2. 地质背景Geology Background
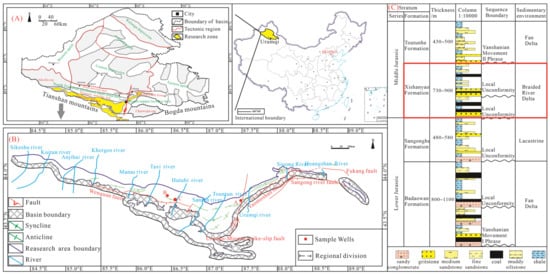
准噶尔盆地位于新疆北部The Junggar basin is located in the northern part of Xinjiang;
它是一个大型的中生代- 新生代坳陷盆地,面积约为13.4× it is a large-scale Mesozoic-Cenozoic depression basin with an area of about 13.4 × 10
4公里 km2平面呈近似三角形,东西宽 and an approximately triangular shape in the plane, with a width of 1120
公里,南北宽800公里 km from east to west and 800 km from north to south [
1,
2,
3]
。自古生代晚期以来,准噶尔盆地经历了海西、印度支那、燕山和喜马拉雅的构造运动,多相应力场的叠加导致了其结构复杂性. Since the Late Paleozoic, the Junggar basin has experienced Hercynian, Indosinian, Yanshan and Himalaya tectonic movements, and the superposition of multi-phase stress fields has led to its structural complexity [
2,
44,
48]
。准噶尔盆地可分为六个构造单元:吕梁隆起、乌伦古洼地、北天山皮埃蒙特冲断带、西部隆起、中央洼地和东部隆起. The Junggar basin can be divided into six structural units: the Luliang uplift, the Ulungu depression, the northern Tianshan piedmont thrust belt, the western uplift, the central depression, and the eastern uplift [
3,
49]
(图 (Figure 1A)。A). The SJB
位于天山北部的皮埃蒙特推力带,东西方向伸长,南北宽近 is located in the northern Tianshan piedmont thrust belt, which elongates east-west direction with a north-south width of nearly 200
公里(图 km (Figure 1B)。天山北皮埃蒙特推力带是多相叠加和继承构造带,通常分为五个次级构造单元,包括四州凹陷、齐固断裂褶皱带、火马图背斜带、桓斜带、阜康断裂带B). The northern Tianshan piedmont thrust belt is a multi-phase superimposed and inherited structural belt, and is usually divided into five secondary structural units, including the Sikeshu sag, Qigu fault–fold belt, Huomatu anticlinal zone, Huan anticlinal zone, and Fukang fault zone [
50]
。.
图Figure 1.地图显示:( Maps showing: (A)准噶尔盆地在中国的位置(由) Location of the Junggar basin in China (modified by [
4]
修改)。(). (B)) Structural outline map (modified by 准噶尔盆地南缘结构轮廓图(经[
10,
51]
修改)。() of the Southern margin of Junggar basin (SJB). (C)地层柱显示) The stratigraphic column shows the Middle-lower Jurassic Strata in SJB
中下侏罗纪地层(经 (modified by [
51]
修正,西山尧组标为红色)。, Xishanyao formation is marked in red).
SJB表面的主要部分被第四纪地层覆盖。SJB地区的地层从旧到新是二叠纪,三叠纪,侏罗纪和古新世(图A major part of the surface of the SJB is covered by quaternary strata. The strata in the SJB area are Permian, Triassic, Jurassic and Palaeocene from old to new (Figure 1
. Among them, the Badaowan formation and Xishanyao formation are the main coal-bearing strata in the study area, which are widely distributed in the SJB (Figure 1
C). The coal-bearing strata of the Xishanyao formation were formed in a lacustrine–deltaic sedimentary system [
]. The Xishanyao formation strata had multiple coal accumulation centers that were greater than 40 m thick between the present-day Horgos River and Sigong River controlled by tectonic and sedimentary conditions [
3. 煤测量砂岩成岩成岩的副成因序列Paragenetic Sequence of Coal Measure Sandstone Diagenesis
3.1. Determination 成岩阶段的测定of Diagenetic Stage
成岩阶段的澄清应基于古温(The clarification of diagenetic stages should be based on paleo-temperature (T
)、镜质体反射率(Ro)、最大热解峰温度(Tmax)和I/S的蒙脱石混合层比(S%)、自生矿物的空间和时间组合以及颗粒之间的接触关系), vitrinite reflectance (Ro), maximum pyrolysis peak temperature (Tmax), and smectite mixed layer ratio (S%) of I/S, spatial and temporal assemblages of authigenic minerals and the contact relationships between particles [
5,
22,
67]
。研究区西山尧组煤测页岩. The Ro
为0.63~0.89%。煤测量砂岩的粘土矿物以I/S、高岭石和伊利石为主,I/S的混合层比(S%)为10-30%(平均为18%)。压实对煤测量砂岩有很大影响,其接触关系由线接触、凹凸接触和缝合接触组成。Wang等人[68]进行的侏罗纪地层热学重建 of coal measure shale in the Xishanyao formation in the study area ranges from 0.63–0.89%. The clay minerals of the coal measure sandstone are dominated by I/S, kaolinite and illite, with the mixed layer ratio (S%) of I/S ranging from 10–30% (avg on 18%). The compaction strongly influences the coal measure sandstone, with contact relationships composed of line contact, concave-convex contact, and suture contact. The reconstructed thermal history of the Jurassic strata, which is conducted by Wang et al.[
68]
发现,西山瑶组的最大埋藏深度超过, found that the maximum burial depth of the Xishanyao formation exceeded 3000
米,古温度超过100°C。 根据碎屑岩成岩阶段分类标准(我国油气行业标准 m and the paleotemperature exceeded 100 °C. According to the diagenetic stage classification standard of clastic rocks (China’s oil and gas industry standard SY/T5477-2003
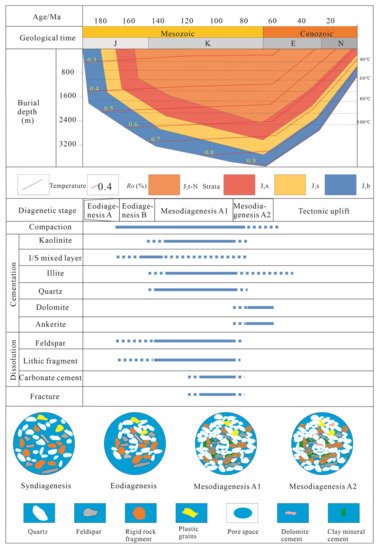
),可以综合确定西山尧组煤测砂岩成岩阶段处于介生系A1和A2阶段(图8)。), it can be comprehensively determined that the diagenetic stage of the Xishanyao formation coal measure sandstone is in the mesodiagenesis A1 and A2 stage (Figure 2).
3.2. 煤测量砂岩的成岩序列Diagenetic Sequences of Coal Measure Sandstone
Combining with the thermal and burial history of the SJB, referring to the division of diagenetic stages in clastic rocks of China’s oil and gas industry standard SY/T5477-2003, the diagenetic evolution of the Xishanyao formation coal measure sandstone in the area is summarized as follows:
结合SJB的热学和埋藏史,参考我国油气行业标准SY/T5477-2003中碎屑岩成岩阶段的划分,总结了该区西山尧组煤测量砂岩的成岩演化情况如下:
在这个阶段,成岩环境尚未与上覆水完全断开。沉积在泥炭沼泽中的有机物产生一氧化碳
In this stage, the diagenetic environment has not been completely disconnected from the overlying water. The organic matter deposited in the peat swamp generates CO
2在微生物的作用下溶解在水中,使成岩环境呈弱酸性。由于沉积水的酸性,碎屑颗粒的表面很少被亚氯酸盐粘土膜覆盖。由于沉积期水动力环境较强,煤测砂岩中含有一定量的碳酸盐塑性硅矿,碳质碎片会掺入砂岩中。 under the action of microorganisms and dissolves in water, making the diagenetic environment weakly acidic. Due to the acidic nature of the sedimentary water, the surface of the detrital particles is rarely coated by a chlorite clay film. Due to the strong hydrodynamic environment during the sedimentary period, the coal measure sandstone contains a certain amount of plastic micrite carbonate and carbonaceous fragments will be blended into the sandstone.
发育阶段成岩作用的类型和程度将影响成岩作用的类型和后期成岩期储集层的物理性质The type and degree of diagenesis in the eodiagenesis stage will affect the type of diagenesis and the physical properties of the reservoir in the later diagenetic stage [
22]
。在这个阶段,成岩环境是弱酸性的,成岩类型包括机械压实,胶结(主要是泥质胶结)和溶解,成岩环境逐渐转变为封闭系统。压实显著降低了初级孔隙率. At this stage, the diagenetic environment is weakly acidic, and the diagenesis types include mechanical compaction, cementation (mainly argillaceous cementation) and dissolution, and the diagenetic environment gradually changes to a closed system. The compaction significantly reduces primary porosity [
69,
70]
,这是由于埋藏深度较浅且沉降率高。岩石处于弱固结和半固结状态,碎屑颗粒的接触关系从点接触到点线接触发生变化。该阶段测煤砂岩的孔隙类型主要是初级孔隙,少量的硅藻土碳酸盐水泥填充孔隙。, due to the shallow burial depth and the high subsidence rate. The rock is in a weakly consolidated and semi-consolidated state, and the contact relationships of the clastic particles change from point contact to point-line contact. Pore types of the coal measure sandstone in this stage are mainly primary pores, and a small amount of micrite carbonate cement fills the pores.
随着气温的升高,煤层和深色页岩逐渐释放出有机酸和一氧化碳。With the increase in temperature, the coal seams and dark shale gradually released organic acid and CO2 [ [64]
,这使得成岩环境逐渐转变为弱酸。长石和碎屑颗粒开始轻微溶解并形成溶解孔(图9)。, which makes the diagenetic environment gradually change to a weak acid. The feldspar and detrital grains began to dissolve slightly and form dissolution pores (Figure 2).
Figure 92. The paragenetic sequence and pore evolution of the Xishanyao formation in the SJB. The thermal evolution history is based on the study of Wang et al. [
68] with some modifications. Solid blue lines represent probable timing based on observed diagenetic and mineralization phases. While the dashed blue lines represent inferred or not well-constrained diagenetic and mineralization phases. J
2x = Xishanyao formation; I/S = illite/smectite; Ro = vitrinite reflectance.
The effect of compaction in the mesodiagenesis A stage was extremely strong, and the compaction type gradually shifted from mechanical compaction to chemical compaction. The contact relationships change from point contact and line contact to line contact, concave–convex contact and suture contact during this stage, along with a large proportion of brittle minerals broken up. The dissolution pores formed in the eodiagenesis stage are damaged under the compaction, and the damage of compaction to the quality of the reservoir is further strengthened. The mesodiagenesis A stage can be further divided into two substages, A1 and A2, according to temperature and Ro. These two substages have certain differences in diagenetic environment and diagenetic reaction:
In the mesodiagenesis A1 stage, the temperature was 70–90 °C, and the Ro was 0.5–0.7%, in an acidic diagenetic environment. The amount of organic acid generated in coal measures reaches the highest level at this temperature [
71], the diagenetic environment is acidic, and the tensity of dissolution reached the highest level (
Figure 92). The massive dissolution of feldspar, aluminosilicate lithic fragments and early micrite carbonate cement formed a large number of dissolution pores and mo
uld pores. Because of the relatively closed diagenetic system, the dissolution products cannot be discharged. This has led to the kaolinite filling pores and quartz overgrowth (part of the SiO
2 comes from the chemical compaction).
In the Mesodiagenesis A2 stage, the temperature was 90–130 °C, and the Ro was 0.7–1.3%. The acidic diagenetic environment is gradually weakened due to the decomposition of organic acids. The effect of dissolution decreases gradually, while the cementation
is gradually increases. The quartz overgrowth gradually decreases, which is manifested as second level quartz cementation. Late period carbonate cementation (dolomite and ankerite) gradually filled the pore space (
Figure 92). The clay minerals appear abundantly and fill the pores, further reducing the porosity.
4. Diagenetic Control of Coal Measure Reservoir Quality
Reservoir quality is influenced by diagenetic activities, such as compaction, cementation, dissolution, recrystallization, and metasomatism [
20,
72]. For the Xishanyao formation coal measure sandstone, compaction, dissolution and cementation are the main diagenetic controlling factors for reservoir quality.
4.1. The Influence of Compaction on Reservoir Quality
The cCompaction is one of the main factors that cause the reduction of intergranular pore volume [
73] and the densification of coal measure sandstone reservoirs. Plastic particles in the sandstone have a weak compaction resistance, while the rigid particles have a high compaction resistance ability [
61,
74]. The coal measure sandstones of the Xishanyao formation contain a high content of plastic grains, such as volcanic lithic fragments, muddy gravel and carbonaceous fragments, which makes its compaction resistance ability weak.
The coal measure sandstone reservoirs are strongly affected by mechanical compaction, which is characteristic of the close contacted clastic particles, the ruptured rigid particles, and the deformed plastic particles. Chemical compaction commonly happens in SJB due to the high intensity of compaction, which may lead to particle suture contact and reduced interparticle space. The intense mechanical and chemical compaction has a great negative effect on the physical properties of the sandstone reservoir.
4.2. The Influence of Cementation on Reservoir Quality
The coal measure sandstone of the Xishanyao formation in the SJB is mainly clay mineral cement, followed by quartz cement and carbonate cement. The development of these cementations is one of the main factors leading to the significant decline in reservoir quality [
74,
75,
76,
77].
The closed diagenetic system of coal measure sandstone prevents the dissolution products from being discharged in time, which also leads to the development of authigenic kaolinite cementation and quartz cementation. The developed kaolinite cement fills the pore space in large quantities, but its loose inter-crystalline structure contains inter-crystalline pores that can resist compaction [
78]. In addition, illite and I/S mainly fill intergranular pores and pore throats, thereby reducing the reservoir quality of the sandstone [
65,
79,
80]. In summary, different types of clay minerals occur widely and fill or divide the pore space, resulting in tortuous pore throats, reducing pore connectivity, and weakening seepage capacity [
13,
37,
65,
79,
80].
The content of volcanic lithic fragments in coal measure sandstone is relatively high, which may inhibit the quartz overgrowth to some extent [
77]. It can be observed that the overgrowth level of the coal measure sandstone is shown in the second stage
(Figure 5A,C). The quartz overgrowth in the eodiagenesis stage can help the sandstone better resist compaction. In the mesodiagenesis, pressure solution, feldspar dissolution and clay mineral transformation produced many SiO
2 (aq), which developed into
the quartz cement [
13,
81,
82].
The carbonate cement is locally developed in coal measure sandstones. In the eodiagenesis stage, several micrite carbonate particles blended in the coal measure sandstone, which blocked and filled the intergranular pores. In the mesodiagenesis A2 stage, the late period dolomite and ankerite cements appeared in the sandstone, which blocked the intergranular pores of the sandstone and reduced the reservoir quality
(Figure 5A,H,I).
4.3. The Influence of Dissolution on Reservoir Quality
The dissolution in diagenesis has a positive effect on reservoir physical properties [
13]. The coal seam and dark shale begin to produce organic acids through the decomposition of plant residues during the eodiagenesis stage [
71] and reach
ing a peak in the mesodiagenesis stage (temperature range from 80 °C to 140 °C, [
37,
83]). The amount of organic acid generated in the coal measure is much higher than in other source rocks [
5,
7,
84].
The sedimentary environment makes the sandstone have good primary physical properties and pore connectivity, and the weak dissolution in the eodiagenesis stage provides a seepage channel for the migration of acidic fluids in the mesodiagenesis stage. The large proportion of aluminosilicate minerals, such as feldspar and volcanic in coal measure sandstone provides a good material basis for the dissolution [
5]. Dissolution is most intense in mesodiagenesis. During this period, the thermal evolution of organic matter releases a large number of organic acids into the diagenetic system of the sandstone, causing the soluble minerals to selectively dissolve and form a large number of intragranular dissolved pores and intergranular dissolution pores [
35]. Overall, the diagenetic stage of the coal measure sandstone in this area is mainly in the A1 and A2 stages of the mesodiagenesis, which happens to be the most intense stage of organic acid dissolution. The dissolution has brought a great positive effect on the physical properties of the reservoir.