Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Ashenafi Feyisa Beyi and Version 2 by Rita Xu.
The enormous and diverse population of microorganisms residing in the digestive tracts of humans and animals influence the development, regulation, and function of the immune system. Recently, the understanding of the association between autoimmune diseases and gut microbiota has been improved due to the innovation of high-throughput sequencing technologies with high resolutions.
- antimicrobial resistance
- autoimmune diseases
- fecal microbiota transplantation
1. Introduction
The resident gut microbiota is composed of a complex consortium of microorganisms, including bacteria, archaea, fungi, protozoans, and viruses, which reside along the alimentary tracts of humans and animals. A newborn acquires a seed microbiota mainly from the vagina of the mother during birth [1]. Following that, the gut microbiota increases in diversity and reaches adult-like compositions and structures at the age of three to five years in humans [2]. Studies show that gut microbiota is crucial for human and animal health, food digestion, production of some useful metabolites, colonization resistance toward pathogenic bacteria, and the development of innate and adaptive immune systems [1][3][1,3]. However, several factors, such as diet, antibiotics, lifestyle, surgical interventions, and bacterial or viral infections, alter the microbial composition and, subsequently, may have detrimental consequences on health.
Gut microbiota has a significant association with autoimmune diseases, including inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), asthma, multiple sclerosis, and type 1 diabetes [4][5][6][4,5,6], and other health problems, such as cancer, mental health, and cardiovascular, respiratory, and metabolic diseases, which were not expected to have associations with the microbiota. Furthermore, disruption of gut microbial diversity and composition has been shown to lead to the occurrence of several health problems including autoimmune diseases [7][8][9][10][7,8,9,10]. Unfortunately, for several of autoimmune diseases, there are no effective or lasting medications. Nevertheless, fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT), where gut microbiota from a healthy person is administered to a sick person to re-establish healthy normal microbiota after infection by pathogens, such as Clostridioides difficile, has recently gained popularity in clinical medicine. The newly acquired breakthrough in effectively treating C. difficile infections using FMT has inspired scientists to develop a treatment for autoimmune diseases and multidrug-resistant infections using this (re)emerging therapy.
Recently, gut microbiota and FMT have received attention from the public, and the “do-it-yourself” FMT movement has been noticed. According to an online survey conducted from January 2018 to February 2019, 82% of 84 respondents involved in this movement have claimed improvement in their conditions. The two main conditions for which the therapy was sought were IBD and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) [11]. However, it should be noted that such treatments could be dangerous unless the procedures are approved by FDA and conducted in licensed medical centers. On the other hand, FMT positively affects decolonization of antimicrobial-resistant bacterial infections (see a review by Davido et al. [12]). FMT was shown to effectively induce decolonization of specific pathogens in 66.7% (102/153) of patients who received this therapy between 2000 and 2020 [13].
The transfer of rumen cud, called transfaunation, from healthy to sick animals was practiced long before the rumen microorganisms were understood [14]. Rumen transfaunation is indicated for indigestion and improves feed conversion efficiency in cattle [15][16][15,16]. FMT has been attempted in dogs and cats to control autoimmune diseases [17][18][17,18], in chickens to mitigate the shedding and spread of foodborne pathogens [19], and in piglets to increase their resistance to infections [20][21][20,21]. Figure 1 depicts the interrelationships between gut microbiota, its beneficial roles, factors that affect microbial diversity and composition, and the benefits and challenges of FMT.
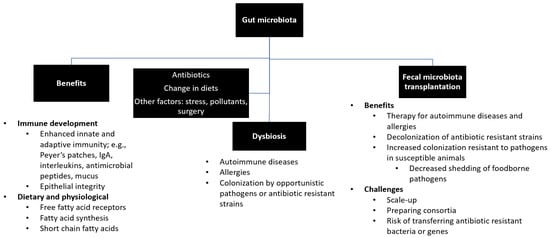
Figure 1. Summary of gut microbiota. Gut microbiota plays beneficial roles in the development of immune system, production and synthesis of essential nutrients, and maintenance of a healthy physiological status. Exposure to antibiotics and changes in diets and lifestyles may lead to disruption of healthy microbial diversity and composition (i.e., dysbiosis), which can be restored by fecal microbiota transfer.
2. Gut Microbiota, Immune Development, and Fecal Microbiota Transplantation
2.1. Overview of Gut Microbiota in Humans
Gut microbiota impacts functional and immunological development in humans [22]. Their beneficial roles include digestion of cellulose, production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), resistance to colonization by pathogenic organisms, and maintaining immune homeostasis [23][24][25][23,24,25]. Gut microbiota, represented by fecal microbiota in most studies for simplicity of sample collections, consists mainly of four phyla of bacteria: Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, Proteobacteria, and Actinobacteria. According to one study, these four phyla comprise 93.5% of 2172 species that were classified into 12 different phyla in humans [26]. Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes account for over 80% of the microbiota. Firmicutes comprises mainly Gram-positive bacteria but also a low number of Gram-negative species (e.g., Veillonella species). Bacteroidetes consists of Gram-negative bacteria, primarily represented by the Bacteroides genus and other frequently detected genera, including Alistipes, Parabacteroides, Prevotella, Tannerella, in the human gut [27][28][29][27,28,29].
2.1.1. Establishment of Gut Microbiota after Birth
Colonization and the establishment of gut microbiota in humans occur gradually during early life. Fetuses acquire their initial microbiota in utero, which is followed by colonization after delivery from the environment during childbirth, primarily from the vagina [30][31][30,31]. Moles and colleagues [30] showed the difference in bacterial types between the meconium of prenatal infants and feces from their first three weeks of life. They demonstrated that postnatal bacterial exposures have primary roles in the establishment of gut microbiota in infants. The gut microbial composition of infants is stable compared to that of adults until the transition from breastfeeding to solid food, which induces remarkable shifts [32][33][32,33]. After the achievement of adult-like gut microbial composition at the age of three to five years [2], the microbial diversity shows little variation throughout adult life unless there are disruptions affecting change, such as diet, antibiotics, infections, cancer, or surgery [34].
2.1.2. Factors Affecting Diversities and Compositions of Gut Microbiota
The perturbation of gut microbiota may lead to a decrease in microbial diversity and a shift of composition and cause an abnormal condition called dysbiosis, which is associated with several disease conditions [35]. As mentioned above, various factors cause the alteration of microbial communities [9][27][36][9,27,36]. There is even a marked difference in microbial compositions between children born by cesarean section and those born naturally, where the former has been shown to have a negative side effect on microbial diversity [6][37][6,37]. Nevertheless, diets and antibiotics are the primary causes of dysbiosis in humans; thus, a brief account of their impacts on gut microbiota is presented below.
- i.
-
Diets
The effects of diet on gut microbiota are not uniformly agreed upon across published studies; however, a large body of scientific literature has documented both negative and positive impacts of various foods on microbiota [24][35][38][39][40][24,35,38,39,40]. Consumption of fiber-rich or plant-originated foods, such as vegetables and fruits, as compared to meats and dairy products, has different effects on the compositions of microbial communities [38][39][38,39].
In a study that compared the microbiota of children in Europe and rural Africa (i.e., Western diets and agrarian diets, respectively), distinct patterns in microbial diversity and composition were observed [24]. In the African children, genera associated with the digestion of cellulose, such as Prevotella species and Xylanibacter species, had significantly higher abundance than in the Europeans. Similarly, a higher amount of SCFAs was produced by the gut microbiota in the African children [24]. Short-chain fatty acids, such as butyrate, acetate, and propionate, have been shown to be beneficial to humans because they have anti-inflammatory effects and enhance intestinal barrier functions by increasing mucus production and enterocyte tight junctions [41][42][41,42]. Enterobacteriaceae, such as Shigella and Escherichia, that have unfavorable health impacts were significantly lower in the African children when compared to European children, suggesting that the establishment of such pathogenic bacteria was prevented by the SCFA-producing bacteria that were abundant in the gut of the Africans [24]. This study demonstrated that diet plays a critical role in shaping the diversity and composition of gut microbiota.
In agreement with these findings, another study reported the enrichment of beneficial gut bacteria and increased production of SCFAs related to consumption of Mediterranean diet (i.e., high-level of cereals, fruit, vegetables, and legumes) compared to a typical Western diet (i.e., animal-fat and protein-based diets) [40]. These and several other studies have provided strong evidence that consumption of processed and high-calorie carbohydrates and meats is associated with the depletion of beneficial gut bacteria from the intestinal microbiota [43][44][45][43,44,45].
- ii.
-
Antibiotics
Similar to diets, the indiscriminate action of antibiotics on both beneficial (i.e., mutualists) and noxious bacteria leads to remarkable changes in gut microbiota [46]. Antibiotics cause the shifting of the microbiota due to antibiotic sensitivity and inability of affected organisms to recover (i.e., lack of resilience) [47][48][47,48]. In addition, the selection of resistant bacteria already presents in the gut or acquisition of exogenous resistant bacteria, owing to the weakening of colonization resistance to external pathogenic bacteria, can perturb gut microbiota as a consequence of antibiotic administration [36][49][50][36,49,50]. An observational study in human patients showed that ciprofloxacin treatment affected the abundance of gut microbiota for more than six months after the termination of the medication, resulting in a substantial reduction in bacterial diversity [25]. Similarly, treatment with broad-spectrum antibiotics such as fluoroquinolones and β-lactams reduced the diversity of gut microbiota by 25%. It was shown that broad-spectrum antibiotic use caused an imbalance of the microbial composition; for instance, the most predominant genus shifted from Faecalibacterium to Bacteroides [27], which would have metabolic effects, such as less SCFAs.
Antibiotics have both short- and long-term effects on gut microbiota [51][52][51,52]. Haak and colleagues [52] reported that the return of microbiota to the pretreatment composition in patients on a combination of antibiotic therapy had taken 8 to 31 months. A mouse model study shows that prenatal exposure of mice to an oral antibiotic in late gestation influences the microbial composition of the neonates [53]. To this end, the route of antibiotic administration has differential impacts on gut microbiota, with the oral route inducing substantial changes in microbial diversities compared to parenteral routes of administration [54]. The oral route of antibiotic delivery exposes the gut microbiota to a higher concentration of drugs before they undergo catabolism, in contrast to parenteral drug administration routes. However, studies have demonstrated that parenteral delivery of antibiotics also has an impact on the gastrointestinal microbiota [55][56][55,56]. In our recent animal study, researcherswe observed that the concentrations of subcutaneously administered fluoroquinolones found in feces were several folds higher than that of plasma [57].
2.2. Effects of Gut Microbiota on the Immune System in Humans
2.2.1. Role of Gut Microbiota in the Development of the Immune System
Colonization of the gut by microbiota starts before birth in infants, as evidenced by the detection of bacteria in the meconium of preterm neonates [30]. The maturation of the immune system coincides with the “evolvement” of gut microbiota, which happens in the first three to five years of age [32]. The gut bacteria influence the development of both innate and adaptive immunity [58][59][60][58,59,60]. Moreover, the effects of the microbiota extend to the peripheral sites as well as central lymphoid tissues, including bone marrow, where hematopoiesis can be affected [61][62][63][64][61,62,63,64].
The role of gut microbiota in the development and maturation of immunity has been well demonstrated following the colonization of germ-free (GF) mice. Proportion and differentiation of myeloid progenitor cells were low in GF mice, which led to higher bacterial load and acute death following a challenge with Listeria monocytogenes compared to the conventionally reared (CONV-R) mice [61]. However, the mechanisms by which the gut microbiota control the immune development in distal sites, such as in the bone marrow, are not well understood. In the GF mice, the defects of myelopoiesis were restored, and mice acquired resistance to L. monocytogenes after colonization by complex microbiota [61]. The same study revealed the effects of gut microbiota on innate immunity through directing hematopoiesis, polymorphonuclear cells in particular.
There is an interaction between gut microbiota and antimicrobial peptides [65]. Studies show that the production of antimicrobial peptides was substantially low in GF mice, and lymphoid tissues in the spleen, thymus, and lymph nodes had defects. At the same time, macrophage phagocytosis was only minimally affected compared to the CONV-R mice [34][58][59][34,58,59]. The gut microbiota affects specific immune cells and mediators as well. For instance, in one study, it was shown that GF mice lack IgA-secreting plasma cells, which expanded to the levels similar to that of the CONV-R mice after repopulating the gut with specific bacteria [60].
Specific bacteria have also been found to have a modulatory effect on T cell development. The polysaccharide A (PSA) produced by Bacteroides fragilis induced balanced numbers of T helper 1 (Th1) and T helper 2 (Th2) cells, which is mediated by TLR2/TLR1 heterodimer on lamina propria dendritic cells [3]. When these bacteria colonized GF mice, the immunomodulatory activities of PSA corrected systemic T cell deficiencies and the imbalance of Th1 and Th2 cells. As detailed by the same authors, this symbiotic factor binds to the TLR2/1 heterodimer and activates dendritic cells, which that direct CD4+ T cells to assume a Treg cell phenotype and to secrete more anti-inflammatory cytokines [66]. These immunomodulatory activities were induced by other gut bacteria as well, such as Lactococcus and Bifidobacterium species [3].
Furthermore, the effects of gut microbiota extend to regulation of the T cell receptor (TCR) recruitment and proliferation [34]. In GF mice, the numbers of αβTCR+ and γδTCR+ T cells in intestinal intraepithelial lymphocyte population were lower than that of CONV-R mice [67]. It has been also demonstrated that colonization of GF mice with bacteria gradually increased the numbers of cells expressing either receptor; within a month, the ex-GF mice reached similar levels of T cells comparable with that of the CONV-R mice [34][67][34,67]. The influence of gut microbiota on adaptive immunity extends to other cells besides T cells; they influence the development of B and invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cell populations, as demonstrated in the GF mice [61].
Aside from direct effects, gut microbes also have an indirect impact on immunity through their fermentation products such as SCFAs. These SCFAs can bind to host cell receptors or induce epigenetic changes in host DNA, which result in activation or repression of the host immune genes [1]. Additionally, a host-specific microbiota is required for the development of a healthy immune system [68][69][68,69]. GF mice colonized by human microbiota had low levels of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, few proliferating T cells, few dendritic cells, and low antimicrobial peptide expression in the intestine. In contrast, colonization of GF mice with mouse-derived segmented filamentous bacteria (SFB) restored Th17 cell numbers to that observed in CONV-R mice, suggesting that mouse-specific organisms may be necessary to attain full immune maturation in mice [68].
2.2.2. Effects of Perturbation of Gut Microbiota on the Immune System
Exposure to complex microbiota during early life, when an individual’s immunity is developing and expanding, has a positive association with immune tolerance later in life [34]. Early sensitization of the immune system by exposure to microbes reduces allergic reactions in adult life [32]. Moreover, literature shows that the presence of microbes prior to weaning is more critical than colonizing after weaning [70][71][70,71]. As discussed above, one of the factors that cause perturbation of gut microbiota is exposure to antibiotics. The effect of antibiotics on autoimmune diseases such as IBD via changing the composition of gut microbiota has been reported in several studies; however, the results are not uniform [1][5][72][1,5,72]. Antibiotics can exacerbate existing conditions and may also contribute to the occurrence of autoimmune diseases. In a case-control study conducted in the UK, the authors reported that early childhood exposure to antibiotics increases the risk of Crohn’s disease (CD) [5]. Their observation was in agreement with the hygiene hypothesis, where reduced exposure to infectious bacteria due to improved sanitary practices and antibiotics during early life was attributed to the rise in the incidence of allergy and asthma in developed Western countries [3]).
Overproduction of Th2 cells and IgE causes asthma; however, as discussed above, gut microbiota affects the Th2 subset and may be a potential treatment option for such types of asthma. This was reported by Mazmanian et al. [3], who demonstrated that GF mice have a higher Th2:Th1 ratio than CONV-R mice. However, the condition was improved following colonization of the mice by microbiota that contained Bacteroides fragilis. The use of microbiota as a treatment for overproduced Th2 cells can become a therapeutic option for patients with low quality of life due to severe asthma.
