2. Modulation of Autophagy in Cancer Cells by Polyphenols
Plant-derived polyphenols are divided into two groups, i.e., non-flavonoids and flavonoids (procyanidins)
[6][38]. Both polyphenolic groups exhibit antitumor activity through modulation of non-canonical, i.e.,
beclin-1-independent, and canonical,
beclin-dependent signaling pathways, as well as regulation of tumor suppressors
[6][38]. The strong antioxidant effect of polyphenols has a significant impact on the modulation of autophagic pathways so that the cell can dispose of defective protein aggregates. Moreover, plant polyphenols were shown to induce the death of neoplastic cells in some model systems
[6][38]. Below,
reswe
archers present a table showing the classification of polyphenols and dietary source (
Table 1).
Table 1.
The examples of dietary compounds rich in antioxidants.
| Dietary Source |
Classification of Polyphenols |
| Pomegranate [7][39] |
Tannins |
| Anthocyanins |
| Ellagic acid |
| Elagotannins such as punicalgin and munialin |
| Acerola [8][40] |
Chlorogenic acid |
| P-coumaric acid |
| Ferulic acid |
| Kaempferol |
| Luteolin |
| Routine |
| Apigenin |
| Anthocyanins (cyanidin, delphinidin 3β-D-glucoside, phloretin, peonidin) |
| Grapes [9][41] |
Resveratrol |
| Quercetin |
| Ellagic acid |
| Kaempferol |
| Green tea catechins [10][42] |
(−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) |
| (−)-epicatechin-3-gallate (ECG) |
| (−)-epigallocatechin (EGC) |
| (−)-epicatechin (EC) |
| Wine [11][43] |
Resveratrol |
| 5.2. Piceatannol |
| Quercetin |
| Kaempferol |
| Myricetin |
| (+)-catechin |
| (−)-EC |
| (−)-ECG |
| (−)-EGC |
Fruits, vegetables, and herbs are rich in flavonoids. In the
current
ry, researchers paper, we aim to review
ed the effects of chosen plant-derived polyphenols on autophagy.
2.1. EGCG
Green tea (
Camellia sinesis) polyphenols, and more specifically main catechin epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) (
Figure 1), have been subjected to a number of studies suggesting induction of autophagy under cell stress conditions in some cancer cell lines
[10][12][13][42,44,45]. EGCG was shown to induce autophagosome induction in human hepatoma (HepG2) cells as well as in bovine endothelial cells
[12][13][44,45]. The cytoprotective mechanism of EGCG was also confirmed in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress response in human embryonic kidney cell line (HEK293T, ATCC, and CRL-3216)
[14][15][16][46,47,48]. The experiment revealed a disturbance of the balance of mTOR-AMPK pathways via GADD34 due to the ER stress
[16][48]. Treatment of cells with EGCG, reduces the negative effect of GADD34 inhibition on the autophagy process
[16][48]. The reduction of the negative impact of GADD34 inhibition in relation to autophagy was achieved by treatment with siGADD34 or with guanabenz
[16][48]. In addition, the thapsigargin (TG) interferes with the accumulation of calcium in the ER
[16][48]. HEK293T cells were treated with rapamycin and EGCG in the experiment. In the study, EGCG induced a delay in apoptotic cell death, also in the absence of GADD34
[16][48]. This is indicative of a shift in the balance of mTOR-AMPK pathways in the event of ER stress due to EGCG treatment to promote cell survival. The results indicate that EGCG activates autophagy via the mTOR-AMPK pathway, but ULK1 is essential in this process
[16][48]. The research clearly indicates an important therapeutic role of EGCG, also in patients suffering from diseases associated with ER stress
[16][48].
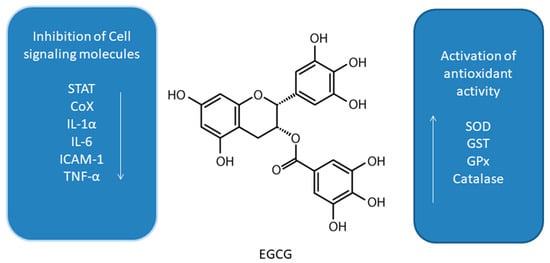
Figure 1. Effect of epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) on interplay between antioxidant activity and inhibition of cell signaling molecules
[10][11][12][13][14][15][16][17][18][19][20][21][22][23][24][25][42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57].
EGCG has anti-tumor activity through the regulation of autophagy via effects on reactive oxygen species (ROS) formation in many cancers. In lymphoma, EGCG inhibited the growth of BC-1 and BABL-1 cells, significantly inducing autophagy
[17][49]. Studies in primary exudative lymphoma (PEL), induced by expansion of cells infected with human herpesvirus 8 (HHV8), have shown induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest as a result of the treatment with EGCG
[17][49]. The results showed that EGCG increased Bax expression and
p53 activation, whereas previous studies showed chemical activation of
p53 to induce cell growth inhibition in the PEL model
[17][49]. The available data also indicate an intense induction of autophagy as well as apoptosis in primary glioblastoma cell cultures
[17][49]. The mechanisms were observed after the incubation with 500 μM EGCG. The authors claim that the use of even 100 nM EGCG activates endogenous mechanisms of protection of primary glioblastoma cell cultures and may have a chemopreventive effect
[17][49].
Green tea catechins play a significant role in supporting the treatment
[18][50] of breast
[19][51], pancreatic
[20][52], and lung cancers
[21][53]. For instance, NSCLC A549 cell line was tested to determine the effect of green tea extract on autophagy
[21][53]. The study used colorimetric assay for assessing cell metabolic activity MTT assay, cell death analysis by annexin V/PI assay, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), acridine orange staining (AO), and immunofluorescent labeling of LC3-I
[21][53]. The authors suggested that autophagy was caused by the induction of cytoprotective autophagy by flavonoids present in green tea extracts
[21][53]. Thus, dietary polyphenols alone may not have a significant effect on the growth of neoplastic cells, but will prove useful in combination therapy with cytostatic drugs to increase the effectiveness of oncological therapy
[21][53]. Activating mutations in the EGFR gene in both wild-type and the mutant forms T790M, L858R, and ELREA are often found in NSCLC patients
[22][54]. Experimental studies were carried out with the use of EGCG and EGFR-TKI (erlotinib)
[22][54]. Positive results of the experiment such as in clarifying the differences in the bonds of both wild-type EGFR and mutant types, indicate that the use of polyphenols in the diet may affect the growth of cancer cells, which at the same time is an important aspect as adjunctive therapy
[22][54].
As previously mentioned, EGFR plays a very important role in NSCLC
[23][55]. The main green tea polyphenol, EGCG, was shown to overcome resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors such as gefitinib in wild-type A549 cells and 16HBE cells—the human bronchial epithelial cell line
[23][55]. The results of the study showed the inhibition of ERK phosphorylation by combining gefitinib and EGCG through a reduction of p-ERK and p-MEK
[23][55].
A significant amount of research is required to confirm the significant role of EGCG in autophagy
[24][56]. One of the studies showed that the combination of a proteasome inhibitor bortezomib with EGCG enhances prostate cancer cell death mediated by an increase in ER stress
[24][56]. EGCG caused an increase in autophagy through antagonizing the toxicity of bortezomib
[24][56]. Subsequently, osteosarcoma stem cells were also investigated to develop the basis of anti-cancer drugs based on the results obtained with EGCG and doxyrubicin
[25][57]. The results showed that the use of EGCG significantly reduced the expression of osteosarcoma stem cell markers, and, in particular, SOX2OT V7, by reducing Notch3/DLL3 signaling
[25][57].
2.2. Oleuropein
It was also shown that leaves of European olive (
Olea europaea L.), rich in phenolic compounds such as verbascoside, apigenin-7-glucoside, luteolin-7-glucoside, and the main polyphenol—oleuropein (OL,
Figure 2), also have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-tumor activities
[26][58]. These features are associated with affecting proliferation and apoptosis by modulating expression of many signaling pathways. OL is a phenolic compound, chemically consisting of benzene-1,2-diol (hydroxytyrosol), 4-2-dyroxyethyl (polyphenols), and elenolic acid (secoiroid)
[26][58].
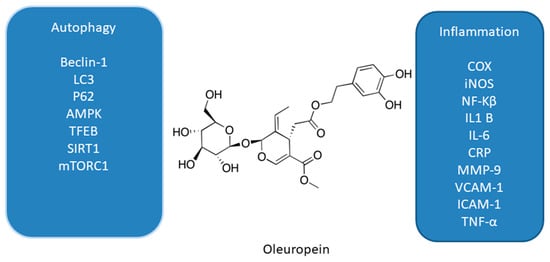
Figure 2. Effect of oleuropein on interplay between autophagy and inflammation [26][27][28][29][30][31][32][33]. Effect of oleuropein on interplay between autophagy and inflammation [58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65].
The suggested anti-tumor mechanism of OL via the induction of autophagy has been recently confirmed in the estrogen receptor (ER)-positive MCF-7 and T47D breast cancer cell lines
[27][28][59,60]. In addition to OL, hydroxytyrosol (HT) which is a metabolite of OL was also administered in the study
[28][60]. MCF-7 and T47D cells were treated with OL and HT along with 3-methyladenine, which is an inhibitor of autophagy, with hepatocyte growth factor, or rapamycin, which is an agonist of autophagy
[27][59]. The metastatic capacity and viability of the cells were assessed using the Western blot and transwell test. Depending on the dose, the viability of breast cancer cells decreased. Moreover, HT stronger than OL inhibited migration and invasion of triple-negative breast cancer cells by activating autophagy in the studied breast cancer cell lines
[27][59]. Furthermore, it was showed that by suppressing autophagy, metastases of these cells can be inhibited
[27][59].
OL was also used in a study determining the cellular and molecular activation mechanisms of autophagy
[28][29][30][31][60,61,62,63]. One of the studies was conducted in an animal model and in cultured SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. In the first study, the authors demonstrated a disruption of the autophagy cascade in SH-SY5Y cell line
[28][60]. In a following work, cells were treated with 50 µM OL for 24 h and then assessed for
beclin-1 and AMPK phosphorylation. OL increased AMPK phosphorylation, an early marker of autophagy
[29][61]. Moreover, OL use leads to mTOR inhibition through the induction of AMPK in the cortex of TgCRND8 mice
[29][61].
The induction of AMPK-dependent autophagy by OL was noted in an experiment in an animal model of a C57BL/6J mouse
[32][64]. Male and female mice were fed a high-fat and normal diet for eight weeks. Increased expression of
Beclin-1,
LC3B, and
p62/Sqstm1 genes was observed in the study. However, OL had no significant effect on the expression of the apoptotic proteins Bcl-2 and caspase 3 in this animal model
[32][64].
The antiproliferative effect of OL and the induction of autophagy were confirmed in cultures of p-53 negative and androgen insensitive PC-3 human prostate cancer cells
[33][65]. Moreover, the use of OL in the daily diet significantly reduced the dose of the cytotoxic doxorubicin—an anthracycline antibiotic with anti-cancer activity necessary to induce cell death
[33][65], The results indicate a significant intensification of autophagy induction by OL, which was confirmed by the immunoblot analysis for LC3. However, it has to be stressed that the complex processes of autophagy induction due to OL use requires more research
[33][65].
2.3. Pomegranate Extract and Punicalgin
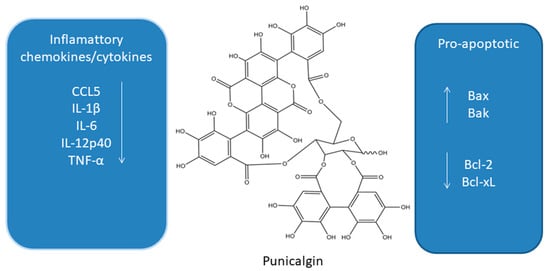
Punicalgin (PUN,
Figure 3) is a polyphenol obtained from pomegranate (
Punica granatum). Depending on the form of antioxidants, it mainly contains anthocyanins, gallic acid, ellagic acid, ellagic tannins, and polyphenols.
[34]. PUN is characterized by antioxidant activity and may inhibit lipoxygenases and cyclooxygenases. In addition, it has potential anti-cancer and chemopreventive effects. Both in vivo and in vitro studies confirm the effectiveness of PUN in the potential prevention of lung, breast, prostate, and colon cancers
[32][33][35][36][37][38][39][40][41][42][64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73].
Influence of punicalgin on apoptosis and inflammatory cytokines [64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76].
The chemopreventive effect of pomegranate polyphenols may be based on the action of a number of proteins and genes, which affect both the growth and progression of cancer
[33][65]. Interestingly, compared with the activity of red wine containing resveratrol and green tea infusion, the antioxidant capacity of pomegranate juice was three times higher
[30][62].
Glioblastoma is one of the most common brain tumors. Unfortunately, the prognosis for this type of cancer remains poor, due to a poor response to medical treatment
[44][75]. Studies indicate that PUN at a concentration of 1–30 μg/ml induced cell death in U87MG glioma cell cultures
[44][75]. It was demonstrated that PUN induced apoptosis by activating the caspase-9/caspase-3 cascade and by cleaving ADP-ribose in the human glioma cell line. In addition, PUN increased autophagosome formation. Since PUN increased the phosphorylation of
p27 T198 and of AMP, it was suggested that cell death mediated by PUN occurs via the apoptotic and autophagy pathways
[44][75].
Pomegranate extract (PE) polyphenols show autophagy modulating effects in, inter alia, human syncytiotrophoblast and neuronal human neuroblastoma SY5Y cells
[45][76]. PE activates the upregulation of both lysosomal and autophagosomal compartments, as well as causing autophagosome replacement and induction of autophagosome formation
[45][76]. Importantly, TFEB activation is induced by the use of PE in a cytosolic Ca
2+-dependent manner, but has no effect on ERK1/2, AKT and mTOR calcineurin signaling. Moreover, PE stimulated PINK1-Parksi mitophagy during of mitochondrial stress
[45][76].
2.4. Apigenin—An Antioxidant from Acerola Fruit
Acerola (
Malpighia glabra) is also known as the Barbados Cherry
[8][40]. Its edible part are small red fruits with juicy flesh. Acerola is a rich source of vitamin C, beneficial to our health
[8][38][40,69]. Acerola, apart from vitamin C and bioflavonoids, also contains pantothenic acid (vitamin B5), magnesium, potassium, thiamine, niacin, riboflavin, and vitamin A
[8][46][40,77].
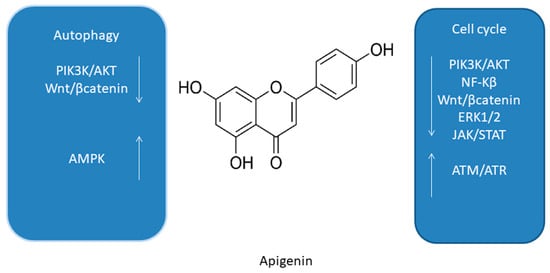
One of the major flavonoids contained in acerola is apigenin (AP,
Figure 4)
[35][66]. A number of studies, both in vitro and in vivo, confirmed the chemopreventive effect of AP
[47][78], which occurred due to the inhibition of inflammation and angiogenesis, a significant delay in cell proliferation, a cellular response to oxidative stress, and the induction of apoptosis and autophagy
[47][78].
Figure 4. Summary of molecular cell cycle and autophagy signaling pathways of apigenin [35][40][47][48][49]. Summary of molecular cell cycle and autophagy signaling pathways of apigenin [66,71,78,79,80].
In one of the studies the influence of AP on the modulation of AMPK in human keratinocytes (HaCaT cell line and primary normal human epidermal keratinocytes) was investigated
[48][79]. AP inhibited the mTOR signaling pathway by inducing autophagy via the activation of AMPK
[40][71]. In addition, results of another study suggest that AP causes autophagy in C6 glioma cells
[37][68]. Treatment of C6 cells resulted in reduced AMPK phosphorylation and, importantly, autophagy was AMPK/mTOR independent
[49][80]. Importantly, it is worth emphasizing that the difference in experimental studies using C6 cells and glioma cells differs in particular in the resistance of HaCaT cells to apoptosis, which can be explained by mutations within the pro-apoptotic
p53 protein alleles
[37][49][68,80].
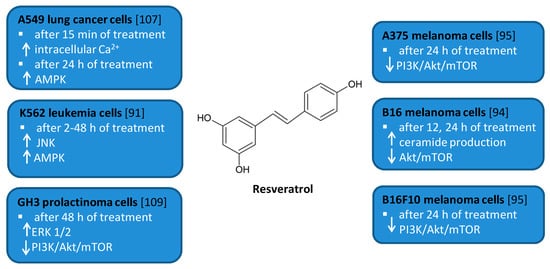
2.5. Resveratrol
Resveratrol (RSV) (trans-3,4′,5-trihydroxystilbene,
Figure 5) is a naturally occurring polyphenol found in berries, peanuts, grapes, and wine
[50][51][52][81,82,83]. It has attracted much attention due to the beneficial biological effects related to its anti-oxidant, anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, anti-diabetic, and cardioprotective activities
[53][54][55][56][57][84,85,86,87,88]. RSV has been shown to modulate autophagy in many cancer cell lines including leukemia, melanoma, glioma as well as renal, esophageal, liver, colon, prostate, breast, ovarian, oral, and lung cancer cell lines
[58][59][60][61][62][63][64][65][66][67][68][69][70][71][72][73][74][75][76][77][89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108].
Figure 5.
Cell signaling pathways triggered by resveratrol in selected cancer cell lines. ↑ activation/increase; ↓ inhibition/decrease.
Several in vitro studies indicated that RSV is able to induce autophagy that plays a pro-survival role and may serve as a resistance mechanism against apoptotic cell death
[63][78][94,109]. For example, RSV triggered protective autophagy rough the ceramide accumulation and inhibition of Akt/mTOR pathway in B16 melanoma cells
[63][94]. Inhibition of autophagy in B16 cells markedly increased RSV-induced apoptosis suggesting that RSV-induced autophagy plays a pro-survival role. In addition, the protective role of autophagy was demonstrated in resveratrol-treated U251 human glioma cells
[65][96]. Similar results concerning the pro-survival role of RSV-induced autophagy were observed in GH3 cell line derived from rat pituitary tumor cells
[78][109]. RSV led to the upregulation of ERK1/2 and the downregulation of PI3K/Akt and mTOR phosphorylation in prolactinoma GH3 cells. In some experimental models, RSV-induced autophagy contributed to the elimination of cancer cells
[60][64][76][91,95,107]. RSV triggered autophagic cell death in imatinib-sensitive and imatinib-resistant K562 chronic myelogenous leukemia cells
[60][91]. It led to the JNK-mediated p62/SQSTM1 expression and it activated AMPK. Thus, both JNK and AMPK pathways were involved in autophagic elimination in K562 cells. The activation of AMPK and JNK participated independently with the initiation and elongation steps of autophagy, respectively. RSV also suppressed the growth of A375 human melanoma cells and B16 F10 murine melanoma cells by promoting autophagy and inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
[64][95]. Moreover, it has also been found to induce autophagic cell death in A549 human lung adenocarcinoma cells via Ca
2+/AMPK-mTOR signaling pathway
[76][107].