Platycodon grandiflorus is a widely used edible, traditional Chinese medicinal herb. It is rich in saponins, flavonoids, phenolic acids, and other compounds. It contains a large number of fatty acids such as linoleic acid (up to 63.24%), a variety of amino acids, vitamins, and multiple essential trace elements. P. grandiflorus has several biological applications, such as in hypotension, lipid reduction, atherosclerosis, inflammation, relieving cough and phlegm, promoting cholic acid secretion, and as an antioxidant. Further, P. grandiflorus is often used Iin this entrye development of cold mixed vegetables, canned vegetables, preserved fruit, salted vegetables, and cosmetics in northeast China, South Korea, Japan, and Korea. In this paper, the active chemical components and the health benefits of P. grandiflorus have been reviewed, providing new ideas for the further development of nutraceutical products to prevent and manage chronic diseases.
- Platycodon grandiflorus
- medicinal food
- saponins
- human health
- applications
1. Introduction
P. grandiflorus has several biological applications, such as in hypotension, lipid reduction, atherosclerosis, inflammation, relieving cough and phlegm, promoting cholic acid secretion, and as an antioxidant. Further, P. grandiflorus is often used in the development of cold mixed vegetables, canned vegetables, preserved fruit, salted vegetables, and cosmetics in northeast China, South Korea, Japan, and Korea.
2. BioSactive Componentins of
2.1. Saponins
Saponin is a type of glycoside whose aglycone is a triterpenoid or spirosterol. Triterpenoid saponins are abundant in P. grandiflorus[1][2] [17,18]. They are the main active component characteristic to P. grandiflorus, and are olefin-type pentacyclic triene derivatives. According to the parent nucleus of the saponins, they can be divided into platycodic acid, platycogenic acid, and polygalacic acid[3][4][5] [19–21]. According to the Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China, the saponin content should not be less than 6.0% by gravimetric method in order to control the quality of medicinal materials[6] [22]. At present, 75 triterpenoid glycosides have been isolated and identified from P. grandiflorus. Among them, platycodin A is considered to be the main saponin of P. grandiflorus.
Studies have also confirmed that PD is the main active compound in the extract of P. grandiflorus[7] [23]. Guo[8] [24] determined that the PD was present in all parts of the P. grandiflorus herb. However, the content of PD in the upper portion of roots and leaves was slightly lower than that of the main root, and the content of PD in the fibrous roots and root bark of the P. grandiflorus was higher than that in the aerial parts. PD is both medicinal and nutritional and has high anti-tussive[9] [25], anti-obesity[10] [26], anti-fibrosis[11] [27], anti-inflammatory, and anti-tumor effects[12] [28]. In vitro experiments showed that platycodin D3 could eliminate phlegm and showed anti-inflammatory activity. In addition, platycodin D2, platycodin D3, and PD have significant antitumor activity[13][14][15] [29–31]. Platycodin A, platycodin C, deapioplatycodin D, and 16-oxo-PD have been shown to have anti-obesity activities[16][17][18][19] [32–35]. The saponins structures are shown in Figure 1.
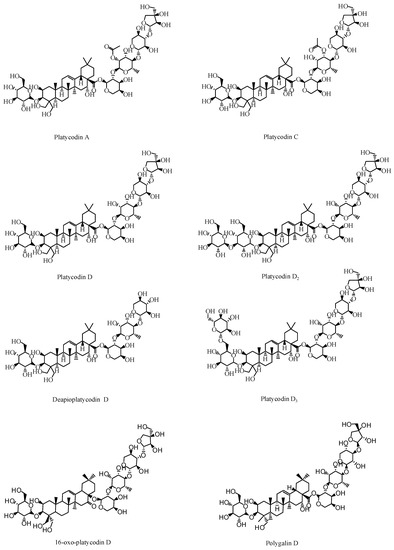
Figure 1. Active triterpenoid saponins in P. grandiflorus.
2.2. Flavonoids
Flavonoids
Flavonoids mainly exist in the upper portion of P. grandiflorus above the soil, mainly comprising of flavonoids, dihydroflavonoids, and flavonoid glycosides. At present, 11 flavonoids have been isolated and identified from P. grandiflorus[20] [36]. It has been shown that six different flavonoids were obtained from the seeds and the flowers of P. grandiflorus, while 3 compounds were isolated from the aboveground part of P. grandiflorus grown in Poland[21] [37]. Of these flavonoids, luteolin-7-O-glucoside and apigenin-7-O-glucoside exhibit strong antioxidant activity[21][22] [37,38]. The structures of the flavonoids are shown in Figure 2, and the other nine flavonoids isolated from P. grandiflorus are listed in Table 1.

Figure 2. Active flavonoids in P. grandiflorus.
Table 1. The other flavonoids components isolated from P. grandiflorus.
|
No. |
Name |
Ref. |
|
1 |
Platyconin |
[36] |
|
2 |
Apigenin |
[36] |
|
3 |
(2R,3R)-taxifolin |
[36] |
|
4 |
Luteolin |
[36] |
|
5 |
Quercetin-7-O-glucoside |
[36,38] |
|
6 |
Quercetin-7-O-rutinoside |
[36,38] |
|
7 |
Platycoside |
[36,39,40] |
|
8 |
Delphinidin-3-rutinoside-7-glucoside |
[36,41] |
|
9 |
Flavoplatycoside |
[36] |
|
No. |
Name |
Ref. |
|
1 |
Platyconin |
[20] |
|
2 |
Apigenin |
[20] |
|
3 |
(2R,3R)-taxifolin |
[20] |
|
4 |
Luteolin |
[20] |
|
5 |
Quercetin-7-O-glucoside |
|
|
6 |
Quercetin-7-O-rutinoside |
|
|
7 |
Platycoside |
|
|
8 |
Delphinidin-3-rutinoside-7-glucoside |
|
|
9 |
Flavoplatycoside |
[20] |
2.3. Other Components
Other Components
In addition to saponins and flavonoids, P. grandiflorus contains other compounds, such as phenolic acids, polyacetylene, sterols, and amino acids[24][25][26][27][28] [40–44]. Phenolic acids are abundant in the roots and aboveground parts of P. grandiflorus; 14 kinds of antioxidant phenolic compounds have been isolated from the P. grandiflorus extract. Five polyacetylene compounds have been obtained from P. grandiflorus, which is an important criterion for the classification of P. grandiflorus[29] [45]. Lobetyol has been found to have an anti-tumor effect.
Macromolecules have also been identified in P. grandiflorus. A study showed that P. grandiflorus contained 18 amino acids[16] [32]. Among these, gamma-aminobutyric acid is an essential neurotransmitter chemical in the brain’s energy metabolism. In addition, the root of P. grandiflorus contains fatty acids, which accounted for 88.28% of the total lipids[30] [46]. Inulin, grandoside, and polysaccharides have also been isolated from P. grandiflorus[31] [47]. Studies have shown that the polysaccharides of P. grandiflorus have strong antioxidant activity[32] [48]. Although the contents of bioactive components of P. grandiflorus were different, they all had high efficiency and low toxicity, which provided a scientific basis for characterizing its pharmacological activities. The structures of the other components are shown in Figure 3, and the other non-active components are listed in Table 2.
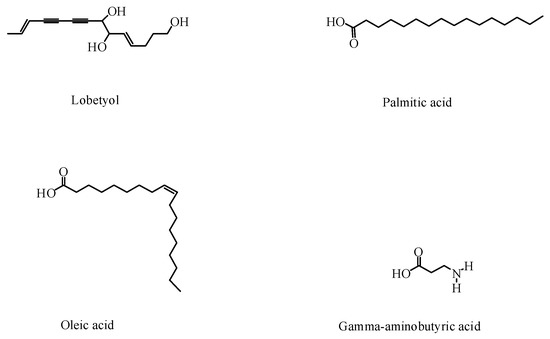
Figure 3. Other active components in P. grandiflorus.
Table 2. The others components isolated from P. grandiflorus.
|
Classes |
No. |
Compound Name |
Ref. |
|
Phenolic acids |
1 |
Caffeic acid |
[42] |
|
|
2 |
3,4-dimethoxycinnamic acid |
[42] |
|
|
3 |
Ferulic acid |
[42] |
|
|
4 |
Isoferulic acid |
[42] |
|
|
5 |
m-coumaric acid |
[42] |
|
|
6 |
p-coumaric acid |
[42] |
|
|
7 |
p-hydroxybenzoic acid |
[42] |
|
|
8 |
α-resorcylic acid |
[42] |
|
|
9 |
2,3-dihydroxybenzoic acid |
[42] |
|
|
10 |
2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzoic acid |
[42] |
|
|
11 |
Homovanillic acid |
[42] |
|
|
12 |
Chlorogenic acid |
[42] |
|
|
13 |
Iobetyol |
[43] |
|
|
14 |
Iobetyolin |
[43] |
|
Polyacetylene |
15 |
lobetyolinin |
[44] |
|
|
16 |
Lobetyolin |
[41] |
|
|
17 |
Platetyolin A |
[36,49] |
|
|
18 |
Platetyolin B |
[36,49] |
|
Sterols |
19 |
Betulin |
[41] |
|
|
20 |
β-sitosterol |
[41] |
|
|
21 |
δ-7-stigmastenone-3 |
[27] |
|
|
22 |
Spinasterol |
[36] |
|
|
23 |
α-spinasteryl-3-O-β-D-glucoside |
[36] |
|
Others |
24 |
Threonine |
[36] |
|
|
25 |
Valine |
[36] |
|
|
26 |
Phenylalanine |
[36] |
|
|
27 |
Methionine |
[36] |
|
|
28 |
Isoleucine |
[36] |
|
|
29 |
Leucine |
[36] |
|
|
30 |
Lysine |
[36] |
|
|
31 |
Inulin |
[36] |
|
|
32 |
Grandoside |
[36] |
|
Classes |
No. |
Compound Name |
Ref. |
|
Phenolic acids |
1 |
Caffeic acid |
[26] |
|
|
2 |
3,4-dimethoxycinnamic acid |
[26] |
|
|
3 |
Ferulic acid |
[26] |
|
|
4 |
Isoferulic acid |
[26] |
|
|
5 |
m-coumaric acid |
[26] |
|
|
6 |
p-coumaric acid |
[26] |
|
|
7 |
p-hydroxybenzoic acid |
[26] |
|
|
8 |
α-resorcylic acid |
[26] |
|
|
9 |
2,3-dihydroxybenzoic acid |
[26] |
|
|
10 |
2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzoic acid |
[26] |
|
|
11 |
Homovanillic acid |
[26] |
|
|
12 |
Chlorogenic acid |
[26] |
|
|
13 |
Iobetyol |
[27] |
|
|
14 |
Iobetyolin |
[27] |
|
Polyacetylene |
15 |
lobetyolinin |
[28] |
|
|
16 |
Lobetyolin |
[28] |
|
|
17 |
Platetyolin A |
|
|
|
18 |
Platetyolin B |
|
|
Sterols |
19 |
Betulin |
[28] |
|
|
20 |
β-sitosterol |
[28] |
|
|
21 |
δ-7-stigmastenone-3 |
[11] |
|
|
22 |
Spinasterol |
[20] |
|
|
23 |
α-spinasteryl-3-O-β-D-glucoside |
[20] |
|
Others |
24 |
Threonine |
[20] |
|
|
25 |
Valine |
[20] |
|
|
26 |
Phenylalanine |
[20] |
|
|
27 |
Methionine |
[20] |
|
|
28 |
Isoleucine |
[20] |
|
|
29 |
Leucine |
[20] |
|
|
30 |
Lysine |
[20] |
|
|
31 |
Inulin |
[20] |
|
|
32 |
Grandoside |
[20] |
