a circle. By subtraction of the two given equations one gets the line equation:
- [math]\displaystyle{ 2(x_2-x_1)x+2(y_2-y_1)y=r_1^2-x_1^2-y_1^2-r_2^2+x_2^2+y_2^2. }[/math]
The intersection of two disks (the interiors of the two circles) forms a shape called a lens.
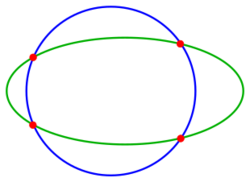
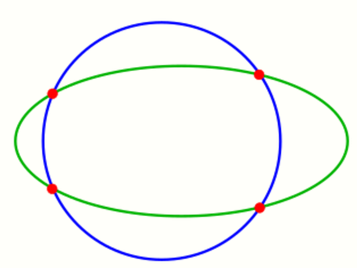
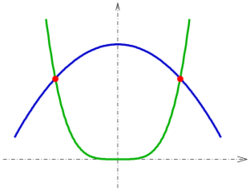
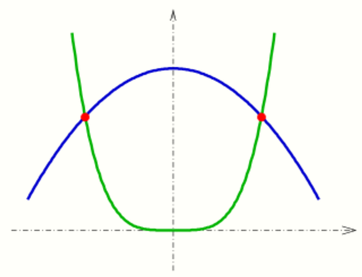
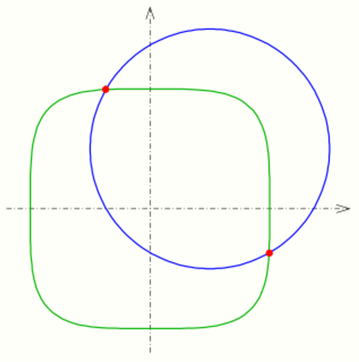
1.5. Two Conic Sections
The problem of intersection of an ellipse/hyperbola/parabola with another conic section leads to a system of quadratic equations, which can be solved in special cases easily by elimination of one coordinate. Special properties of conic sections may be used to obtain a solution. In general the intersection points can be determined by solving the equation by a Newton iteration. If a) both conics are given implicitly (by an equation) a 2-dimensional Newton iteration b) one implicitly and the other parametrically given a 1-dimensional Newton iteration is necessary. See next section.
1.6. Two Smooth Curves
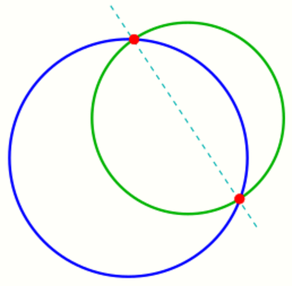
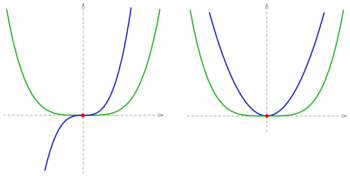
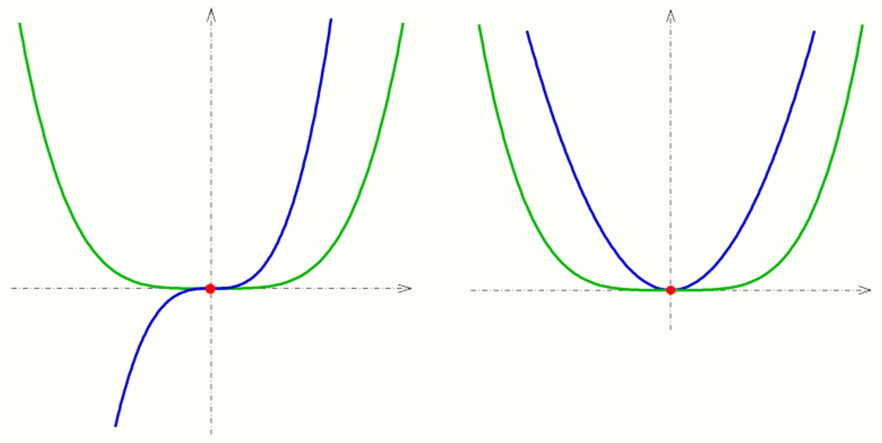
Two curves in [math]\displaystyle{ \R^2 }[/math] (two-dimensional space), which are continuously differentiable (i.e. there is no sharp bend), have an intersection point, if they have a point of the plane in common and have at this point
- a: different tangent lines (transversal intersection), or
- b: the tangent line in common and they are crossing each other (touching intersection, see diagram).
If both the curves have a point S and the tangent line there in common but do not cross each other, they are just touching at point S.
Because touching intersections appear rarely and are difficult to deal with, the following considerations omit this case. In any case below all necessary differential conditions are presupposed. The determination of intersection points always leads to one or two non-linear equations which can be solved by Newton iteration. A list of the appearing cases follows:
- If both curves are explicitly given: [math]\displaystyle{ y=f_1(x), \ y=f_2(x) }[/math], equating them yields the equation
-
- [math]\displaystyle{ f_1(x)=f_2(x) \ . }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ f_1(x)=f_2(x) \ . }[/math]
- If both curves are parametrically given: [math]\displaystyle{ C_1: (x_1(t),y_1(t)), \ C_2: (x_2(s),y_2(s)). }[/math]
- Equating them yields two equations in two variables:
- [math]\displaystyle{ x_1(t)=x_2(s), \ y_1(t)=y_2(s) \ . }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ x_1(t)=x_2(s), \ y_1(t)=y_2(s) \ . }[/math]
- If one curve is parametrically and the other implicitly given: [math]\displaystyle{ C_1: (x_1(t),y_1(t)), \ C_2: f(x,y)=0. }[/math]
- This is the simplest case besides the explicit case. One has to insert the parametric representation of [math]\displaystyle{ C_1 }[/math] into the equation [math]\displaystyle{ f(x,y)=0 }[/math] of curve [math]\displaystyle{ C_2 }[/math] and one gets the equation:
- [math]\displaystyle{ f(x_1(t),y_2(t))=0 \ . }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ f(x_1(t),y_2(t))=0 \ . }[/math]
- If both curves are implicitly given: [math]\displaystyle{ C_1: f_1(x,y)=0, \ C_2: f_2(x,y)=0. }[/math]
- Here, an intersection point is a solution of the system
- [math]\displaystyle{ f_1(x,y)=0, \ f_2(x,y)=0 \ . }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ f_1(x,y)=0, \ f_2(x,y)=0 \ . }[/math]
Any Newton iteration needs convenient starting values, which can be derived by a visualization of both the curves. A parametrically or explicitly given curve can easily be visualized, because to any parameter t or x respectively it is easy to calculate the corresponding point. For implicitly given curves this task is not as easy. In this case one has to determine a curve point with help of starting values and an iteration. See .[2]
Examples:
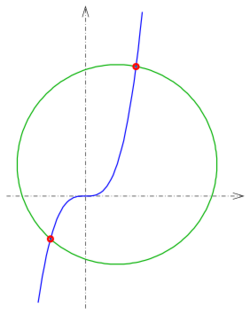
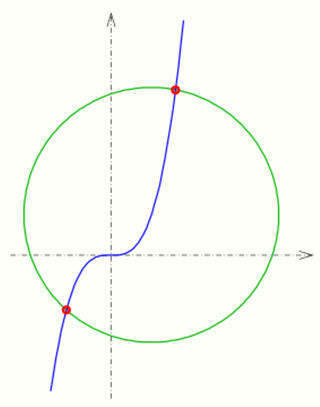
- 1: [math]\displaystyle{ C_1: (t,t^3) }[/math] and circle [math]\displaystyle{ C_2: (x-1)^2+(y-1)^2-10=0 }[/math] (see diagram).
- The Newton iteration [math]\displaystyle{ t_{n+1}:=t_n-\frac{f(t_n)}{f'(t_n)} }[/math] for function
- [math]\displaystyle{ f(t)=(t-1)^2+(t^3-1)^2-10 }[/math] has to be done. As start values one can choose −1 and 1.5.
-
- The intersection points are: (−1.1073, −1.3578), (1.6011, 4.1046)
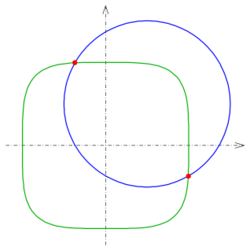
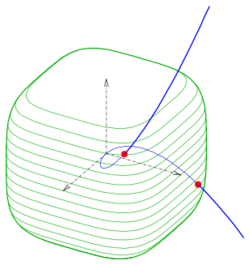
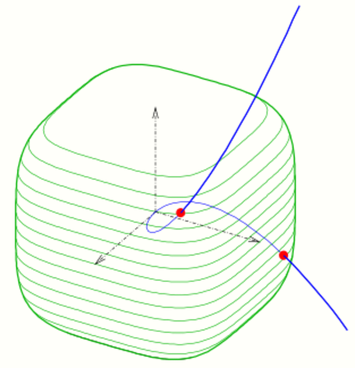
- 2:[math]\displaystyle{ C_1: f_1(x,y)=x^4+y^4-1=0, }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ C_2: f_2(x,y)=(x-0.5)^2+(y-0.5)^2-1=0 }[/math] (see diagram).
- The Newton iteration
- [math]\displaystyle{ {x_{n+1}\choose y_{n+1}}={x_{n}+\delta_x\choose y_n+\delta_y} }[/math] has to be performed, where [math]\displaystyle{ {\delta_x \choose \delta_y} }[/math] is the solution of the linear system
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{pmatrix} \frac{\partial f_1}{\partial x} & \frac{\partial f_1}{\partial y} \\ \frac{\partial f_2}{\partial x} & \frac{\partial f_2}{\partial y} \end{pmatrix}{\delta_x \choose \delta_y}={-f_1\choose -f_2} }[/math] at point [math]\displaystyle{ (x_n,y_n) }[/math]. As starting values one can choose(−0.5, 1) and (1, −0.5).
-
- The linear system can be solved by Cramer's rule.
- The intersection points are (−0.3686, 0.9953) and (0.9953, −0.3686).
- The intersection points are (−0.3686, 0.9953) and (0.9953, −0.3686).
- The linear system can be solved by Cramer's rule.
-
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{pmatrix} \frac{\partial f_1}{\partial x} & \frac{\partial f_1}{\partial y} \\ \frac{\partial f_2}{\partial x} & \frac{\partial f_2}{\partial y} \end{pmatrix}{\delta_x \choose \delta_y}={-f_1\choose -f_2} }[/math] at point [math]\displaystyle{ (x_n,y_n) }[/math]. As starting values one can choose(−0.5, 1) and (1, −0.5).
- [math]\displaystyle{ {x_{n+1}\choose y_{n+1}}={x_{n}+\delta_x\choose y_n+\delta_y} }[/math] has to be performed, where [math]\displaystyle{ {\delta_x \choose \delta_y} }[/math] is the solution of the linear system
- The Newton iteration
- [math]\displaystyle{ C_2: f_2(x,y)=(x-0.5)^2+(y-0.5)^2-1=0 }[/math] (see diagram).
- The intersection points are: (−1.1073, −1.3578), (1.6011, 4.1046)
-
- [math]\displaystyle{ f(t)=(t-1)^2+(t^3-1)^2-10 }[/math] has to be done. As start values one can choose −1 and 1.5.
- The Newton iteration [math]\displaystyle{ t_{n+1}:=t_n-\frac{f(t_n)}{f'(t_n)} }[/math] for function
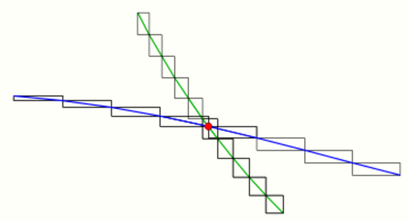
1.7. Two Polygons
If one wants to determine the intersection points of two polygons, one can check the intersection of any pair of line segments of the polygons (see above). For polygons with many segments this method is rather time-consuming. In practice one accelerates the intersection algorithm by using window tests. In this case one divides the polygons into small sub-polygons and determines the smallest window (rectangle with sides parallel to the coordinate axes) for any sub-polygon. Before starting the time-consuming determination of the intersection point of two line segments any pair of windows is tested for common points. See.[3]
2. In Space (Three Dimensions)
In 3-dimensional space there are intersection points (common points) between curves and surfaces. In the following sections we consider transversal intersection only.
2.1. A Line and a Plane
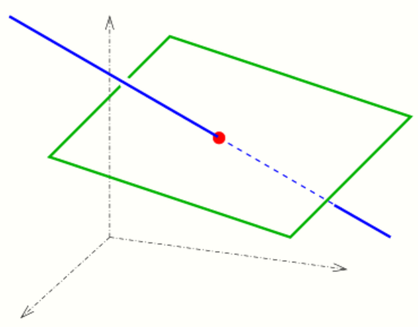
The intersection of a line and a plane in general position in three dimensions is a point.
Commonly a line in space is represented parametrically [math]\displaystyle{ (x(t),y(t),z(t)) }[/math] and a plane by an equation [math]\displaystyle{ ax+by+cz=d }[/math]. Inserting the parameter representation into the equation yields the linear equation
- [math]\displaystyle{ ax(t)+by(t)+cz(t)=d\ , }[/math]
for parameter [math]\displaystyle{ t_0 }[/math] of the intersection point [math]\displaystyle{ (x(t_0),y(t_0),z(t_0)) }[/math].
If the linear equation has no solution, the line either lies on the plane or is parallel to it.
2.2. Three Planes
If a line is defined by two intersecting planes [math]\displaystyle{ \varepsilon_i: \ \vec n_i\cdot\vec x=d_i, \ i=1,2 }[/math] and should be intersected by a third plane [math]\displaystyle{ \varepsilon_3: \ \vec n_3\cdot\vec x=d_3 }[/math], the common intersection point of the three planes has to be evaluated.
Three planes [math]\displaystyle{ \varepsilon_i: \ \vec n_i\cdot\vec x=d_i, \ i=1,2,3 }[/math] with linear independent normal vectors [math]\displaystyle{ \vec n_1,\vec n_2, \vec n_3 }[/math] have the intersection point
- [math]\displaystyle{ \vec p_0=\frac{d_1(\vec n_2\times \vec n_3) +d_2(\vec n_3\times \vec n_1) + d_3(\vec n_1\times \vec n_2)}{\vec n_1\cdot(\vec n_2\times \vec n_3)} \ . }[/math]
For the proof one should establish [math]\displaystyle{ \vec n_i\cdot\vec p_0=d_i, \ i=1,2,3 , }[/math] using the rules of a scalar triple product. If the scalar triple product equals to 0, then planes either do not have the triple intersection or it is a line (or a plane, if all three planes are the same).
2.3. A Curve and a Surface
Analogously to the plane case the following cases lead to non-linear systems, which can be solved using a 1- or 3-dimensional Newton iteration.[4]
- parametric curve [math]\displaystyle{ C: (x(t),y(t),z(t)) }[/math] and
- parametric surface [math]\displaystyle{ S: (x(u,v),y(u,v),z(u,v))\ , }[/math]
- parametric curve [math]\displaystyle{ C: (x(t),y(t),z(t)) }[/math] and
- implicit surface [math]\displaystyle{ S: f(x,y,z)=0\ . }[/math]
Example:
- parametric curve [math]\displaystyle{ C: (t,t^2,t^3) }[/math] and
- implicit surface [math]\displaystyle{ S: x^4+y^4+z^4-1=0 }[/math] (s. picture).
- The intersection points are: (−0.8587, 0.7374, −0.6332), (0.8587, 0.7374, 0.6332).
A line–sphere intersection is a simple special case.
Like the case of a line and a plane, the intersection of a curve and a surface in general position consists of discrete points, but a curve may be partly or totally contained in a surface.
2.4. Two Surfaces
Two transversally intersecting surfaces give an intersection curve. The most simple case the intersection line of two non-parallel planes.
References
- Erich Hartmann: Geometry and Algorithms for COMPUTER AIDED DESIGN. Lecture notes, Technische Universität Darmstadt, October 2003, p. 17 http://www.mathematik.tu-darmstadt.de/~ehartmann/cdgen0104.pdf
- Erich Hartmann: Geometry and Algorithms for COMPUTER AIDED DESIGN. Lecture notes, Technische Universität Darmstadt, October 2003, p. 33 http://www.mathematik.tu-darmstadt.de/~ehartmann/cdgen0104.pdf
- Erich Hartmann: CDKG: Computerunterstützte Darstellende und Konstruktive Geometrie. Lecture notes, TU Darmstadt, 1997, p. 79 (PDF; 3,4 MB) http://www.mathematik.tu-darmstadt.de/~ehartmann/cdg-skript-1998.pdf
- Erich Hartmann: Geometry and Algorithms for COMPUTER AIDED DESIGN. Lecture notes, Technische Universität Darmstadt, October 2003, p. 93 http://www.mathematik.tu-darmstadt.de/~ehartmann/cdgen0104.pdf