The digital polymerase chain reaction (dPCR) is considered to be the third-generation polymerase chain reaction (PCR), as it yields direct, absolute and precise measures of target sequences. dPCR has proven particularly useful for the accurate detection and quantification of low-abundance nucleic acids, highlighting its advantages in cancer diagnosis and in predicting recurrence and monitoring minimal residual disease, mostly coupled with next generation sequencing.
- digital PCR
- dPCR
- next-generation sequencing
- NGS
1. Introduction
2. dPCR for Detecting Somatic Mutations
dPCR has been applied for the detection of several somatic mutations, both for absolute allele quantification and for rare mutation detection (Figure 1). The most numerous studies in this regard have been conducted on Philadelphia negative (Ph-) chronic Myeloproliferative Neoplasms (MPNs), such as polycythemia vera (PV), essential thrombocythemia (ET) and myelofibrosis (MF). Ph- MPNs are associated with driver genes mutations, like JAK2 in nearly 90% of PV patients and in around 50% of all ET and MF patients [22][32], and CALR, present in about 20%–35% of patients affected by ET and primary MF [23][33]. Gene expression dysregulation due to chromosomal rearrangements has rarely been reported in Ph- MPNs [24][34]. The first report dates back to 2015, when Fontanelli et al. compared qPCR and ddPCR in detecting the JAK2V617F mutation, the major MPN diagnostic criterion [25][35]. They identified 225 MPN patients presenting the JAK2V617F mutation by conventional qPCR and 99 of these were evaluated also by ddPCR. The specificity was absolutely concordant between the two methods, but the sensitivity was half a log higher for ddPCR than qPCR [25][35]. Similar conclusions were obtained in other subsequent studies, allowing researchers to state that ddPCR is a very suitable, precise, and sensitive method for the quantification of the JAK2V617F mutation, allowing a sensitivity of 0.01%, equitable with that achieved by Kröger et al. with an ARMS qPCR in 2007 [22][26][27][28][32,36,37,38]. Moreover, Nystrand et al. explored the use of ddPCR to test if serum is a good material for the detection and quantification of the JAK2V617F mutation. At first, the JAK2 mutation was detected in peripheral blood (PB) samples of 47 patients, and afterwards, among these, 45 of 47 corresponding serum samples showed a very strong correlation between PB and serum. The overall detection sensitivity was 96% and the mutation was detected in all cases where the mutant allele load was above 1%. The observation of a significantly higher allele burden detected in serum compared to PB highlighted the point that ddPCR could be a reliable method for detecting the JAK2V617F mutation also in serum [29][39].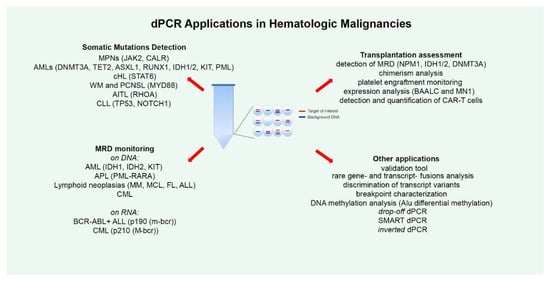
3. dPCR for MRD Monitoring
MRD is the strongest prognostic factor in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL), able to predict response to treatment and risk of relapse [30][107]. However, to date, only few studies have explored the utility of dPCR application in ALL MRD assessment. The reasons for this paucity could lie in the assumption that qPCR is a consolidated tool for MRD monitoring, despite the demonstration of a superior sensitivity of dPCR. In fact, qPCR is not always able to precisely define the amount of residual disease, frequently classifying samples with a very low MRD level as “positive not-quantifiable” (PNQ), a definition that is poorly interpretable. Indeed, another important limitation of qPCR is the need for a standard curve based on diagnostic DNA. In 2016, Della Starza and colleagues compared the two quantification techniques in the analysis of 50 ALL cases, reporting a sensitivity and accuracy for ddPCR that was at least comparable to those of qPCR [31][108]. Subsequently, in 2019, the same research group focused attention on FU adult ALL samples with a very low disease load (qPCR MRD levels ≤10−4), using ddPCR and NGS for analyzing immunoglobulin/T-cell receptor gene rearrangements as molecular markers [32][109]. This comparison showed a concordance rate of 57% (13/23) for qPCR/ddPCR and 52% (12/23) for qPCR/NGS; indeed, ddPCR and NGS also identified positivity in samples with a very low disease burden, yielding concordant MRD results in 87% of samples. Moreover, ddPCR/NGS analysis significantly reduced the number of PNQ samples compared to qPCR, increasing the number of quantifiable samples and helping to identify three relapses in patients that resulted PNQ/NEG through qPCR, as already previously reported [33][110]. These data demonstrated that in ALL, dPCR and NGS could more precisely stratify samples with very low MRD, for which qPCR is unable to detect or to quantify the disease burden [32][109]. As regards expression analysis, two studies employed dPCR for ALL MRD monitoring, analyzing Philadelphia-positive (Ph+) cases with the BCR-ABL1 p190 fusion transcript (m-bcr), which account for 20%–30% of adult ALLs [34][35][36][111,112,113]. In the study reported in 2014 by Iacobucci et al., 60 BCR-ABL1+ ALL samples in hematologic and cytogenetic remission were analyzed using the microfluidic dPCR approach (Biomark system from Fluidigm) [37][114]. They demonstrated that the assay was able to detect until a single copy of BCR-ABL1 transcript, with results at least comparable with those obtained with the conventional qPCR test. However, as compared to the dPCR technologies available today, this system was less sensitive and accurate, as only about 9000 partitions could be generated and the total assay volume was limited to 8 µl; indeed, for each sample the total amount of analyzed RNA was about 20ng [37][38][39][23,114,115]. More recently, Coccaro et al. conducted a second study, this time performing ddPCR to define its possible predictive molecular value during BCR-ABL1+ ALL FU [40][116]. With ddPCR, the evaluable sample volume is 20 ul, and partitioning reaches 20,000 droplets, allowing for higher accuracy and sensitivity [38][23]. FU samples showed that the p190 ddPCR assay was able to quantify very small disease levels by loading a high quantity of cDNA (up to 750ng per well) in different wells and combining the counts from multiple replicates. Of note, scaling up the ddPCR reaction to 750 ng of cDNA did not have a negative impact on the reaction performance, as data from serial dilutions performed loading such amount of cDNA showed remarkable linearity, reliability, and a precision of up to 0.001%. Comparison of the results obtained with conventional PCR and ddPCR in 117 FU samples showed discordant results in 27% cases, and further analysis through qPCR showed 19 ddPCR positive samples with a low tumor burden that was negative to PCR, failing to provide quantitative results in 63% of cases, classifying three samples as negative and nine as PNQ. This emphasizes the concept, that for qPCR, there is a gap between the sensitivity and the quantitative range. This is a critical limitation, as borderline cases that fall in the range of inadequate quantification cannot be classified though qPCR, whereas this can be carried out with ddPCR. The demonstrated higher sensitivity of the digital p190 assay as regards PCR and/or qPCR was, indeed, demonstrated to be able to predict molecular relapse, offering a timely advantage for patient management. In fact, it may allow a rapid change of therapy before hematological relapse [41][42][43][44][45][46][117,118,119,120,121,122] and thus improve the chances of preventing disease progression [40][116].
4. dPCR and Transplantation
dPCR has also been demonstrated to be useful for monitoring platelet engraftment after allo-HSCT. It is normally examined by daily platelet counts, but any necessary platelet transfusions performed in the patient can obscure the detection of platelet engraftment. Using ddPCR, Doescher at al. drew up an experimental assay based on mitochondrial DNA isolated from platelets in order to quantify circulating platelets derived from the stem cell graft, distinguishing them from transfused single-donor apheresis platelets [47][129]. Consecutive daily PB samples from day 7 to day 20 after transplantation were collected from 22 patients. The authors defined platelet engraftment as the third of at least three consecutive days of increasing levels exceeding 1000/mL of endogenous platelets. They assessed platelet counts according to the engraftment criteria of the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research (CIBMTR) [48][130] and the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT) [49][131]. When analyzing the results in detail, they found evidence that the moment of platelet engraftment based on the EBMT criteria corresponded to the ddPCR observation of transplantation-derived platelets, confirming that this ddPCR test is a sensitive method for monitoring platelet engraftment without interference due to platelet transfusions [47][129].
5. Other dPCR Applications and Evolution
dPCR is useful for discriminating transcript variants: some researchers employed the method in a study on CML to establish qPCR efficiency in identifying BCR-ABL1 transcript variants. Kjaer et al. analyzed 219 CML patients with either the e13a2 (n = 113) or e14a2 (n = 106) variant, enrolled at three Danish diagnostic centers, and the data obtained suggested that the qPCR assay may underestimate the e14a2 variant compared to the e13a2 variant, since the analysis of qPCR vs. ddPCR values revealed a significant average difference in the bias between the variants (e3a2/e14a2) at the three centers. These data were concomitantly confirmed by Bernardi et al. [50][51][171,172]. ddPCR was also employed as an alternative to FISH in CML for breakpoint characterization, noting, apart from improved specificity and sensitivity, the possibility of identifying variant translocation patterns, including derivative chromosome 9 deletions [52][173].
Another potential application of dPCR is DNA methylation analysis, which has been explored in several studies of malignancies [53][155]. In the hematologic field, Orsini et al. recently proposed a ddPCR method to investigate Alu differential methylation for the use in profiling patients affected by hematologic malignancies for diagnostic/prognostic purposes [54][174].
