Intestinal microorganisms are composed of bacteria, archaea, eukaryotes, and viruses, and more than 肠道微生物由细菌、古细菌、真核生物和病毒组成,其中99% of them are bacteria. Approximately 以上是细菌。已知大约有 10 14种细菌构成成人肠道中的肠道菌群,这个数量是人体体细胞数量的 bacteria are known to constitute the intestinal flora in the adult gut, and this number is 10 times the number of human somatic cells.10 倍。
- intestinal flora
- homeostatic imbalances
- diseases
1. Introduction
一、简介
The intestinal flora co-exists harmoniously with the host, participate in the digestion and the absorption of nutrients, and also help to maintain the integrity of the host's immune system so as to prevent pathogen colonization 肠道菌群与宿主和谐共存,参与营养物质的消化吸收,也有助于维持宿主免疫系统的完整性,防止病原体定植[ 1 ]. Additionally, intestinal flora consists of various bacteria in low or high abundance, which co-evolve with the host. While the host provides nutrients and a suitable survival place for the intestinal flora, the intestinal flora assists the host in absorbing nutrients, such as vitamins and short-chain fatty acids, in a more efficient manner in order to drive growth processes and to support the functions of the intestinal system and the immune system 。此外,肠道菌群由低或高丰度的各种细菌组成,它们与宿主共同进化。在宿主为肠道菌群提供营养和合适的生存场所的同时,肠道菌群帮助宿主以更有效的方式吸收维生素和短链脂肪酸等营养物质,以驱动生长过程并支持肠道菌群的生长。肠道系统和免疫系统的功能[ 2 ]。
2. Architecture and Composition of the Intestinal Flora肠道菌群的结构和组成
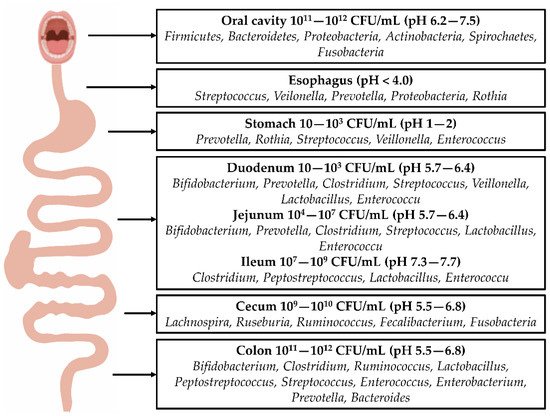
Figure 图1. Distribution of gastrointestinal bacteria: The distribution of intestinal bacteria in the digestive tract varies, and there are many types and quantities of bacteria in the oral cavity. Following their entry into the esophagus, the colonization of bacteria is reduced. Due to the secretion of gastric acid, most bacteria in the stomach cannot survive, allowing more acid-tolerant bacteria, such as Prevotella, Roche, and Streptococcus, to dominate. The number of bacteria increases from the duodenum to jejunum and ileum. These bacteria include Clostridium, Lactobacillus, and Enterococcus. A large number of bacteria exist in the colon, including Bifidobacterium, Clostridium, Ruminococcus, Bacteroides, Streptococcus, and Prevotella.
.胃肠道细菌分布:消化道肠道细菌的分布各不相同,口腔内的细菌种类和数量很多。进入食道后,细菌的定植减少。由于胃酸的分泌,胃中的大部分细菌无法存活,让更多的耐酸细菌,如普氏菌、罗氏菌、链球菌等占据主导地位。细菌的数量从十二指肠到空肠和回肠增加。这些细菌包括梭菌属、乳杆菌属和肠球菌属。结肠中存在大量细菌,包括双歧杆菌属、梭菌属、瘤胃球菌属、拟杆菌属、链球菌属和普氏菌属。Table 表1. Classification of bacterial species in the intestinal flora: According to classification by natural properties, intestinal bacteria can be divided into six categories for the most part: Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, Proteobacteria, Actinobacteria, Fusobacteria, and Verrucomicrobia. Each category includes bacterial species.
|
门 |
班级 |
命令 |
家庭 |
属 |
物种 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
厚壁菌门 |
梭状芽孢杆菌 |
梭菌目 |
梭菌科 |
粪杆菌 |
粪杆菌 |
|
梭菌属 |
梭菌属 |
||||
|
毛螺菌科 |
粪球菌 |
真球菌 |
|||
|
消化链球菌科 |
消化链球菌 |
厌氧消化链球菌 |
|||
|
韦荣菌科 |
韦永内拉 |
韦荣内拉小 |
|||
|
杆菌 |
乳酸杆菌目 |
乳酸杆菌科 |
乳酸杆菌 |
嗜酸乳杆菌 |
|
|
肠球菌科 |
肠球菌 |
粪肠球菌 |
|||
|
杆菌目 |
李斯特科 |
李斯特菌 |
李斯特菌 |
||
|
拟杆菌门 |
黄杆菌 |
黄杆菌目 |
黄杆菌科 |
黄杆菌属 |
|
|
拟杆菌门 |
拟杆菌目 |
拟杆菌科 |
拟杆菌属 |
脆弱拟杆菌 |
|
|
拟杆菌 |
|||||
|
化脓性拟杆菌 |
|||||
|
卟啉单胞菌科 |
卟啉单胞菌 |
||||
|
副拟杆菌属 |
拟杆菌属 |
||||
|
理科 |
阿里斯蒂佩斯 |
细金螟 |
|||
|
普氏菌科 |
普雷沃泰拉 |
普氏菌属 |
|||
|
变形菌门 |
伽玛变形菌 |
肠杆菌 |
肠杆菌科 |
大肠埃希菌 |
大肠杆菌 |
|
肠杆菌属 |
产肠杆菌 |
||||
|
三角洲变形菌 |
脱硫弧菌目 脱硫杆菌目 |
脱硫弧菌科 脱硫杆菌科 |
脱硫弧菌 |
肠脱硫弧菌 |
|
|
脱硫杆菌 |
|||||
|
ε变形菌 |
弯曲杆菌目 |
幽门螺杆菌科 |
幽门螺杆菌 |
幽门螺杆菌 |
|
|
放线菌 |
放线菌 |
放线菌目 |
放线菌科 |
放线杆菌 |
|
|
棒状杆菌科 |
棒状杆菌 |
谷氨酸棒杆菌 |
|||
|
双歧杆菌 |
双歧杆菌科 |
双歧杆菌 |
青春双歧杆菌 |
||
|
长双歧杆菌 |
|||||
|
梭杆菌 |
梭杆菌 |
梭杆菌目 |
梭杆菌科 |
梭杆菌属 |
具核梭杆菌 |
|
疣微菌 |
疣微菌 |
疣状微生物 |
疣微菌科 |
阿克曼西亚 |
阿克曼氏菌 |
|
Phylum |
Class |
Order |
Family |
Genus |
Species |
|
Firmicutes |
Clostridia |
Clostridiales |
Clostridiaceae |
Faecalibacterium |
Faecalibacterium prausnitzii |
|
Clostridium |
Clostridium spp. |
||||
|
Lachnospiraceae |
Coprocococcus |
Coprococcus eutactus |
|||
|
Peptostreptococcaceae |
Peptostreptococcus |
Peptostreptococcus anaerobius |
|||
|
Veillonellaceae |
Veillonella |
Veillonella parvula |
|||
|
Bacilli |
Lactobacillales |
Lactobacillaceae |
Lactobacillus |
Lactobacillus acidophilus |
|
|
Enterococcaceae |
Enterococcus |
Enterococcus faecalis |
|||
|
Bacillales |
Listeriaceae |
Listeria |
Listeria iuanuii |
||
|
Bacteroidetes |
Flavobacteria |
Flavobacteriales |
Flavobacteriaceae |
Flavobacterium |
|
|
Bacteroidetes |
Bacteroidales |
Bacteroidaceae |
Bacteroides |
Bacteroides fragilis |
|
|
Bacteroides caccae |
|||||
|
Bacteroides pyogenes |
|||||
|
Porphyromonadaceae |
Porphyromonas |
|
|||
|
Parabacteroides |
Parabacteroides distasonis |
||||
|
Rikenellaceae |
Alistipes |
Alistipes finegoldii |
|||
|
Prevotellaceae |
Prevotella |
Prevotella spp. |
|||
|
Proteobacteria |
Gamma proteobacteria |
Enterobacteriales |
Enterobacteriaceae |
Escherichia |
Escherichia coli |
|
Enterobacter |
Enterobacter areogenes |
||||
|
Delta proteobacteria |
Desulfovibrionales Desulfobacterales |
Desulfovibrionaceae Desulfobacteraceae |
Desulfovibrio |
Desulfovibrio intestinalis |
|
|
Desulfobacter |
|
||||
|
Epsilon proteobacteria |
Campylobacterales |
Helicobacteraceae |
Helicobacter |
Helicobacter pylori |
|
|
Actinobacteria |
Actinobacteria |
Actinomycetales |
Actinomycetaceae |
Actinobaculum |
|
|
Corynebacteriaceae |
Corynebacterium |
Corynebacterium glutamicum |
|||
|
Bifidobacteriales |
Bifidobacteriaceae |
Bifidobacterium |
Bifidobacterium adolescentis |
||
|
Bifidobacterium longum |
|||||
|
Fusobacteria |
Fusobacteria |
Fusobacteriales |
Fusobacteriaceae |
Fusobacterium |
Fusobacterium nucleatum |
|
Verrucomicrobia |
Verrucomicrobiae |
Verrucomicrobiales |
Verrucomicrobiaceae |
Akkermansia |
Akkermansia muciniphila |
References
- Albhaisi, S.A.M.; Bajaj, J.S.; Sanyal, A.J. Role of gut microbiota in liver disease. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2020, 318, G84–G98.
- Shi, N.; Li, N.; Duan, X.; Niu, H. Interaction between the gut microbiome and mucosal immune system. Mil. Med. Res. 2017, 4, 14.
- Milani, C.; Ferrario, C.; Turroni, F.; Duranti, S.; Mangifesta, M.; van Sinderen, D.; Ventura, M. The human gut microbiota and its interactive connections to diet. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2016, 29, 539–546.
- Tanaka, M.; Sanefuji, M.; Morokuma, S.; Yoden, M.; Momoda, R.; Sonomoto, K.; Ogawa, M.; Kato, K.; Nakayama, J. The association between gut microbiota development and maturation of intestinal bile acid metabolism in the first 3 y of healthy Japanese infants. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 205–216.
- Adlerberth, I.; Wold, A.E. Establishment of the gut microbiota in Western infants. Acta Paediatr. 2009, 98, 229–238.
- Durack, J.; Lynch, S.V. The gut microbiome: Relationships with disease and opportunities for therapy. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 216, 20–40.
- Hollister, E.B.; Riehle, K.; Luna, R.A.; Weidler, E.M.; Rubio-Gonzales, M.; Mistretta, T.A.; Raza, S.; Doddapaneni, H.V.; Metcalf, G.A.; Muzny, D.M.; et al. Structure and function of the healthy pre-adolescent pediatric gut microbiome. Microbiome 2015, 3, 36.
- Adak, A.; Khan, M.R. An insight into gut microbiota and its functionalities. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 473–493.
- Gomaa, E.Z. Human gut microbiota/microbiome in health and diseases: A review. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2020, 113, 2019–2040.
- Gonzalez Olmo, B.M.; Butler, M.J.; Barrientos, R.M. Evolution of the Human Diet and Its Impact on Gut Microbiota, Immune Responses, and Brain Health. Nutrients 2021, 13, 196.
- Dewhirst, F.E.; Chen, T.; Izard, J.; Paster, B.J.; Tanner, A.C.; Yu, W.H.; Lakshmanan, A.; Wade, W.G. The human oral microbiome. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 5002–5017.
- Wade, W.G. The oral microbiome in health and disease. Pharmacol. Res. 2013, 69, 137–143.
- Martinez-Guryn, K.; Leone, V.; Chang, E.B. Regional Diversity of the Gastrointestinal Microbiome. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 26, 314–324.
- Pei, Z.; Bini, E.J.; Yang, L.; Zhou, M.; Francois, F.; Blaser, M.J. Bacterial biota in the human distal esophagus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 4250–4255.
- Jandhyala, S.M.; Talukdar, R.; Subramanyam, C.; Vuyyuru, H.; Sasikala, M.; Nageshwar Reddy, D. Role of the normal gut microbiota. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 8787–8803.
- Nardone, G.; Compare, D. The human gastric microbiota: Is it time to rethink the pathogenesis of stomach diseases? United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2015, 3, 255–260.
- O’Hara, A.M.; Shanahan, F. The gut flora as a forgotten organ. EMBO Rep. 2006, 7, 688–693.
- Weaver, K.E. Enterococcal Genetics. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7, 7.2.11.
- Ma, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, P.; Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Tang, Z.; Wang, T.; Luo, L.; Wang, C.; Wang, T.; et al. Research progress in the relationship between type 2 diabetes mellitus and intestinal flora. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 117, 109138.
- Krawczyk, B.; Wityk, P.; Galecka, M.; Michalik, M. The Many Faces of Enterococcus spp.-Commensal, Probiotic and Opportunistic Pathogen. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1900.
- Murphy, E.C.; Frick, I.M. Gram-positive anaerobic cocci—Commensals and opportunistic pathogens. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 520–553.
- Martin, R.M.; Bachman, M.A. Colonization, Infection, and the Accessory Genome of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 4.
