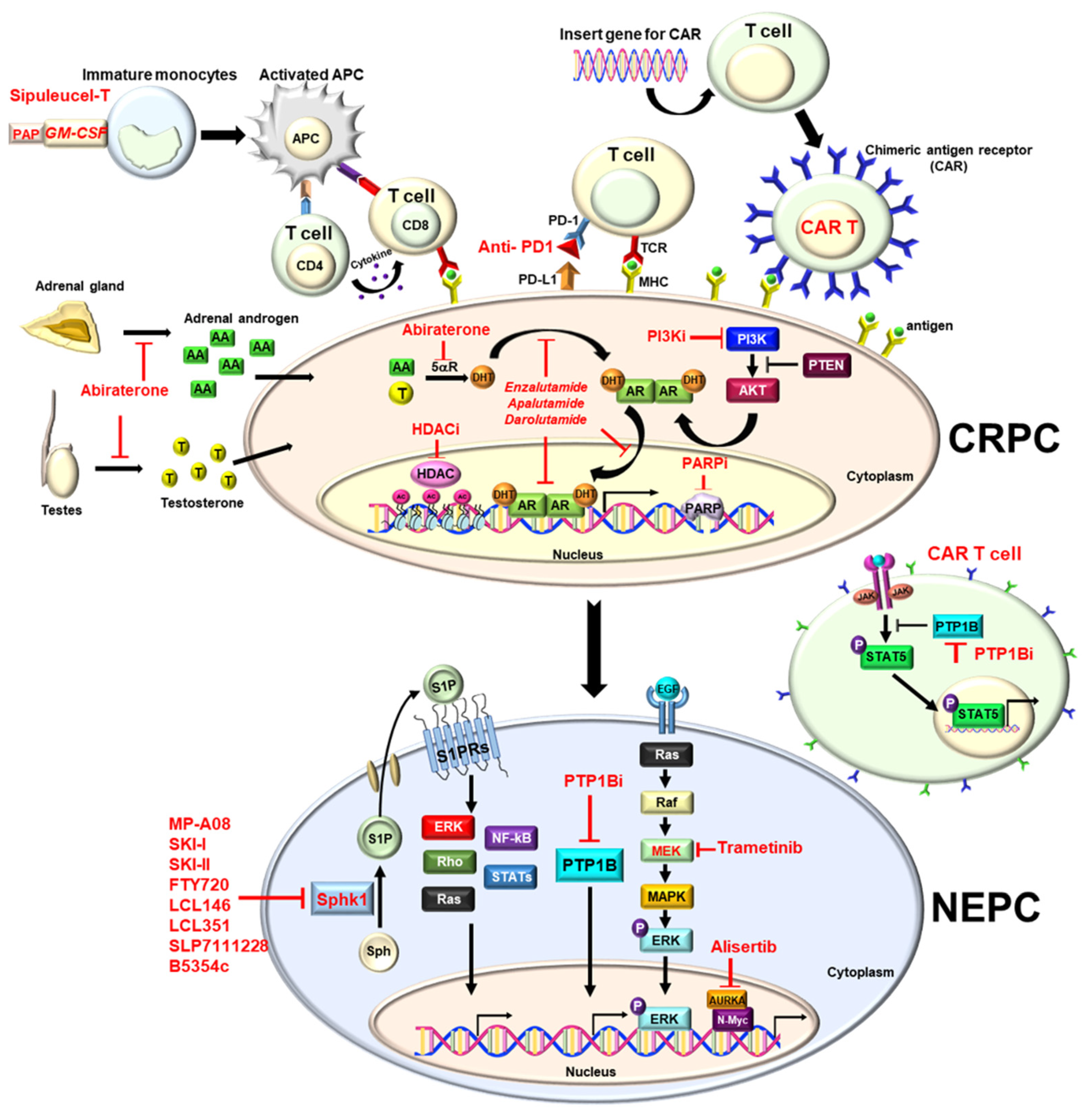
Prostate cancer (PCa) is the most common cancer and the second deadliest cancer among men in the United States, which is mainly due to metastatic disease. In general, surgery or radiation is potentially a curative treatment for localized disease. Since PCa is characterized as a typical androgen-dependent disease, hormone therapy (i.e., androgen deprivation therapy (ADT)) is the most effective therapy to control metastatic disease. However, almost all patients eventually develop castration-resistant PCa (CRPC) within 12 to 18 months, with a median survival of 14 to 26 months. Nowadays, new anti-androgens (Enzalutamide or Abiraterone), radiotherapy (Radium-223) or immunotherapy (sipuleucel-T) have been approved for metastatic CRPC (mCRPC) patients to prolong the overall survival. Inevitably, mCRPC further acquires resistance and becomes therapy- and castration-resistant PCa (t-CRPC), which is considered as an end-stage disease without effective therapy, and on which new therapeutic strategies have been actively explored.
- castration-resistant prostate cancer
- recurrent therapy and castration-resistant prostate cancer
- precision medicine
1. Enzalutamide
| Drug Class | Therapy | Indication | Clinical Trial |
Efficacy (Mon.) |
Impact on PCa Treatment | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2nd-generation antiandrogen | Enzalutamide | mCRPC | AFFIRM | OS 18.4 vs. 13.6 | ENZ improves OS after chemotherapy |
[4] |
| PREVAIL | OS 35.3 vs. 31.3 | ENZ improves OS in chemotherapy naïve |
[5][6] | |||
| nmCRPC | PROSPER | MFS 36.6 vs. 14.7 | ENZ decreases the risk of metastasis | [7] | ||
| mCSPC | ENZEMET | 80% vs. 72% (3-year OS) |
ENZ improves OS and decreases disease progression | [8] | ||
| ARCHES | rPFS NR vs. 19.0 |
ENZ decreases the risk of metastatic progression | [9] | |||
| Apalutamide | nmCRPC | SPARTAN | MFS 40.5 vs. 16.2 | APA decreasse the risk of metastasis | [10] | |
| mCSPC | TITAN | 2-year OS 82.4 vs. 73.5 |
APA improves OS and PFS | [11] | ||
| Darolutamide | nmCRPC | ARAMIS | MFS 40.4 vs. 18.4 | DA decreases the risk of metastasis | [12] | |
| Abiraterone | mCRPC | COA-301 | OS 15.8 vs. 11.2 | AB improves OS after chemotherapy |
[13] | |
| COA-302 | OS 34.7 vs. 30.3 | AB improves OS in chemotherapy naïve |
[14] | |||
| High-volume CSPC | LATITUDE | OS 53.3 vs. 36.5 | AB improves OS in high-risk CSPC |
[15][16] | ||
| Radiotherapy | Radium 223 | CRPC with symptomatic bone metastasis, no visceral metastasis | ALSYMPCA | OS 14.9 vs. 11.3 | RA-223 improves OS in symptomatic bony metastatic mCRPC | [17] |
| 177Lu-PSMA 617 | PSMA-positive mCRPC and already treated with ARB and chemotherapy | VISION | OS 15.3 vs. 11.3 rPFS 8.7 vs. 3.4 |
177Lu-PSMA 617 improves OS and rPFS in PSMA-positive mCRPC | [18] | |
| Immunotherapy | Sipuleucel-T | mCRPC | IMPACT | OS 25.8 vs. 21.7 | Sipuleucel-T improves OS in mCRPC | [19] |
| PARP-I | Olaparib | mCRPC with HRR genes mutation after ENZ or AB | PROfound | OS 18.5 vs.15.1 rPFS 7.4 vs. 3.6 |
Olaparib improves OS and rPFS in mCRPC with HRR gene mutation | [20] |
| Rubraca | mCRPC with BRCA genes after ARB or chemotherapy | TRITON2 (phase2) TRITON3 (phase3) |
ORR 43.5% (IRR) PSA response rate 54.8% |
Rubraca has the antitumor activity in mCRPC with BRCA gene mutation | [21][22] |
2. Apalutamide
3. Darolutamide
4. Abiraterone
References
- Tran, C.; Ouk, S.; Clegg, N.J.; Chen, Y.; Watson, P.A.; Arora, V.; Wongvipat, J.; Smith-Jones, P.M.; Yoo, D.; Kwon, A.; et al. Development of a second-generation antiandrogen for treatment of advanced prostate cancer. Science 2009, 324, 787–790.
- Heidegger, I.; Brandt, M.P.; Heck, M.M. Treatment of non-metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer in 2020: What is the best? Urol. Oncol. 2020, 38, 129–136.
- Fizazi, K.; Scher, H.I.; Miller, K.; Basch, E.; Sternberg, C.N.; Cella, D.; Forer, D.; Hirmand, M.; de Bono, J.S. Effect of enzalutamide on time to first skeletal-related event, pain, and quality of life in men with castration-resistant prostate cancer: Results from the randomised, phase 3 AFFIRM trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 1147–1156.
- Scher, H.I.; Fizazi, K.; Saad, F.; Taplin, M.E.; Sternberg, C.N.; Miller, K.; de Wit, R.; Mulders, P.; Chi, K.N.; Shore, N.D.; et al. Increased survival with enzalutamide in prostate cancer after chemotherapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1187–1197.
- Beer, T.M.; Armstrong, A.J.; Rathkopf, D.; Loriot, Y.; Sternberg, C.N.; Higano, C.S.; Iversen, P.; Evans, C.P.; Kim, C.S.; Kimura, G.; et al. Enzalutamide in Men with Chemotherapy-naïve Metastatic Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer: Extended Analysis of the Phase 3 PREVAIL Study. Eur. Urol. 2017, 71, 151–154.
- Beer, T.M.; Armstrong, A.J.; Rathkopf, D.E.; Loriot, Y.; Sternberg, C.N.; Higano, C.S.; Iversen, P.; Bhattacharya, S.; Carles, J.; Chowdhury, S.; et al. Enzalutamide in metastatic prostate cancer before chemotherapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 424–433.
- Hussain, M.; Fizazi, K.; Saad, F.; Rathenborg, P.; Shore, N.; Ferreira, U.; Ivashchenko, P.; Demirhan, E.; Modelska, K.; Phung, D.; et al. Enzalutamide in Men with Nonmetastatic, Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 2465–2474.
- Davis, I.D.; Martin, A.J.; Stockler, M.R.; Begbie, S.; Chi, K.N.; Chowdhury, S.; Coskinas, X.; Frydenberg, M.; Hague, W.E.; Horvath, L.G.; et al. Enzalutamide with Standard First-Line Therapy in Metastatic Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 121–131.
- Armstrong, A.J.; Szmulewitz, R.Z.; Petrylak, D.P.; Holzbeierlein, J.; Villers, A.; Azad, A.; Alcaraz, A.; Alekseev, B.; Iguchi, T.; Shore, N.D.; et al. ARCHES: A Randomized, Phase III Study of Androgen Deprivation Therapy with Enzalutamide or Placebo in Men With Metastatic Hormone-Sensitive Prostate Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 2974–2986.
- Smith, M.R.; Saad, F.; Chowdhury, S.; Oudard, S.; Hadaschik, B.A.; Graff, J.N.; Olmos, D.; Mainwaring, P.N.; Lee, J.Y.; Uemura, H.; et al. Apalutamide Treatment and Metastasis-free Survival in Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1408–1418.
- Chi, K.N.; Agarwal, N.; Bjartell, A.; Chung, B.H.; Pereira de Santana Gomes, A.J.; Given, R.; Juárez Soto, Á.; Merseburger, A.S.; Özgüroğlu, M.; Uemura, H.; et al. Apalutamide for Metastatic, Castration-Sensitive Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 13–24.
- Fizazi, K.; Shore, N.; Tammela, T.L.; Ulys, A.; Vjaters, E.; Polyakov, S.; Jievaltas, M.; Luz, M.; Alekseev, B.; Kuss, I.; et al. Darolutamide in Nonmetastatic, Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1235–1246.
- Fizazi, K.; Scher, H.I.; Molina, A.; Logothetis, C.J.; Chi, K.N.; Jones, R.J.; Staffurth, J.N.; North, S.; Vogelzang, N.J.; Saad, F.; et al. Abiraterone acetate for treatment of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: Final overall survival analysis of the COU-AA-301 randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 983–992.
- Ryan, C.J.; Smith, M.R.; Fizazi, K.; Saad, F.; Mulders, P.F.; Sternberg, C.N.; Miller, K.; Logothetis, C.J.; Shore, N.D.; Small, E.J.; et al. Abiraterone acetate plus prednisone versus placebo plus prednisone in chemotherapy-naive men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (COU-AA-302): Final overall survival analysis of a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 152–160.
- Fizazi, K.; Tran, N.; Fein, L.; Matsubara, N.; Rodriguez-Antolin, A.; Alekseev, B.Y.; Özgüroğlu, M.; Ye, D.; Feyerabend, S.; Protheroe, A.; et al. Abiraterone plus Prednisone in Metastatic, Castration-Sensitive Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 352–360.
- Fizazi, K.; Tran, N.; Fein, L.; Matsubara, N.; Rodriguez-Antolin, A.; Alekseev, B.Y.; Özgüroğlu, M.; Ye, D.; Feyerabend, S.; Protheroe, A.; et al. Abiraterone acetate plus prednisone in patients with newly diagnosed high-risk metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer (LATITUDE): Final overall survival analysis of a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 686–700.
- Parker, C.; Nilsson, S.; Heinrich, D.; Helle, S.I.; O’Sullivan, J.M.; Fosså, S.D.; Chodacki, A.; Wiechno, P.; Logue, J.; Seke, M.; et al. Alpha emitter radium-223 and survival in metastatic prostate cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 213–223.
- Sartor, O.; de Bono, J.; Chi, K.N.; Fizazi, K.; Herrmann, K.; Rahbar, K.; Tagawa, S.T.; Nordquist, L.T.; Vaishampayan, N.; El-Haddad, G.; et al. Lutetium-177-PSMA-617 for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1091–1103.
- Kantoff, P.W.; Higano, C.S.; Shore, N.D.; Berger, E.R.; Small, E.J.; Penson, D.F.; Redfern, C.H.; Ferrari, A.C.; Dreicer, R.; Sims, R.B.; et al. Sipuleucel-T immunotherapy for castration-resistant prostate cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 411–422.
- de Bono, J.; Mateo, J.; Fizazi, K.; Saad, F.; Shore, N.; Sandhu, S.; Chi, K.N.; Sartor, O.; Agarwal, N.; Olmos, D.; et al. Olaparib for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2091–2102.
- Abida, W.; Patnaik, A.; Campbell, D.; Shapiro, J.; Bryce, A.H.; McDermott, R.; Sautois, B.; Vogelzang, N.J.; Bambury, R.M.; Voog, E.; et al. Rucaparib in Men with Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Harboring a BRCA1 or BRCA2 Gene Alteration. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3763–3772.
- A Study of Rucaparib Versus Physician’s Choice of Therapy in Patients with Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer and Homologous Recombination Gene Deficiency (TRITON3). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02975934?term=TRITON3&draw=2&rank=1 (accessed on 15 July 2022).
- Moilanen, A.M.; Riikonen, R.; Oksala, R.; Ravanti, L.; Aho, E.; Wohlfahrt, G.; Nykänen, P.S.; Törmäkangas, O.P.; Palvimo, J.J.; Kallio, P.J. Discovery of ODM-201, a new-generation androgen receptor inhibitor targeting resistance mechanisms to androgen signaling-directed prostate cancer therapies. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12007.
- Smith, M.R.; Hussain, M.; Saad, F.; Fizazi, K.; Sternberg, C.N.; Crawford, E.D.; Kopyltsov, E.; Park, C.H.; Alekseev, B.; Montesa-Pino, Á.; et al. Darolutamide and Survival in Metastatic, Hormone-Sensitive Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1132–1142.
- Barrie, S.E.; Haynes, B.P.; Potter, G.A.; Chan, F.C.; Goddard, P.M.; Dowsett, M.; Jarman, M. Biochemistry and pharmacokinetics of potent non-steroidal cytochrome P450(17alpha) inhibitors. J. Steroid. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1997, 60, 347–351.
- Ryan, C.J.; Smith, M.R.; de Bono, J.S.; Molina, A.; Logothetis, C.J.; de Souza, P.; Fizazi, K.; Mainwaring, P.; Piulats, J.M.; Ng, S.; et al. Abiraterone in metastatic prostate cancer without previous chemotherapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 138–148.
- Molina, A.; Belldegrun, A. Novel therapeutic strategies for castration resistant prostate cancer: Inhibition of persistent androgen production and androgen receptor mediated signaling. J. Urol. 2011, 185, 787–794.
- Naseer, F.; Ahmad, T.; Kousar, K.; Anjum, S. Advanced Therapeutic Options for Treatment of Metastatic Castration Resistant Prostatic Adenocarcinoma. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 728054.
- Geng, C.; He, B.; Xu, L.; Barbieri, C.E.; Eedunuri, V.K.; Chew, S.A.; Zimmermann, M.; Bond, R.; Shou, J.; Li, C.; et al. Prostate cancer-associated mutations in speckle-type POZ protein (SPOP) regulate steroid receptor coactivator 3 protein turnover. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 6997–7002.
- Barbieri, C.E.; Baca, S.C.; Lawrence, M.S.; Demichelis, F.; Blattner, M.; Theurillat, J.P.; White, T.A.; Stojanov, P.; Van Allen, E.; Stransky, N.; et al. Exome sequencing identifies recurrent SPOP, FOXA1 and MED12 mutations in prostate cancer. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 685–689.
- Blattner, M.; Lee, D.J.; O’Reilly, C.; Park, K.; MacDonald, T.Y.; Khani, F.; Turner, K.R.; Chiu, Y.L.; Wild, P.J.; Dolgalev, I.; et al. SPOP mutations in prostate cancer across demographically diverse patient cohorts. Neoplasia 2014, 16, 14–20.
- Karantanos, T.; Corn, P.G.; Thompson, T.C. Prostate cancer progression after androgen deprivation therapy: Mechanisms of castrate resistance and novel therapeutic approaches. Oncogene 2013, 32, 5501–5511.
- Nakazawa, M.; Fang, M.; Marshall, C.H.; Lotan, T.L.; Isaacsson Velho, P.; Antonarakis, E.S. Clinical and genomic features of SPOP-mutant prostate cancer. Prostate 2022, 82, 260–268.
- Hoogland, A.I.; Jim, H.S.L.; Gonzalez, B.D.; Small, B.J.; Gilvary, D.; Breen, E.C.; Bower, J.E.; Fishman, M.; Zachariah, B.; Jacobsen, P.B. Systemic inflammation and symptomatology in patients with prostate cancer treated with androgen deprivation therapy: Preliminary findings. Cancer 2021, 127, 1476–1482.
- Sciarra, A.; Gentilucci, A.; Salciccia, S.; Pierella, F.; Del Bianco, F.; Gentile, V.; Silvestri, I.; Cattarino, S. Prognostic value of inflammation in prostate cancer progression and response to therapeutic: A critical review. J. Inflamm. 2016, 13, 35.
- Nguyen, D.P.; Li, J.; Tewari, A.K. Inflammation and prostate cancer: The role of interleukin 6 (IL-6). BJU Int. 2014, 113, 986–992.
