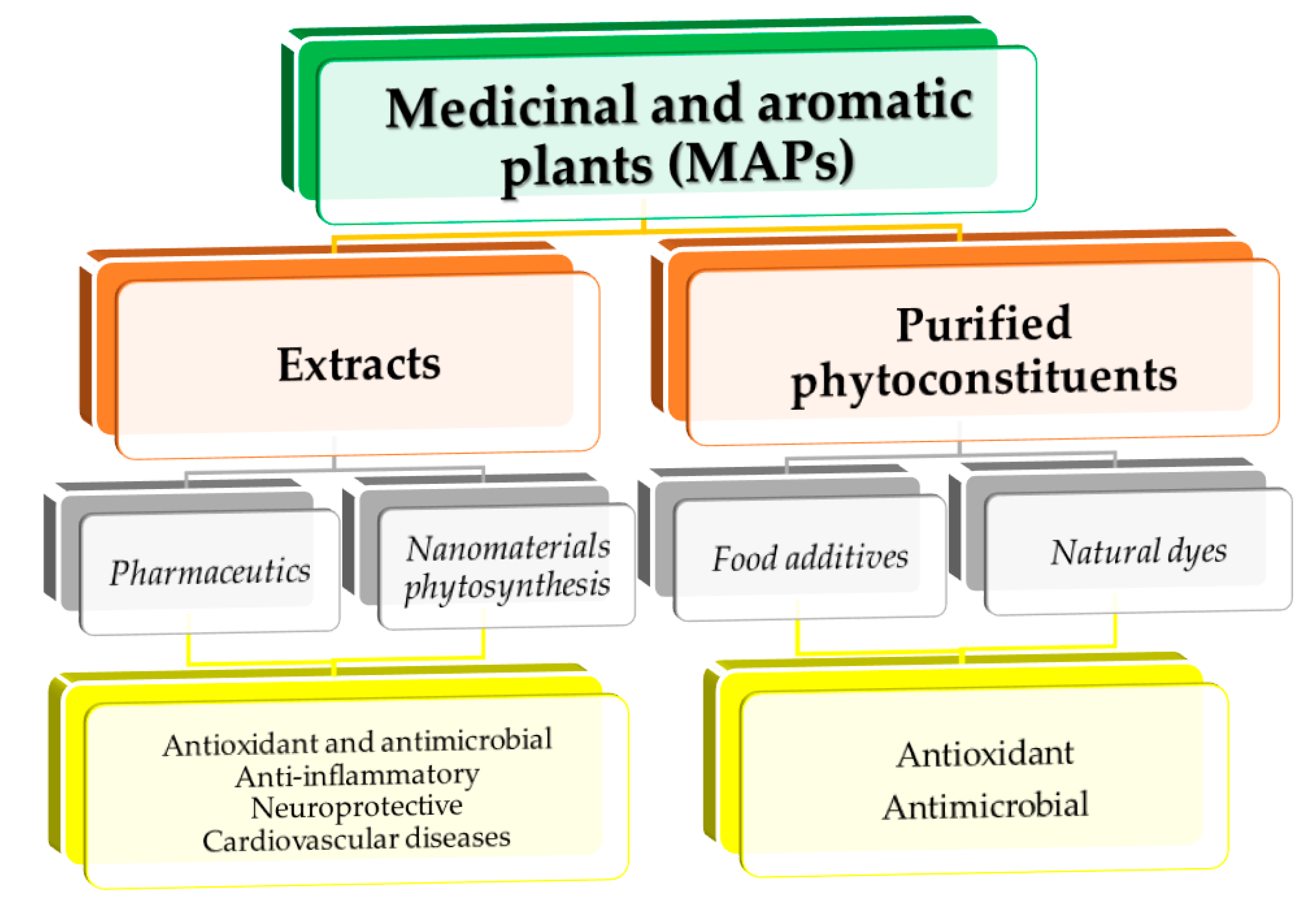
Natural compounds obtained from different medicinal and aromatic plants have gained respect as alternative treatments to synthetic drugs, as well as raw materials for different applications (cosmetic, food and feed industries, environment protection, and many others). Based on a literature survey on dedicated databases, the content includes a critical discussion of aspects regarding classical extraction versus modern extraction techniques; possibilities to scale up (advantages and disadvantages of different extraction methods usually applied and the influence of extraction parameters); and different medicinal and aromatic plants’ different applications (medical and industrial applications, as well as the potential use in nanotechnology).
- medicinal plants
- bioactive compounds
- biomedical applications
- industrial applications
1. Introduction
2. Classical Extraction Versus Modern Extraction Techniques: Possibilities to Scale up
| Plant | Extraction Method | Extraction Conditions |
Obtained Compounds |
Extraction Yield | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allium sativum Linn. |
Microwave-assisted hydro-distillation | Solvent: deionized water/diethyl ether 2:1; 100 g vegetal material; MP = 700 W; t = 30 min; |
Diallyl sulfides (mono-, di-, tri-, and tetra-); Methyl allyl sulfides (di- and tri-); Vinyl dithiins |
0.22% | [22] |
| Ultrasound-assisted extraction | Solvent: diethyl ether (50 mL); F = 35 kHz; T = 25 °C; t = 30 min. |
0.13% | |||
| Lickens–Nickerson apparatus | Solvent: water/diethyl ether = 1:10; 100 g. vegetal material; T = −10 °C; t = 2 h. | 0.23% | |||
| Hippophae rhamnoides L. | Solvent-free microwave-assisted extraction | 400 g vegetal material atmospheric pressure; P = 400 W; T = 20–100 °C; t = 15 min. |
Polyphenols with an increased yield of recovery for microwave extraction method | 1147 mg GAE/g (d.w.) | [23] |
| Classical extraction | Solvent: methanol 80% (50 mL); 5 g vegetal material; 8000 rpm; t = 5 min. |
741.9 mg GAE/g (d.w.) | |||
| Matricaria chamomilla L. | Subcritical water extraction |
Solvent: water (300 mL); 10 g vegetal material; P = 30, 45 and 60 bars; T = 100 °C; t = 30 min; |
Polyphenols | 127–3226 mg/kg | [24] |
| Maceration | Solvent: water (100 mL); 2.5 g vegetal material—oven-dried chamomile at low temperatures (i.e., 40 °C); T = 100 °C; t = 120 min. |
Polyphenols | 19.7 ± 0.5 mg/g (d.w.) | [25] | |
| Mentha spp. | Microwave hydro- diffusion |
Solvent-free; 500 g vegetal material; MP 1 W/g; F 2.45 GHz t = 20 min. |
Essential oil | 0.95% | [26] |
| Soxhlet extraction | Solvent: water: ethanol = 3:7 (250 mL); 1.5 g dry plant material; T = 95 °C |
Polyphenols | 18,381–87,024 mg GAE/kg (d.w.) | [27] | |
| Origanum vulgare L., 1753 | Supercritical extraction |
CO2 flow rate = 2.4 kg/h; 0.6 kg of vegetal material: CO2/plant ratio = 20 kg/kg; P = 30 MPa; T = 40 °C. | Carnosic acid | 3.18 ± 0.40% | [28] |
| Hydro-distillation | 300 g vegetal material; t = 45 min |
Essential oil rich in terpenes | 0.75% (d.w.) | [29] | |
| Rosmarinus officinalis L. | Maceration | Solvent: dichloromethane/ethanol = 3/1 (15 mL); 1 g vegetal material; T = 35 °C; t 3 h. |
Carnosic acid, rosmarinic acid, carnosol | 16.82; 0.12; 9.31 mg/g (f.w.) | [30] |
| Supercritical fluid extraction |
Solvent-free CO2 extraction; flow rate: 5 g/min; 100 g vegetal material; P = 100–300 bar; T = 40 °C; t = 3 h. |
Carnosic acid, rosmarinic acid, camphor, 1,8-cineole | 1.0730; 0.1242; 0.44; 0.029% (d.w.) | [31] | |
| Microwave-assisted extraction | Solvent: ethanol 96 %; 25 g milled leaves; Liquid/solid ratio = 6/1 (v/w); t = 7 min. |
Carnosic acid, rosmarinic acid |
3.3 ± 0.2 % (w/v) 3.1 ± 1.2 % (w/v) |
[32] | |
| Salvia officinalis L. |
Supercritical CO2 extraction |
Solvent-free CO2 extraction; flow rate: 1–3 kg/h; 50 g. of vegetal material; P = 15 or 20 MPa; T = 25 °C; t = 90 min. |
Terpenes and phenolic compounds |
0.659–5.477 % (w/v) | [33] |
| Hydro distillation (Clevenger-type apparatus) |
Solvent: water (1 L); 100 g vegetal material; t = 180 min. |
Terpenes and phenolic compounds | 2.0–2.1% (v/w) | [34] | |
| Maceration | Solvent: ethanol (70%)—25 mL; 5 g of vegetal material; t = 2 days; |
Rosmarinic acid, carnosic acid, carnosol and methyl carnosate | n.p. | [35] | |
| Satureja hortensis L. | Maceration | Solvent: ethanol 96% (300 mL); 10 g vegetal material; T = 22 °C; t = 7 days. |
Phenolic compounds |
125.34 mg GAE/g | [36] |
| Soxhlet extraction | Solvent: ethanol 96% (600 mL); 75 g vegetal material; t = 8 h. |
119.28 mg GAE/g | |||
| Microwave extraction | Solvent: ethanol 96% (100 mL); 5 g vegetal material; t = 30 min |
147.21 mg GAE/g | |||
| Thymus daenensis Celak. and Thymus kotschyanus Boiss. and Hohen |
Hydro-distillation (Clevenger-type apparatus) |
50 g vegetal material; t = 3 h. |
Thymol, p-cymene, β-caryophyllene methyl carvacrol |
1.2–2.4% | [37] |
| Thymus munbyanus Boiss. & Reut., 1852 | Pressurized liquid extraction |
Solvent: acetone; ethanol; water; 20 g. vegetal material; P = 45 MPa; T = 70 °C; t = 10 min |
Oxygenated monoterpenoids; sesquiterpenoids and monoterpenoids | 21.2 ± 0.6% | [38] |
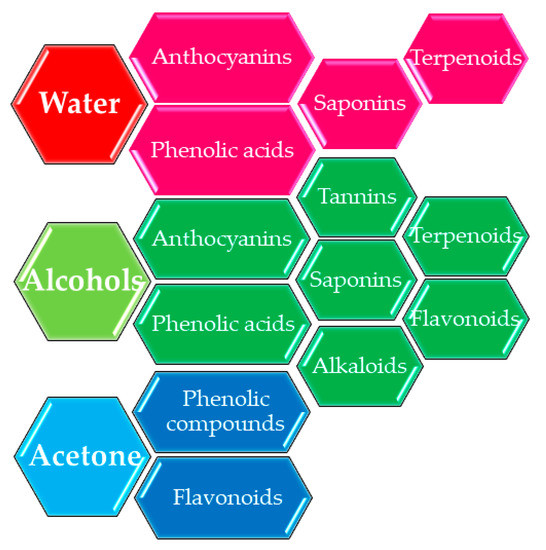
3. The Influence of Extraction Conditions
References
- Fierascu, R.C.; Fierascu, I.; Ortan, A.; Georgiev, M.I.; Sieniawska, E. Innovative approaches for recovery of phytoconstituents from medicinal/aromatic plants and biotechnological production. Molecules 2020, 25, 309.
- Manousi, N.; Sarakatsianos, I.; Samanidou, V. Extraction techniques of phenolic compounds and other bioactive compounds from medicinal and aromatic plants. In Engineering Tools in the Beverage Industry. Volume 3: The Science of Beverages; Grumezescu, A.M., Holban, A.M., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Duxford, UK, 2019; pp. 283–314.
- Saha, A.; Basak, B.B. Scope of value addition and utilization of residual biomass from medicinal and aromatic plants. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 145, 111979.
- Zengin, G.; Mollica, A.; Aumeeruddy, M.Z.; Rengasamy, K.R.; Mahomoodally, M.F. Phenolic profile and pharmacological propensities of Gynandriris sisyrinchium through in vitro and in silico perspectives. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 121, 328–337.
- Fierascu, I.; Georgiev, M.I.; Ortan, A.; Fierascu, R.C.; Avramescu, S.M.; Ionescu, D.; Sutan, A.; Brinzan, A.; Ditu, L.M. Phyto-mediated metallic nano-architectures via Melissa officinalis L.: Synthesis, characterization and biological properties. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12428.
- Saha, A.; Tripathy, V.; Basak, B.B.; Kumar, J. Entrapment of distilled palmarosa (Cymbopogon martinii) wastes in alginate beads for adsorptive removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2018, 37, 1942–1953.
- Elfalleh, W.; Kirkan, B.; Sarikurkcu, C. Antioxidant potential and phenolic composition of extracts from Stachys tmolea: An endemic plant from Turkey. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 127, 212–216.
- Volenzo, T.; Odiyo, J. Integrating endemic medicinal plants into the global value chains: The ecological degradation challenges and opportunities. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04970.
- Bazak, R.; Houri, M.; Achy, S.E.; Hussein, W.; Refaat, T. Passive targeting of nanoparticles to cancer: A comprehensive review of the literature. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 2, 904908.
- Chen, R.J.Y.; Jinn, T.R.; Chen, Y.C.; Chung, T.Y.; Yang, W.H.; Tzen, J.T.C. Active ingredients in Chinese medicines promoting blood circulation as Na+/K+-ATPase inhibitors. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2011, 32, 141–151.
- Pacher, P.; Steffens, S.; Haskó, G.; Schindler, T.H.; Kunos, G. Cardiovascular effects of marijuana and synthetic cannabinoids: The good, the bad, and the ugly. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2018, 15, 151–166.
- Chandrashekhar, V.M.; Ranpariya, V.L.; Ganapaty, S.; Parashar, A.; Muchandi, A.A. Neuroprotective activity of Matricaria recutita L. against global model ofischemia in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 127, 645–651.
- Berger, R.G.; Lunkenbein, S.; Ströhle, A.; Hahn, A. Antioxidants in food: Mere myth or magic medicine? Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2012, 52, 162–171.
- Bouayed, J.; Bohn, T. Exogenous antioxidants—double-edged swords in cellular redox state: Health beneficial effects at physiologic doses versus deleterious effects at high doses. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2010, 3, 228–237.
- Bessada, S.M.F.; Barreira, J.C.M.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P. Asteraceae species with most prominent bioactivity and their potential applications: A review. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 76, 604–615.
- El-Sayed, S.M.; Youssef, A.M. Potential application of herbs and spices and their effects in functional dairy products. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01989.
- Faccio, G. Plant complexity and cosmetic innovation. IScience 2020, 23, 101358.
- Jha, P.; Sen, R.; Jobby, R.; Sachar, S.; Bhatkalkar, S.; Desai, N. Biotransformation of xenobiotics by hairy roots. Phytochemistry 2020, 176, 112421.
- Rassem, H.H.A.; Nour, A.H.; Yunus, R.M. Techniques for extraction of essential oils from plants: A review. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2016, 10, 117–127.
- Frohlich, P.C.; Santos, K.A.; Palú, F.; Cardozo-Filho, L.; da Silva, C.; da Silva, E.A. Evaluation of the effects of temperature and pressure on the extraction of eugenol from clove (Syzygium aromaticum) leaves using supercritical CO2. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2019, 143, 313–320.
- Saleh, I.A.; Vinatoru, M.; Mason, T.J.; Abdel-Azim, N.S.; Aboutabl, E.A.; Hammouda, F.M. A possible general mechanism for ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) suggested from the results of UAE of chlorogenic acid from Cynara scolymus L. (artichoke) leaves. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 31, 330–336.
- Kimbaris, A.C.; Siatis, M.G.; Daferera, D.J.; Tarantilis, P.A.; Pappas, C.S.; Polissiou, M.G. Comparison of distillation and ultrasound-assisted extraction methods for the isolation of sensitive aroma compounds from garlic (Allium sativum). Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 13, 54–60.
- Périno-Issartier, S.; Zill-e-Huma; Abert-Vian, M.; Chemat, F. Solvent free microwave-assisted extraction of antioxidants from sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides) food by-products. Food Bioproc. Technol. 2011, 4, 1020–1028.
- Cvetanović, A.; Švarc-Gajić, J.; Zeković, Z.; Gašić, U.; Tešić, Z.; Zengin, G.; Mašković, P.; Mahomoodally, M.F.; Đurović, S. Subcritical water extraction as a cutting edge technology for the extraction of bioactive compounds from chamomile: Influence of pressure on chemical composition and bioactivity of extracts. Food Chem. 2018, 266, 389–396.
- Harbourne, N.; Jacquier, J.C.; O’Riordan, D. Optimisation of the extraction and processing conditions of chamomile (Matricaria chamomilla L.) for incorporation into a beverage. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 15–19.
- Vian, M.A.; Fernandez, V.; Visinoni, F.; Chemat, F. Microwave hydrodiffusion and gravity, a new technique for extraction of essential oils. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1190, 14–17.
- Patonay, K.; Szalontai, H.; Csugány, J.; Szabó-Hudák, O.; Kónya, E.P.; Németh, E.Z. Comparison of extraction methods for the assessment of total polyphenol content and in vitro antioxidant capacity of horsemint (Mentha longifolia (L.). J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2019, 15, 100220.
- Fornari, T.; Ruiz-Rodriguez, A.; Vicente, G.; Vázquez, E.; García-Risco, M.R.; Reglero, G. Kinetic study of the supercritical CO2 extraction of different plants from Lamiaceae family. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2012, 64, 1–8.
- Binello, A.; Orio, L.; Pignata, G.; Nicola, S.; Chemat, F.; Cravotto, G. Effect of microwaves on the in situ hydrodistillation of four different Lamiaceae. Compt. Rendus Chim. 2014, 17, 181–186.
- Wellwood, C.R.L.; Cole, R.A. Relevance of carnosic acid concentrations to the selection of rosemary, Rosmarinus officinalis (L.), accessions for optimization of antioxidant yield. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 6101–6107.
- Carvalho, R.N.; Moura, L.S.; Rosa, P.T.V.; Meireles, M.A.A. Supercritical fluid extraction from rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis): Kinetic data, extract’s global yield, composition, and antioxidant activity. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2005, 35, 197–204.
- Rodríguez-Rojo, S.; Visentin, A.; Maestri, D.; Cocero, M.J. Assisted extraction of rosemary antioxidants with green solvents. J. Food Eng. 2012, 109, 98–103.
- Jokić, S.; Molnar, M.; Jakovljević, M.; Aladić, K.; Jerković, I. Optimization of supercritical CO2 extraction of Salvia officinalis L. leaves targeted on oxygenated monoterpenes, α-humulene, viridiflorol and Manool. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2018, 133, 253–262.
- Miguel, G.; Cruz, C.; Faleiro, M.L.; Simões, M.T.F.; Figueiredo, A.C.; Barroso, J.G.; Pedro, L.G. Salvia officinalis L. essential oils: Effect of hydrodistillation time on the chemical composition, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities. Nat. Prod. Res. 2011, 25, 526–541.
- Ollanketo, M.; Peltoketo, A.; Hartonen, K.; Hiltunen, R.; Riekkola, M.L. Extraction of sage (Salvia officinalis L.) by pressurized hot water and conventional methods: Antioxidant activity of the extracts. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2002, 215, 158–163.
- Mašković, P.; Veličković, V.; Mitić, M.; Đurović, S.; Zeković, Z.; Radojković, M.; Cvetanović, A.; Švarc-Gajić, J.; Vujić, J. Summer savory extracts prepared by novel extraction methods resulted in enhanced biological activity. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 109, 875–881.
- Nickavar, B.; Mojab, F.; Dolat-Abadi, R. Analysis of the essential oils of two Thymus species from Iran. Food Chem. 2005, 90, 609–611.
- Bendif, H.; Adouni, K.; Miara, M.D.; Baranauskienė, R.; Kraujalis, P.; Venskutonis, P.R.; Nabavi, S.M.; Maggi, F. Essential oils (EOs), pressurized liquid extracts (PLE) and carbon dioxide supercritical fluid extracts (SFE-CO2) from Algerian Thymus munbyanus as valuable sources of antioxidants to be used on an industrial level. Food Chem. 2018, 260, 289–298.
- Armenta, S.; Garrigues, S.; de la Guardia, M. The role of green extraction techniques in green analytical chemistry. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 71, 2–8.
- Armenta, S.; de la Guardia, M.; Namiesnik, J. Green microextraction. In Analytical Microextraction Techniques; Valcarcel, M., Ed.; Bentham Science Publishers: Sharjah, UAE, 2017; pp. 3–27.
- Armenta, S.; Esteve-Turrillas, F.A.; Garrigues, S.; de la Guardia, M. Green Analytical Chemistry: The Role of Green Extraction Techniques. In Green Extraction Techniques Principles, Advances and Applications; Ibáñez, E., Cifuente, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 76, pp. 1–25.
- Bravo, J.; Monente, C.; Juániz, I.; De Peña, M.P.; Cid, C. Influence of extraction process on antioxidant capacity of spent coffee. Food Res. Int. 2013, 50, 610–616.
- Espino, M.; de los Ángeles Fernández, M.; Gomez, F.J.V.; Silva, M.F. Natural designer solvents for greening analytical chemistry. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 76, 126–136.
- Espino, M.; de los Ángeles Fernández, M.; Gomez, F.J.V.; Boiteux, J.; Silva, M.F. Green analytical chemistry metrics: Towards a sustainable phenolics extraction from medicinal plants. Microchem. J. 2018, 141, 438–443.
- Khaw, K.Y.; Parat, M.O.; Shaw, P.N.; Falconer, J.R. Solvent supercritical fluid technologies to extract bioactive compounds from natural sources: A review. Molecules 2017, 22, 1186.
- Lefebvre, T.; Destandau, E.; Lesellier, E. Selective extraction of bioactive compounds from plants using recent extraction techniques: A review. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1635, 461770.
- Latif, S.; Anwar, F. Physicochemical studies of hemp (Cannabis sativa) seed oil using enzyme-assisted cold-pressing. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2009, 111, 1042–1048.
- Cvetanović, A.; Švarc-Gajić, J.; Mašković, P.; Savić, S.; Nikolić, L.J. Antioxidant and biological activity of chamomile extracts obtained by different techniques: Perspective of using superheated water for isolation of biologically active compounds. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 65, 582–591.
- Belwal, T.; Chemat, F.; Venskutonis, P.R.; Cravotto, G.; Jaiswal, D.K.; Bhatt, I.D.; Devkota, H.P.; Luo, Z. Recent advances in scaling-up of non-conventional extraction techniques: Learning from successes and failures. TrAC Trend Anal. Chem. 2020, 127, 115895.
- Kotnik, P.; Skerget, M.; Knez, Z. Supercritical fluid extraction of chamomile flower heads: Comparison with conventional extraction, kinetics and scale-up. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2017, 43, 192–198.
- Meullemiestre, A.; Petitcolas, E.; Maache-Rezzoug, Z.; Chemat Rezzoug, S.A. Impact of ultrasound on solid–liquid extraction of phenolic compounds from maritime pine sawdust waste. Kinetics, optimization and large-scale experiments. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 28, 230–239.
- Fierascu, R.C.; Sieniawska, E.; Ortan, A.; Fierascu, I.; Xiao, J. Fruits by-products—A source of valuable active principles. A short review. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 319.
- Ferreira, L.F.; Minuzzi, N.M.; Rodrigues, R.F.; Pauletto, R.; Rodrigues, E.; Emanuelli, T.; Bochi, V.C. Citric acid water-based solution for blueberry bagasse anthocyanins recovery: Optimization and comparisons with microwave-assisted extraction (MAE). LWT 2020, 133, 110064.
- Yang, Y.; Kayan, B.; Bozer, N.; Pate, B.; Baker, C.; Gizir, A.M. Terpene degradation and extraction from basil and oregano leaves using subcritical water. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1152, 262–267.
- Rodrigues, L.G.G.; Mazzutti, S.; Vitali, L.; Micke, G.A.; Ferreira, S.R.S. Recovery of bioactive phenolic compounds from papaya seeds agroindustrial residue using subcritical water extraction. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 22, 101367.
- Majeed, M.; Hussain, A.I.; Chatha, S.A.; Khosa, M.K.; Kamal, G.M.; Kamal, M.A.; Zhang, X.; Liu, M. Optimization protocol for the extraction of antioxidant components from Origanum vulgare leaves using response surface methodology. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 23, 389–396.
- Aziz, N.A.A.; Hasham, R.; Sarmidi, M.R.; Suhaimi, S.H.; Idris, M.K.H. A review on extraction techniques and therapeutic value of polar bioactives from Asian medicinal herbs: Case study on Orthosiphon aristatus, Eurycoma longifolia and Andrographis paniculate. Saudi Pharm. J. 2021.
- Švarc-Gajić, J.; Stojanović, Z.; Carretero, A.S.; Román, D.A.; Borrás, I.; Vasiljević, I. Development of a microwave-assisted extraction for the analysis of phenolic compounds from Rosmarinus officinalis. J. Food Eng. 2013, 119, 525–532.
- Thuy Pham, T.P.; Cho, C.W.; Yun, Y.S. Environmental fate and toxicity of ionic liquids: A review. Water Res. 2010, 44, 352–372.
- Zhang, L.; Geng, Y.; Duan, W.; Wang, D.; Fu, M.; Wang, X. Ionic liquid-based ultrasoundassisted extraction of fangchinoline and tetrandrine from Stephaniae tetrandrae. J. Sep. Sci. 2009, 32, 3550–3554.
- Cao, X.; Ye, X.; Lu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Mo, W. Ionic liquid-based ultrasonic-assisted extraction of piperine from white pepper. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 640, 47–51.
- Mbous, Y.P.; Hayyan, M.; Hayyan, A.; Wong, W.F.; Hashim, M.A.; Looi, C.Y. Applications of deep eutectic solvents in biotechnology and bioengineering—Promises and challenges. Biotechnol. Adv. 2017, 35, 105–134.
- Chemat, F.; Vian, M.A.; Ravi, H.K.; Khadhraoui, B.; Hilali, S.; Perino, S.; Tixier, A.S.F. Review of alternative solvents for green extraction of food and natural products: Panorama, principles, applications and prospects. Molecules 2019, 24, 3007.
- Fierascu, R.C.; Fierascu, I.; Avramescu, S.M.; Sieniawska, E. Recovery of natural antioxidants from agro-industrial side streams through advanced extraction techniques. Molecules 2019, 24, 4212.
- Skarpalezos, D.; Detsi, A. Deep eutectic solvents as extraction media for valuable flavonoids from natural sources. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4169.
- Pan, G.; Yu, G.; Zhu, C.; Qiao, J. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) of flavonoids compounds (FC) from hawthorn seed (HS). Ultrason. Sonochem. 2012, 19, 486–490.
- Sarfarazi, M.; Jafari, S.M.; Rajabzadeh, G.; Feizi, J. Development of an environmentally-friendly solvent-free extraction of saffron bioactives using subcritical water. LWT 2019, 114, 108428.
- Fan, R.; Xiang, J.; Li, N.; Jiang, X.; Gao, Y. Impact of extraction parameters on chemical composition and antioxidant activity of bioactive compounds from Chinese licorice (Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch.) by subcritical water. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 609–621.
- Munir, M.T.; Kheirkhah, H.; Baroutian, S.; Quek, S.Y.; Young, B.R. Subcritical water extraction of bioactive compounds from waste onion skin. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 183, 487–494.
- Amza, T.; Balla, A.; Tounkara, F.; Man, L.; Zhou, H.M. Effect of hydrolysis time on nutritional, functional and antioxidant properties of protein hydrolysates prepared from gingerbread plum (Neocarya macrophylla) seeds. Int. Food Res. J. 2013, 20, 2081–2090.
