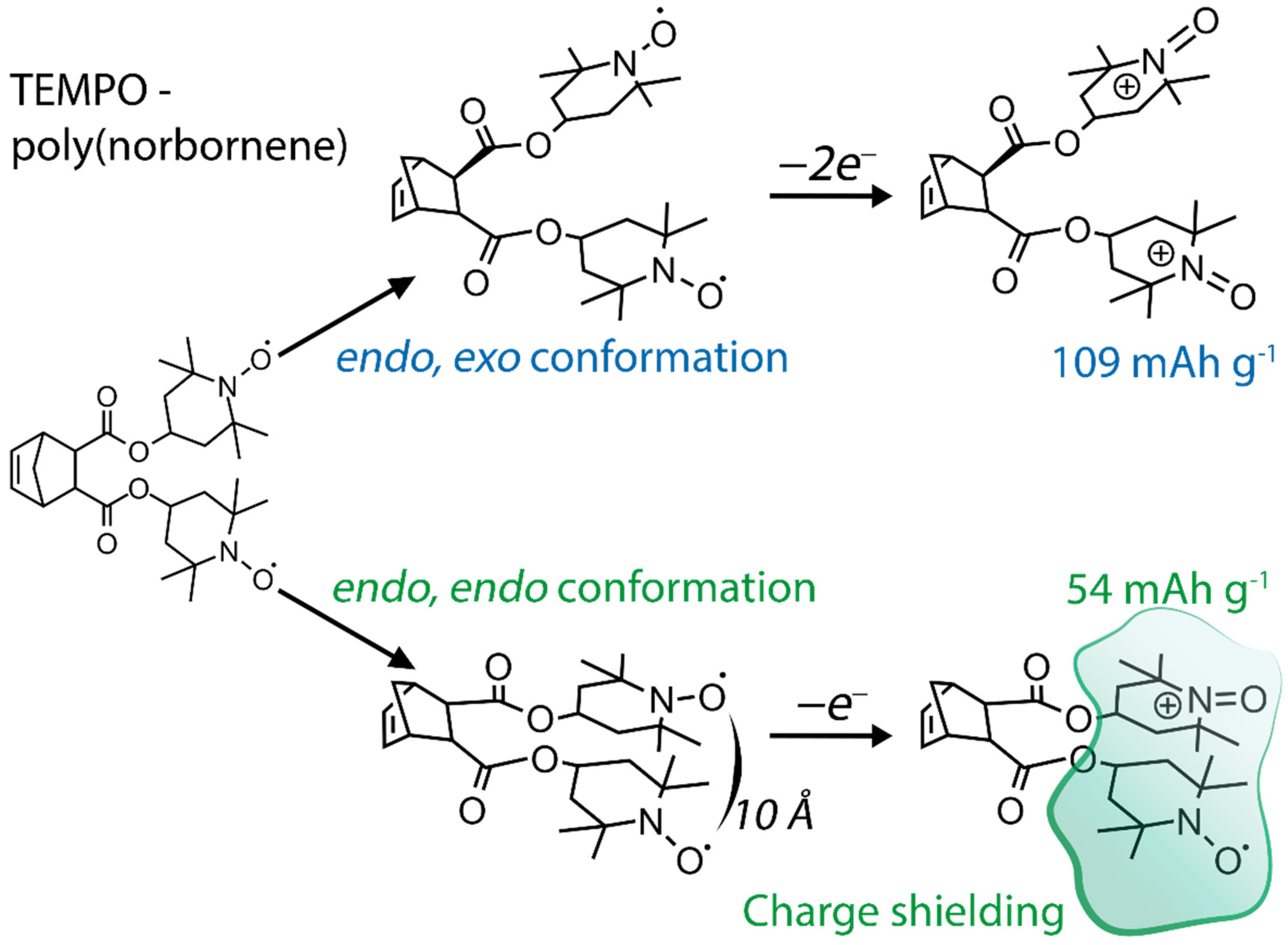
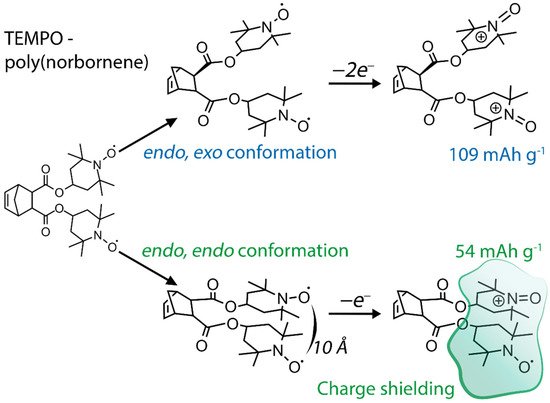
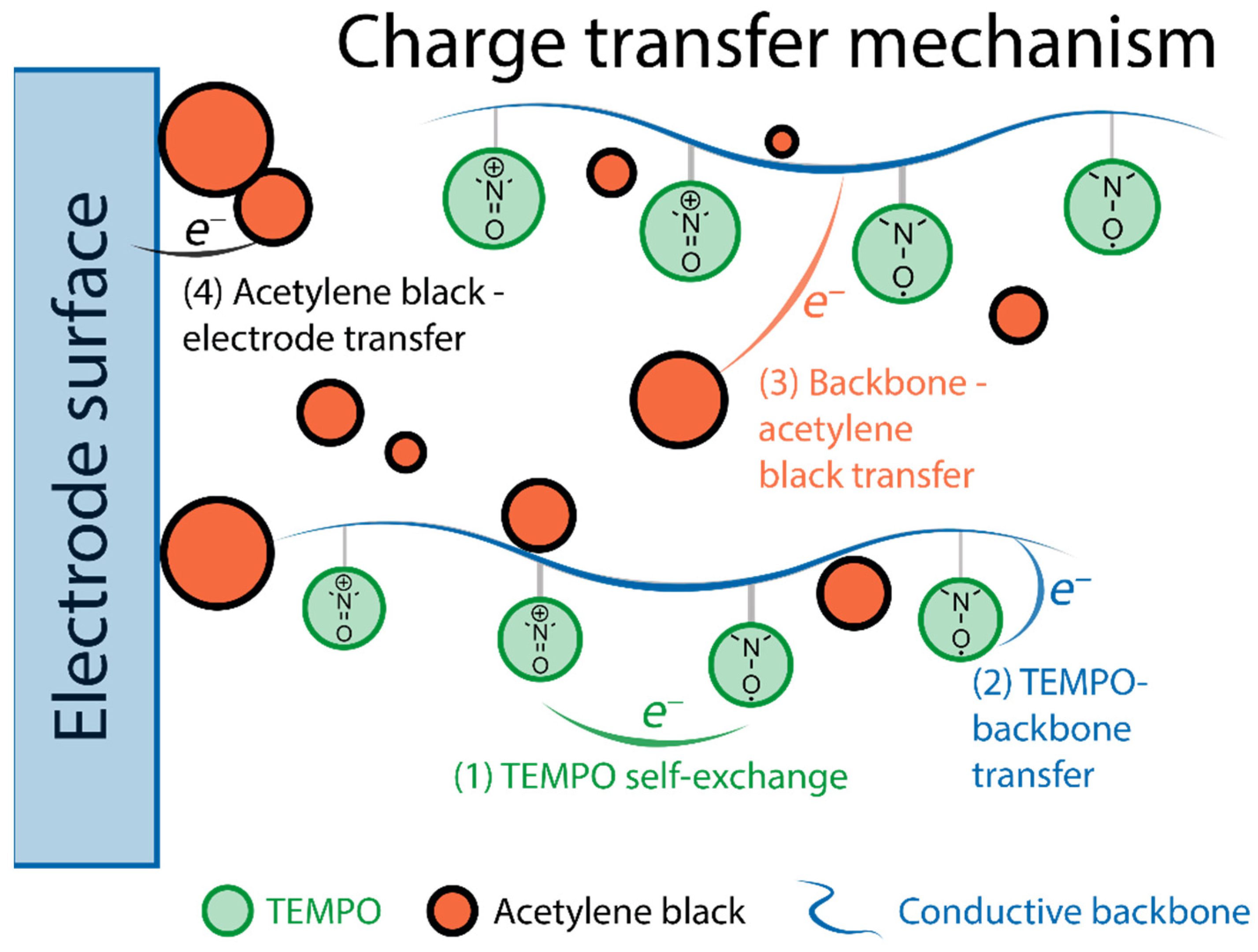
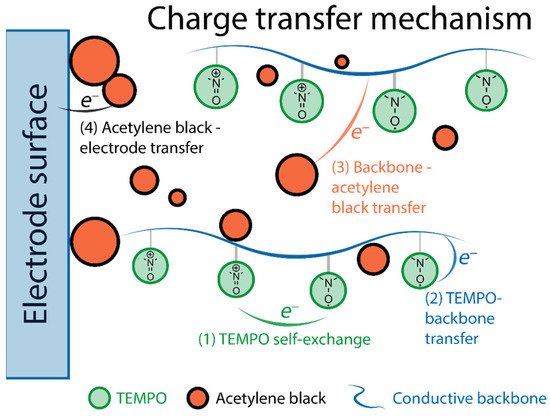
The redox-active TEMPO (2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidin-1-oxyl-4-yl) fragment is a popular component of organic energy storage and catalytic systemsystems, as its benefits include remarkable electrochemical performance and decent physical properties. TEMPO is a verstile compound that finds its use in various chemical and biological systems, and is also lso known to be an efficient catalyst for alcohol oxidation, oxygen reduction, and various complex organic reactions. It can be attached to various aliphatic and conductive polymers to form energy storage compounds for organic batteries or high-loading catalysis systems. The performance and efficiency of TEMPO-containing materials strongly depend on the molecular structure, and thus rational design of such compounds is vital for successful implementation.
- TEMPO
- nitroxyl
- stable radicals
- redox polymers
- conductive polymers
- organic radical polymers
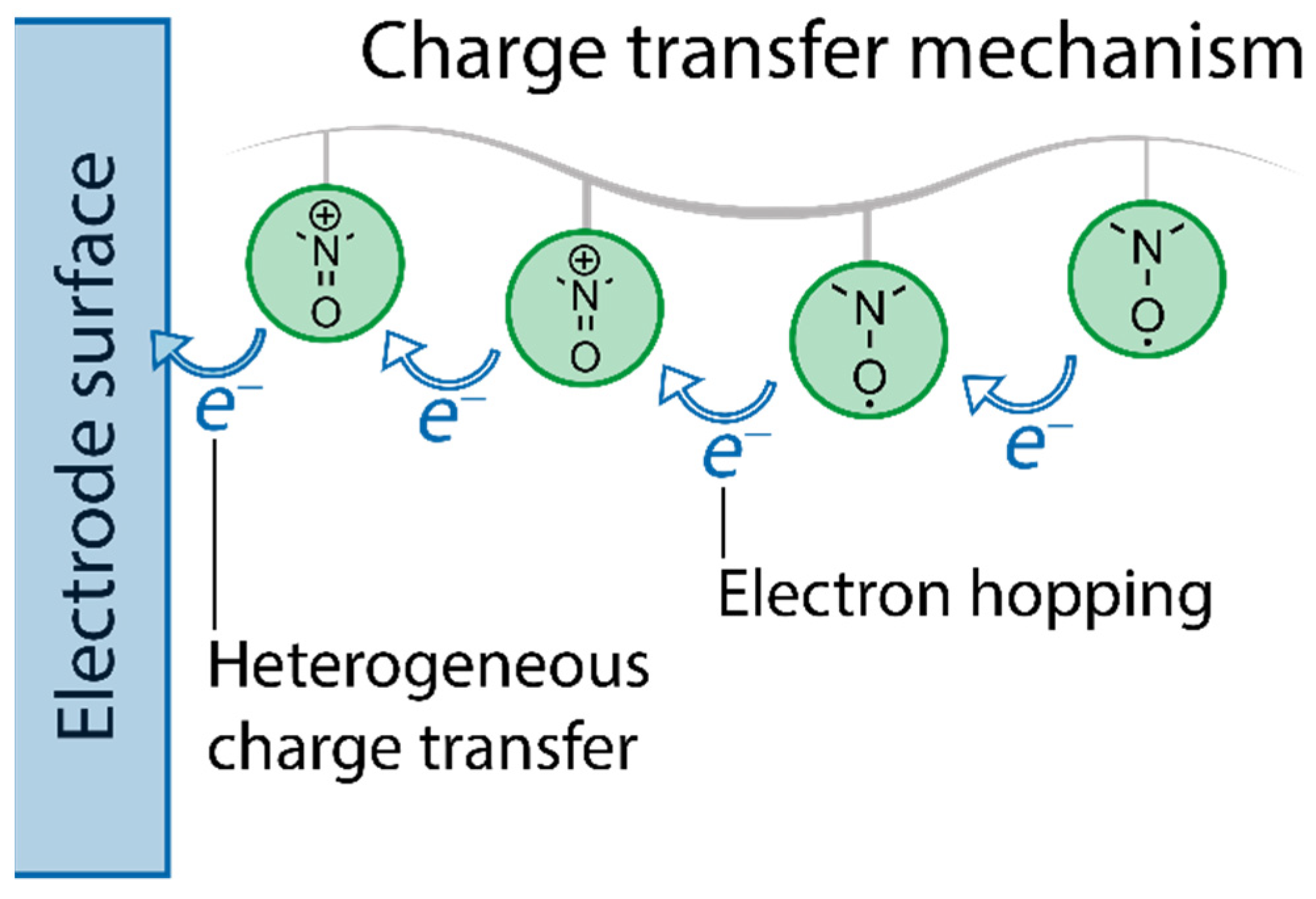
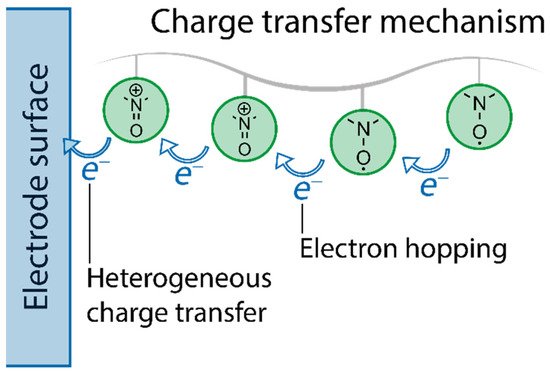
- charge transfer mechanisms
1. Introduction
2. Electroactive Materials Based on TEMPO
2.1. Synthetic Approaches
Due to continuously growing production, the cost of TEMPO derivatives, and especially 4-hydroxy-TEMPO (TEMPOL) is drastically decreasing. For example, according to the Sigma-Aldrich catalogues, the price of the TEMPOL in 2010 was EUR 295.5 per 25 g of 97% purity substance, while in 2022 the same package costs only EUR 49.9, and the price of the technical grade substance on industrial marketplaces lies below EUR 10/kg. The synthetic route for TEMPO consists of three simple stages, namely condensation of acetone with ammonia, reduction of the carbonyl group and oxidation of the N-H fragment, which makes the TEMPOL an inexpensive building block for industrial production of the functional materials for energy storage and other applications. TEMPOL itself is an ecological-friendly and non-toxic (LD50 1 g/kg, oral, rat) substance, considered as an antioxidant and drug precursor [15][16]. Unlike many inorganic high-energy materials, TEMPO-based polymers have no tendency of thermal runaway, are non-toxic and non-corrosive and, like most of the polymeric materials, can be disposed of by incineration. Due to these factors, TEMPO provides environmental and operational safety.2.1.1. Non-Conductive Backbones
Proper selection of the compatible polymeric backbones to bear TEMPO groups is the main step in obtaining the material with the best properties for the desired purpose. Such factors as dissolution of the material, which directly causes device self-discharge [10], and its electrochemical stability, define the choice of backbone polymers [7]. At the same time, due to the complex chemical behavior of nitroxyl compounds, synthetic availability also plays a significant role. Due to this reason, low-cost 4-hydroxy-TEMPO, or TEMPOL, is the most popular precursor for the synthesis of TEMPO-containing monomers by attachment via the hydroxyl group. Alternatively, significantly more expensive 4-carboxy- or 4-amino-derivatives of TEMPO may be used. Although most of the reported syntheses of these polymers use TEMPO-containing monomers, another option is to introduce TEMPO by the polymer-analogous transformations. Without any doubt, poly(2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine-N-oxyl-4-oxymethacrylate) (PTMA) is the most popular TEMPO-containing polymer for energy storage purposes. Despite the presence of the nitroxide moiety imposing appreciable restrictions on the polymerization techniques, PTMA can be obtained by direct polymerization of 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine-N-oxyl-4-oxymethacrylate using anionic [17] or group-transfer polymerization [18]. The same synthetic approaches are used to prepare other TEMPO-modified polyalkenes based on acrylamides [19], vinyl ethers [20] or more complicated systems [21]. Another way to introduce nitroxide functionality is by oxidation of the properly functionalized polymers using peroxide oxidants [22] or using starting materials with the reduced TEMPO protected by O-alkylation [23] (2. Electroactive Materials Based on TEMPO
2.1. Synthetic Approaches
2.1.1. Non-Conductive Backbones
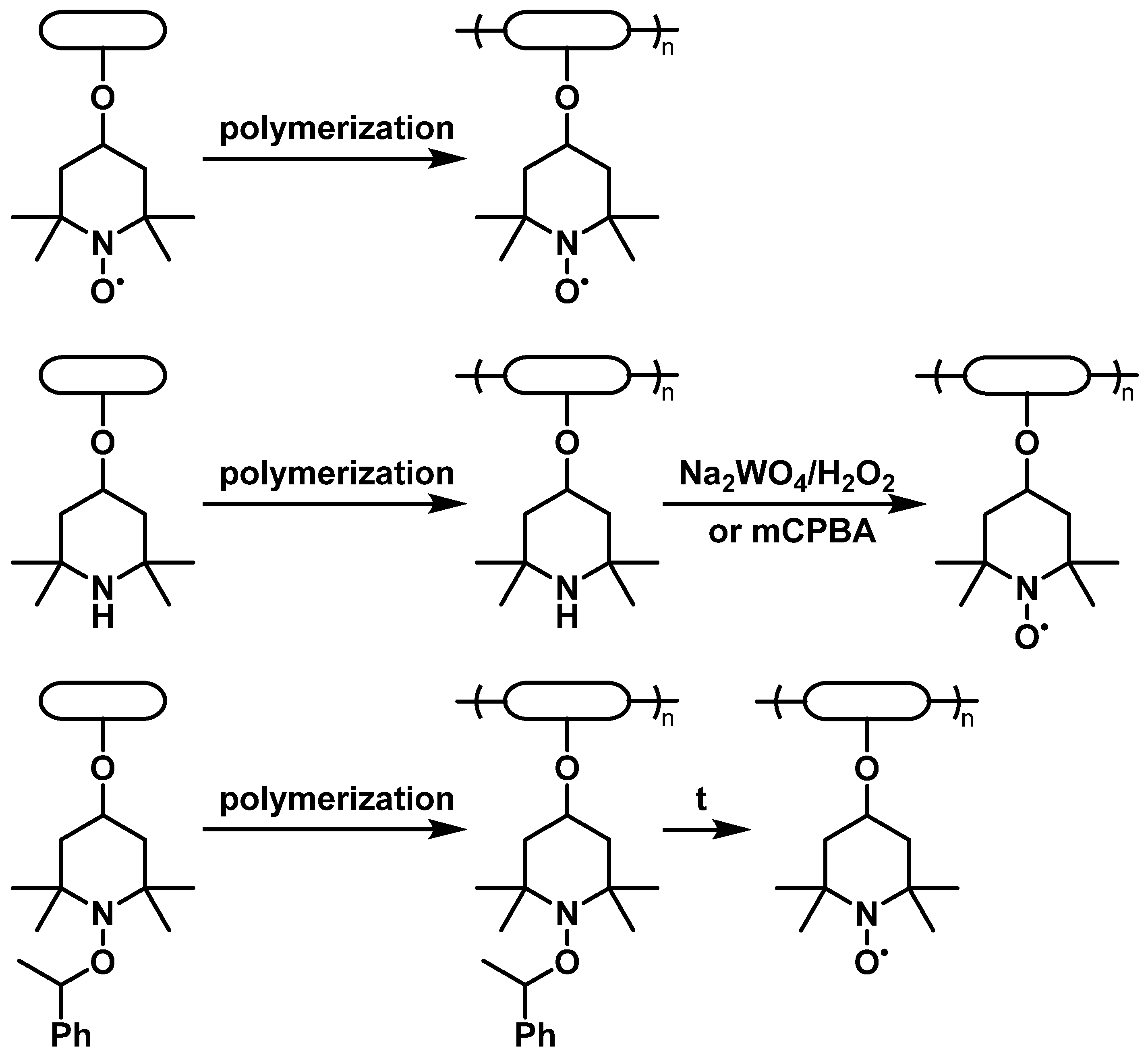
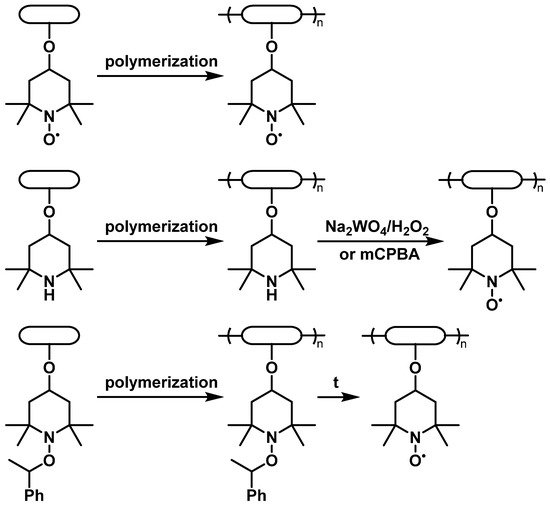
2.1.2. Conductive Backbones
Most TEMPO-bearing conductive polymers are prepared by electrochemical or chemical oxidative polymerization of TEMPO-containing monomers (2.1.2. Conductive Backbones
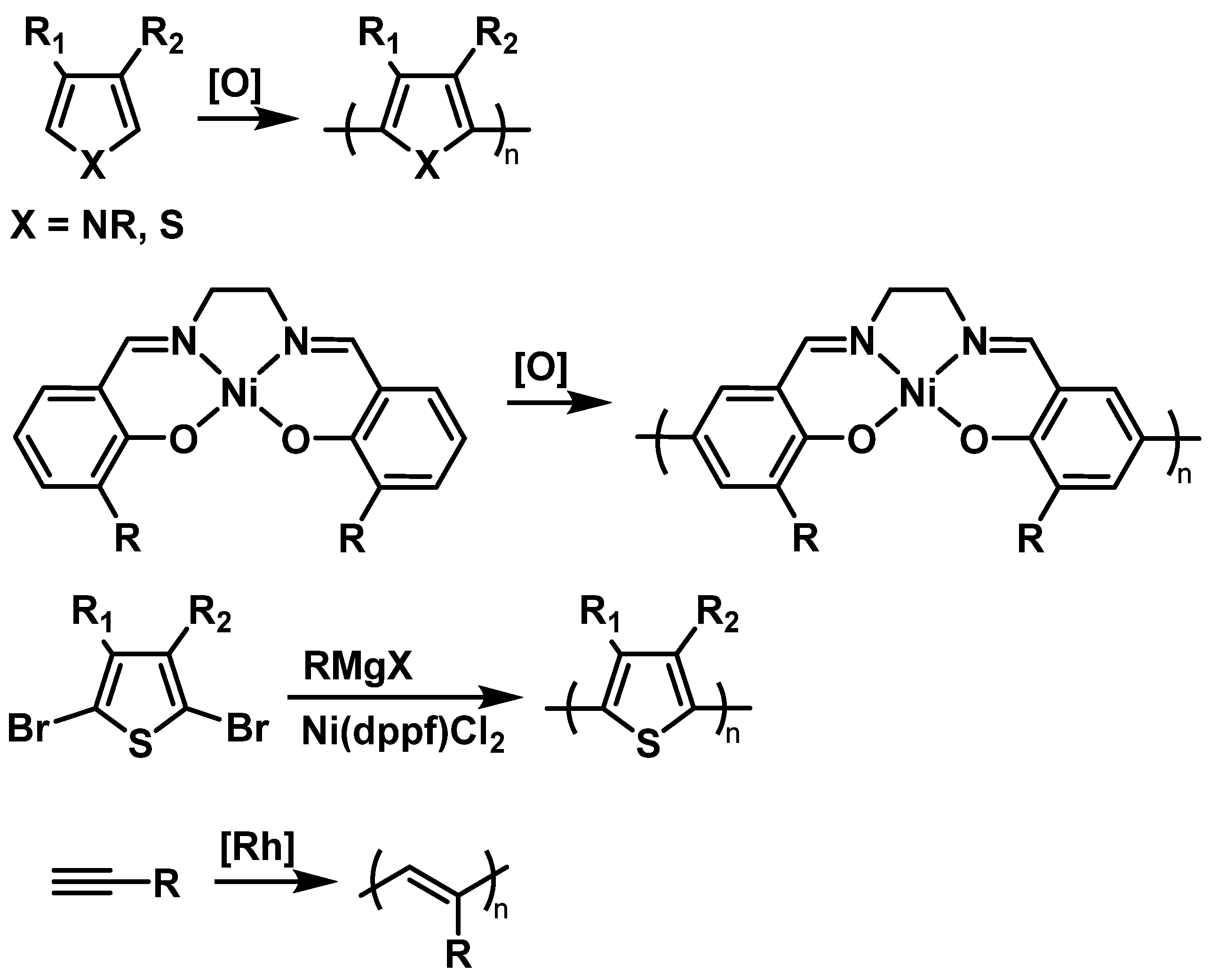
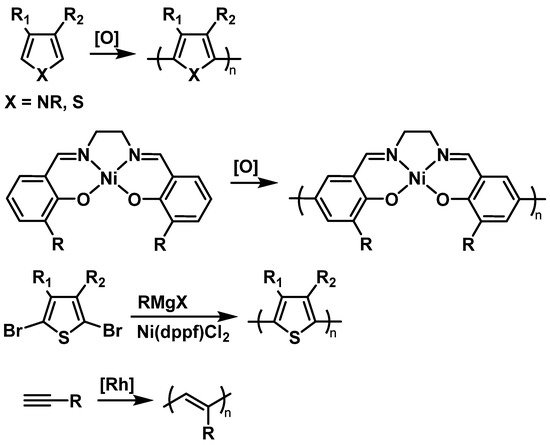
2.2. Fundamental Electrochemistry of TEMPO Transformations
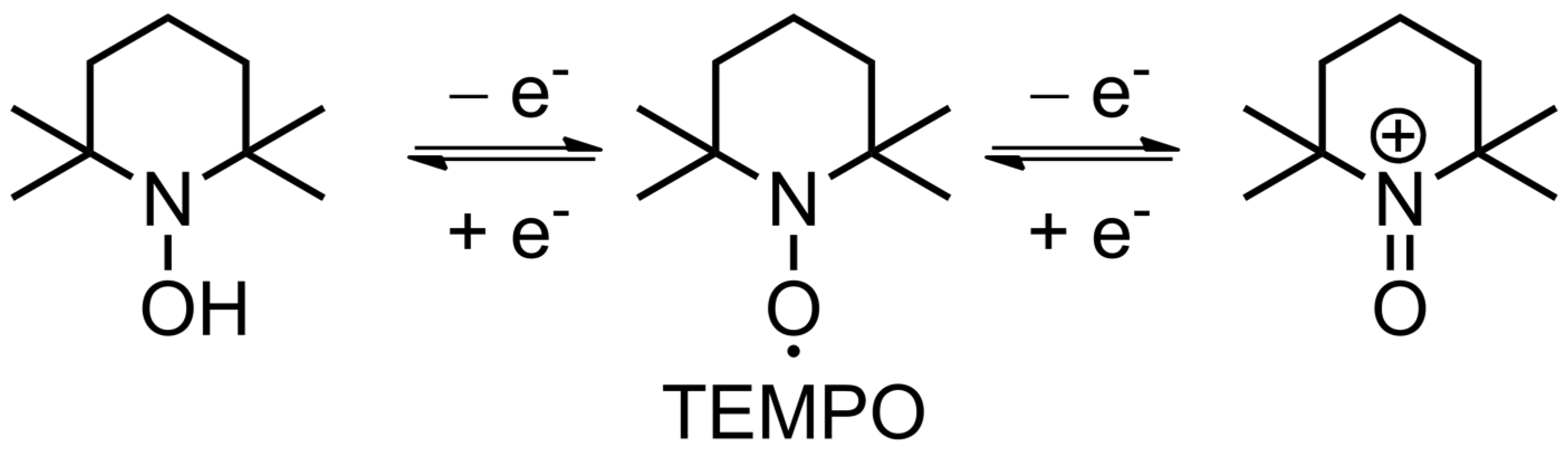
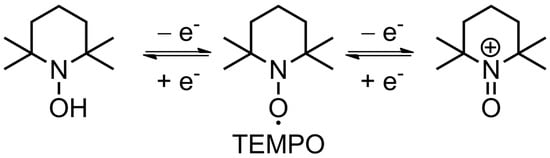
TEMPO is the founding piece among organic radicals for energy storage applications, as well as a touchstone for other similar materials. Its use for lithium-ion batteries can be traced back to 2002 [43], when Nakahara et al. employed a TEMPO-bearing poly(methacrylate) (PTMA) as an electrode material. Since then, a multitude of polymer backbones has been used in combination with TEMPO and other stable organic radicals [44], as such materials are quite promising. Their main advantages include high stability in standard lithium-ion electrolytes (recharging with negligible loss up to 2000 cycles [31]), and fast recharging time (available current rates of up to 100 C [45]), which results in impressive power density [11][12]. The nitroxide radical can either reversibly oxidize to form an oxoammonium cation (p-doping) or reduce to an aminoxyl anion (n-doping), which is the basis of electrochemical transformations in such materials (2.2. Fundamental Electrochemistry of TEMPO Transformations