Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Babatunde Solomon Ojelade and Version 2 by Rita Xu.
To meet the demands of farmers and combat weed problems, woodlands and farmlands are sprayed with agrochemicals, primarily glyphosate-based herbicides. Farmers increasingly embrace these herbicides containing glyphosate. Glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA), a key metabolite of glyphosate, have been reported as toxicological concerns when they become more prevalent in the food chain.
- glyphosate-based herbicide
- AMPA
- toxicological effect
1. Introduction
Increasing numbers of synthetic molecules are being released into the environment to achieve specific outcomes [1]. Those molecules may adversely affect human health and ecosystem services [1][2][1,2]. An in-depth understanding of how those molecules behave in the natural world combined with an estimate of their complexity can help regulate their use and enable users to take precautionary measures to protect human health [3]. Although regulations have set the highest points for known pollutants found in water supplies or drinking water [4], and food [5], there are none for soil residue [3]. Indeed, the United Nations’ Food and Agriculture Organization recently released a report that exposes the unseen truth of soil degradation [6]. Agrochemicals, primarily herbicides, are used on agricultural lands to suit farmers’ demands and overcome weed resistance [7]. Formulation, approval, use, and monitoring of these herbicides, especially glyphosate-based herbicides (GBHs) involve numerous stakeholders [3].
Following World War II, food scarcity was a problem around the world. As a result, today farmers across the globe use several herbicides that are synthetic to manage pests and weeds. However, the formulation of glyphosate has been considered as the most important herbicide in that area [8]. Glyphosate-based herbicides (GBHs) come in a variety of commercial formulations, including broad-spectrum, non-selective, post-emergent, and synthetic herbicides [9]. The first glyphosate was developed in 1950, and its herbicidal properties were only discovered in 1970 when GBHs were resynthesized and tested [10]. The herbicide Roundup contains ‘GLY’ as an active component, which was introduced and commercialized by Monsanto Corporation in 1974 [11]. Agricultural weed control with glyphosate quickly became popular with farmers, who gained the ability to eliminate weeds without causing crop damage [8]. According to Zhang et al. [12], the glyphosate hinders the synthesis of amino acids including tyrosine, phenylalanine, and tryptophan, thereby killing weeds without destroying the agricultural crops. Its use has progressively increased in non-agricultural and agricultural settings, and it is now the most common herbicide worldwide [13][14][13,14]. In addition, many agrochemical companies market GLY formulations in various strengths and with various adjuvants, because they have already been reviewed and registered by regulatory organizations [11][15][11,15]. It was decided by the European Union Council on 27 November 2017 that glyphosate would be permitted to be used for five more years with the majority of 18 member nations voting in favor of allowing the use [16]. As a result, GLY can be used as a component of plant protection products (PPPs) through the end of 2022 [17]. Agencies in Europe, such as the European Food Safety Authority and the European Chemicals Agency, conducted a thorough assessment of GLY in recent years based on concerns over its environmental and human health consequences [18]. Based on current scientific data, the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) concluded that glyphosate does not meet the criteria for a carcinogenicity hazard classification, and cannot be categorized as a carcinogen, reproductively harmful substance or mutagen [16][19][16,19]. As part of EFSA’s risk-assessment process, the scientific committee has been asked to create guidelines on how to describe, record, and justify uncertainty [20]. In order to continue the renewal as an element in PPPs, GLY must not have a negative impact on the environment or human or animal health, according to European laws [21].
Glyphosate’s widespread use stems from its effectiveness in weed control at a reasonable price, its presumed low toxicity, fast uptake by plants, and gradual weed resistance development to glyphosate [22]. Due to the accumulation of residues in the food chain, glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA), one of its main metabolites, are reported to be toxicologically problematic [23]. Several environmental conditions can affect the degradation of glyphosate, depending on its structural affinity with certain transformations [24]. Despite AMPA’s longer half-life in soil, with 23–958 days compared to glyphosate’s (1–197 days), most studies examined only glyphosate [25][26][27][28][25,26,27,28]. In the long term, contaminants with a long half-life and slow degradation can damage the environment [29]. This occurs most frequently in agricultural and forestry settings where repeated applications are common. Due to its extremely low vapour pressure, it cannot be volatilized significantly even if it undergoes mineralization, immobilization, or leaching once applied [29][30][29,30]. As a result of glyphosate mineralization, AMPA, methyl phosphonic acid, sarcosine and glycine are produced [30][31][30,31]. After that, AMPA is mineralized to methylamine and phosphate, which when decomposed to produce carbon dioxide and ammonium [29][32][29,32]. In research, the presence of glyphosate in the environment was established. As a result, potential health risks associated with glyphosate must be assessed.
2. Factors Affecting the Degradation Mechanisms of Glyphosate Pollution
Factors and mechanisms of degrading glyphosate pollution in soil include mineralization, immobilization and leaching having physical and chemical properties that influence the mechanism.2.1. Mineralization
In some circumstances, biochemical properties of a soil can result in glyphosate and AMPA mineralization occurring very quickly [30]. Increased phosphate content, soil pH, and low Fe and Cu content accelerate glyphosate mineralization, driven primarily by increased microbial mineralization [30][33][34][30,33,34]. Adsorption of glyphosate to organic carbon (C) may provide environmental benefits such as delaying leaching, promoting soil degradation, and slowing the release of the herbicide. If the glyphosate use continues, the organic C system may eventually become saturated. Thus, soil biochemical properties, microbial diversity and activities are all factors in glyphosate degradation [23].2.2. Immobilization and Leaching
The high adsorption of glyphosate results in its rapid immobilization in most natural situations after application [26][35][26,35]. Influential factors in the immobilization of glyphosate include minerals, soil organic matter, and clay. It has also been reported by Shushkova et al. [36] that adsorption to soil occurs within 3 h of the application when about 20% of glyphosate quantity is initially applied. High levels of clay, organic matter, iron, and aluminium are required for high adsorption, soils with low pH and phosphate concentrations, and high levels of clay [35][36][37][38][35,36,37,38]. Contrarily, soils with high levels of phosphate, high pH, and low levels of organic matter, Fe, and Al are more prone to glyphosate and AMPA losses because of a reduced capacity for adsorption and a larger propensity for leaching [36][38][36,38]. According to Bai and Ogbourne [23], the leaching of glyphosate and resulting contamination of water sources is increasingly due to the recurrent finding of glyphosate and AMPA residues in the water.3. Environmental Hazards Posed by Glyphosate and AMPA Residues
A wide range of environmental risks has been created due to the relatively persistence of GLY and AMPA in the environment. There is not much information regarding the toxicity, health, or safety of glyphosate and AMPA on frequent and prolonged exposure, so it is difficult to predict their consequence and magnitude. Several issues surround these compounds’ ecotoxicological and toxicological assessments, which may contribute heavily to the toxicological properties of formulated herbicides [39][40][39,40]. Because it is extremely difficult to assess safe, marketable products (as these products have properties that are only known to their manufacturers and are partially unknowable to regulatory agencies and research scientists), it can be suggested that all herbicide formulation ingredients must be declared and regulated. As a result, this review focuses on the existence of glyphosate and AMPA residues in soil and water bodies and the risks to human and animal health. Roundup formulations are among the most extensively utilized GBH products that consist of other surfactants and chemical adjuvants. The active ingredients in Roundup are IPA-salt, polyethoxylated tallow amine (POEA) and other constituents [41]. These adjuvants can sometimes be even more toxic than glyphosate [42][43][42,43]. A thorough examination of surfactant co-formulants in glyphosate-based herbicides is urgently needed. There are several classes of POEA molecules with common structural characteristics [44]. Over many decades, ethoxylated amines, also known as POEA, have been the most common surfactants used in GBH formulations [45]. For instance, according to Guilherme et al. [46], in a study on the Roundup Ultra formulation, POEA was detected at a concentration of 16%. Nonetheless, the labeled Roundup Ultra in Portugal (MON 52276) contains neither POEA nor propoxylated quaternary ammonium surfactants [47]. There are many instances in which authors cite the brand without citing the source country of the formulation. The co-formulants found in a formulation called Roundup Ultra vary depending on the country of sale. For example, Roundup Ultra is sold under the MON 76473 label in Ireland, whereas it has the MON 52256 label in Germany, the MON 79351 label in Greece, and the MON 77360 label in the United States [47]. It is not surprising that the same assay used to test the same GBH brand yields different results in different laboratories worldwide because it is difficult to identify substances across studies. Mesnage et al. [48] confirmed that formulated herbicides are possibly more hazardous than the active substances alone, as evidenced by studies using glyphosate-based herbicides including a variety of other active components. It has become apparent that glyphosate has a wide range of harmful consequences [49], and co-formulants in Roundup have endocrine-disrupting effects in human cells [50]. As a result of these impacts, agrochemicals like GBHs will affect agricultural products and the environment, notably as chemical residues in goods produced by agriculture and as adverse effects on nontarget organisms [51]. Various studies on glyphosate and AMPA in several countries is described by Gillezeau et al. [52] in Table 1 given below. Even though the values of GLY and AMPA (in the table) may or may not be harmful, accumulating them over time will result in various health problems.Table 1. Description of glyphosate and AMPA studies in several countries.
| Country | Subjects | Type of Sample | Year of Sampling | Lab Methods | Glyphosate LOD |
Effects of Glyphosate | AMPA LOD |
Effects of AMPA | References | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EXPOSURE IN THE WORKPLACE | ||||||||||||||
| United State | United States (South Carolina, Minnesota) | Forty-eight farm families (farmers and wives, with 79 children aged between 4 and 18) on the day of application and three days later. | Urine | Unreported | ||||||||||
| (Midwest) | 2002 | HPLC | 1 µg per litre | On application day, farmers’ geometric mean ± SD: 3.2 ± 6.4 μg/L (range < 1–233); while on day 3, 1.0 ± 3.6 (<1–68) μg per litre. Less than 25% of the wives or kids displayed values that could be identified. | Unreported | Unreported | Of the sampled streams, 36% were positive/about 8.7 g/L. | [128] | [53] | |||||
| Finland | Five forest workers sprayed 8% Roundup solution 6 h a day for one week | Urine | 1988 | |||||||||||
| GC with a 63 Ni-electron capture detector | 100 µg per litre | Samples of urine remained below LOD for glyphosate. A subsequent quantified urine sample contained 85 µg per litre of glyphosate. | 50 µg per litre | (Midwest) | For AMPA, urine samples remained below the limit of detection | 2013 | [ | Of the sampled streams, 44% were positive/about 27.8 µg/L. | 54] | |||||
| [ | 129 | ] | France | Herbicides based on glyphosate are used by a farmer and his family (5 in the household) | Urine | Unreported | ||||||||
| (Washington, Maryland, Iowa, Wyoming) | 2005–2006 | Positive outcomes in all of the sampled streams/about 328 µg/L. | [130] | LC-MS | 1 µg per litre | A 9.5 µg per litre concentration was found on the farmer following spraying and about 2 µg per litre after 2 days; After 2 days, 2 µg per litre was also measured in one child. No measurable levels were present in the mother or the other two kids. | Unreported | Unreported | [55] | |||||
| Ireland | Amenity horticulturalists (17 males and 1 female), prior to and following spraying. | Urine | 2015 | LC MS-MS | 0.5 µg per litre | Prior to spraying, mean ± SD: 0.71 ± 0.92. After spraying: 1.35 ± 2.18 μg per litre |
Unreported | Unreported | [56] | |||||
| (Iowa, Indiana, Mississippi) | 2004–2008 | Positive results for most of the sampled rivers/about 430 µg/L after a storm. | [131] | Mexico | 76 farmers | Urine | Unreported | ELISA | 0.05 µg per litre (in water) | In farming areas (Mean ± SD): 0.26 ± 0.23 μg per litre, (median: 0.28) | Unreported | Unreported | [57 | |
| Spain | ] | |||||||||||||
| 2007–2010 | Of the groundwater samples, 41% were positive/about 2.5 µg/L. | [ | 90] | Sri Lanka | Ten farmers in good health from regions where chronic renal disorders are endemic | Urine | Unreported | ELISA | 0.6 µg per litre | Ranged between 40.2–>80 μg per litre, (Median: 73.5) | Unreported | Unreported | [58] | |
| Canada | 2002 | Of the samples, 22% were positive/about 6.07 µg/L. | [132] | GENERAL POPULATION WITHOUT DIRECT CONTACT | ||||||||||
| Argentina | 2012 | Of the surface water samples, 35% were positive/0.1–7.6 µg/L. | [133] | Sri Lanka | Ten healthy non-farmers from regions without a long-standing endemic kidney illness. | Urine | ||||||||
| Switzerland | Unreported | ELISA | 2016 | 0.6 μg per litre | Ranged between 1.2–5.5 μg per litre, (Median: 3.3) | Unreported | Unreported | Positive results for most of the stream samples/about 2.1 µg/L. | [58] | |||||
| [ | 134 | ] | US (Iowa) | Households who do not farm (23 fathers, 24 mothers, 51 children) | Urine | 2001 | FCMIA | 0.9 μg per litre | For the non-farm fathers, djusted geometric mean was 1.5 μg per litre | Unreported | Unreported | [59] | ||
| US (Washington and Idaho) | A total of 41 lactating women of greater than 18 years old | Milk (41), Urine (40) | 2014–2015 | LC-MS | 1 μg per litre in Milk; 0.02 μg per litre in Urine |
For milk, glyphosate is below LOD. For urine, the glyphosate mean is 0.28 ± 0.38 μg per litre. Glyphosate detectable in 37/40 of the urine samples. There are no statistically significant differences between consuming conventional or organic food or living in an urban or suburban region. |
In milk: 1 μg per litre; while 0.03 μg per litre was detected in Urine | In milk, AMPA is below the LOD. In urine: AMPA mean is 0.30 ± 0.33 μg per litre |
[60] | |||||
| Canada | Similar in age and BMI of pregnant (30) and non-pregnant women (39), and 30 umbilical cords | Maternal and umbilical cord serum | unreported | GC-MS | 15 μg per litre | No glyphosate found in the umbilical cord or in pregnant women. Mean of glyphosate found in non-pregnant women is 73.6 ± 28.2 μg per litre | 10 μg per litre | In none of the samples was AMPA found. | [61] | |||||
| US (Indiana) | Pregnant women (71) between the ages of 18 and 39 | Urine and drinking water | 2015-2016 | LC MS-MS | In urine: 0.1 μg per litre; while in water: 0.2 μg per litre. | Glyphosate found in the urine: mean (SD) 3.40 (±1.24) μg per litre. No glyphosate was found in the drinking water. | Unreported | Unreported | [62] | |||||
| Ireland | Fifty Irish persons over the age of 18 who do not have any special dietary preferences, with no pesticide usage in their line of works | Urine | 2017 | LC-MS-MS | 0.5 μg per litre. | A total of 47 samples were examined, and their urinary creatinine levels ranged from 3.0 to 30 nmol/L. 20% of the samples had Glyphosate levels above LOD. Glyphosate levels in samples with medians above the LOD (Range): 0.87 (0.80–1.35) μg per litre. | Unreported | Unreported | [63] | |||||
| Denmark | A total of 13 mothers and 14 children (6–11 years old) in rural and urban communities | Urine | 2011-2012 | ELISA | 2.5 ppb | For children, the mean was 1.96 (range: 0.85–3.31) μg per litre. For mothers, the mean was 1.28 (range: 0.49–3.22) μg per litre | Unreported | Unreported | [64] | |||||
| Germany | 399 individuals aged 20 – 29 years | Urine | 2001-2015 | GC-MS-MS | LOQ: 0.1 μg per litre | A total of 31.8% of the samples (127 samples) were found to have glyphosate level above LOD. The highest levels were found in males. | LOQ: 0.1 μg per litre | AMPA: 160 (40.1%) > LOD. | [65] | |||||
| 18 European countries | 182 volunteers | Urine | 2013 | GC-MS-MS | LOQ: 0.15 μg per litre | 44% of the samples (of about 80 samples) were found to have glyphosate level above LOQ; Latvia had the highest glyphosate concentration, which is 1.8 μg per litre. | LOQ: 0.15 μg per litre | 36% > LOQ AMPA;) highest AMPA concentration: 2.6 μg per litre (Croatia) | [66] | |||||
| Colombia | A total of 112 people who live in locations where glyphosate was applied aerially | Urine | 2006 | GC with a detector for electron micro-capture | 0.5 μg per litre | For the glyphosate (mean ± SD): 7.6 ± 18.6 μg per litre, ranged from 0–130 μg per litre. There were quantifiable AMPA levels in 4/42 participants with quantifiable glyphosate levels: Mean glyphosate: 58.8 μg per litre (range: 28–130 μg per litre). |
1.0 μg per litre | AMPA: 1.6 to 8.4 μg per litre (range: 0–56 μg per litre) | [67] | |||||
| Thailand | A total of 82 expectant women, aged 19 to 35, who gave birth in a participating hospital | Umbilical cord and maternal serum | 2011 | HPLC | 0.4 μg per litre | Median for maternal serum: 17.5 μg per litre (range 0.2–189.1), while for the umbilical cord serum: 0.2 μg per litre (range 0.2–94.9). 50.7% of the umbilical cord serum samples are below LOD, 46.3% maternal serum samples are below LOD. | UUnreported | Unreported | [68] | |||||
3.1. Soil with Glyphosate
Given the widespread usage of glyphosate, understanding how it interacts with the soil ecosystem is critical for environmental safety assessment and practical application. Despite not being sprayed directly on the ground, glyphosate-based herbicides can contaminate the soil in and surrounding treated areas due to spray drift during application and leaf surfaces that have been washed away by rain. Mineralization, degradation, immobilization, and leaching are all factors in glyphosate’s fate in soil. Several kinds of research have been published in recent years, attempting to discover and comprehend the processes that determine how chemicals behave in the environment and produce pollution, particularly in soil and water [12]. Mesnage et al. [69] analyzed the most prevalent surfactants used as co-formulants in glyphosate-based herbicides. They looked at how adding surfactants (such as Triton CG-110) would impact the soil’s glyphosate adsorption, mineralization and leaching processes. Soil composition, physicochemical factors, biological properties, chemical properties of the individual pesticide, and timing of precipitation and pesticide application all influence the fate of glyphosate [25][26][70][71][72][25,26,70,71,72]. Total organic carbon, pH, and temperature fluctuations in German soil were recently discovered to affect glyphosate mineralization kinetics, level of bio-NER formation, and the amount of recoverable glyphosate over time [73]. In most soils, glyphosate degrades quite quickly, with an estimated half-life of 7 to 130 days on-site [74]. Because glyphosate degrades relatively quickly, it has a low impact on the environment, particularly water and soil resources. On the other hand, its metabolites, AMPA and/or sarcosine, may boost the pollution risk. According to Grandcoin et al. [14], the herbicide molecule can be degraded in two ways (Figure 1). The first technique relies on the dissolution of the carbon-nitrogen bond, which forms AMPA (glyphosate’s main metabolite) via the enzyme glyphosate oxidoreductase, which is broken down to carbon dioxide. In contrast, the second process relies on the broken carbon–phosphorus (C–P) bond, which is accomplished through the C–P lyase enzyme and results in the synthesis of glycine and sarcosine [75][76][77][75,76,77]. However, as an aminopolyphosphonate photodegradation product in water, AMPA can also be found in the natural world [78].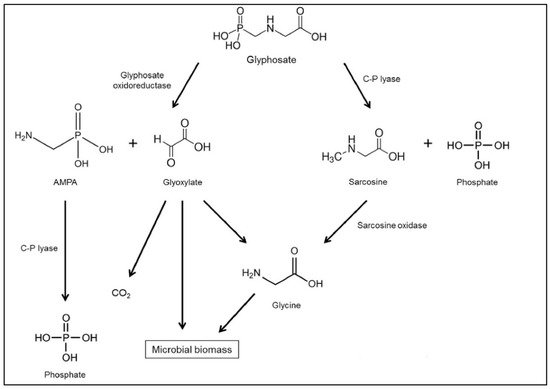
3.2. Water with Glyphosate
A metabolite of glyphosate, AMPA, and its residues are increasingly discovered in water sources, with runoff being one source of water contamination [110]. Glyphosate concentrations of more than 400 g/L harm some aquatic animals, including amphibians and fish [111][112][111,112]. According to Mercurio et al. [113], glyphosate has been reported in the marine ecosystem, and its persistence in saltwater is now being investigated. Table 2 showed the occurrence and concentrations of glyphosate in various water bodies across several countries in America and Europe. Although, they proved to be safe according to their respective guidelines, persistent exposure to glyphosate can pose a health threat. Regarding risks posed to human health, the maximum concentration level (MCL) of glyphosate in the United States of America [23] and Australia is 700 µg L−1 and 1000 µg L−1 respectively. In Europe, glyphosate concentrations in drinking water are permitted to be less than 0.1 g/L, but 77 g/L are considered tolerable, according to reports by Horth and Blackmore [114]. According to European criteria, glyphosate residue in human drinking water must be reduced; however, glyphosate water treatment is expensive. Although these remedies have little influence on the presence of glyphosate in the water supply, the long-term impacts of glyphosate remain a worry [23]. Saunders and Pezeshki [81] urged that correct management measures, such as lower application rates and vegetation buffers, be used to limit glyphosate’s eco-toxicity hazards.3.3. Glyphosate in Nontarget Plant Species
In spite of the specified waiting period in harvested crops, glyphosate and AMPA residues are observed in unintended plant species after weed spraying [23]. Glyphosate residues in tree foliage that are unusually high (e.g., 1000 mg/kg) may be attributable to direct absorption into tree leaves due to airborne herbicide drift contamination [115]. In addition to the possible health problems associated with food contamination, glyphosate exposure can have phytotoxic effects. Reduced absorption of vital nutrients is one way phytotoxicity affects plant performance [116], nutritional imbalances, reduced yield, and poor food quality [117][118][117,118]. Various studies have reported that about 50% of plant biomass being reduced following glyphosate contamination in some nontarget plant species [116][119][116,119]. Following the application of GBH to crops, residual GLY and AMPA may remain in harvested crops and processed foods [120]. According to testing conducted by the UK Food Standard Agency, 27 out of 109 samples of bread had glyphosate residues of at least 0.2 mg/kg. The US Department of Agriculture Tests in 2011 revealed that 90.3% of 300 samples of soybeans contained glyphosate and 95.7% of which included AMPA with concentrations of 1.9 and 2.3 ppm, respectively [120]. Consumers are exposed to more glyphosate residues through their food, so this exposure should also be considered [51]. By drifting, leaching, and surface runoff, biologically active herbicide interacts with biomass and is absorbed by soil and water [121]. Among other places, glyphosate contamination is found in human urine, animal urine, ground water, and human milk and meat from farm animals [32][122][123][124][125][32,122,123,124,125]. Therefore, interactions with other stressors should be investigated in a more realistic situation when interacting with biological systems or the environment [126][127][126,127].Table 2. Investigation of the presence and levels of glyphosate in surface and ground water samples collected from several countries in Europe, South America, and North America.
| Country | Year | Presence of Glyphosate/Concentration | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| France | |||
| 2003–2004 | |||
| Positive results from 91% of stream samples/up to 165 µg/L. | |||
| [ | |||
| 135 | |||
| ] | |||
| Hungary | 2010–2011 | Positive results for most rivers and groundwater samples/about 0.001 µg/L. | [136] |
| Denmark | 1999–2009 | Of the surface water samples, 25% were positive/about 31 µg/L. Of the groundwater samples, 4% were positive/up to 0.67 µg/L. |
[137] |
| Mexico | 2015 | The groundwater samples were all positive/about 1.42 µg/L. | [57] |
| Germany | 1998 | Only a few positive samples in two tributaries of the Ruhr River/with concentrations up to 0.59 µg/L. | [138] |
