Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Ali Rezaei-Matehkolaei and Version 2 by Rita Xu.
Trichophyton (T.) indotineae
is a newly identified dermatophyte species that has been found in a near-epidemic form on the Indian subcontinent. There is evidence of its spread from the Indian subcontinent to a number of countries worldwide. The fungus is identical to genotype VIII within the
T. mentagrophytes/T. interdigitale
species complex, which was described in 2019 by sequencing the Internal Transcribed Spacer (ITS) region of ribosomal DNA of the dermatophyte.
- dermatophytoses
- tinea corporis
1. Introduction
There is an ongoing epidemic of dermatophytosis in India and other neighboring countries in the subcontinent. The incriminated fungus is predominantly transmitted from person to person and often leads to refractory dermatophytosis. The causative dermatophyte has replaced the anthropophilic Trichophyton (T.) rubrum, the erstwhile predominant dermatophyte not only responsible for tinea pedis and onychomycosis, but also for dermatophytosis involving the whole body, worldwide—including India over the past few decades [1][2][3][1,2,3]. The newly emerged fungus—T. mentagrophytes genotype VIII, now called T. indotineae—often causes inflammatory and pruritic forms of difficult-to-treat tinea cruris, tinea corporis, and tinea faciei (Figure 1) [4]. As a result of globalization, this new emerging pathogen has been isolated in many countries outside Asia. Infections caused by the predominantly terbinafine-resistant dermatophytes—most prominently T. indotineae—are now found worldwide. T. indotineae appears to be spreading towards Europe, with notable presence in countries including United Arab Emirates, Oman, Bahrain, [5] and Iran [6]. Within Europe, the majority of non-Indian patients with tinea caused by this species have been reported in Germany (Figure 2) [7]. Furthermore, dermatophytoses due to T. indotineae has been described in France [8][9][8,9], Belgium [10], Switzerland [11], Greece [12], Denmark [13], China, Australia, Canada [14][15][14,15], and recently, in Vietnam [16].
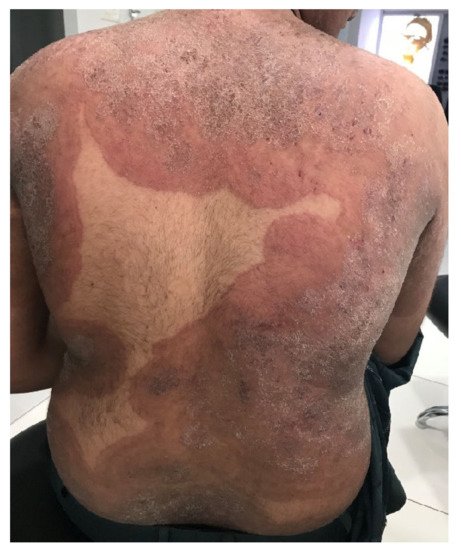
Figure 1. Tinea corporis generalisata in an Indian patient. The itchy erythematosquamous plaques converge over a large area and are sharply limited to the unaffected skin of the environment. Differential diagnosis includes psoriasis vulgaris, microbial eczema, or seborrheic eczema. The diagnosis can be confirmed by detection of the dermatophyte Trichophyton mentagrophytes genotype VIII or Trichophyton indotineae from skin scales. (Dr Bhavesh Devani, Drashti Skin & Eye Care Hospital-Cosmetic Laser & Hair Care Center, Rajkot, Gujarat, India).
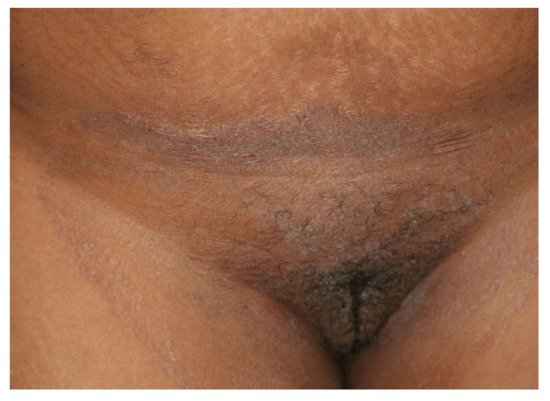
Figure 2. Tinea cruris and tinea genitalis in a 24-year-old patient by Trichophyton indotineae. (Dr. Lars Köhler, dermatologist, Mainz, Germany).
2. Pathogen Change from Trichophyton rubrum to Trichophyton mentagrophytes
Epidemiological studies in India have shown a trend towards an increased occurrence of T. mentagrophytes [17]. T. mentagrophytes surprisingly turned out to be the most common dermatophyte with prevalence of up to 75.9 to 77.5% [18], followed by T. rubrum but sometimes also by other Trichophyton species. At the same time, parallel to the emergence of morphologically new, therapy-refractory forms of tinea in India, a pathogen change from T. rubrum to T. mentagrophytes has evidently taken place. This dermatophyte prevails against the pathogens previously found in India—primarily T. rubrum—and largely displaces them as the cause of tinea cruris, tinea corporis, and tinea faciei [19].
In theour own multicenter experience on tinea cruris, tinea corporis, and tinea faciei in India, T. mentagrophytes was detectable in 138 (92.62%) of all culture-positive skin samples. T. rubrum, however, was isolated in only 11 (7.38%) samples [20]. Similar results were obtained with a PCR-ELISA, where 162 of 201 samples (80.56%) were dermatophyte-positive. Of these, 151 (93.21%) were identified as T. mentagrophytes and 11 (6.79%) as T. rubrum. Both old and newer studies from India still report a mix of Trichophyton species associated with this outbreak. This includes a higher proportion of T. rubrum cases than in theour series. It is possible that these other reports include misidentifications due to morphological identification of dermatophytes. SOur studies were based on molecular identification using sequencing of the DNA of all dermatophyte strains isolated.
3. Trichophyton mentagrophytes Genotype VIII
Until 2007, T. mentagrophytes was essentially a morphologically defined species that included a large number of subtypes or variants [21]. Those included zoophilic variants like T. mentagrophytes variatio (var.) granulosum (from rodents, e.g., mice, rats, guinea pigs, hamsters, or from lagomorphs, e.g., rabbits), var. asteroides (from rodents), var. erinacei (from hedgehogs), and var. quinckeanum (from camels and mice), which contrasted with anthropophilic variants like T. mentagrophytes var. interdigitale, var. goetzii (synonym T. krajdenii), and var. nodulare. The first revision of the taxonomy and classification of dermatophytes in 2008 [22] included genetic characteristics and simplified the nomenclature. T. mentagrophytes var. granulosum, var. asteroides, var. interdigitale, var. goetzii, and var. nodulare, which showed no or only single polymorphisms in the used genetic marker (ITS region), were assigned to the species T. interdigitale. The differences related to the ecological niche have been neglected. T. mentagrophytes (sensu stricto), on the other hand, included only the former var. quinckeanum from 2008 onwards (formerly, also known as Trichophyton sarkisovii Ivanova & Polyakov). T. erinacei was also classified as a separate species based on the results.
The nomenclature of dermatophytes was revised yet again in 2017, on the basis of extended polyphasic investigations (morphology, multiple genetic markers, physiology, ecological niche, propagation form) and especially via the use of several genetic markers, which demonstrated a separation of zoophilic and anthropophilic strains within T. interdigitale. Furthermore, the taxonomy at the genus level was also clarified. This group of dermatophytes is currently divided into seven distinct genera and at least 56 old and new species [23]. The ITS region of the rDNA has established itself as the decisive criterion for identification, for which single nucleotide polymorphisms are crucial for classification at the species level.
As of 2017, four species, anthropophilic T. interdigitale and zoophilic T. mentagrophytes, T. erinacei, and T. quinckeanum, have evolved from the former variants listed above [24].
Both the variants and the species have always been difficult to identify solely on the basis of morphological characteristics [25]. The inclusion of ecological and physiological characteristics appears essential for their identification. Fortunately, with molecular methods, such as PCR-based methods, rwesearchers now have a tool at hand that allows for clear differentiation. Sequencing of the Internal Transcribed Spacer (ITS) region of the rDNA also identified the new dermatophyte, first isolated in India, as ITS genotype VIII of T. mentagrophytes (Figure 3).
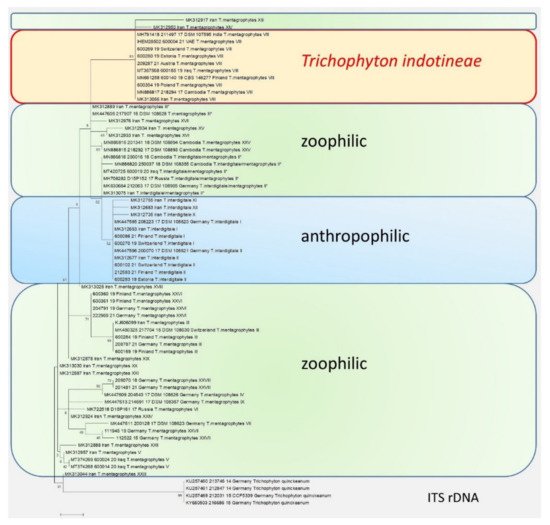
Figure 3. The phylogenetic analysis of the T. mentagrophytes/T. interdigitale complex based on the sequencing of the ITS regions of the rDNA. The calculations are based on the maximum likelihood method and the Tamura–Nei model from [26]. The phylogenetic family tree shows the distinction between the previously known genotypes of T. interdigitale and T. mentagrophytes, based on the sequencing of the ITS regions of rDNA genes. Genotypes I and II of the anthropophilic species T. interdigitale are found in the upper part of the dendrogram. Within the species T. mentagrophytes there are a total of 11 different genotypes—III, III*, IV, V, VII, IX, XXV, XXVI, XXVII, and XXVIII—including T. mentagrophytes ITS VIII (T. indotineae). The so-called mixed type or intermediate genotype (II*) is located between the clusters of T. interdigitale and T. mentagrophytes. The phylogenetic family tree was rooted with Trichophyton quinckeanum. Labeling after transmission.
