Human–robot interaction (HRI) is a broad research topic, which is defined as understanding, designing, developing, and evaluating the robotic system to be used with or by humans.
- human–robot interaction
- robot control
- variable admittance control
- co-manipulation tasks
- performance's comparison
- methods
1. Introduction
2. Compliance Control (Impedance/Admittance)
|
Parameter |
Compliance Control |
|
|---|---|---|
Control |
1- It is the impedance control based on position [13]. 2- The position or velocity controller is used to control the robot and the desired compliant behavior is understood by the outer control loop. |
1- The force-based impedance control is used. 2- It is not only the controlled manipulator is required, but also the controller itself should have the impedance causality. |
|
Representation |
|
|
|
Schemes of Control |
Work Space |
Measured Variables |
Appropriate Applied Situations |
Control Aims |
|
Admittance Controller |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Position Control | ||||
Impedance Controller | ||||
Task space |
Position |
Free motion |
Desired position |
|
|
Force Control |
Task space |
Contact Force |
Constrained motion |
Desired contact force |
|
Hybrid Control |
Position subspace |
Position |
All motion kinds |
Desired position |
|
Force subspace |
Contact Force |
Desired contact force |
||
|
Impedance/ Admittance Control |
Task space |
Position, Contact Force |
All motion kinds |
Impedance/ Admittance |
|
Use |
It is used with HRI in which there is no interaction between the robot and the stiff environment. |
The main aim of the methodology of impedance control is modulating the manipulator’s mechanical impedance [6]. |
||
|
Inputs and Outputs |
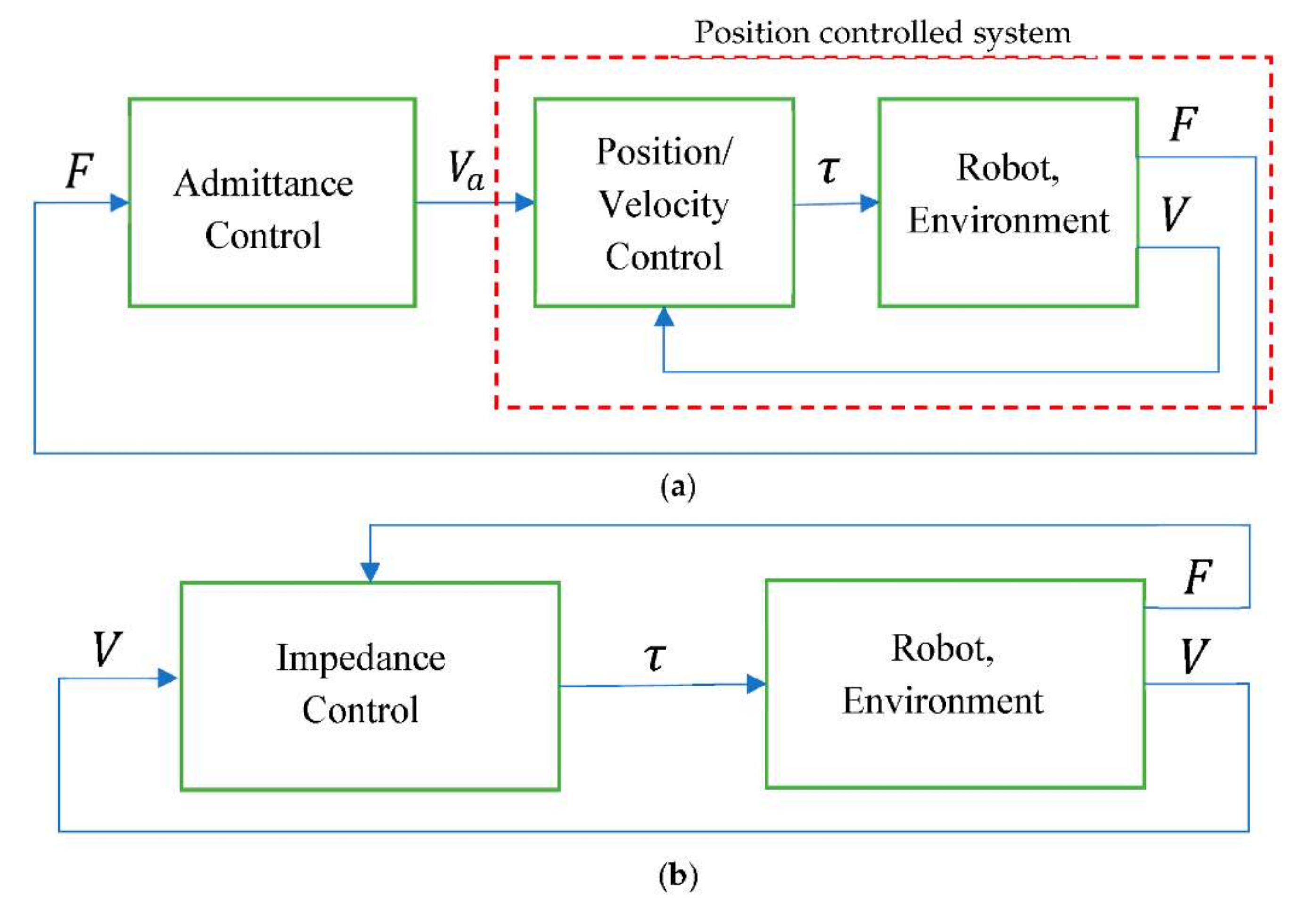
It maps the applied forces into robot motion, as shown in Figure 1a. |
The motion is the input, whereas the output is the force as shown in Figure 1b [8][9]. |
||
|
Rendering |
1- It can render only the virtual stiff surfaces, whereas it cannot render the low inertia. 2- It is negatively affected during the dynamic interaction with the real stiff surfaces (constrained motion) [10][11][12]. |
1- It can render low inertia, whereas it cannot render the virtual stiff surfaces. 2- It is negatively affected during the dynamic interaction with the low inertia (free motion) [12]. |


