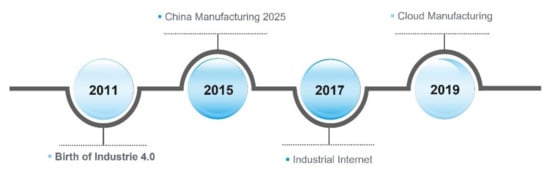
“China Manufacturing 2025” was a strategic initiative brought out by Prime Minister Li Keqiang. An official document was issued by the State Council in May 2015 meant to strengthen the manufacturing capability of the Chinese economy.
The China Manufacturing 2025 Plan is also known as the “China Version of The Industrie 4.0 Plan”. The concept of “China Manufacturing 2025” was first proposed by the Chinese Academy of Engineering. Under the overall planning of the State Council, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) took the lead in working with more than 20 ministries and commissions such as the National Development and Reform Commission, the Ministry of Science and Technology and more than 50 academicians to formally compile the “China Manufacturing 2025 Plan”
[5].
The core goal of “China Manufacturing 2025” was to transform China from a manufacturing supplier to a manufacturing driver. The year 2025 was chosen after careful analysis of China’s status of manufacturing capabilities and the overall market environment at that time (2015). It was set as a goal to transform, in 10 years, its capability from simply providing low-cost labor for manufacturing outsourcing, to the form where demands of the new era will challenge the supply end and thus bring added value to the industry by driving innovations in the supplier technologies.
2.1.2. Industrial Internet
The concept of “Industrial Internet” actually originated in America. It was first proposed by General Electric (GE) in 2012 through the release of the white paper “
Industrial Internet: Pushing the boundaries of minds and machines”
[6], which elaborated on the connotation and future vision of the Industrial Internet from the aspects of technical architecture, development opportunities, potential benefits, application conditions, etc. In essence, industrial interconnectivity is the integration and innovation of industrial and IT capabilities. Subsequently, five industry giants in the United States joined forces to form the Industrial Internet Consortium (IIC), which vigorously promoted the concept of Industrial Internet and set off a wave of Industrial Internet movement in the world.
In 2015, MIIT issued the documents “
Implementation of the State Council on actively promoting the Internet + Guidance action plans (year 2015–2018)” [7], clearly stating the guidelines for the internet to be widely integrated into the entire process of production and manufacturing, the entire value chain and the whole life cycle of products, cultivating and developing an open innovative R&D model, and accelerating the development and application of industrial big data.
In February 2016, China established the Alliance of Industrial Internet (AII). Jointly initiated by the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology and related enterprises such as manufacturing, communications industry, and the Internet, the alliance actively carries out work in the research of major issues of the Industrial Internet, the development of standards, technical test verification, and industry promotion. In the same year, AII released version 1.0 of the Industrial Internet Architecture.
Since then, hundreds of industrial internet platforms have been founded and have entered the market, providing solutions and services to the manufacturing industry.
2.1.3. Cloud Manufacturing
In 2009, the research team led by Prof. Li Bohu, an academician of the Chinese Academy of Engineering and Professor Zhang Lin, then deputy dean of the School of Automation Science and Electrical Engineering of Beihang University, realized that the deep integration of advanced information technologies such as cloud computing and the Internet of Things with the manufacturing industry will bring profound changes to the manufacturing industry and they took the lead in proposing the concept of “Cloud Manufacturing”
[8]. They pointed out that “cloud manufacturing was a kind of network and service platform, organizing online manufacturing resources according to user needs”, to provide users with a variety of on-demand manufacturing services.
Cloud manufacturing provides a new model and means for China to move from a manufacturing outsourcer to a manufacturing driver. The initiative was jointly supported by more than 300 researchers and developers from 28 organizations of universities, research institutes and enterprises across the country, and achieved a number of pioneering research results
[9][10][9,10].
Prof. Li Bohu, Prof. Zhang Lin and their team members have publicized and introduced the concept and research results of cloud manufacturing by organizing international conferences or forums, publishing academic papers, carrying out academic exchanges and other forms, which have made important contributions to the recognition and attention of international counterparts for cloud manufacturing research, and gradually forming a new research direction in the world. Cloud manufacturing is one of the very few academic directions initiated by China that attracted the attentions of international academies.