The global market is experiencing stagnation and recession in the “untact era”, and the emergence of the metaverse provides platform support and presents a new paradigm. The “metaverse” platform services combine 5G network technology, advanced lightweight graphic technology, and cutting-edge display device technology. The emergence of the metaverse platform presents a new global market paradigm in the ongoing recession caused by COVID-19 and has attracted attention as a new growth engine that connects industry and content [1]. The metaverse is not bound by time and space, which is conducive to a contactless era, and provides a virtual experience with a high degree of immersion and connectivity, resulting in increased user value. The metaverse can be based on PCs and mobile devices, and is characterized by access at anytime and anywhere.
1. The Concept of the Metaverse
Metaverse is a compound word of meta and the universe, which signifies “virtuality” and “transcendence”, and is a more evolved term than VR. Alternatively, the metaverse is defined as an independent service provided for various social phenomena that appear in the market environment as technology develops [6]. The metaverse emerged in the early 2000s as a part of the gaming industry, providing independent communication services among users. However, with the invention of smartphones and social networking services that highlight convenience and accessibility, users have flocked to social media, and the number of users in the metaverse has gradually declined [7,8]. However, the market environment has abruptly changed since the outbreak of COVID-19, and the metaverse has returned in full swing as the digital platform that connects consumers, and producers have converged with 5G networks and sophisticated devices. Specifically, the metaverse can be considered a technology optimized for the market environment created by the commercialization of 5G, boasting ultra-fast, ultra-connected, and ultra-low latency services, boosted by the COVID-19 pandemic in early 2020. With the commercialization of 5G, technologies that can implement VR, AR, and mixed reality (MR) have emerged, and the metaverse is drawing more attention as a platform for contactless environments.
In its nascent stage, the term metaverse was used interchangeably with VR, but its use expanded in diverse ways. For example, the Second Life game, released in 2003, was created to generate profits through social exchanges and the economic activities of multiple users in a virtual space based on 3D graphics. Based on this, a VR version of Sansar was released [9]. In Niel Stephenson’s 1992 novel Snow Crash, the scope of the metaverse, a space where everyday life and economic activities were made possible through avatars, was further expanded [10]. Travis Scott, an American hip-hop artist, presented a metaverse performance on the Fortnite platform in 2020, with more than 12 million viewers watching the performance in real-time. It is estimated that the revenue from a single metaverse performance would be at least USD 1 million, with an estimated total of USD 20 million [11]. Kwok and Koh [12] argued that, as reality and virtuality interact and evolve within a space, they transform into a world that creates value through social, cultural, and economic activities. Thus, the current metaverse is defined as an extended virtual world in which emphasis is placed on artificial reality and AR [13]. Bolger [14] divided the metaverse into four types according to the space and nature of the information implemented on the platform. The first is “lifelogging”, which automatically records, stores, and shares information that individuals experience and feel in their daily lives in the digital world through social media services, such as Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter. The second is “AR”, which summons 3D objects in reality to provide realistic digital information, such as Pokemon Go and Snow. The third is “mirror world”, in which Google Earth and Kakao Maps render a digital implementation of the real world to the virtual world and link it back to the real world. The fourth is “VR”, which implies experiencing a new virtual world that does not exist as an individual-centered virtual world in spaces, such as Zepeto and Roblox [9]. The current status of the metaverse is that there are countless key technologies for implementing them. It is diverse, spanning the basic technologies of 3D, blockchain, AI, 5G, MR, AR, and VR to the applied technologies of avatar and cryptocurrency [15].
1. The Concept of the Metaverse
Metaverse is a compound word of meta and the universe, which signifies “virtuality” and “transcendence”, and is a more evolved term than VR. Alternatively, the metaverse is defined as an independent service provided for various social phenomena that appear in the market environment as technology develops [1]. The metaverse emerged in the early 2000s as a part of the gaming industry, providing independent communication services among users. However, with the invention of smartphones and social networking services that highlight convenience and accessibility, users have flocked to social media, and the number of users in the metaverse has gradually declined [2][3]. However, the market environment has abruptly changed since the outbreak of COVID-19, and the metaverse has returned in full swing as the digital platform that connects consumers, and producers have converged with 5G networks and sophisticated devices. Specifically, the metaverse can be considered a technology optimized for the market environment created by the commercialization of 5G, boasting ultra-fast, ultra-connected, and ultra-low latency services, boosted by the COVID-19 pandemic in early 2020. With the commercialization of 5G, technologies that can implement VR, AR, and mixed reality (MR) have emerged, and the metaverse is drawing more attention as a platform for contactless environments.
In its nascent stage, the term metaverse was used interchangeably with VR, but its use expanded in diverse ways. For example, the Second Life game, released in 2003, was created to generate profits through social exchanges and the economic activities of multiple users in a virtual space based on 3D graphics. Based on this, a VR version of Sansar was released [4]. In Niel Stephenson’s 1992 novel Snow Crash, the scope of the metaverse, a space where everyday life and economic activities were made possible through avatars, was further expanded [5]. Travis Scott, an American hip-hop artist, presented a metaverse performance on the Fortnite platform in 2020, with more than 12 million viewers watching the performance in real-time. It is estimated that the revenue from a single metaverse performance would be at least USD 1 million, with an estimated total of USD 20 million [6]. Kwok and Koh [7] argued that, as reality and virtuality interact and evolve within a space, they transform into a world that creates value through social, cultural, and economic activities. Thus, the current metaverse is defined as an extended virtual world in which emphasis is placed on artificial reality and AR [8]. Bolger [9] divided the metaverse into four types according to the space and nature of the information implemented on the platform. The first is “lifelogging”, which automatically records, stores, and shares information that individuals experience and feel in their daily lives in the digital world through social media services, such as Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter. The second is “AR”, which summons 3D objects in reality to provide realistic digital information, such as Pokemon Go and Snow. The third is “mirror world”, in which Google Earth and Kakao Maps render a digital implementation of the real world to the virtual world and link it back to the real world. The fourth is “VR”, which implies experiencing a new virtual world that does not exist as an individual-centered virtual world in spaces, such as Zepeto and Roblox [4]. The current status of the metaverse is that there are countless key technologies for implementing them. It is diverse, spanning the basic technologies of 3D, blockchain, AI, 5G, MR, AR, and VR to the applied technologies of avatar and cryptocurrency [10].
2. The SPICE Model
2. The SPICE Model
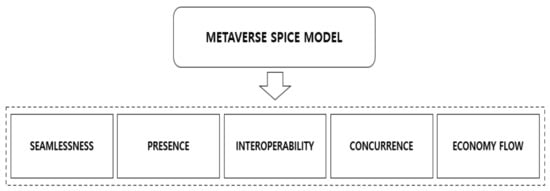
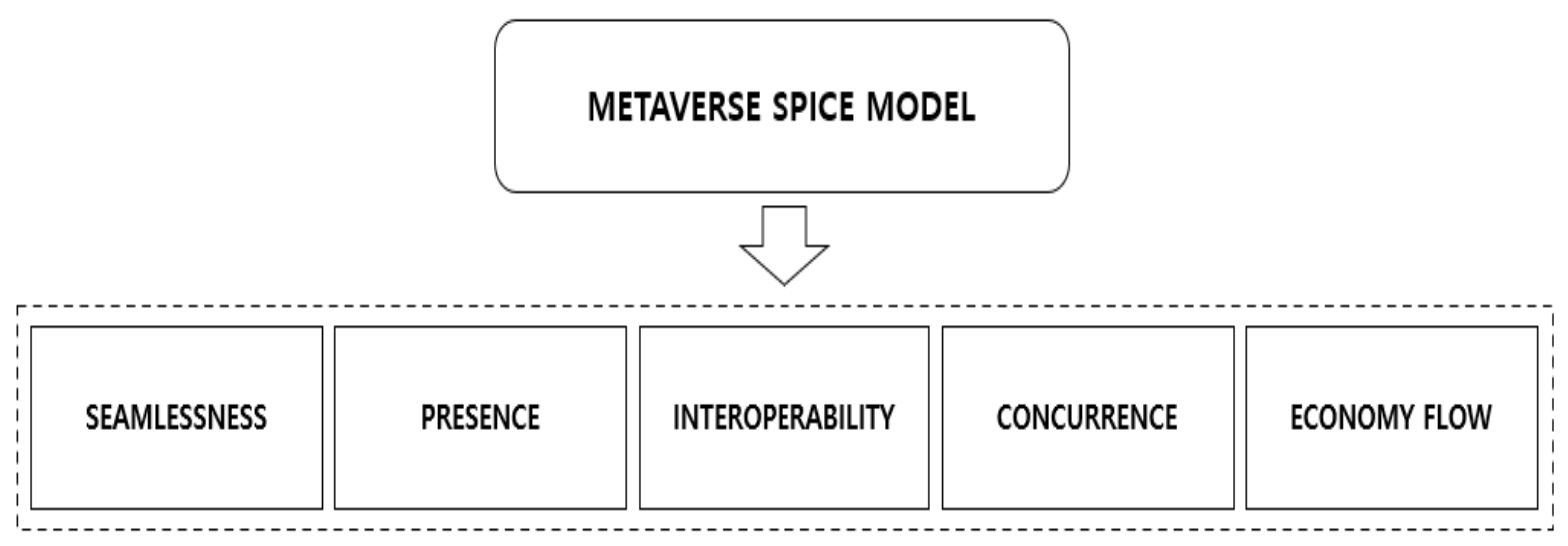
The main feature that makes up the metaverse can be described using the seamlessness, presence, interoperability, concurrence, and economic flow (SPICE) model (
The main feature that makes up the metaverse can be described using the seamlessness, presence, interoperability, concurrence, and economic flow (SPICE) model (
Figure 1). Seamlessness is a continuous connection between various experiences on a single platform, which means that even when a specific character is connected to a previous situation, it can continue the experience without disruption by retaining actions or experiences on the platform [16]. A sense of presence refers to a situation in which the user spatially or temporally feels they are on the platform even though physical contact is impossible. In other words, because the metaverse is a virtual space where the user cannot actually make physical contact, the sense of reality becomes a very important factor. Interoperability means that the data and information of the metaverse are interconnected in the real world [17]. In short, this means that a user’s experience and the information that needs to be obtained on a platform are not only applied to the virtual world, but complement each other by linking to the real world. Concurrence refers to an environment in which multiple users can simultaneously acquire different experiences and information regarding a meter. In the real world, owing to limited physical environmental factors, multiple users cannot have various experiences in one space; however, this is possible in the VR-based metaverse. As such, economic flows in the metaverse are generally characterized by beyond the traditional market principles in which sellers and consumers interact. Thus, there is an economic flow in which users can trade freely with others using the currency provided on the platform.
). Seamlessness is a continuous connection between various experiences on a single platform, which means that even when a specific character is connected to a previous situation, it can continue the experience without disruption by retaining actions or experiences on the platform [11]. A sense of presence refers to a situation in which the user spatially or temporally feels they are on the platform even though physical contact is impossible. In other words, because the metaverse is a virtual space where the user cannot actually make physical contact, the sense of reality becomes a very important factor. Interoperability means that the data and information of the metaverse are interconnected in the real world [12]. In short, this means that a user’s experience and the information that needs to be obtained on a platform are not only applied to the virtual world, but complement each other by linking to the real world. Concurrence refers to an environment in which multiple users can simultaneously acquire different experiences and information regarding a meter. In the real world, owing to limited physical environmental factors, multiple users cannot have various experiences in one space; however, this is possible in the VR-based metaverse. As such, economic flows in the metaverse are generally characterized by beyond the traditional market principles in which sellers and consumers interact. Thus, there is an economic flow in which users can trade freely with others using the currency provided on the platform.
Figure 1. Metaverse SPICE model.
3. Cases of Metaverse Uses
The metaverse, an immersive next-generation version of the Internet rendered by VR and AR technologies, was created approximately 20 years ago. The forerunners of the metaverse were 2D electronic games for entertainment, driven by the development of the Internet and 3D graphics technology [13]. Thereafter, the “Lifelogging” type of metaverse, such as Facebook, became widely popular as a medium for communication to share experiences, connect with friends and family, and build communities, accompanied by the spread and popularization of desktop computers and smartphones [14]. Imm et al. [15] classified the metaverse into two types, the game-type metaverse and the life-type metaverse, depending on several criteria, such as virtual world status, purpose, content creation, and content consumption. Game- and life-type metaverses began in the early 2000s and 2010s, respectively, resulting in the current metaverse of the 2020s ushering in a new era for present generations. Metaverse is no longer merely about gaming or entertainment. Companies, schools, government offices, fashion, and popular culture have built businesses to provide goods and services for the metaverse, which has considerable implications for society. For Generation MZ, which includes millennials (those born in the early 1980s and the early 2000s) and Generation Z (those born in the mid-1990s and the early 2000s), who are familiar with the Internet and digital devices, the metaverse is becoming a way of online social life. As the metaverse allows users to immerse themselves in a space where the digital and physical worlds converge, they can realize daily life in a virtual space where the boundary between reality and virtuality has blurred [16].
3. Cases of Metaverse Uses
The metaverse, an immersive next-generation version of the Internet rendered by VR and AR technologies, was created approximately 20 years ago. The forerunners of the metaverse were 2D electronic games for entertainment, driven by the development of the Internet and 3D graphics technology [18]. Thereafter, the “Lifelogging” type of metaverse, such as Facebook, became widely popular as a medium for communication to share experiences, connect with friends and family, and build communities, accompanied by the spread and popularization of desktop computers and smartphones [19]. Imm et al. [20] classified the metaverse into two types, the game-type metaverse and the life-type metaverse, depending on several criteria, such as virtual world status, purpose, content creation, and content consumption. Game- and life-type metaverses began in the early 2000s and 2010s, respectively, resulting in the current metaverse of the 2020s ushering in a new era for present generations. Metaverse is no longer merely about gaming or entertainment. Companies, schools, government offices, fashion, and popular culture have built businesses to provide goods and services for the metaverse, which has considerable implications for society. For Generation MZ, which includes millennials (those born in the early 1980s and the early 2000s) and Generation Z (those born in the mid-1990s and the early 2000s), who are familiar with the Internet and digital devices, the metaverse is becoming a way of online social life. As the metaverse allows users to immerse themselves in a space where the digital and physical worlds converge, they can realize daily life in a virtual space where the boundary between reality and virtuality has blurred [21].
Metaverse technology, which was initially used for games, is now actively utilized for diverse purposes in several fields, such as meetings, incentives, conferences, exhibitions, schools, corporations, sports, entertainment, fashion, and retail businesses, particularly due to the need for “contactless culture” (“untact”) after the COVID-19 outbreak. Korean girl groups “Blackpink” and “ITZY” successfully held a fan signing event and a fan meeting on Zepeto, a metaverse platform, in September 2020 and in February 2021, respectively [22]. Global fashion companies, such as Gucci and Christian Louboutin not only promote their brands and goods in the metaverse but also directly sell items worn by avatars [23]. At convenience stores, avatars cook and eat ramen in the metaverse, as in a real store, and stage performances, such as singing and dancing, in the busking space. In summary, the use of the metaverse in various industries is increasing. In addition, the global metaverse market size is estimated to reach approximately USD 280 billion by 2025, and is expected to result in the development of new markets and cultural industries as its utility increases among companies targeting young customers.
Metaverse technology, which was initially used for games, is now actively utilized for diverse purposes in several fields, such as meetings, incentives, conferences, exhibitions, schools, corporations, sports, entertainment, fashion, and retail businesses, particularly due to the need for “contactless culture” (“untact”) after the COVID-19 outbreak. Korean girl groups “Blackpink” and “ITZY” successfully held a fan signing event and a fan meeting on Zepeto, a metaverse platform, in September 2020 and in February 2021, respectively [17]. Global fashion companies, such as Gucci and Christian Louboutin not only promote their brands and goods in the metaverse but also directly sell items worn by avatars [18]. At convenience stores, avatars cook and eat ramen in the metaverse, as in a real store, and stage performances, such as singing and dancing, in the busking space. In summary, the use of the metaverse in various industries is increasing. In addition, the global metaverse market size is estimated to reach approximately USD 280 billion by 2025, and is expected to result in the development of new markets and cultural industries as its utility increases among companies targeting young customers.