You're using an outdated browser. Please upgrade to a modern browser for the best experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 3 by Jessie Wu and Version 2 by Jessie Wu.
The marine macroalgae produce a collection of bioactive polysaccharides, of which the sulfated heteropolysaccharide fucoidan produced by brown algae of the class Phaeophyceae has received worldwide attention because of its particular biological actions that confer nutritional and health benefits to humans and animals. The biological actions of fucoidan are determined by their structure and chemical composition, which are largely influenced by the geographical location, harvest season, extraction process, etc.
- fucoidan
- C2-
- algal biomass
1. Marine Macroalgal Sources of Fucoidan
Macroalgae, also called seaweeds, are taxonomically categorized into the phyla Chlorophyta (green algae), Rhodophyta (red algae) and Phaeophyta (brown algae). Brown seaweeds are benthic, and they inhabit the coastal ecosystems in temperate and cold-water seas [1]. Brown macroalgae produce the fucoidan polysaccharide [2] (Table 1). The brown seaweeds, such as Ecklonia cava, Ascophyllum nodosum, Cladosiphon okamuranus, Undaria pinnatifida, Saccharina longicruris, Saccharina latissima, Sargassum polycystum, Laminaria japonica, Fucus vesiculosus and Fucus serratus, are abundant sources of fucoidans [3][4][5][6][7][8][9].
Table 1. Marine macroalgal sources of fucoidan polysaccharides.
| Marine Macroalga | Chemical Composition/Structure | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Fucus evanescens | ([→3)-α-L-Fucp(2,4O SO3−)-(1→4)-α-L-Fucp(2OSO3−)-(1→])n | [10] |
| Sargassum horneri | repeating →3-α-l-Fucp(2 SO3−)-1→4-α-l-Fucp(2,3SO(3)(-))-1→ fragment, with insertions of →3-α-l-Fucp(2,4SO(3)(-))-1→ fragment | [11] |
| Laminaria longipes | [→3)-α-l-Fucp-(2SO(3)-)-(1→4)-α-l-Fucp-(1→2)-α-l-Fucp-(4 SO3−)-(1→]n | [12] |
| Laminaria hyperborea | (1→3)-α-L-fuco-pyranose (31.9%) to be the dominant residue, followed by 1→2-linked (13.2%) and 1→4-linked (7.7%) fuco-pyranose | [13] |
| Fucus evanescens | ([→3)-α-L-Fucp(2,4O SO3−)-(1→4)-α-L-Fucp(2OSO3-)-(1→]n) | [10] |
| Ascophyllum nodosum | [→3)-α-l-Fuc(2SO3−)-(1→4)-α-l-Fuc(2,3diSO3−)-(1]n | [6] |
| Fucus evanescens | [→3)-α-l-Fucp(2SO3−)-(1→4)-α-l-Fucp(2SO3−)-(1→]n | [14] |
| Fucus distichus | [→3)-α-l-Fucp-(2,4-di-SO3−)-(1→4)-α-l-Fucp-(2SO3−)-(1→]n | [15] |
2. Composition, Structure and Physicochemical Properties of Fucoidan
The fundamental subunit of fucoidan is fucose (C6H12O5) which is a deoxyhexose sugar [16]. The amount of L-fucose in fucoidan outweighs other monosaccharides and accounts for more than 90% of its total sugar composition [2]. The other monosaccharides in fucoidan comprise varying proportions of uronic acid, galactose, glucose, xylose, mannose, rhamnose, arabinose and acetyl groups [9][17][18][19]. The composition and complexity of fucoidan polysaccharides vary among different species of brown macroalgae (Table 1) and are largely influenced by geographical location and seasonal variations [19][20]. The diverse chemical compositions are reminiscent of their differences in biosynthesis. Although fucoidans do not have a universal chemical structure [2][21], the scientific literature available to date suggests principally two structural types of fucoidans: Type I fucoidan has repeating units of α-(1→3)-linked α-L-fucopyranose and Type II fucoidan has alternately repeating units of α-(1→3)- and α-(1→4)-linked α-L-fucopyranose (Figure 1) [12][17][19][22]. Several representatives of the orders Chordariales and Laminariales contain Type I fucoidan, whereas those from the order Fucales contain Type II fucoidan [6][11][14][15][23]. The fucose-linked sulfate groups in Type I fucoidan are found in C2- and C4-positions, whereas in Type II fucoidans they are found in C2-, C3- and C4 positions [12][22].
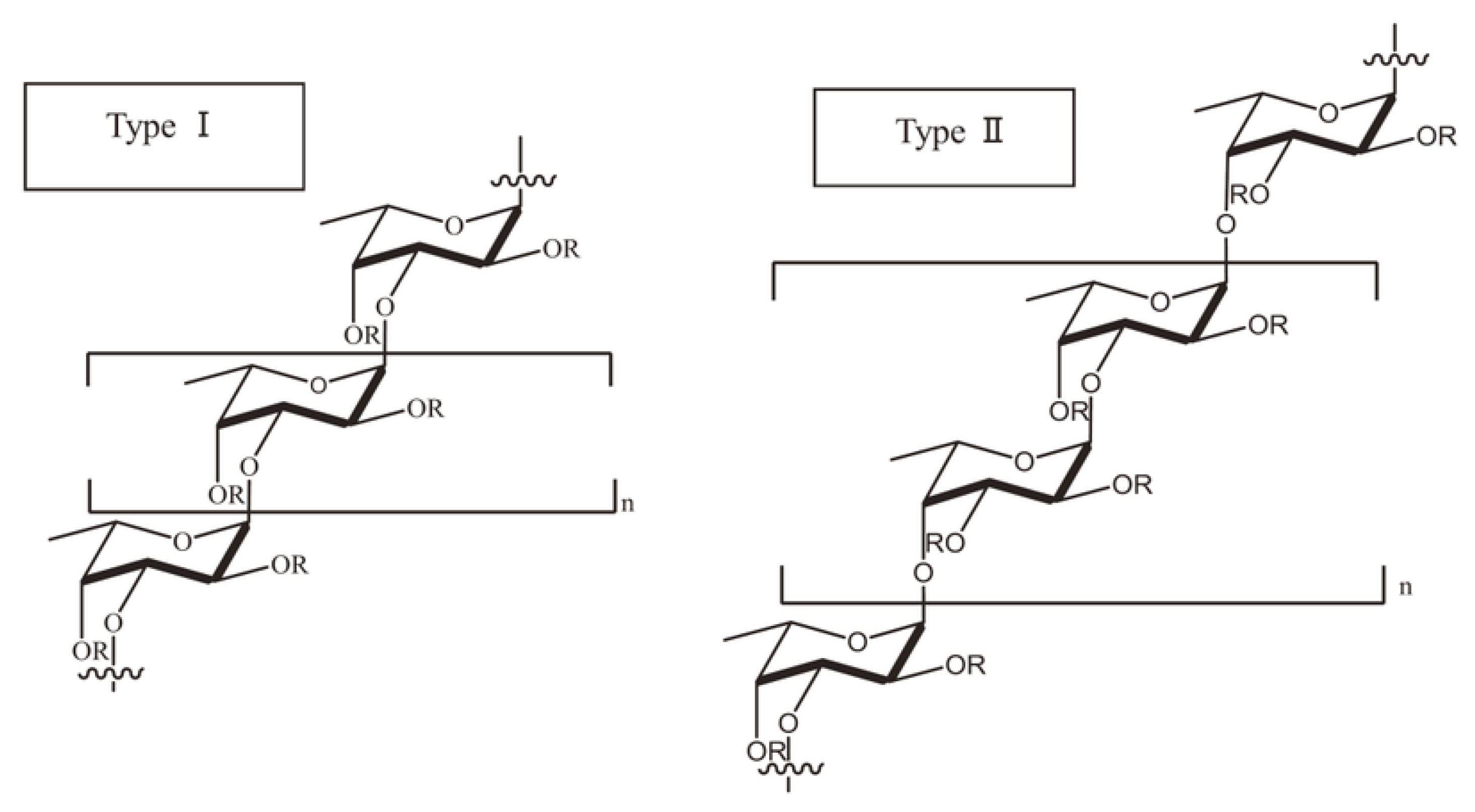
Figure 1. Structure of fucoidan. Type I fucoidan has repeating units of α-(1→3)-linked α-L-fucopyranose and Type II fucoidan has alternately repeating units of α-(1→3)- and α-(1→4)-linked α-L-fucopyranose [17].
Different sets of fucoidans may be produced by the same species of brown seaweeds. For example, the brown seaweed Sargassum stenophyllum synthesizes two different sets of fucoidans [24]. One set of fucoidan contains α-L-fucose as the major component and substantial amounts of other sugars, such as β-D-galactose, β-D-mannose, α-D-glucuronic acid, α-D-glucose and β-D-xylose, with higher percentages of glucuronic acid and fewer sulfate groups located on different sugar units. The other set of fucoidan contains small amounts of α-D-glucuronic acid and high percentages of sulfate groups, which are concentrated on fucose residues, with only fucose and galactose as major components. Similarly, the brown seaweed Adenocystis utricularis also produces two different types of fucoidans; one type, called the galactofucan, is mainly composed of L-fucose, D-galactose and ester sulfate groups, whereas the other type, called the uronofucoidan, is composed mainly of fucose along with several other monosaccharides and significant amounts of uronic acids and fewer amounts of sulfate esters [25]. Cui et al. [26] extracted six different kinds of fucoidans from Saccharina japonica which varied in their monosaccharide compositions, sulfate contents and molecular weights.
The biological activities of fucoidan, such as the antioxidant and anticoagulant activities, are influenced by the variations in uronic acid and degrees of sulfation [18][27]. The degree of sulfation may vary from 15 to 30% depending on the species of brown macroalgae [22]. The high number of branch points in the macromolecular skeleton increases the complexity of the fucoidan structure [2][11].
Fucoidans are generally high molecular weight macromolecular structures [2][27] ranging from approximately 10 kDa [28] to 2000 kDa [29]. The method of extraction is decisive in the molecular size of fucoidan as high temperature induces breaks in the molecule, resulting in fragmentation, whereas the use of strong chemicals can introduce chemical groups into the polysaccharide structure [27].
The fucoidans are anionic owing to the negative charge of the macromolecular skeleton imparted by the presence of sulfate ester groups. The biological interactions of fucoidans with various macromolecular structures, such as proteins, are based on their charge density and fine chemical characteristics [2]. It is a highly hygroscopic polysaccharide and is soluble in water and acidic solutions [17]. The solubility of fucoidan is largely dependent on the level of branching and the number of sulfate groups. Though water-soluble, fucoidans do not yield highly viscous solutions and are not used as gelling agents for industrial applications. However, the addition of NaCl, CaCl2 and sugars can increase the dynamic viscoelasticity of fucoidan [30]. The dynamic viscoelasticity of fucoidan in an aqueous solution is determined by several factors, such as the originating species, concentration of fucoidan and its molecular weight, sulfate content, branching points, pH and temperature. The fucoidan obtained from the commercially cultured C. okamuranus showed stable dynamic viscoelasticity over a wide range of pH, whereas it decreased with an increase in temperature [30]. Blending with other polymers, such as chitosan [31] and poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) [32], of opposite net charge can facilitate electrostatic interaction with the negatively charged sulfate groups of fucoidan and thus improve its rheological properties and gel formation. Additionally, blending with such biocompatible polymers makes fucoidan suitable for biomedical applications.
3. Extraction, Purification and Structural Modification of Fucoidan
The sulfated heteropolysaccharides from marine seaweeds are obtained through various time- and resource-intensive sequential steps, such as harvesting, washing, mechanical, chemical or enzymatic pretreatment of algal raw material, followed by extraction of the polysaccharides using various extraction agents, isolation, purification and finally lyophilization and preservation for various intended applications (Figure 2).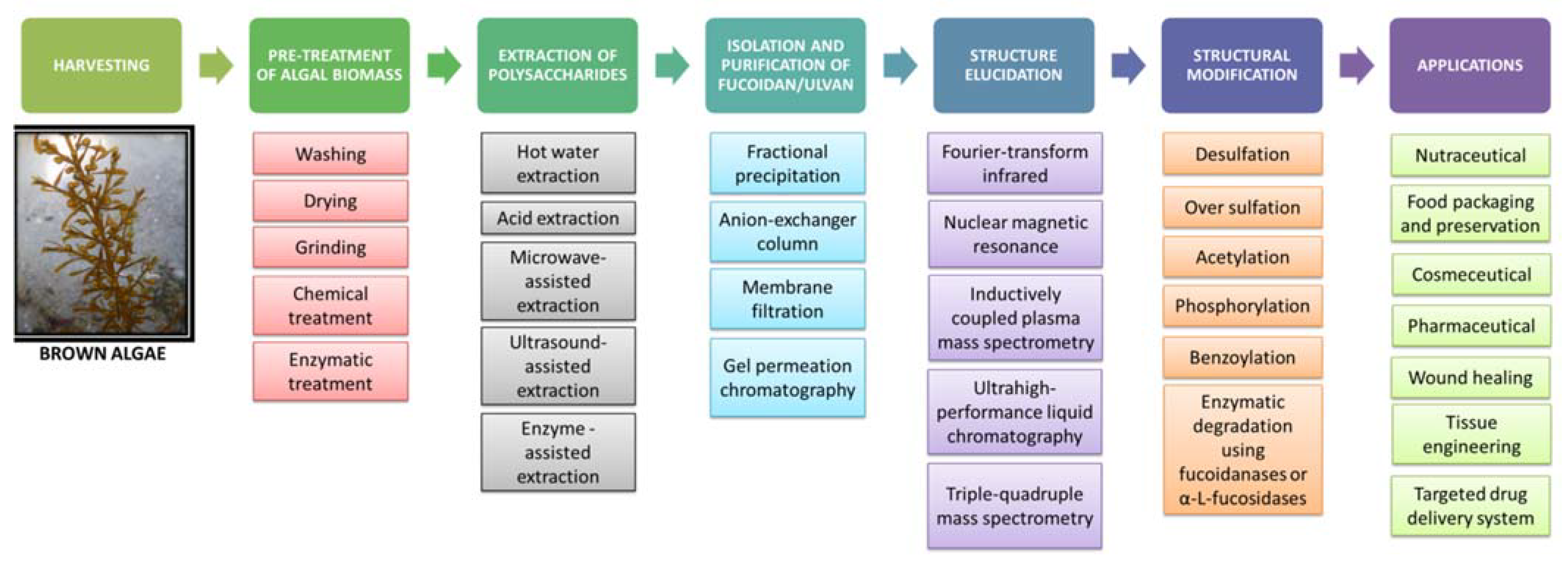
Figure 2. Processes in the extraction, purification and applications of fucoidan.
3.1. Harvesting and Pretreatment of Algal Biomass
Numerous microbes and epiphytes are found inhabiting the surface of macroalgae and they produce polysaccharides which need to be removed by surface sterilization protocol to prevent hampering of the purity of fucoidan. The harvested algae are first washed to remove salt, sand and epiphytes. The washed algae are then dried in shade, and ground into powder to increase the surface area for the action of extraction agents to be used in the subsequent steps and to enhance the release of polysaccharides. The algal biomass contains macromolecules other than fucoidan, such as other polysaccharides, proteins, lipids and pigments, which may blemish the purity of the final product. Chemical or enzymatic pretreatment steps are employed to remove these impurities. Treating the algal biomass with ethanol or acetone removes lipids and pigments [33]. The compounds, such as polyphenyl, chlorophyll and aroma extracts, can be removed by adsorption onto activated charcoal. Chloroform/methanol solvent mixture is also used for the removal of algal pigments [34]. The polysaccharides in algal biomass other than the desired fucoidan can be removed by sequential extraction and precipitation [34].3.2. Extraction of Fucoidan
The conventional methods of extraction of fucoidan are hot water extraction and acid extraction [35]. Hot water extraction is performed at 80–90 °C in solutions containing sodium oxalate or ammonium oxalate as divalent cation chelator that can chelate the Ca2+ that crosslinks the sulfated polysaccharide strands in the algal cell wall [36]. Acid extraction is performed using dilute HCl [25][36]. The residual algal biomass obtained by filtration or centrifugation after the initial extraction of polysaccharides is usually subjected to several extraction cycles to maximize the yield of polysaccharides. Table 2 summarizes the various extraction methodologies reported for the extraction of fucoidan polysaccharides from marine macroalgal biomass.Table 2. Methods of extraction of fucoidan from macroalgal biomass.
| Macroalgal Species | Extraction Method | Extraction Yield/Efficiency | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ascophyllum nodosum | Microwave-assisted extraction | 16.08% | [37] |
| Fucus vesiculosus | Pressurized liquid extraction at high temperature | 25.99 ± 2.22% | [38] |
| Fucus vesiculosus | Microwave-assisted extraction | 18.2 ± 1.4% | [39] |
| Fucus vesiculosus | Autohydrolysis process | 16.5 ± 1.2% | [39] |
| Fucus vesiculosus | Microwave-assisted extraction | 18.22% | [40] |
| Nizamuddinia zanardinii | Ultrasound-assisted extraction | 3.51% | [41] |
| Sargassum myriocystum | Enzyme-assisted extraction | 6.2% | [33] |
| Turbinaria decurrens | Soaking in chloroform/methanol, sequential extraction in CaCl2, HCl | 5.58% (crude) 1.28% (purified) |
[34] |
| Sargassum ilicifolium | Probe sonication–microwave assisted extraction method Hot water extraction method |
8 ± 0.9% 6 ± 0.5% |
[42] |
3.3. Isolation and Purification of Fucoidan
The algal extracts obtained through the different extraction protocols are crude mixtures of different polysaccharides, proteins, phenolic compounds and pigments. The crude algal extracts are to be subjected to rigorous purification steps, such as fractional precipitation, ion exchange column chromatography, membrane filtration, size exclusion chromatography or affinity chromatography [47]. The sulfated polysaccharides are less soluble in polar solvents, which facilitate their isolation from the aqueous phase by fractional precipitation using ethanol, calcium chloride [25][34], or using anion exchanger columns [34]. Sulfated polysaccharides are polydisperse and fucoidans of varying molecular weight may be produced by the same algal species. Membrane filtration using different molecular weight cut-off membranes is used for the fractional separation of fucoidans from other polysaccharides and also to separate their different molecular variants [36]. Size exclusion chromatography, also known as gel permeation chromatography, is also used for the fractional separation of fucoidan according to their molecular sizes [13][19].3.4. Structure Elucidation of Fucoidan
The composition and structure of sulfated heteropolysaccharides are so highly diverse and complex that the elucidation of the chemical structure of the whole polymer is time- and resource-intensive and requires the use of several techniques. The minutiae of the structural features of polysaccharides can be elucidated by spectrometric techniques, such as Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) [19][48][49], inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) [13] and Raman spectroscopy [13]. Ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography coupled with triple-quadruple mass spectrometry (UHPLC/QqQ-MS) that performs analysis in multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode for rapid and simultaneous determination of glycosidic linkages in polysaccharides is also emerging [50]. The combined use of spectrophotometric methods and regio- and stereoselective enzymes can also give insight into their chemical structure [11]. The molecular weight characteristics are determined by gel filtration chromatography [28].3.5. Structural Modification of Fucoidan
Structural modification of sulfated polysaccharides by chemical and enzymatic means can yield novel derivatives of algal polysaccharides with improved and more effective biological activity [51]. The chemical modification involves desulfation, over-sulfation, acetylation, phosphorylation and benzoylation. The acid-based extraction protocol removes the sulfate groups from sulfated algal polysaccharides [21]. The anticoagulant activity of fucoidans from brown algae depends on their molecular weight, the degree of sulfation and the distribution of sulfate groups in the repeating monosaccharide units. The benzoylated derivative of fucoidan extracted from L. japonica had strong scavenging activity on superoxide, hydroxyl and 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical [52]. The phosphorylated and aminated derivatives of synthesized fucoidan showed stronger antioxidant ability than native fucoidan [53]. Low molecular weight derivatives of algal sulfated polysaccharides with varied biological activities can be obtained by chemical, physical or enzymatic methods. Enzymatic degradation of sulfated algal polysaccharides using fucoidanases or α-L-fucosidases to yield bioactive oligosaccharides is advantageous over chemical methods since the former selectively hydrolyzes the glycosidic bonds, preserving the sulfation pattern essential for biological activity [2][21][54].References
- Kawai, H.; Henry, E.C. Phaeophyta. In Handbook of the Protists; Archibald, J., Simpson, A., Slamovits, C., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 267–304.
- Zayed, A.; El-Aasr, M.; Ibrahim, A.S.; Ulber, R. Fucoidan Characterization: Determination of Purity and Physicochemical and Chemical Properties. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 571.
- Bilan, M.I.; Grachev, A.A.; Shashkov, A.S.; Nifantiev, N.E.; Usov, A.I. Structure of a Fucoidan from the Brown Seaweed Fucus serratus L. Carbohydr. Res. 2006, 341, 238–245.
- Bilan, M.I.; Grachev, A.A.; Shashkov, A.S.; Kelly, M.; Sanderson, C.J.; Nifantiev, N.E.; Usov, A.I. Further Studies on the Composition and Structure of a Fucoidan Preparation from the Brown Alga Saccharina latissima. Carbohydr. Res. 2010, 345, 2038–2047.
- Bilan, M.I.; Grachev, A.A.; Shashkov, A.S.; Thuy, T.T.T.; Van, T.T.T.; Ly, B.M.; Nifantiev, N.E.; Usov, A.I. Preliminary Investigation of a Highly Sulfated Galactofucan Fraction Isolated from the Brown Alga Sargassum polycystum. Carbohydr. Res. 2013, 377, 48–57.
- Chevolot, L.; Mulloy, B.; Ratiskol, J.; Foucault, A.; Colliec-Jouault, S. A disaccharide repeat unit is the major structure in fucoidans from two species of brown algae. Carbohydr. Res. 2001, 330, 529–535.
- Elizondo-Gonzalez, R.; Cruz-Suarez, L.E.; Ricque-Marie, D.; Mendoza-Gamboa, E.; Rodriguez-Padilla, C.; Trejo-Avila, L.M. In vitro characterization of the antiviral activity of fucoidan from Cladosiphon okamuranus against Newcastle Disease Virus. Virol. J. 2012, 9, 307.
- Rioux, L.E.; Turgeon, S.L.; Beaulieu, M. Structural Characterization of Laminaran and Galactofucan Extracted from the Brown Seaweed Saccharina longicruris. Phytochemistry 2010, 71, 1586–1595.
- Wijesinghe, W.A.J.P.; Jeon, Y.-J. Enzyme-assistant extraction (EAE) of bioactive components: A useful approach for recovery of industrially important metabolites from seaweeds: A review. Fitoterapia 2012, 83, 6–12.
- Krylova, N.V.; Ermakova, S.P.; Lavrov, V.F.; Leneva, I.A.; Kompanets, G.G.; Iunikhina, O.V.; Nosik, M.N.; Ebralidze, L.K.; Falynskova, I.N.; Silchenko, A.S.; et al. The Comparative Analysis of Antiviral Activity of Native and Modified Fucoidans from Brown Algae Fucus evanescens In Vitro and In Vivo. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 224.
- Silchenko, A.S.; Rasin, A.B.; Kusaykin, M.I.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Miansong, Z.; Changheng, L.; Malyarenko, O.; Zueva, A.O.; Zvyagintseva, T.N.; Ermakova, S.P. Structure, enzymatic transformation, anticancer activity of fucoidan and sulphated fucooligosaccharides from Sargassum horneri. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 175, 654–660.
- Usoltseva, R.V.; Shevchenko, N.M.; Malyarenko, O.S.; Anastyuk, S.D.; Kasprik, A.E.; Zvyagintsev, N.V.; Ermakova, S.P. Fucoidans from brown algae Laminaria longipes and Saccharina cichorioides: Structural characteristics, anticancer and radiosensitizing activity in vitro. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 221, 157–165.
- Kopplin, G.; Rokstad, A.M.; Mélida, H.; Bulone, V.; Skjåk-Bræk, G.; Aachmann, F.L. Structural Characterization of Fucoidan from Laminaria hyperborea: Assessment of Coagulation and Inflammatory Properties and Their Structure-Function Relationship. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2018, 1, 1880–1892.
- Bilan, M.I.; Grachev, A.A.; Ustuzhanina, N.E.; Shashkov, A.S.; Nifantiev, N.E.; Usov, A.I. Structure of a fucoidan from the brown seaweed Fucus evanescens C.Ag. Carbohydr. Res. 2002, 337, 719–730.
- Bilan, M.I.; Grachev, A.A.; Ustuzhanina, N.E.; Shashkov, A.S.; Nifantiev, N.E.; Usov, A.I. A highly regular fraction of a fucoidan from the brown seaweed Fucus distichus L. Carbohydr. Res. 2004, 339, 511–517.
- Wijesinghe, W.A.J.P.; Jeon, Y. Biological activities and potential industrial applications of fucose rich sulfated polysaccharides and fucoidans isolated from brown seaweeds: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 88, 13–20.
- Luthuli, S.; Siya, W.; Cheng, Y.; Zheng, X.; Wu, M.; Tong, H. Therapeutic Effects of Fucoidan: A Review on Recent Studies. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 487.
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z. Antioxidant activity of sulfated polysaccharide fractions extracted from Laminaria japonica. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2008, 42, 127–132.
- Yu, J.; Li, Q.; Wu, J.; Yang, X.; Yang, S.; Zhu, W.; Liu, Y. Fucoidan Extracted From Sporophyll of Undaria pinnatifida Grown in Weihai, China—Chemical Composition and Comparison of Antioxidant Activity of Different Molecular Weight Fractions. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 636930.
- Lim, S.; Choi, J.; Park, H. Antioxidant activities of fucoidan degraded by gamma irradiation and acidic hydrolysis. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2015, 109, 23–26.
- Cunha, L.; Grenha, A. Sulfated Seaweed Polysaccharides as Multifunctional Materials in Drug Delivery Applications. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 42.
- Gotteland, M.; Riveros, K.; Gasaly, N.; Carcamo, C. The Pros and Cons of Using Algal Polysaccharides as Prebiotics. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 163.
- Ale, M.T.; Mikkelsen, J.D.; Meyer, A.S. Important Determinants for Fucoidan Bioactivity: A Critical Review of Structure-Function Relations and Extraction Methods for Fucose-Containing Sulfated Polysaccharides from Brown Seaweeds. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2106–2130.
- Duarte, M.E.R.; Cardoso, M.A.; Noseda, M.D.; Cerezo, A.S. Structural studies on fucoidans from the brown seaweed Sargassum stenophyllum. Carbohydr. Res. 2001, 333, 281–293.
- Ponce, N.M.A.; Pujol, C.A.; Damonte, E.B.; Flores, M.L.; Stortz, C.A. Fucoidans from the brown seaweed Adenocystis utricularis: Extraction methods, antiviral activity and structural studies. Carbohydr. Res. 2003, 338, 153–165.
- Cui, M.; Li, X.; Geng, L.; Wu, N.; Wang, J.; Deng, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Q. Comparative study of the immunomodulatory effects of different fucoidans from Saccharina japonica mediated by scavenger receptors on RAW264.7 macrophages. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 215, 253–261.
- Silva, M.M.C.L.; dos Santos Lisboa, L.; Paiva, W.S.; Batista, L.A.N.C.; Luchiari, A.C.; Rocha, H.A.O.; Camara, R.B.G. Comparison of in vitro and in vivo antioxidant activities of commercial fucoidans from Macrocystis pyrifera, Undaria pinnatifida, and Fucus vesiculosus. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 216, 757–767.
- Nishino, T.; Aizu, Y.; Nagumo, T. The relationship between the molecular weight and the anticoagulant activity of two types of fucan sulfates from the brown seaweed Ecklonia kurome. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1991, 55, 791–796.
- Fitton, J.H.; Dell’Acqua, G.; Gardiner, V.-A.; Karpiniec, S.S.; Stringer, D.N.; Davis, E. Topical Benefits of Two Fucoidan-Rich Extracts from Marine Macroalgae. Cosmetics 2015, 2, 66–81.
- Tako, M. Rheological Characteristics of Fucoidan Isolated from Commercially Cultured Cladosiphon okamuranus. Bot. Mar. 2003, 46, 465.
- Sezer, A.D.; Cevher, E.; Hatipoglu, F.; Ogurtan, Z.; Bas, A.L.; Akbuga, J. Preparation of Fucoidan-Chitosan Hydrogel and Its Application as Burn. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2008, 31, 2326–2333.
- Lee, H.M.; Kim, J.-K.; Cho, T.-S. Applications of ophthalmic biomaterials embedded with fucoidan. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2012, 18, 1197–1201.
- Badrinathan, S.; Shiju, T.M.; Christa, A.S.S.; Arya, R.; Pragasam, V. Purification and Structural Characterization of Sulfated Polysaccharide from Sargassum myriocystum and its Efficacy in Scavenging Free Radicals. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 74, 549–555.
- Shanthi, N.; Arumugam, P.; Murugan, M.; Sudhakar, M.P.; Arunkumar, K. Extraction of Fucoidan from Turbinaria decurrens and the Synthesis of Fucoidan-Coated AgNPs for Anticoagulant Application. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 30998–31008.
- Luan, F.; Zou, J.; Rao, Z.; Ji, Y.; Lei, Z.; Peng, L.; Yang, Y.; He, X.; Zeng, N. Polysaccharides from Laminaria japonica: An insight into the current research on structural features and biological properties. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 4254–4283.
- Aguilar-Briseño, J.A.; Cruz-Suarez, L.E.; Ricque-Marie, D.; Zapata-Benavides, P.; Mendoza-Gamboa, E.; Rodríguez-Padilla, C.; Maria Trejo-Avila, L. Sulphated Polysaccharides from Ulva clathrata and Cladosiphon okamuranus Seaweeds both Inhibit Viral Attachment/Entry and Cell-Cell Fusion, in NDV Infection. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 697–712.
- Yuan, Y.; Macquarrie, D. Microwave assisted extraction of sulfated polysaccharides (fucoidan) from Ascophyllum nodosum and its antioxidant activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 129, 101–107.
- Getachew, A.T.; Holdt, S.L.; Meyer, A.S.; Jacobsen, C. Effect of Extraction Temperature on Pressurized Liquid Extraction of Bioactive Compounds from Fucus vesiculosus. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 263.
- Rodriguez-Jasso, R.; Mussatto, S.; Pastrana, L.; Aguilar, C.; Teixeira, J. Chemical composition and antioxidant activity of sulphated polysaccharides extracted from Fucus vesiculosus using different hydrothermal processes. Chem. Pap. 2014, 68, 203–209.
- Rodriguez-Jasso, R.M.; Mussatto, S.I.; Pastrana, L.; Aguilar, C.N.; Teixeira, J.A. Microwave-assisted extraction of sulfated polysaccharides (fucoidan) from brown seaweed. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 1137–1144.
- Alboofetileh, M.; Rezaei, M.; Tabarsa, M.; You, S. Ultrasound-assisted extraction of sulfated polysaccharide from Nizamuddinia zanardinii: Process optimization, structural characterization, and biological properties. J. Food Process Eng. 2019, 42, e12979.
- Devi, G.V.Y.; Nagendra, A.H.; Sudheer, S.P.; Chatterjee, K.; Venkatesan, J. Isolation and purification of fucoidan from Sargassum ilicifolium: Osteogenic differentiation potential in mesenchymal stem cells for bone tissue engineering. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2022, 136, 104418.
- Agregán, R.; Munekata, P.E.S.; Franco, D.; Carballo, J.; Barba, F.J.; Lorenzo, J.M. Antioxidant Potential of Extracts Obtained from Macro- (Ascophyllum nodosum, Fucus vesiculosus and Bifurcaria bifurcata) and Micro-Algae (Chlorella vulgaris and Spirulina platensis) Assisted by Ultrasound. Medicines 2018, 5, 33.
- My, P.L.T.; Sung, V.V.; Dat, T.D.; Nam, H.M.; Phong, M.T.; Hieu, N.H. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Fucoidan from Vietnamese Brown Seaweed Sargassum mcclurei and Testing Bioactivities of the Extract. Chem. Sel. 2020, 5, 4371–4380.
- Garcia-Vaquero, M.; Doherty, J.V.O.; Tiwari, B.K.; Sweeney, T. Enhancing the Extraction of Polysaccharides and Antioxidants from Macroalgae Using Sequential Hydrothermal-Assisted Extraction Followed by Ultrasound and Thermal Technologies. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 457.
- Patel, A.K.; Vadrale, A.P.; Singhania, R.R.; Michaud, P.; Pandey, A.; Chen, S.-J.; Chen, C.-W. Algal polysaccharides: Current status and future prospects. Phytochem. Rev. 2022, 5, 1–30.
- Flórez-Fernández, N.; Balboa, E.M.; Domínguez, H. Extraction and Purification of Fucoidan from Marine Sources. In Encyclopedia of Marine Biotechnology; Kim, S.-K., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020.
- Koh, H.S.A.; Lu, J.; Zhou, W. Structure characterization and antioxidant activity of fucoidan isolated from Undaria pinnatifida grown in New Zealand. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 212, 178–185.
- Usoltseva, R.V.; Anastyuk, S.D.; Shevchenko, N.M.; Surits, V.V.; Silchenko, A.S.; Isakov, V.V.; Zvyagintseva, T.N.; Thinh, P.D.; Ermakova, S.P. Polysaccharides from brown algae Sargassum duplicatum: The structure and anticancer activity in vitro. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 175, 547–556.
- Galermo, A.G.; Nandita, E.; Barboza, M.; Amicucci, M.J.; Vo, T.-T.T.; Lebrilla, C.B. Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry Approach for Determining Glycosidic Linkages. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 13073–13080.
- Jiao, G.; Yu, G.; Zhang, J.; Ewart, H.S. Chemical Structures and Bioactivities of Sulfated Polysaccharides from Marine Algae. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 196–223.
- Wang, J.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, X.; Li, P. Synthesized different derivatives of low molecular fucoidan extracted from Laminaria japonica and their potential antioxidant activity in vitro. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2009, 44, 379–384.
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, P. Synthesized phosphorylated and aminated derivatives of fucoidan and their potential antioxidant activity in vitro. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2009, 44, 170–174.
- Ale, M.T.; Meyer, A.S. Fucoidans from brown seaweeds: An update on structures, extraction techniques and use of enzymes as tools for structural elucidation. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 8131–8141.
More
