Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Suyash Niraula and Version 2 by Camila Xu.
Bones are categorized into two major groups, namely cortical bones, and cancellous bones. Cortical bones are compact bones and are responsible for providing mechanical strength, structural rigidity, and movement. They account for 80% of the mass of the bones in the human body. Cancellous bones, also known as trabecular bones, are soft, spongy bones and are responsible for providing structural support to the cortical bones, flexibility, and reduction in weight.
- additive manufacturing
- porous Ti64
- bone implants
- fatigue behavior
1. Bone Structure
Bones are categorized into two major groups, namely cortical bones, and cancellous bones. Cortical bones are compact bones and are responsible for providing mechanical strength, structural rigidity, and movement. They account for 80% of the mass of the bones in the human body. Cancellous bones, also known as trabecular bones, are soft, spongy bones and are responsible for providing structural support to the cortical bones, flexibility, and reduction in weight. Most of the active functions including blood cell production and ion exchange take place in the trabecular bones. They account for roughly 20% of the total mass of the skeleton. From the porous structure perspective, cancellous bone has porosities between 50% and 90%, whereas cortical bone has a porosity less than 10% [1].
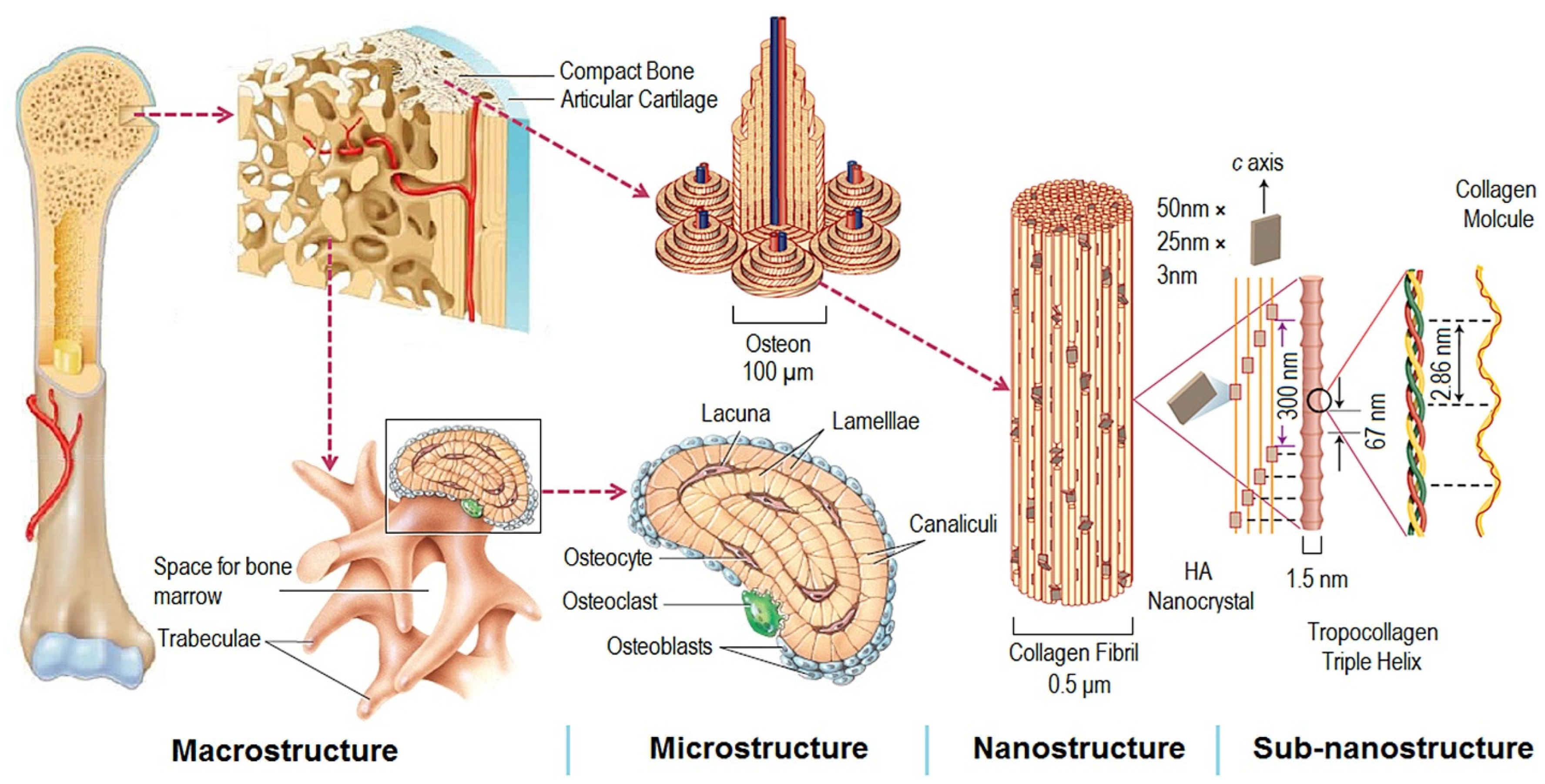
The natural bone acts as a heterogeneous and anisotropic nanocomposite [2], of which the principal components are organized hierarchically into several structural levels, from macro to the nanometer scale as shown in
Bones are categorized into two major groups, namely cortical bones, and cancellous bones. Cortical bones are compact bones and are responsible for providing mechanical strength, structural rigidity, and movement. They account for 80% of the mass of the bones in the human body. Cancellous bones, also known as trabecular bones, are soft, spongy bones and are responsible for providing structural support to the cortical bones, flexibility, and reduction in weight. Most of the active functions including blood cell production and ion exchange take place in the trabecular bones. They account for roughly 20% of the total mass of the skeleton. From the porous structure perspective, cancellous bone has porosities between 50% and 90%, whereas cortical bone has a porosity less than 10% [41].
The natural bone acts as a heterogeneous and anisotropic nanocomposite [55], of which the principal components are organized hierarchically into several structural levels, from macro to the nanometer scale as shown in
Figure 1.

.
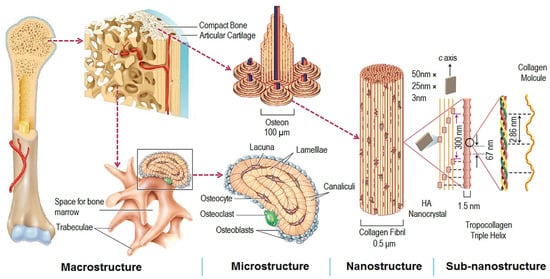

Figure 1. Structural levels of bone from macro to subnanometer scale. Reprinted with permission from ref. [3]. 2016, Elsevier Ltd.
Macroscale arrangements of the bone involve both compact/cortical bone at the surface and spongy/trabecular bone (foam-like material with ~100 µm thick struts) in the interior. Compact bone is composed of Osteons and Haversian canals, which surround blood vessels. Osteons have a lamellar structure, with individual lamella consisting of fibers arranged in geometrical patterns. The fibers comprise several mineralized collagen fibrils, composed of collagen protein molecules (tropocollagen) formed from three chains of amino acids and nanocrystals of hydroxyapatite (HA) and linked by organic phase to form fibril arrays [2].
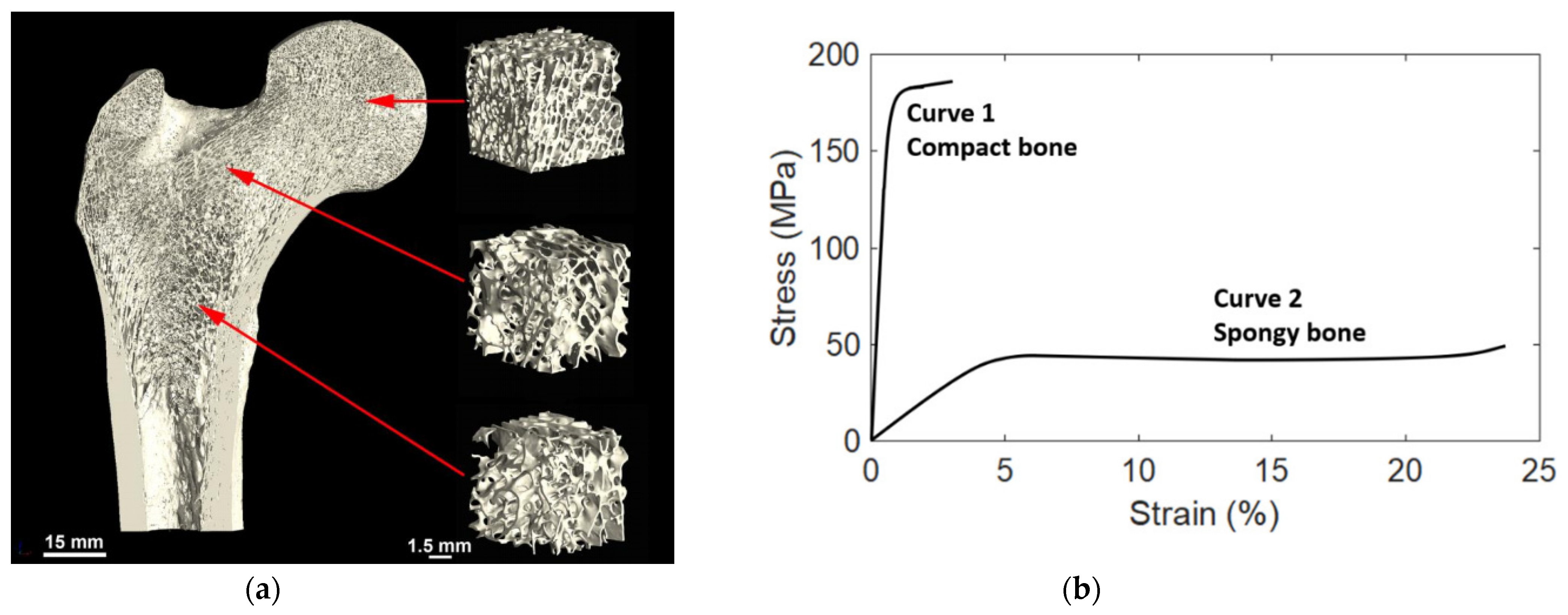
The cortical bone thickness and the density and pore structure of the trabecular bone may vary significantly by location in the body and even within one bone, depending on the local requirements. Near the joints the trabecular bone is denser due to varying mechanical load requirements (strength and angles of loading), while in the central part of the bone there is less dense and less isotropic trabecular bone, which is more directionally aligned as shown in
Structural levels of bone from macro to subnanometer scale. Reprinted with permission from ref. [17]. 2016, Elsevier Ltd.
Macroscale arrangements of the bone involve both compact/cortical bone at the surface and spongy/trabecular bone (foam-like material with ~100 µm thick struts) in the interior. Compact bone is composed of Osteons and Haversian canals, which surround blood vessels. Osteons have a lamellar structure, with individual lamella consisting of fibers arranged in geometrical patterns. The fibers comprise several mineralized collagen fibrils, composed of collagen protein molecules (tropocollagen) formed from three chains of amino acids and nanocrystals of hydroxyapatite (HA) and linked by organic phase to form fibril arrays [55].
The cortical bone thickness and the density and pore structure of the trabecular bone may vary significantly by location in the body and even within one bone, depending on the local requirements. Near the joints the trabecular bone is denser due to varying mechanical load requirements (strength and angles of loading), while in the central part of the bone there is less dense and less isotropic trabecular bone, which is more directionally aligned as shown in
Figure 2a.

a.
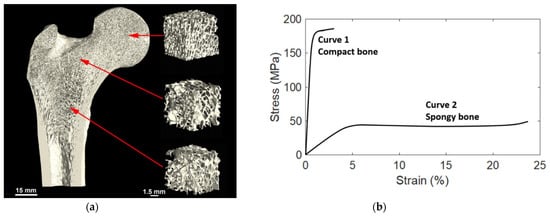

Figure 2.
(
a) Variation in the trabecular bone structure by location, in this example from the human femur of a 26-year-old male. Reprinted with permission from ref. [4]. 2019, Elsevier Inc. (
) Variation in the trabecular bone structure by location, in this example from the human femur of a 26-year-old male. Reprinted with permission from ref. [56]. 2019, Elsevier Inc. (
b) Typical stress-strain curves of compact (Cortical) and spongy (Trabecular) bones. Reprinted with permission from ref. [5]. 2021, MDPI.
2. Mechanical Properties
) Typical stress-strain curves of compact (Cortical) and spongy (Trabecular) bones. Reprinted with permission from ref. [57]. 2021, MDPI.
2. Mechanical Properties
Figure 2b shows a load-deformation curve for a specimen of hydrated bone loaded in tension [6]. The bone follows the normal load-deformation trend for that of metals. First, there is a rising part where the load is proportional to deformation. At the yield point, the situation changes, and the curve becomes much flatter. With a slight increase in load, there is a substantial increase in deformation. Then the specimen breaks. This load-deformation curve can be normalized and turned into a stress-strain curve. The total area under the curve is the amount of energy per unit volume that a material can absorb before rupturing, also known as the material toughness.
Cortical Bone: The Modulus of Elasticity of cortical bone is about 15 GPa. At the yield point, the stress is 120 MPa, and the strain is 0.008.
b shows a load-deformation curve for a specimen of hydrated bone loaded in tension [58]. The bone follows the normal load-deformation trend for that of metals. First, there is a rising part where the load is proportional to deformation. At the yield point, the situation changes, and the curve becomes much flatter. With a slight increase in load, there is a substantial increase in deformation. Then the specimen breaks. This load-deformation curve can be normalized and turned into a stress-strain curve. The total area under the curve is the amount of energy per unit volume that a material can absorb before rupturing, also known as the material toughness.
Cortical Bone: The Modulus of Elasticity of cortical bone is about 15 GPa. At the yield point, the stress is 120 MPa, and the strain is 0.008.
Table 1
gives some representative values of the mechanical properties of cortical bone loaded along the length of the bone. This is an approximation table, but gives some guidance as to the properties and their potential range.
Table 1. Some values of mechanical properties of cortical bone. Reprinted with permission from ref. [6]. 2008, Woodhead Publishing Limited.
Some values of mechanical properties of cortical bone. Reprinted with permission from ref. [58]. 2008, Woodhead Publishing Limited.
| Property | Upper Limit | Lower Limit | Modal Value |
|---|
| Young’s Modulus of Elasticity (E) | 45 GPa | 6 GPa | 15 GPa |
| Tensile Yield Stress | N/A | 10 MPa | 120 MPa |
| Tensile Strength | 300 MPa | 15 MPa | 150 MPa |
].
4. Hindrance for Bone Healing
A wide variety of factors can slow down the healing process of a fractured bone. Movement of fractured bone fragments and weight-bearing too soon delays bone formation. The implant must be securely fixed to the host bone such that osseointegration is not inhibited. The interactions between the implant and the proteinous monolayer create the basis for osseointegration and ossification (bone formation) and are crucial to the proper healing of the wound, and ultimately, successful implantation [60,61]. In addition, smoking, medical conditions, such as diabetes, hormone-related problems or vascular disease, some medications, such as corticosteroids and other immunosuppressants, severe and complicated fractures, old age, poor nutrition or impaired metabolism, and low levels of calcium and vitamin D all hinder bone healing.
5. Need for Porous Structure and Its Advantages
Implants are made from biomaterials and their alloys. These materials, compared to bone, have a very high modulus of elasticity. It is well known that the stress transfer between an implant and a bone is not homogeneous when Young’s moduli of the implant and the bone are different; this is defined as stress shielding. In such conditions, bone atrophy occurs and leads to the loosening of the implant and refracturing of the bone. Therefore, it is desirable if the stiffness (Young’s modulus) value is as close as possible to that of the bone [62].
Porosities in the bone implants have two (2) major advantages:
-
Provide space and 3D structure for bone ingrowth.
| Ultimate Tensile Strain |
| 0.12 |
| 0.002 |
| 0.03 |
| Compressive Strength | |||
| N/A | |||
| N/A | 250 MPa | ||
| Bending Strength | N/A | N/A | 250 MPa |
| Fatigue Life at 0–100 MPa Tension | N/A |
Cancellous Bone: Cancellous bone is soft bone. The bone does not form closed cells, so the bone, and the marrow, are always interconnected. The Young’s modulus of such bone is as low as 1.9 GPa and can go up to 6 GPa [58].
3. Bone Healing Mechanism
Most of the fractured bone goes through the same healing process or recovery mechanism. This holds true for the bone whether it has been operated on during the surgical procedure or fractured by being involved in an accident. Usually, the bone healing mechanism experiences an overlap of three stages, namely inflammation, bone production, and bone remodeling [59], as described below:
-
Inflammation is the first step of the healing mechanism, and this starts right after the bone breaks. After the bone fractures, the blood vessels’ connections in the bone are also ruptured and this results in bleeding into the fractured area. This process is called inflammation where the blood starts to clot in the fractured site and swelling is observed. Inflammation lasts for several days and thus provides the initial framework and stability to the fractured bone for developing new bone;
- The bone production step follows the inflammation step in the healing process. The clotted blood from inflammation is gradually replaced by the growth of soft callus cartilage and fibrous tissues. Eventually, when healing progresses, this soft callus cartilage is replaced with hard bone known as a hard callus. This bone is thus detectable by x-rays afterward;
| 200 |
| 1000 |
3. Bone Healing Mechanism
Most of the fractured bone goes through the same healing process or recovery mechanism. This holds true for the bone whether it has been operated on during the surgical procedure or fractured by being involved in an accident. Usually, the bone healing mechanism experiences an overlap of three stages, namely inflammation, bone production, and bone remodeling [7], as described below:- Bone remodeling is the final phase of the healing process and could last for weeks or several months. The hard callus bone continues to form and becomes compact, returns to its original shape and form, ruptured blood vessels grow, and blood circulation improves in the area. Sufficient healing of the bone after several weeks gradually remodels the bone for usual weight-bearing activities such as standing and walking, and it provides necessary support to the structure
- [8]. More importantly, the loading magnitude and loading frequency have significant effects on bone remodeling and thus have a major impact on the bone healing process [1].Bone remodeling is the final phase of the healing process and could last for weeks or several months. The hard callus bone continues to form and becomes compact, returns to its original shape and form, ruptured blood vessels grow, and blood circulation improves in the area. Sufficient healing of the bone after several weeks gradually remodels the bone for usual weight-bearing activities such as standing and walking, and it provides necessary support to the structure [60]. More importantly, the loading magnitude and loading frequency have significant effects on bone remodeling and thus have a major impact on the bone healing process [41].
4. Hindrance for Bone Healing
A wide variety of factors can slow down the healing process of a fractured bone. Movement of fractured bone fragments and weight-bearing too soon delays bone formation. The implant must be securely fixed to the host bone such that osseointegration is not inhibited. The interactions between the implant and the proteinous monolayer create the basis for osseointegration and ossification (bone formation) and are crucial to the proper healing of the wound, and ultimately, successful implantation [8][9]. In addition, smoking, medical conditions, such as diabetes, hormone-related problems or vascular disease, some medications, such as corticosteroids and other immunosuppressants, severe and complicated fractures, old age, poor nutrition or impaired metabolism, and low levels of calcium and vitamin D all hinder bone healing.5. Need for Porous Structure and Its Advantages
Implants are made from biomaterials and their alloys. These materials, compared to bone, have a very high modulus of elasticity. It is well known that the stress transfer between an implant and a bone is not homogeneous when Young’s moduli of the implant and the bone are different; this is defined as stress shielding. In such conditions, bone atrophy occurs and leads to the loosening of the implant and refracturing of the bone. Therefore, it is desirable if the stiffness (Young’s modulus) value is as close as possible to that of the bone [10]. Porosities in the bone implants have two (2) major advantages:In addition, the implant-bone healing process can be briefly summarized in the following five stages: (1) primary implant fixation; (2) blood-implant contact; (3) platelet activation and coagulation; (4) inflammation and angiogenesis; and (5) bone formation [61
Based on the literature reviewed in this study, the porosity ranging from 25% to 90% and pore size ranging from 200 µm to 1500 µm were found to be mostly used in the design of porous Ti64 implants. During the porous implant design, often there exists a trade-off between the porosity percentage and mechanical strength. An increase in mechanical interlock strength of a porous implant can be observed through osseointegration, however a design with porosity greater than 80% results in a decrease in both strength and bone ingrowth [64]. Proper tailoring of porosity percentage, porosity gradient and its direction, and transition region height are required such that the biomimetic implant design can be possible without compromising the mechanical properties requirements, especially porous implant strength.
The premise of bone ingrowth is that cells adhere to the surface of materials and migrate to the inner space, thus porosities play a vital role in bone tissue engineering as it facilitates the ingrowth of mineralized tissue into a porous network. It is also suitable for seeding cells, delivering drugs, capillary tissue action, and osteoprogenitor cell migration [48,65].
In this study, we have focused on Titanium alloy, namely Ti64. This is an alpha-beta titanium alloy, which has excellent corrosion resistance to chlorides, seawater, and sour and oxidizing acid media, and acts as an ideal candidate for orthopedic and dental implants [66]. The biocompatibility with living tissues and the high strength-to-weight ratio of Ti64 alloy make it an ideal candidate for bone implants. Furthermore, Ti64 shows good osseointegration property, which is defined as the functional bone adherence property where a new bone is laid down directly on the implant surface and helps the implant to exhibit mechanical stability [67,68]. More importantly, Ti64 alloy also has a low modulus of elasticity, which is roughly half that of steel and nickel alloys, making it more similar to bone in terms of mechanical properties [66]. Further, the bioinert and biocompatible nature of Ti64 with spontaneous formation of oxide layer ensures its stability in the body after implantation [69].
Titanium is generally non-magnetic in nature, generating insignificant forces in a strong magnetic field, and is considered safe to be present in clinical MRI systems. However, it has weak paramagnetic property and becomes magnetized within the MRI field resulting in either a loss of signal or distortion in the MRI image (known as susceptibility effect) due to changes in magnetic field from the presence of Ti64 implant [28,70]. This effect limits the use of MRI to visualize the tissue surrounding implants hindering future investigations in the region or diagnosis of post-operative complications. AM porous structures may be an upstream method for reducing susceptibility artifacts in Ti64 implants, helping in improving post-operative diagnosis capability [28].
